Professional Documents
Culture Documents
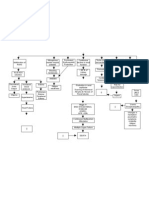
Chronic-kidney-failure-Patho Diagram Sheet1 PDF
Chronic-kidney-failure-Patho Diagram Sheet1 PDF
Uploaded by
GinoTevesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chronic-kidney-failure-Patho Diagram Sheet1 PDF
Chronic-kidney-failure-Patho Diagram Sheet1 PDF
Uploaded by
GinoTevesCopyright:
Available Formats
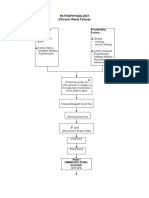
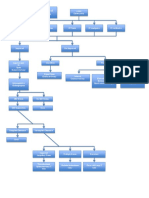
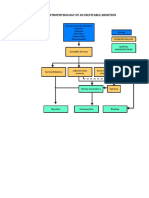
Non-‐modifiable
risk
factors:
-‐Hereditary
(gene9cally
Modifiable
risk
factors:
determined
abnormali9es
in
-‐Diabetes
mellitus
kidney
development
or
-‐Hypertension
integrity,
immune
complex
-‐Diet
-‐Smoking
deposi9on
and
inflamma9on
in
certain
types
of
-‐Use
of
analgesics
glomerulonephri9s)
-‐Toxin
inges9on
(toxin
exposure
in
-‐Age
greater
than
60
years
old
certain
diseases
of
the
renal
tubules
and
-‐Gender
inters99um
-‐Race
Reduc9on in renal mass
Increased intrarenal ac9vity of Hypertension PE:
the renin-‐angiotensin axis BP:
200/80mmHg
Increased pressure
Decreased
GFR
Ini9al
adap9ve
hyperfiltra9on
S9mula9on
of
TGF-‐B
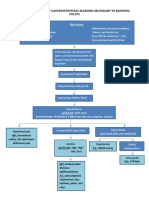
Disrup9on
of
sodium/potassium
balance
Impaired elimina9on of Increased glomerular Maladap9ve hypertrophy
nitrogenous wastes permeability and sclerosis
Increased
intravascular volume
Reduced excre9on
Uremia of phosphate Increased filtra9on of PE:
Inability to concentrate urine
proteins and Grade II bipedal
Fluid extravasa9on
macromolecules edema
Further loss of HPI:
Increased dyspnea Edema Dehydra9on
synthesis of PTH nephron func9on
PE: bilateral
and parathyroid rales
growth mass Conges9ve heart
Loss of nonexcretory renal failuire
func9on
Secondary Decreased renal
hyperparathyroidism perfusion
Diminished
calcitriol
Failure
to
produce
Impaired
insulin
Decreased
ammonia
Increased
Immune
Distrubances
in
produc9on
erythropoe9n
ac9on
produc9on
produc9on
of
lipids
impairment
reporduc9on
Decreased
ionized
Anemia
High
blood
glucose
Metabolic
Advanced
Delayed
wound
Infec9on
Decreased
libido
calcium
levels/errac9c
blood
acidosis
atherosclerosis
healing
and
infer9lity
glucose
levels
PE:
Pale
palpebral
Hypocalcemia
conjunc9vae
You might also like
- Fighting Inflammation - Harvard HealthDocument2 pagesFighting Inflammation - Harvard HealthJaZz SF0% (3)
- Concept Map On Renal FailureDocument1 pageConcept Map On Renal FailureJessilda Damian VeranoNo ratings yet
- Ninja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1Document42 pagesNinja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1pp100% (1)
- PiperacillinDocument3 pagesPiperacillinMario Magtaka0% (1)
- Diabetes 1&2 Rough RevisionDocument2 pagesDiabetes 1&2 Rough RevisionartsbyvanethenaNo ratings yet
- Common DiseasesDocument24 pagesCommon DiseasesNicole GayetaNo ratings yet
- MS EndoDocument9 pagesMS EndoTimothy LascoNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument4 pagesPharmacologys748jNo ratings yet
- FinalsDocument14 pagesFinalsZarina AvesNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument6 pagesGram Positive CoccirefuapalackyNo ratings yet
- Drug To Xi CitiesDocument1 pageDrug To Xi CitiesGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- Table 4-16 - Use of Mood Stabilizing Medications For BipolarDocument1 pageTable 4-16 - Use of Mood Stabilizing Medications For BipolarDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Table: Selected Antibacterial Antibiotics Antibiotics THAT . Mechanism of Action Names of Drugs Notes and ProblemsDocument4 pagesTable: Selected Antibacterial Antibiotics Antibiotics THAT . Mechanism of Action Names of Drugs Notes and ProblemsTJNo ratings yet
- Senng - Ch/6Mo) 76Nmlhlmalle8I: MenfalareeDocument5 pagesSenng - Ch/6Mo) 76Nmlhlmalle8I: MenfalareeGachibag IdNo ratings yet
- Chapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney DisordersDocument40 pagesChapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney Disordersjericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory Drug: CELECOXIBDocument4 pagesAnti-Inflammatory Drug: CELECOXIBYlrenne DyNo ratings yet
- EndokrinologiDocument26 pagesEndokrinologiAhmad Rafi Satrio PrayogoNo ratings yet
- All Diuretics - Sheet1Document1 pageAll Diuretics - Sheet1Anisha GillNo ratings yet
- Micro 22 RATIO by Clerky StubuDocument13 pagesMicro 22 RATIO by Clerky StubuJohn RamosNo ratings yet
- IM Pneumonia Harrisons and CPG NotesDocument2 pagesIM Pneumonia Harrisons and CPG NotesJoanna ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Gynaecology Revision PDFDocument13 pagesGynaecology Revision PDFAadhi AadhiNo ratings yet
- 4上cs 第一次心智圖Document1 page4上cs 第一次心智圖Eric LinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Document3 pagesPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- مخططات ذهنية ENDOCRINE فارما - 2022 - يونس الحماديDocument17 pagesمخططات ذهنية ENDOCRINE فارما - 2022 - يونس الحماديMohned AlhababiNo ratings yet
- Analgesia For InternsDocument4 pagesAnalgesia For InternsjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- KlebsiellaDocument3 pagesKlebsiellaFATHIMA ANo ratings yet
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDocument1 pagePathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroNo ratings yet
- Granules Speciality PDFDocument2 pagesGranules Speciality PDFMadhavi VutukuruNo ratings yet
- Kepincangan ABODocument2 pagesKepincangan ABOakmal syuhadaNo ratings yet
- Reniyasw: Ioptnlnosnsisunwnsionlsngdngims VioovyDocument3 pagesReniyasw: Ioptnlnosnsisunwnsionlsngdngims Vioovyวชิรพล คำแก้วNo ratings yet
- Moduleiii:Summativeevaluation: Pheochromocytoma. (2020) - N Ational Library of M EdicineDocument1 pageModuleiii:Summativeevaluation: Pheochromocytoma. (2020) - N Ational Library of M EdicineKashley DangliNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument44 pagesPHARMACOLOGYshruti sangwan100% (1)
- 2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13Document6 pages2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13A HNo ratings yet
- Surgery X-Rays E2-1Document34 pagesSurgery X-Rays E2-1Aishwarya ThakurNo ratings yet
- Portal Hypertension MindMapDocument1 pagePortal Hypertension MindMapjeeva pkpNo ratings yet
- Gynaecology Revision PDFDocument12 pagesGynaecology Revision PDFPranjal DevappaNo ratings yet
- RFT - Theory Notes-: (Important For Practical Also)Document13 pagesRFT - Theory Notes-: (Important For Practical Also)ammuNo ratings yet
- Endocrino Unidad 2 Diabetes Cont.Document33 pagesEndocrino Unidad 2 Diabetes Cont.GenesisGissellPlazaQuesadaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemMuhammad Jefri LukmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - InfarctionDocument4 pagesDrug Study - InfarctionJohn Bernard Ting TizonNo ratings yet
- Nota Rápida 2Document1 pageNota Rápida 2Emma CuevasNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- Pa Tho Physiology of GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of GlomerulonephritisJhaziel BermejoNo ratings yet
- SurgeryDocument11 pagesSurgerykittituch2gbNo ratings yet
- Ew Anu PDFDocument2 pagesEw Anu PDFrachel wongNo ratings yet
- Guest Lecture Hypertension NotesDocument4 pagesGuest Lecture Hypertension NotesKellyNo ratings yet
- All SummariesDocument28 pagesAll SummariesEsarpy (Nana)No ratings yet
- 22Document6 pages22ATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- Daniel - Assignment On AntibioticsDocument6 pagesDaniel - Assignment On AntibioticsArun Roa DanielNo ratings yet
- Intravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc SerumDocument2 pagesIntravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc Serumazhar hussinNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Data Instalasi Rawat Jalan Bln. Desember 2017: TOT: 173 SKTM: 6Document2 pagesRekapitulasi Data Instalasi Rawat Jalan Bln. Desember 2017: TOT: 173 SKTM: 6freddy laksaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure (Condensed) Part 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure (Condensed) Part 2deborah malnegro100% (5)
- You Created This PDF From An Application That Is Not Licensed To Print To Novapdf PrinterDocument21 pagesYou Created This PDF From An Application That Is Not Licensed To Print To Novapdf PrinterRóbinson GuzmánNo ratings yet
- This Is An Example .Docx File. Try Convert It With Word2PdfconverterDocument1 pageThis Is An Example .Docx File. Try Convert It With Word2PdfconverterGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- 020406s078 021428s025lbl PDFDocument27 pages020406s078 021428s025lbl PDFGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Michigan: Topic: Alcohol ConsumptionDocument2 pagesMichigan: Topic: Alcohol ConsumptionGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- TX Algo GBDocument1 pageTX Algo GBGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CA PathoDocument1 pageOvarian CA PathoGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Functions Sources Diseases Caused by Deficiencies TriviaDocument4 pagesVitamin Functions Sources Diseases Caused by Deficiencies TriviaGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Non Pharma and Monitoring and Follow-UpDocument1 pageNon Pharma and Monitoring and Follow-UpGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysioDocument1 pagePath o PhysioGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CA PathoDocument1 pageOvarian CA PathoGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Appendicitis: Vague, Dull, Diffuse Pain in The Midabdomen or EpigastriumDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Appendicitis: Vague, Dull, Diffuse Pain in The Midabdomen or EpigastriumGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Algorithm in The Management of Acute Calculous CholecystitisDocument1 pageAlgorithm in The Management of Acute Calculous CholecystitisGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- DKA Pharma PediaDocument1 pageDKA Pharma PediaGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gastrointestinal Bleeding Secondary To Bleeding PolypsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Gastrointestinal Bleeding Secondary To Bleeding PolypsGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Transvaginal Sonography: Rule in Rule OutDocument1 pageTransvaginal Sonography: Rule in Rule OutGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of An Inevitable AbortionDocument1 pageThe Pathophysiology of An Inevitable AbortionGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- 31 .9c Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake DisorderDocument1 page31 .9c Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake DisorderGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics of Multiple Dosing: Under The Guidence of Presented byDocument34 pagesPharmacokinetics of Multiple Dosing: Under The Guidence of Presented byRAVINDRA BABUNo ratings yet
- Gracewell Product Faq's & Competetor KnockoutsDocument25 pagesGracewell Product Faq's & Competetor KnockoutskurutalaNo ratings yet
- Satiereal Product Sheet - 2016Document2 pagesSatiereal Product Sheet - 2016JudyCobbettNo ratings yet
- Pet Therapy PosterDocument1 pagePet Therapy Posterapi-659758740No ratings yet
- Student'S Health Information Form: (E.g. Frequency, Extent, Duration, Ongoing Therapy, Etc.)Document2 pagesStudent'S Health Information Form: (E.g. Frequency, Extent, Duration, Ongoing Therapy, Etc.)Susan Loida SorianoNo ratings yet
- Venous DiseaseDocument45 pagesVenous DiseaseNinch Nagac100% (1)
- Ma. Subramanian: Health and Family Welfare DepartmentDocument3 pagesMa. Subramanian: Health and Family Welfare DepartmentMdnowfalNo ratings yet
- COLD Vs FLU ChartDocument1 pageCOLD Vs FLU ChartAllysha VarugheseNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Klinis Dan Laboratorium Pada Pasien Pneumonia Di Icu Rsud Raden Mattaher JambiDocument7 pagesGambaran Klinis Dan Laboratorium Pada Pasien Pneumonia Di Icu Rsud Raden Mattaher JambigusdeNo ratings yet
- s11882 018 0806 6 PDFDocument7 pagess11882 018 0806 6 PDFHildreth Rosel SabioNo ratings yet
- IMG Current Issues (2011)Document24 pagesIMG Current Issues (2011)Jasmik SinghNo ratings yet
- Announcement PKBDocument8 pagesAnnouncement PKBlo tek huiNo ratings yet
- Certificat EU VaccinareDocument2 pagesCertificat EU VaccinareAlina ComanNo ratings yet
- GoreDocument12 pagesGoreSong SongNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Bacterial Agents Isolated From Aspirate Cultures of Covid 19 General Intensivecare Patients Compared To Pre Pandemic ConditionsDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Bacterial Agents Isolated From Aspirate Cultures of Covid 19 General Intensivecare Patients Compared To Pre Pandemic ConditionsRicardo ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- 10 Herbal Medicines Approved by Doh and Their UsesDocument8 pages10 Herbal Medicines Approved by Doh and Their UsesRichard MendejaNo ratings yet
- DefibrillationDocument11 pagesDefibrillationAli Al-AhmedyNo ratings yet
- Speaking AVCN2Document6 pagesSpeaking AVCN22253010690No ratings yet
- COVID-19 RT-PCR Test (Qualitative)Document1 pageCOVID-19 RT-PCR Test (Qualitative)IT'S RAJNo ratings yet
- Chen 2013Document9 pagesChen 2013Santa Maria PangaribuanNo ratings yet
- 5.respiratory Distress Dental LectureDocument40 pages5.respiratory Distress Dental LecturehaneeneeNo ratings yet
- Lateral Femoral Wall Thickness: TraumaDocument5 pagesLateral Femoral Wall Thickness: TraumaLobozNo ratings yet
- Component Therapy-Transfusion of TheDocument8 pagesComponent Therapy-Transfusion of TheGennelyn Ross Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1itsmeayaNo ratings yet
- First Aid BookDocument3 pagesFirst Aid BookPontuChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- BronkiolitisDocument32 pagesBronkiolitisDewa Ayu LisnaNo ratings yet
- Application of Data Mining Diabetes Health Care in Youngand Old PatientsDocument3 pagesApplication of Data Mining Diabetes Health Care in Youngand Old PatientsHussain SajidNo ratings yet
- Situs Inversus TotalisDocument3 pagesSitus Inversus TotalisAlin MihetiuNo ratings yet
- NLE Comprehensive Exam 3Document27 pagesNLE Comprehensive Exam 3Jofel Laygan Porras RN100% (1)