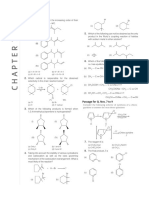
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Haloalkanes MS
Uploaded by
Grace KamauOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Haloalkanes MS
Uploaded by
Grace KamauCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS
1. (i) Cl2 → 2Cl• / ½ Cl2 → Cl• (1) 1
(ii) Cl•+ C6H5CH3 → C6H5CH2• + HCl (1)
C6H5CH2• + Cl2 → Cl• + C6H5CH2Cl (1) 2
(iii) C6H5CHCl2 / C6H5CCl3 / C6H5 CHCHC6 H5 /
other correct possible answer (1) 1
[4]
2. (a) (i) (free–)radical substitution 1
(both words required for the mark)
(ii) uv light OR sunlight OR high temperature OR 150oC to 500oC 1
(iii) Propagation 1
(ignore “chain”, “first”, “second” in front of the word propagation)
(iv) Termination 1
·CH2CH3 + Br· → CH3CH2Br
OR 2·CH2CH3 → C4H10 1
(penalise if radical dot is obviously on CH3, but not otherwise)
(penalise C2H5·)
(credit 2Br· → Br2)
(ignore “chain” in front of the word termination)
(b) (i) Fractional distillation OR fractionation 1
(credit gas–liquid chromatography, GLC)
(ii) CH3CH3 + 6Br2 → C2Br6 + 6HBr 1
(credit C2H6 for ethane)
[7]
3. (a) (i) (free–) radical substitution 1
(both words required for the mark)
initiation Cl2 → 2Cl· 1
(credit correct half arrows, but penalise double headed arrows)
first propagation CH3Cl + Cl· → ·CH2Cl + HCl 1
second propagation ·CH2Cl + Cl2 → CH2Cl2 + Cl· 1
(penalise the absence of dots on radicals once only)
(penalise radical dot on Cl of CH2Cl once only)
(ii) CH3Cl + Cl2 → CH2Cl2 + HCl 1
(penalise if any radicals appear in this equation)
Mill Hill High School 1
(b) M1: mol C = 10.1/12.0 and mol Cl = 89.9/35.5 1
M2: Ratio 0.842 : 2.53 OR 1: 3 OR CCl3 1
M3: 237.0/Mr of CCl3 = 237.0/118.5 = 2 Therefore C2Cl6 1
(correct answer gains full credit)
OR
M1: 237.0 × 10.1/100 and 237 × 89.9/100 1
M2: Ratio 23.9/12.0 : 213/35.5 OR 2 : 6 1
M3: C2Cl6 1
(correct answer gains full credit)
(c) any two from CHBr3 or CBr4 or C2H2Br4 (or CHBr2CHBr2) or C2Br6
(or CBr3CBr3) 2
(ignore HBr or H2)
(ignore equations and ignore names when given in addition to formulae)
(penalise names alone)
[10]
4. (a) (i) substitution or hydrolysis (1)
nucleophile (1)
CH 3
H3C CH(CH 3 ) 2
–
(ii) HO: C Br (1) HO C CH(CH 3 ) 2
(1)
CH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3
(1)
or H3C CH(CH 3 ) 2 H3 C CH(CH 3 ) 2
– +
C Br HO: C
CH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3
(b) (i) Type of reaction elimination (1)
Role of reagent base or proton acceptor (1)
Mill Hill High School 2
(ii) Structure of the alkene (CH3)2C=C(CH3)CH2CH3 (1)
Mechanism
(1)
–
:OH
H (1) H
(CH 3 ) 2 C (CH 3 ) 2 C (1) CH 2 CH 3
C Br +C
H 3C
CH 2 CH 3 CH 3
–
H :OH
or (CH 3 ) 2 C
C Br
H 3C
CH 2 CH 3
(iii) Structure of second alkene (CH3)2CHC(CH3)=CHCH3 (1)
Name 3,4-dimethylpent-2-ene (1)
Structure of third alkene (CH3)2CHC(C2H5)=CH2 (1)
Name 2-ethyl-3-methylbut-1-ene(1) 10
[15]
5. (i) M1 curly arrow from lone pair of electrons on oxygen of hydroxide ion 1
(insist on a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom and a
negative charge, but only credit this mark if the attack is to a
correct H atom)
M2 curly arrow from the middle of the C–H bond to the middle of
the C–C bond. 1
(only credit this mark if the arrow originates from the correct
C–H bond and if an attempt has been made at M1)
M3 curly arrow from the middle of the C–Br bond towards/alongside
the Br atom. 1
(credit M3 independently unless the bond breaking is
contradicted by an additional arrow)
(penalise M3 curly arrow if the C–Br has a formal positive charge)
(ignore partial charges on the C–Br bond, but penalise if incorrect)
(credit full marks for an E1 mechanism, with M2 awarded for a correct
curly arrow on the correct carbocation)
(award a maximum of two marks for an incorrect haloalkane)
(ignore products)
Mill Hill High School 3
(ii) Haloalkane/C2H5Br is made from ethane
OR haloalkane is not (readily) available
OR haloalkane is expensive
OR it is (too) expensive/costly
OR (reaction) yield is too low/poor
OR it is too slow
OR a valid reference to nucleophilic substitution/alcohol formation
occurring as an alternative reaction. 1
(ignore references to temperature or to energy consumption)
(do not credit statements which refer to the idea that this route
is not chosen, because industry chooses another route e.g. cracking)
[4]
6.
(i) M1: potassium cyanide OR KCN OR sodium Cyanide OR NaCN; 1
(ignore conditions - dissolved in (aq) or (alc) or KOH(aq) all
work) (penalise HCN)
M2: propanenitrile; 1
(credit propan-1-nitrile OR propan nitrile, but not propanitrile)
(ii) M1: ammonia OR NH3; 1
(If formula is written, insist that it is correct)
(ignore conditions, but penalise acidic)
M2: ethylamine; 1
(credit aminoethane)
(iii) M1: curly arrow from lone pair on nitrogen of (correct formula for)
ammonia towards/alongside C atom of C-Br; 1
(penalise M1 if formula of ammonia is wrong or has a negative
charge or has no lone pair or arrow is from negative charge)
M2: curly arrow from C-Br bond towards/alongside side Br atom; 1
(credit M2 independently)
(penalise M2 if formal positive charge on C atom of C-Br)
M3: correct structure of the ethylammonium ion; 1
(credit the structure drawn out with all four bonds around the
nitrogen atom OR written as C2H5NH3+ OR CH3CH2NH3+)
M4: curly arrow from the middle of one of the H-N bonds towards the
positive N atom; 1
(possible to credit M4 on an incorrect ethylammonium ion with
no positive charge)
(ignore use of ammonia or bromide ion etc. to remove proton
from ethylammonium ion)
(If the wrong haloalkane is used, award MAX. 3 marks for the
mechanism) (If SN 1 mechanism is used, give full credit in which
M1 is for a curly arrow from the lone pair of the N atom of
(correct formula for) ammonia towards/alongside the positive
carbon atom of CH3CH2+)
[8]
Mill Hill High School 4
7. (a) CH 3 CH CH CH 3 or CH 3 CHBrCH(CH 3 )2 1
Br CH 3
(1)
H3C CH 3
(b) (i)
C C or CH 3 CH C(CH 3 ) 2
H CH 3
(1)
(ii) (nucleophilic) elimination
(1) –
:OH
H
(1)
+
CH 3 CH C CH 3 or via CH 3 CHCH(CH 3 ) 2
(1) Br CH 3
5
(c) 3–methylbut–1–ene (1) 1
[7]
8. (i) Mechanism:
–
HO: (1) M1
.. –
CH3 CH CH 3 CH3 CH CH 3 + Cl
(1)
Cl M2 OH
–
HO:
Credit M1 for
CH3 CH CH 3
+
M1 and M2 independent
Curly arrows must be from a bond or a lone pair
Do not penalise sticks
Penalise M1 if Na OH precedes (penalise this once)
Penalise incorrect δ+ δ– for M2
Penalise + on C atom for M2
Only allow M1 for incorrect haloalkane
Role of the hydroxide ion: nucleophile (1)
electron pair donor
lone pair donor
NOT nucleophilic substitution
Mill Hill High School 5
(ii) Mechanism:
–
HO: (1) M1
M2
H (1)H
.. –
H C C CH 3 H 2C CHCH 3 + Cl + H 2 O
(1)
H Cl M3
–
HO:
H H
H C C CH 3
+
H
Only allow M1 and M2 for incorrect haloalkane unless RE on (i)
+ charge on H on molecule, penalise M1
M3 independent
M2 must be to correct C–C
M1 must be correct H atom
Credit M1 and M2 via carbocation mechanism
No marks after any attack of C ⊕ by OH–
Role of the hydroxide ion: base (1) 7
proton acceptor
accepts H+
[7]
9. (a) (i) Structure: OH insist on
H3C CH CH 3 (1) C OH bond
No credit for propan-1-ol even when named correctly
Credit propane-2-ol
Name: propan-2-ol (1)
Not 2-hydroxypropane
(ii) Name of mechanism: nucleophilic substitution (1) (both words)
(NOT SN1 orSN2)
M1
arrow (1) Br
:
Mechanism: H3C CH CH 3 CH 3 CH(OH)CH 3 + Br –
–
HO: (1) arrow from
(M2) lone pair
penalise incorrect polarity on C-Br (M1)
Credit the arrows even if incorrect haloalkane
If SN1, both marks possible
–
:
i.e. M1 C Br M2 HO correct carbocation
5
Mill Hill High School 6
(b) (i) elimination (1)
(ii) base (1)
OR proton acceptor
NOT nucleophile (base)
2
[7]
10. (a) M1 NaOH OR KOH OR correct name 1
M2 aqueous or solution in water (ignore heat, reflux etc.) 1
(Penalise M1 for hydroxide ion alone, but mark on and credit M2)
(Credit M2 ONLY for H2O as reagent and heat / warm / T=50 to
100oC)
(NaOH(aq) scores M1 and M2 provided it is not contradicted)
(Penalise M2 if NaOH(aq) followed by concentrated or ethanol)
(Penalise M1 and M2 if followed by acid)
(b) Ethanolic OR alcoholic OR CH3CH2OH / CH3OH solvent OR 1
aqueous ethanol/alcohol
OR higher temperature (must be comparative)
(Ignore heat or heat under reflux)
(Credit part (c) independently from part (b))
(Penalise “ethanoic”)
[3]
11. (i) 2–methylpropanenitrile (1)
(ii) Reagent KCN (1)
Conditions alcoholic/aq (1)
(iii) Name of mechanism nucleophilic substitution (1)
CH 3 CH 3
[1]
Mechanism
CH 3 C Br CH 3 C CN
–
H [1] H
NC: [1] –
+ :Br
7
[7]
Mill Hill High School 7
12. (a) Name of mechanism: nucleophilic substitution (1)
Mechanism:
CH 3 (1) (1) CH 3 (M3 is for correct
carbocation - if
CH 3 C Br CH 3 C H used wrong
+
(1) H H N H halogenoalkane
lose M3)
:NH 3 N (1)
( :NH 3 (
(wrong dipole
δ– δ+ +
C Br or C Br
loses C Br
mark)
Marks SN1 using same points
CH 3
∴ M2 requires
CH 3 C Br
+
:NH 3
(b) Role of potassium hydroxide: Base (1)
Mechanism:
H (1) H
CH 3 C Br CH 3 C (1)
(1)
H C H CH 2
–
H :OH
(1)
Mark E1 using same points
H H
∴ M2/M3
CH 3 C C H
+
H
:OH – 5
[10]
13. elimination (1) 1
[1]
14. (i) CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CN (1) Not C4 H9 CN
Pentanenitrile (1)
allow pentanonitrile, ignore numbers
Mill Hill High School 8
(ii) Nucleophilic substitution (1)
H M1
(1)
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 C Br
H
(1) –
M2 :CN
SN1 mechanism
M1 formation of carbocation including C Br
M2 attack by :CN–
allow mechanism showing ‘Cl’
If ‘+’ onC’ lose M1
If K–CN shown lose M2
δ+
If δ–c– Bs lose M1
(iii) C–F bond is strong (er) (1)
Must imply C–F is stronger than C–Br bond
ignore references to electronegativity, bond polarity etc.
6
[6]
15. (a) (base) elimination 1
(penalise other words before ‘elimination’ e.g. nucleophilic)
M1: curly arrow from lone pair of electrons on oxygen of hydroxide ion 1
(insist on a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom and a negative
charge, but only credit this mark if the attack is to a correct H atom) 1
M2: curly arrow from the middle of the C-H bond to the middle
of the C–C bond 1
(only credit this mark if the arrow originates from the correct C–H
bond and if an attempt has been made at M1)
M3: curly arrow from the middle of the C–Br bond towards/alongside
the Br atom
(credit M3 independently unless the bond breaking is contradicted
by an additional arrow)
(penalise curly arrow if the C–Br has a formal positive charge)
(credit full marks for an E1 mechanism, with M2 awarded for a correct
curly arrow on the correct carbocation)
(award a maximum of two marks for either an incorrect haloalkane or
an incorrect organic product)
(maximum 2 marks for use of .sticks. for the haloalkane, unless RE
from 2(b), when credit can be given)
(b) nucleophile or electron pair donor 1
(penalise ‘base’)
Mill Hill High School 9
(c) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + 2NH3 → CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2 + NH4Br 2
(M1 correct product)
(M2 balanced equation using 2NH3 and leading to NH4Br)
(penalise M1 for use of C4H9NH2 or for incorrect haloalkane,
but allow consequent correct balancing of equation with 2 moles
of ammonia)
(1–)butylamine 1
(credit 1–aminobutane and butyl–1–amine)
(award QoL mark for correct spelling)
[8]
16. (i) potassium or sodium hydroxide (or other specific strong base) (1)
allow formula; not just ‘hydroxide’
in ethanolic /alcoholic solution (independent of first mark) (1) 2
allow ‘in ethanol’, not just ‘ethanol’/ ‘with ethanol’
ignore references to heat / pressure
H H H H
H H H H
C C C C
H H H H
(ii) C C + KOH C C + KBr + H 2 O
H H H H
C C C C
H H H H
H Br
structure of cyclohexene showing double bond (1)
minimum structure needed is a ring with CH2 units implied
and double bond:
do not allow KOH over arrow
equation correct overall ie balanced
allow ionic equation (1) 2
(iii) elimination / dehydrohalogenation 1
ignore nucleophilic / electrophilic etc.
[5]
17.
(a) (i) CH3CH2CH2Br + KCN → CH3CH2CH2CN + KBr (1) 1
allow C3H7Br allow C4H7N
(ii) nucleophilic substitution / SN2 (1) 1
(b) CN– or NC– (1)
lone pair of electrons on C atom (1) 2
[4]
Mill Hill High School 10
18. (a) 2-bromobutane; 1
(b) Elimination; 1
(penalise “nucleophilic” OR “electrophilic” before the word
“elimination”)
M1: curly arrow from lone pair on oxygen of hydroxide ion to H atom
on correct C-H adjacent to C-Br; 1
(penalise M1 if KOH shown as covalent with an arrow breaking
the bond)
M2: curly arrow from single bond of adjacent C-H to adjacent single bond C-C; 1
(only credit M2 if M1 is being attempted to correct H atom)
M3: curly arrow from C-Br bond to side of Br atom; 1
(credit M3 independently unless arrows contradict)
(Credit possible repeat error from 2(c)(iii) for M3)
(If the wrong haloalkane is used OR but-1-ene is produced,
award MAX. 2 marks for the mechanism)
(If E1 mechanism is used, give full credit in which M1 and M2
are for correct curly arrows on the correct carbocation)
[5]
19. (a) (i) CH3Cl + 2Cl2 → CHCl3 + 2HCl (1)
(ii) step in which radicals are used and formed (1)
(iii) CH3Cl + Cl• → •CH2Cl + HCl (1)
(iv) •CHCl2 + Cl2 → CHCl3 + Cl• 4
(b) Equation CH3Cl + 2NH3 → CH3NH2 + NH4Cl (1)
Mecanism
H
(1) (1)
+
H 3 N: CH 3 Cl CH 3 N H
(1) (1)
H
:NH 3 5
[9]
20. CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl (1)
Initiation: Cl2 → 2Cl. (1)
Propagation: CH4 + Cl. → CH3. + HCl (1)
CH3. + Cl2 → CH3Cl + Cl. (1)
Termination: Cl. + Cl. → Cl2 (1)
or CH3. + CH3. → C2H6 5
[5]
Mill Hill High School 11
21. Reaction 5 NH3 (1) 1
For Reaction 4; credit dil H2SO4 OR H2SO4(aq) OR HCl (aq)
but NOT steam and NOT NaOH(aq)
[1]
22. nucleophilic substitution 1
(both words needed)
Mechanism M1 curly arrow from lone pair on oxygen of hydroxide 1
ion to C atom of C-Br
Mechanism M2 curly arrow from C-Br bond to side of Br atom 1
(a possible repeat error here from Question 4a)
(award a maximum of one mark for the wrong haloalkane)
(credit an SNl mechanism in which Ml will be a curly arrow from
the lone pair on oxygen of the hydroxide ion to the correct
positive carbon atom)
Y is susceptible to attack by hydroxide ions for one of the following reasons 1
o the C-Br bond is polar
o the carbon atom is partially positive (or shown as such)
o the carbon atom is electron deficient
[4]
23. (a) Reaction 2: NaOH OR KOH (1) M1 alcohol (ic) OR ethanol (ic)(1) M2
ignore heat
Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M2 if OH–
or base or alkali mentioned
2
(b) Mechanism:
– M1
HO: (1)
M2
H(1) H
..
H C C H( H2C CH 2 + H2 O + CL – )
(1)
H Cl M3
Award M3 (C Cl) independently
M1 and M2 must be to / from correct places
H H
E1 mechanism possible in which M2 H C C H
+
H
Name: of mechanism = elimination (1)
NOT dehydrohalogenation
Ignore “base” OR “nucleophilic” before elimination
Reason: Reaction 2 has (very) low yield (1) 5
QoL OR chloroethane has to be made (from ethane)
OR chloroethane is expensive
OR chloroethane is not redily available
[7]
Mill Hill High School 12
24. (a) Alcohol: Reaction = Substitution (/ hydrolysis) (1)
Ignore reference to nucleophilic, but electrophilic give zero
Alcohol: Role = nucleophile (/ lone pair donor) (1)
Alkene: reaction = elimination (1)
Ignore ref to nucleophilic or electrophilic
Alkene: base (/ proton acceptor) (1) 4
(b) Alcohol = butan-2-ol (1)
Not 2-hydroxybutane or but-2-ol
Appropriate structure for CH3CH(OH) CH2CH3 (1)
Brackets not essential
SN2 version SN1 version
δ+ δ−
C – Br bond is polar C–Br bond is polar (1)
Lone pair of OH– C–Br bond breaks (1)
Attacks the Cδ+ forming carbocation / carbonium ion (1)
M1 can be scored from a diagram, M2 and M3 from written
explanation only 5
[9]
25. (i) 2-chloro(-2-)methylpropane / (2)methyl 2 chloropropane (1) 1
(ii) appropriate unambiguous formula for either but-1-ene or but-2-ene (1)
appropriate unambiguous formula for the remaining structural isomer
allow 1 mark if candidate draws cis and trans but-2-ene (1) 2
(iii) unambiguous structure for 2-methylpropan-1-ol – may be
from mechanism (1)
curly arrow / attack by OH– curly arrow from lone pair or
charge only (1)
do not allow if Na -OH
curly arrow from bond to Cl / dipole shown on
C-Cl bond / intermediate showing 3 full and 2 partial bonds to C (1)
loss of Cl– NaCl or Na+:Cl– (1)
–
not allowed 4
if SN1 mechanism given:
first mark as above - independent
second mark for correct carbocation formed including curly
arrow from C to Cl or CS+ –ClS –
third mark for hydroxide attack as above
final mark not available (wrong mechanism)
penalise missing proton once only
[7]
Mill Hill High School 13
26.
(1)
Br
CH 3
(1) OH +
CH 3 CH 2 C CH 3 CH 3 CH C
base CH 3
(1)
(1)
HO CH 3 H
(1)
HO (1)
OH
nucleophile
(1)
CH3CH=C(CH3)2 (1)
CH3CH2C(OH)( CH3)2 (1) 2-methylbut-2-ene (1)
2-methylbutan-2-ol (1) also loss of H+ from CH3 (1)
or
Br
CH 3 CH C CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 C = CH 2 (1)
(1) CH 3
H CH 3
HO (1)
2- methylbut - l - ene (1)
14
[14]
Mill Hill High School 14
You might also like
- Solution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringFrom EverandSolution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Organics, Synthesis and Enthalpy MSDocument47 pagesOrganics, Synthesis and Enthalpy MSAnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- 2.10 Alcohols Extra Questions Ms 1.: Mill Hill High School 1Document15 pages2.10 Alcohols Extra Questions Ms 1.: Mill Hill High School 1Emil Van Der MeerNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes MarkschemeDocument23 pagesHaloalkanes MarkschemeqwedsaNo ratings yet
- 4.08-4.09 Amino Acids and Polymers MSDocument9 pages4.08-4.09 Amino Acids and Polymers MSpillboxsesame0sNo ratings yet
- KIITEE Chemistry PaperDocument7 pagesKIITEE Chemistry PaperPrasan NandaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 Alkanes - AnswersDocument7 pagesTutorial 10 Alkanes - AnswersEugene ChanNo ratings yet
- GgasfjofwojfosDocument68 pagesGgasfjofwojfosG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument18 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesBhavesh KNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 4 NeetDocument5 pagesUnit Test 4 Neetmanan10jas1529No ratings yet
- Fuels & Alkanes 3 MSDocument4 pagesFuels & Alkanes 3 MSRiya PatelNo ratings yet
- Al KanesDocument6 pagesAl KanesSLNo ratings yet
- BR (D) BR (C) : (A) I II III IV (B) IV III II I (C) IV III I II (D) I II IV IIIDocument2 pagesBR (D) BR (C) : (A) I II III IV (B) IV III II I (C) IV III I II (D) I II IV IIIHemendra PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Assessed Homework Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesAssessed Homework Mark SchemelfcluishoughtonNo ratings yet
- DPP 6Document3 pagesDPP 6ashutosh99878No ratings yet
- Premock 2 Mark Scheme (2016-17) Class: XI Section ADocument3 pagesPremock 2 Mark Scheme (2016-17) Class: XI Section AFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- HCU Chemistry 2011-2017 - Career EndeavourDocument78 pagesHCU Chemistry 2011-2017 - Career EndeavourSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- 2701 Chemistry Paper With Answer EveningDocument5 pages2701 Chemistry Paper With Answer Eveningthakartanishq07No ratings yet
- Bottom of Pyramid - Test # 3 - Haloalkanes & Haloarenes: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document7 pagesBottom of Pyramid - Test # 3 - Haloalkanes & Haloarenes: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Jay PatelNo ratings yet
- 4.06 - 4.07 Aromatic Chemistry and Amines MSDocument20 pages4.06 - 4.07 Aromatic Chemistry and Amines MSAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of ADocument67 pagesEnthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of AG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in BondDocument67 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in BondG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Objectives: CH - OHDocument18 pagesObjectives: CH - OHHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- Anic Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundsDocument6 pagesAnic Chemistry Carbonyl Compoundseamcetmaterials100% (1)
- Enthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of ADocument67 pagesEnthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of AG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in Bond Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentDocument68 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in Bond Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3: ChemistryDocument13 pagesSample Paper 3: ChemistryPr SathishNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 3 MSDocument5 pagesStoichiometry 3 MSEbaad RehmanNo ratings yet
- Rasi WPT Xi Che Neet 01-1-1-24Document3 pagesRasi WPT Xi Che Neet 01-1-1-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Gate 2001 CyDocument9 pagesGate 2001 CySumanta- 14No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon (SCH Sir)Document5 pagesHydrocarbon (SCH Sir)ArthGadaNo ratings yet
- Mark SheetDocument8 pagesMark SheetLearn With SaadiNo ratings yet
- UKChO 2003 Round 1 Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesUKChO 2003 Round 1 Mark SchemeLIU YUEYANG RVHS STU 2018No ratings yet
- GOC DPP 1 - StudentDocument3 pagesGOC DPP 1 - StudentVanshdip RawatNo ratings yet
- ( ) (1) ( ) Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentDocument67 pages( ) (1) ( ) Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Answer Assignment-04 On Hydrocarbon (Alkane, Alkene & Alkynes)Document2 pagesAnswer Assignment-04 On Hydrocarbon (Alkane, Alkene & Alkynes)mew090506No ratings yet
- M-Caps-34: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Document5 pagesM-Caps-34: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Vishal SinghNo ratings yet
- MHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Document3 pagesMHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Sank DamNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in BondDocument68 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in BondG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Goc 2Document2 pagesGoc 2Jayanth KNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of ADocument68 pagesEnthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of AG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- How Far MSDocument6 pagesHow Far MSsaadNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions-T-5Document2 pagesRedox Reactions-T-5Soham SagaonkarNo ratings yet
- 717Document13 pages717Himanshu GoelNo ratings yet
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides - DPP-02 - NEET - Haloalkane and Haloarene (DPP-02) - LakshayDocument3 pagesAlkyl and Aryl Halides - DPP-02 - NEET - Haloalkane and Haloarene (DPP-02) - LakshayDarsh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Xii ChemistryDocument10 pagesXii Chemistrysuraj0222222No ratings yet
- Anic Chemistry 222-300Document12 pagesAnic Chemistry 222-300eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- (Career Endeavour) IIT JAM CHEMISTRY PDFDocument88 pages(Career Endeavour) IIT JAM CHEMISTRY PDFKiran Mandal100% (1)
- Green Park Educational Institutions, Namakkal: Long Term - Chemistry (Worksheet)Document4 pagesGreen Park Educational Institutions, Namakkal: Long Term - Chemistry (Worksheet)Monalisa PremkumarNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims s60, MPL & LTC Aits Grand Test - 19 Paper (29!04!2023)Document30 pagesSR Elite, Aiims s60, MPL & LTC Aits Grand Test - 19 Paper (29!04!2023)vulurakashsharma2005No ratings yet
- Arihant HydrocarbonDocument7 pagesArihant Hydrocarbonlovishg10No ratings yet
- Goc TestDocument10 pagesGoc TestbalramsharmaNo ratings yet
- ND SPL Test Xii Che Neet 15-12-23Document7 pagesND SPL Test Xii Che Neet 15-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Jee Main 2019 Chemistry Sample Question Paper IDocument6 pagesJee Main 2019 Chemistry Sample Question Paper ImisostudyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29-Jun-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 29-Jun-2023Sudhir KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: DPP 13 (Of Lec 14) - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesHydrocarbon: DPP 13 (Of Lec 14) - Lakshya JEE 2.0 20244rhmhv9vf5No ratings yet
- ProjectDocument17 pagesProjectrudrashah4777No ratings yet
- LT RPT 1 Jee Che Iit 11-02-24Document3 pagesLT RPT 1 Jee Che Iit 11-02-24pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals Test Mark Scheme /30 Name 1Document3 pagesTransition Metals Test Mark Scheme /30 Name 1Corey NNo ratings yet
- Org Che Carbonyl CompoundsDocument6 pagesOrg Che Carbonyl Compoundsrafiyashaik943No ratings yet
- A2 Hydrocarbons: Zahid Iqbal Warraich 0333-4200541Document7 pagesA2 Hydrocarbons: Zahid Iqbal Warraich 0333-4200541Grace KamauNo ratings yet
- June 2015 (v3) QP - Paper 3 CIE Chemistry A-Level PDFDocument12 pagesJune 2015 (v3) QP - Paper 3 CIE Chemistry A-Level PDFGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- 13 English Mark SchemeDocument12 pages13 English Mark SchemeGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- Case Study of A Drainage BasinDocument8 pagesCase Study of A Drainage BasinGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- AerospaceDocument8 pagesAerospaceGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- Halogenoalkanes, Nucleophilic Substitution, Elimination Reactions, Uses and CFC Problems PDFDocument7 pagesHalogenoalkanes, Nucleophilic Substitution, Elimination Reactions, Uses and CFC Problems PDFGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- Emma JonesDocument3 pagesEmma JonesGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- 2015 Case Studies BOOKLET With DetailDocument28 pages2015 Case Studies BOOKLET With DetailGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- 2016 Specimen Paper 2 InsertDocument2 pages2016 Specimen Paper 2 InsertGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- RevisionChecklistIGCSEICE0417 PDFDocument42 pagesRevisionChecklistIGCSEICE0417 PDFGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Group 18, Group 1 and Group 17 ElementsDocument2 pagesPhysical Properties of Group 18, Group 1 and Group 17 ElementsJames Chua Hong KhengNo ratings yet
- Active Matter in Anionic Surfactants by Potentiometric TitrationDocument4 pagesActive Matter in Anionic Surfactants by Potentiometric Titrationmkaseem74No ratings yet
- Casing and Cementing HardwareDocument4 pagesCasing and Cementing Hardwarezapspaz100% (1)
- Rsia Artha Mahinrus: Jl. Pasar 3 No. 151 - Terusan Tuasan, 20237Document15 pagesRsia Artha Mahinrus: Jl. Pasar 3 No. 151 - Terusan Tuasan, 20237Rabyatul Maulida NasutionNo ratings yet
- Rits-13 Solution With Answer KeyDocument7 pagesRits-13 Solution With Answer KeyComputer GuyNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument9 pagesCorrosionhesampirNo ratings yet
- Beets Take Home AssignmentDocument5 pagesBeets Take Home Assignmentapi-487667605No ratings yet
- Stock Per 17 Okt 20 HargaDocument13 pagesStock Per 17 Okt 20 HargaLutfi QamariNo ratings yet
- Material Price ListDocument43 pagesMaterial Price ListSathish RagavanNo ratings yet
- MSDS - 134aDocument9 pagesMSDS - 134aUpul Samantha LiyanaarachchiNo ratings yet
- Aeg Lav72800 PDFDocument36 pagesAeg Lav72800 PDFGerardoNo ratings yet
- Solubility CurveDocument2 pagesSolubility CurveDanni SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology HandoutDocument21 pagesConcrete Technology HandoutsainathNo ratings yet
- Geographical Organisation: Marketing ManagerDocument10 pagesGeographical Organisation: Marketing ManagerVinod MalkarNo ratings yet
- (Donald Mackay) Multimedia Environmental ModelsDocument273 pages(Donald Mackay) Multimedia Environmental ModelsKim HiềnNo ratings yet
- 5070 s03 QP 4Document16 pages5070 s03 QP 4karan79No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 2Document16 pagesChemical Bonding 2yvg95100% (1)
- Experiment 3 - Themodynamic Functions From EMF MeasurementsDocument5 pagesExperiment 3 - Themodynamic Functions From EMF MeasurementsjojoNo ratings yet
- Alexbook - Divadjac Joe Cell PDFDocument29 pagesAlexbook - Divadjac Joe Cell PDFstella8880% (1)
- Bioinspiration and BiomimeticsDocument7 pagesBioinspiration and BiomimeticsAyush 100niNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Purification of Astaxanthin From Shrimp Shells and TheDocument6 pagesExtraction and Purification of Astaxanthin From Shrimp Shells and TheMarco CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Colorants of BeveragesDocument12 pagesPresentation On Colorants of BeveragesNISHANTNo ratings yet
- REPORT 2021 - CONSTRUCTION OF FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT BY USING PLASTICdemoDocument25 pagesREPORT 2021 - CONSTRUCTION OF FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT BY USING PLASTICdemoAkash AhireNo ratings yet
- Phyto-Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles of BerberisDocument31 pagesPhyto-Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles of BerberisRabeea NasirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0211 With AnswersDocument17 pagesChapter 0211 With Answersjosephjoy123050% (1)
- AlkalinityDocument33 pagesAlkalinityAinunNo ratings yet
- STD PipingDocument51 pagesSTD PipingRodrigo Iván Latorre AlmirallNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid ChartDocument6 pagesAmino Acid ChartCleveland BrownNo ratings yet
- Heating Catalogue 2019Document44 pagesHeating Catalogue 2019Zoran SimanicNo ratings yet
- Iso 13734 2013 (E)Document18 pagesIso 13734 2013 (E)Freddy Santiago Cabarcas LandinezNo ratings yet