Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical Energy Problems and Solutions
Uploaded by
Basic Physics0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views1 pageA 2-kg box decelerated from 10 m/s to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Acceleration
due to gravity is 10 m/s 2 . What is the magnitude of displacement ?
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA 2-kg box decelerated from 10 m/s to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Acceleration
due to gravity is 10 m/s 2 . What is the magnitude of displacement ?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views1 pageMechanical Energy Problems and Solutions
Uploaded by
Basic PhysicsA 2-kg box decelerated from 10 m/s to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Acceleration
due to gravity is 10 m/s 2 . What is the magnitude of displacement ?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
https://physics.gurumuda.
net
Work-mechanical energy principle – problems and solutions
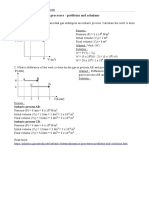
1. A 2-kg box decelerated from 10 m/s to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Acceleration
due to gravity is 10 m/s2. What is the magnitude of displacement ?
Known ;
Mass (m) = 2 kg
Initial velocity (vo) = 10 m/s
Final velocity (vt) = 0 m/s
The coefficient of kinetic friction (μk) = 0.2
weight (w) = m g = (1 kg)(10 m/s2) = 10 kg m/s2 = 10 N
Wanted : The magnitude of displacement (d)
Solution :
The work-mechanical energy principle :
Wnc = ΔEM
Wnc = ΔEK + ΔEP
Wnc = ½ m (vt2 – vo2) + m g h
Wnc = work done by nonconservative force acting on the object
ΔEK = the change in kinetic energy
ΔEP = the change in potential energy
m = mass
v = velocity
g = acceleration due to gravity
h = the change in height
The change in height h = 0 so ΔEP = 0
Wnc = ΔEK
Work done by nonconservative force :
Wnc = -Fc d = - μk N d = - μk w d = - μk m g d
Wnc = -(0.2)(2)(10)(s)
Wnc = - (4)(2)
The minus sign indicates that the direction of kinetic friction force is opposite with the direction of
displacement.
The change in kinetic energy :
ΔEK = ½ m (vt2 – vo2) = ½ (2)(0 – 102) = 0 – 100 = -100
The magnitude of displacement :
Read more
https://physics.gurumuda.net/work-mechanical-energy-principle-problems-and-solutions.htm
You might also like
- Quarter 2 Week 1 Activity 1: Mechanical Energy and WorkDocument4 pagesQuarter 2 Week 1 Activity 1: Mechanical Energy and WorkJ-heart Basabas MalpalNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Problem Sets Week 9Document10 pagesWork and Energy Problem Sets Week 9nics100% (1)
- Work - Kinetic Energy Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageWork - Kinetic Energy Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Work done, power, energy and impulse calculationsDocument6 pagesWork done, power, energy and impulse calculationsWemn JuniofNo ratings yet
- Physics ProblemDocument6 pagesPhysics ProblemWemn JuniofNo ratings yet
- Solution To Assigment Problem - Chapter - 6 - Work and Kinetic Energy - R K ParidaDocument2 pagesSolution To Assigment Problem - Chapter - 6 - Work and Kinetic Energy - R K Paridaajaysahu1441No ratings yet
- Work and Energy Conservation LabDocument11 pagesWork and Energy Conservation LabMarvin ItolondoNo ratings yet
- Ngel of God, My Guardian Dear, To Whom God's Love Commits Me Here, Ever This Day, Be at My Side To Light and Guard, To Rule and GuideDocument10 pagesNgel of God, My Guardian Dear, To Whom God's Love Commits Me Here, Ever This Day, Be at My Side To Light and Guard, To Rule and GuideClaire Valdeavilla - DudasNo ratings yet
- Energy Problems 1Document22 pagesEnergy Problems 1Cassidy GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Work - Power - EnergyDocument83 pagesWork - Power - EnergyKy VergaraNo ratings yet
- swk10d4 EnergyDocument21 pagesswk10d4 EnergyErayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - : Work and EnergyDocument25 pagesChapter 6 - : Work and EnergyMaimaiFabilonaDumalaogNo ratings yet
- (C) Work and Power 20-21Document39 pages(C) Work and Power 20-21Mariam AlgaoudNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 Kinetic EnergyDocument46 pagesWEEK 4 Kinetic EnergyJun De FontanozaNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageGravitational Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS HOLIDAY HOMEWorKDocument7 pagesPHYSICS HOLIDAY HOMEWorKdaansaiieNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy test-9TH-SCIENCE-AnswersheetDocument4 pagesWork Power Energy test-9TH-SCIENCE-AnswersheetviveksbbdNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument32 pagesWork, Energy and PowerHahahahahahahahahaNo ratings yet
- Work Power and EnergyDocument33 pagesWork Power and EnergyYfel UndagNo ratings yet
- Roll Number 124Document6 pagesRoll Number 124ahmadrafaqat351No ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument3 pagesDynamicsKlucifer XinNo ratings yet
- Physics Solutions: Advance Level Problems Target: Jee (Iits)Document7 pagesPhysics Solutions: Advance Level Problems Target: Jee (Iits)SJAIN12No ratings yet
- Work, Energy, & Power: Chapter 6 (C&J) Chapter 10 (Glencoe)Document29 pagesWork, Energy, & Power: Chapter 6 (C&J) Chapter 10 (Glencoe)Emieleah Lorenzo PauigNo ratings yet
- University Physics With Modern Physics 2nd Edition Bauer Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesUniversity Physics With Modern Physics 2nd Edition Bauer Solutions Manual 1jessicaballxidbrcgpsj100% (13)
- Solution Manual For Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics Si Edition 1St Edition Reisel 1285056485 9781285056487 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics Si Edition 1St Edition Reisel 1285056485 9781285056487 Full Chapter PDFkathleen.osorio990100% (14)
- Giancoli Prob - Solution Chap.6Document6 pagesGiancoli Prob - Solution Chap.6Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics 1St Edition Reisel 1285056477 9781285056470 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics 1St Edition Reisel 1285056477 9781285056470 Full Chapter PDFkathleen.osorio990100% (15)
- Physics 1 Our ProjectDocument203 pagesPhysics 1 Our ProjectAviona LaycoNo ratings yet
- Learning-TasksDocument10 pagesLearning-TasksAlecel May PacardoNo ratings yet
- Today: Homework Due Conservation of Energy Read Chap 13, Sections 6 To 9 Homework: Chap. 13, Problems 57, 61, 67, 76Document12 pagesToday: Homework Due Conservation of Energy Read Chap 13, Sections 6 To 9 Homework: Chap. 13, Problems 57, 61, 67, 76Tony LoogmanNo ratings yet
- Newtown's Law of MotionDocument3 pagesNewtown's Law of MotionSaly Zydny Almasco PalenciaNo ratings yet
- MOMENTUMDocument4 pagesMOMENTUMAriane Nicole Barayang DamianNo ratings yet
- Problem: A 300 KG Car Has A Kinetic Energy of 500 J. Find Its SpeedDocument2 pagesProblem: A 300 KG Car Has A Kinetic Energy of 500 J. Find Its Speedreielleceana07No ratings yet
- Physics (SCIENVP) : Conservation of Mechanical EnergyDocument23 pagesPhysics (SCIENVP) : Conservation of Mechanical Energy7 bitNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power-1Document32 pagesWork, Energy and Power-1Ian HaroldNo ratings yet
- PHYS101 Impulse and MomentumDocument22 pagesPHYS101 Impulse and Momentumjojo basenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledYhace CaranguianNo ratings yet
- Igcse 43 Work&PowerDocument39 pagesIgcse 43 Work&PowerHany ElGezawy67% (3)
- Lesson 5 Work and EnergyDocument18 pagesLesson 5 Work and EnergyanonymousNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test BDocument3 pagesChapter Test BKenzyNo ratings yet
- Slide Presentation For ET2Document37 pagesSlide Presentation For ET2Redzwan KadirNo ratings yet
- C7Document18 pagesC7jungdjudfNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy FormulasDocument45 pagesWork and Energy FormulasAnghel jhed ViescaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Work Energy Power Solved Numerical Questions - 7Document4 pagesClass 9 Work Energy Power Solved Numerical Questions - 7tamishraza26No ratings yet
- Forms of Energy (Tutorial Part 2)Document3 pagesForms of Energy (Tutorial Part 2)asapamore100% (1)
- Yr 9 Work Power Energy RevisionDocument71 pagesYr 9 Work Power Energy RevisionJunho RyooNo ratings yet
- 13.6 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: W F DX MVDocument3 pages13.6 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: W F DX MVsreejitha KNo ratings yet
- Calculating the Work Done by a Centrifugal PumpDocument4 pagesCalculating the Work Done by a Centrifugal PumpFrancis DacutananNo ratings yet
- p6 Merged PDFDocument251 pagesp6 Merged PDFVal Andrea TuazonNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy and Energy ConservationDocument32 pagesPotential Energy and Energy Conservationelchappoo kalboNo ratings yet
- 1 Energy and Momentum Assig.Document3 pages1 Energy and Momentum Assig.Namdeo JadhavNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm 02Document8 pagesPractice Midterm 02Ha ViNo ratings yet
- The Period of A Mass On A SpringDocument16 pagesThe Period of A Mass On A SpringPatrick SibandaNo ratings yet
- Application of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Up and Down Motion in Free Fall MotionDocument1 pageApplication of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Up and Down Motion in Free Fall MotionBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3B - Work and EnergyDocument22 pagesChapter 3B - Work and Energyjaymart villarta100% (1)
- Kinetic Energy Practice Questions Answer KeyDocument2 pagesKinetic Energy Practice Questions Answer KeyRachel Alibo100% (1)
- Essential Physics Formulas Under 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesEssential Physics Formulas Under 40 CharactersMica :pNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power SlidesDocument36 pagesWork Energy Power Slidessweehian844100% (1)
- U V S Acceleration A M: Chapter 6: Topics K.E. and Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesU V S Acceleration A M: Chapter 6: Topics K.E. and Potential EnergyNavin RaiNo ratings yet
- Application of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Motion On Curve SurfaceDocument1 pageApplication of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Motion On Curve SurfaceBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Work Done by Force Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageWork Done by Force Problems and SolutionsBasic Physics100% (1)
- Potential Energy of Elastic Spring Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pagePotential Energy of Elastic Spring Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Power Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pagePower Problems and SolutionsBasic Physics100% (1)
- Application of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Free Fall MotionDocument1 pageApplication of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Free Fall MotionBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine (Application of The Second Law of Thermodynamics) Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageHeat Engine (Application of The Second Law of Thermodynamics) Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Application of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Motion On Inclined PlaneDocument1 pageApplication of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Motion On Inclined PlaneBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Application of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Up and Down Motion in Free Fall MotionDocument1 pageApplication of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Up and Down Motion in Free Fall MotionBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Isochoric Thermodynamics Processes Problems and Solutions PDFDocument1 pageIsochoric Thermodynamics Processes Problems and Solutions PDFBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Application of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Projectile MotionDocument1 pageApplication of Conservation of Mechanical Energy For Projectile MotionBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageGravitational Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Heat Problems and Solutions PDFDocument1 pageHeat Problems and Solutions PDFBasic Physics75% (4)
- Isobaric Thermodynamics Processes Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageIsobaric Thermodynamics Processes Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Carnot Engine (Application of The Second Law of Thermodynamics) Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageCarnot Engine (Application of The Second Law of Thermodynamics) Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- The First Law of Thermodynamics Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageThe First Law of Thermodynamics Problems and SolutionsBasic Physics100% (3)
- Application of The First Law of Thermodynamics in Some Thermodynamics ProcessesDocument1 pageApplication of The First Law of Thermodynamics in Some Thermodynamics ProcessesBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Linear Expansion Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageLinear Expansion Problems and SolutionsBasic Physics56% (9)
- Volume Expansion Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageVolume Expansion Problems and SolutionsBasic Physics0% (1)
- Area Expansion Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageArea Expansion Problems and SolutionsBasic Physics100% (1)
- Isothermal Thermodynamic Processes Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageIsothermal Thermodynamic Processes Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Converting Temperature Scales (Kelvin Scale, Celsius Scale, Fahrenheit Scale) Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageConverting Temperature Scales (Kelvin Scale, Celsius Scale, Fahrenheit Scale) Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat and Heat Capacity Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageSpecific Heat and Heat Capacity Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageElectric Potential Problems and SolutionsBasic Physics50% (2)
- Latent Heat, Heat of Fusion, Heat of Vaporization Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageLatent Heat, Heat of Fusion, Heat of Vaporization Problems and SolutionsBasic Physics50% (2)
- Mechanical Equivalent of Heat Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageMechanical Equivalent of Heat Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageElectric Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation For Heat Transfer Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageEnergy Conservation For Heat Transfer Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Parallel-Plate Capacitor Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageParallel-Plate Capacitor Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet