0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pageNormas Técnicas de Diseño por Viento
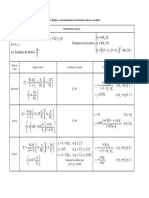
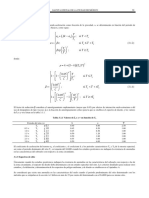
This document outlines technical standards for wind load design in Mexico City. It covers general considerations, classification of structures, wind speed and pressure determination methods, interior pressures, exposed area, pressure coefficients, roof element design, dynamic wind loads parallel to wind, vortex-induced vibration effects, and permissible displacements. Key aspects include classifying structures by importance and dynamic response, determining design wind speed and pressure, using simplified or static methods, and accounting for dynamic effects in various structural configurations.
Uploaded by
Mark24_12Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pageNormas Técnicas de Diseño por Viento
This document outlines technical standards for wind load design in Mexico City. It covers general considerations, classification of structures, wind speed and pressure determination methods, interior pressures, exposed area, pressure coefficients, roof element design, dynamic wind loads parallel to wind, vortex-induced vibration effects, and permissible displacements. Key aspects include classifying structures by importance and dynamic response, determining design wind speed and pressure, using simplified or static methods, and accounting for dynamic effects in various structural configurations.
Uploaded by
Mark24_12Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd