Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Look at The Image
Uploaded by
Ghalih Hakiki KavisaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Look at The Image
Uploaded by
Ghalih Hakiki KavisaCopyright:
Available Formats
Look at the image
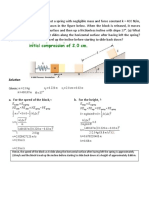
An object whose mass is 1 kg falls freely from a height of 25 m as shown. Compute:
a. Kinetic energy at point A
b. The kinetic energy of the object while at point B (10 m above ground)!
Discussion:
a. Kinetic energy at point A
In the above problem, the object undergoes free fall motion so that vA = 0. Then the kinetic
energy when dititik A:
Va = 0 m/s
1
EkA = mvA2
2
1
EkA = 1 kg (0 m/s)2
2
EkA = 0
b. Kinetic energy at point B
With the law of conservation of mechanical energy:
EMA = EMB
EpA+EkA = EpB + EkB
1
m.g.hA + 2 mvA2 = m.g.hB +EkB
1
(1 kg)( 10 m/s2 )(25m) + 2 (1 kg)(0 m/s)2 = (1 kg) (10 m/s2 )(10 m) + EkB
250 Joule = 100 Joule + EkB
EkB = 150 Joule
Konversion to Britihs
1m = 3,2808 ft
1 kg = 2,2046 lb
1 m/s = 3,2808 ft/s
1 m/s2 = 3,2808 ft/s2
1 kJ = 0,9478 Btu
Discussion:
a. Kinetic energy at point A
In the above problem, the object undergoes free fall motion so that vA = 0. Then the kinetic
energy when dititik A:
Va = 0 m(3,2808 ft/m)/s
Va = 0 ft/m
1
EkA = mvA2
2
1
EkA = 1 kg (0 m/s)2
2
EkA = 0 Joule (0,9478 x10-3 Btu/J )
EkA = 0 Btu
b. Kinetic energy at point B
With the law of conservation of mechanical energy:
EMA = EMB
EpA+EkA = EpB + EkB
1
m.g.hA + 2 mvA2 = m.g.hB +EkB
1
(1 kg)( 10 m/s2 )(25m) + 2 (1 kg)(0 m/s)2 = (1 kg) (10 m/s2 )(10 m) + EkB
250 Joule = 100 Joule + EkB
EkB = 150 Joule (0,9478 x10-3 Btu/J )
EkB = 0,14217 Btu
You might also like
- Conservation of MomentumDocument37 pagesConservation of MomentumJessMalanumNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power SlidesDocument36 pagesWork Energy Power Slidessweehian844100% (1)
- Law of Conservation of Energy ExplainedDocument25 pagesLaw of Conservation of Energy ExplainedJireh Ann Mejino100% (1)
- Work, Energy and Power-1Document32 pagesWork, Energy and Power-1Ian HaroldNo ratings yet
- PHYS101 Impulse and MomentumDocument22 pagesPHYS101 Impulse and Momentumjojo basenNo ratings yet
- The Period of A Mass On A SpringDocument16 pagesThe Period of A Mass On A SpringPatrick SibandaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Week 1 Activity 1: Mechanical Energy and WorkDocument4 pagesQuarter 2 Week 1 Activity 1: Mechanical Energy and WorkJ-heart Basabas MalpalNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document4 pagesPhysics 2John Arnel L. MiculobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Momentum Impulse and CollisionsDocument12 pagesChapter 8 Momentum Impulse and Collisionskiyemi8123No ratings yet
- Today: Homework Due Conservation of Energy Read Chap 13, Sections 6 To 9 Homework: Chap. 13, Problems 57, 61, 67, 76Document12 pagesToday: Homework Due Conservation of Energy Read Chap 13, Sections 6 To 9 Homework: Chap. 13, Problems 57, 61, 67, 76Tony LoogmanNo ratings yet
- Problem - 7A PDFDocument9 pagesProblem - 7A PDFMonicaNo ratings yet
- MOMENTUMDocument4 pagesMOMENTUMAriane Nicole Barayang DamianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9B - Conservation of MomentumDocument36 pagesChapter 9B - Conservation of MomentumRoda Gayle RañadaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 151 - Notes For Online Lecture #19: Conservation of Linear Momentum in 2-DDocument4 pagesPHYSICS 151 - Notes For Online Lecture #19: Conservation of Linear Momentum in 2-DCece SantosNo ratings yet
- Problem: A 300 KG Car Has A Kinetic Energy of 500 J. Find Its SpeedDocument2 pagesProblem: A 300 KG Car Has A Kinetic Energy of 500 J. Find Its Speedreielleceana07No ratings yet
- Force and Motion LessonsDocument2 pagesForce and Motion LessonsAriane Nicole Barayang DamianNo ratings yet
- COLLISIONDocument26 pagesCOLLISIONFatima salasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems: EI 294772.2 N.MDocument3 pagesTutorial Problems: EI 294772.2 N.MTerry McManamanNo ratings yet
- Calculating the Work Done by a Centrifugal PumpDocument4 pagesCalculating the Work Done by a Centrifugal PumpFrancis DacutananNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document4 pagesCH 087766xh82xsNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Work EnergyDocument17 pagesGroup 3 - Work EnergyPrincess JeannyNo ratings yet
- Assumptions 1) This Is A Steady-Flow Process Since There Is No Change With Time. 2) The Kinetic andDocument5 pagesAssumptions 1) This Is A Steady-Flow Process Since There Is No Change With Time. 2) The Kinetic andKarumon UtsumiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Thirteen Solutions Chapter Thirteen SolutionsDocument13 pagesChapter Thirteen Solutions Chapter Thirteen Solutionsdavid bustilloNo ratings yet
- Physics 5Document12 pagesPhysics 5ジョンNo ratings yet
- Slide Presentation For ET2Document37 pagesSlide Presentation For ET2Redzwan KadirNo ratings yet
- q1 A Block of Mass M 500 KG Is Released Form Rest FromDocument2 pagesq1 A Block of Mass M 500 KG Is Released Form Rest Frommon chériNo ratings yet
- The maximum velocity occurs when the displacement is zero, which happens when ωt = π/2, 3π/2, etcDocument27 pagesThe maximum velocity occurs when the displacement is zero, which happens when ωt = π/2, 3π/2, etcKazaValiShaikNo ratings yet
- Problem - 5A PDFDocument13 pagesProblem - 5A PDFMonicaNo ratings yet
- Solution To Assigment Problem - Chapter - 6 - Work and Kinetic Energy - R K ParidaDocument2 pagesSolution To Assigment Problem - Chapter - 6 - Work and Kinetic Energy - R K Paridaajaysahu1441No ratings yet
- Mechanical Energy Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageMechanical Energy Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- BPHE-101: Ans 1 B) I)Document4 pagesBPHE-101: Ans 1 B) I)AakashMalhotraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Student Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Student Solutions ManualGabriela Alves de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Chapter 7 MomentumDocument2 pagesForce and Motion Chapter 7 MomentumMavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)Document41 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion (SHM)neoeverestNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Conservation LabDocument11 pagesWork and Energy Conservation LabMarvin ItolondoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Work and EnergyDocument18 pagesLesson 5 Work and EnergyanonymousNo ratings yet
- Work - Power - EnergyDocument83 pagesWork - Power - EnergyKy VergaraNo ratings yet
- Conservation of EnergyDocument1 pageConservation of EnergyRegina100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics 1St Edition Reisel 1285056477 9781285056470 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics 1St Edition Reisel 1285056477 9781285056470 Full Chapter PDFkathleen.osorio990100% (15)
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument4 pagesWork, Energy and PowerGianne Karl AlmarinesNo ratings yet
- PY 21 LECTURE Module 8.1 Momentum and ImpulseDocument2 pagesPY 21 LECTURE Module 8.1 Momentum and ImpulseJho A Nes PakipacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy: Answers To Even-Numbered Conceptual QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 8: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy: Answers To Even-Numbered Conceptual QuestionsRoger Lenin Maya MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lesson8 PPT - Forces On Accelerating ObjectsDocument37 pagesLesson8 PPT - Forces On Accelerating ObjectsYara Jeah Ingay BaliliNo ratings yet
- COLLISIONSDocument3 pagesCOLLISIONSMartha Glorie Manalo WallisNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Linear MomentumDocument28 pagesTopic 4 - Linear Momentumbonbon.kentbriannNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Problem Sets Week 9Document10 pagesWork and Energy Problem Sets Week 9nics100% (1)
- PHYS 1110: Assignment 8Document5 pagesPHYS 1110: Assignment 8Anson ChanNo ratings yet
- Finding The Force On An Elevator Cable When:: There Are 2 Approaches For Solving This Problem Using ForcesDocument6 pagesFinding The Force On An Elevator Cable When:: There Are 2 Approaches For Solving This Problem Using ForcesengkankwNo ratings yet
- K MG/X (65 KG) (9.80 M/s F (K/M)Document21 pagesK MG/X (65 KG) (9.80 M/s F (K/M)Juju SaputriNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics Si Edition 1St Edition Reisel 1285056485 9781285056487 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics Si Edition 1St Edition Reisel 1285056485 9781285056487 Full Chapter PDFkathleen.osorio990100% (14)
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument32 pagesWork, Energy and PowerHahahahahahahahahaNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument2 pagesSolutionssNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 Kinetic EnergyDocument46 pagesWEEK 4 Kinetic EnergyJun De FontanozaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pertama Termodinamika Kelompok 1Document4 pagesTugas Pertama Termodinamika Kelompok 1Gita CristyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Solutions Chapter 16Document4 pagesFundamentals of Physics Solutions Chapter 16Ahmar KhanNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument13 pagesMomentumAlyssa Marie L. PalamianoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Quiz SolutionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Quiz SolutionsILAGAN ANNE FRANCINENo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4: 0 KG M/sDocument4 pagesProblem Set 4: 0 KG M/sMahid DandamunNo ratings yet
- swk10d4 EnergyDocument21 pagesswk10d4 EnergyErayNo ratings yet
- NO Penyanyi 1 Micael Jakson 2 Calum Scot 3 Jason Mraz 4 Ed Sheeran 5 Ed Sheeran 6 Justin Bieber 7 Bob Marley 8 9 10 11 12 13Document5 pagesNO Penyanyi 1 Micael Jakson 2 Calum Scot 3 Jason Mraz 4 Ed Sheeran 5 Ed Sheeran 6 Justin Bieber 7 Bob Marley 8 9 10 11 12 13Ghalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal P0Document8 pagesJurnal P0Ghalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Rekayasa BiofuelDocument23 pagesRekayasa BiofuelGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Soal UtsDocument1 pageSoal UtsGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan FluidisasiDocument10 pagesPerhitungan FluidisasiGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- 1 Model N Comp ProcessDocument35 pages1 Model N Comp ProcessScandyinHavia EmmuachhNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan FluidisasiDocument10 pagesPerhitungan FluidisasiGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Anova Soal 2Document2 pagesAnova Soal 2Ghalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Look at The ImageDocument2 pagesLook at The ImageGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Intro Sci LabDocument87 pagesIntro Sci LabandysarmientoNo ratings yet
- Fieldbus Technology:: PLC ArchitectureDocument6 pagesFieldbus Technology:: PLC ArchitectureGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Lembar Perhitungan HMJDocument6 pagesLembar Perhitungan HMJLya WulandariNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pengpros HooDocument6 pagesTugas Pengpros HooGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Follow UpDocument2 pagesFollow UpGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control System: Steam TC Product Stream SetpointDocument3 pagesFeedback Control System: Steam TC Product Stream SetpointGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Motion Graphic CV Ghalih Hakiki KavisaDocument5 pagesMotion Graphic CV Ghalih Hakiki KavisaGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation EditedDocument19 pagesSedimentation EditedGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Mission ImpossibleDocument6 pagesMission ImpossibleGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- Look at The ImageDocument2 pagesLook at The ImageGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet
- List of Dimensionlss NumberDocument2 pagesList of Dimensionlss NumberGhalih Hakiki KavisaNo ratings yet