Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Planar Transmission Line 1
Uploaded by
Maxwell_RhodeszCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Planar Transmission Line 1
Uploaded by
Maxwell_RhodeszCopyright:
Available Formats
15/03/2019 Planar transmission line - Wikipedia
Quasi-TEM modes
Transverse modes
Longitudinal-section modes
Other important parameters
Substrates
Types
Stripline
Suspended stripline
Other stripline variants
Microstrip
Microstrip variants
Coplanar waveguide and coplanar strips
Coplanar variants
Slotline
Slotline variants
Substrate integrated waveguide
SIW variants
Finline
Finline variants
Imageline
Imageline variants and other dielectric lines
Multiple layers
Transitions
History
Circuit gallery
References
Bibliography
General properties
Planar transmission lines are those transmission lines in which the conductors are
essentially flat. The conductors consist of flat strips, and there are usually one or more
ground planes parallel to the flat surface of the conductors. The conductors are
separated from the ground planes, sometimes with air between them but more often
with a solid dielectric material. Transmission lines can also be constructed in non-
planar formats such as wires or coaxial line. As well as interconnections, there are a
wide range of circuits that can be implemented in transmission lines. These include
filters, power dividers, directional couplers, impedance matching networks, and choke
An RF power amplifier incorporating
circuits to deliver biasing to active components. The principal advantage of the planar
planar circuit structures. The
types is that they can be manufactured using the same processes used to make printed
amplifier on the left feeds its output
circuits and integrated circuits, particularly through the photolithography process. The into a set of planar transmission line
planar technologies are thus particularly well suited to mass production of such filters in the centre. The third circuit
components.[1] block on the right is a circulator to
protect the amplifier from accidental
Making circuit elements out of transmission lines is most useful at microwave reflections of the power back from
frequencies. At lower frequencies the longer wavelength makes these components too the antenna.
bulky. At the higher microwave frequencies planar transmission line types are generally
too lossy and waveguide is used instead. Waveguide, however, is bulkier and more
expensive to manufacture. At still higher frequencies dielectric waveguide (such as optical fibre) becomes the technology of choice,
but there are planar types of dielectric waveguide available.[2] The most widely used planar transmission lines (of any kind) are
stripline, microstrip, suspended stripline, and coplanar waveguide.[3]
Modes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Planar_transmission_line 2/15
You might also like
- CM0416Document116 pagesCM0416Jazz Drum100% (3)
- Emi AND EmcDocument7 pagesEmi AND Emcmanojkumar9No ratings yet
- The Digital Representation of SoundDocument8 pagesThe Digital Representation of SoundrichietrangNo ratings yet
- A Full Wave RectifierDocument14 pagesA Full Wave RectifierVarun Jain50% (6)
- 519 - Transmission Line Theory by VishnuDocument20 pages519 - Transmission Line Theory by VishnuMahesh HNo ratings yet
- PV MPPT PoDocument26 pagesPV MPPT PoBaidyanath JenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PLCDocument38 pagesChapter 4 PLCDilip TheLip100% (1)
- Advanced Microwave Circuits and Ed by Vitaliy Zhurbenko 2010)Document499 pagesAdvanced Microwave Circuits and Ed by Vitaliy Zhurbenko 2010)Luqiao Liu100% (3)
- USSD Call Flows PDFDocument2 pagesUSSD Call Flows PDFAntariksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Microwave Filters-1965Document20 pagesMicrowave Filters-1965alokcena007No ratings yet
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsFrom EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Report - Planar Transmission LinesDocument9 pagesReport - Planar Transmission LinesAmeer AliNo ratings yet
- Planar Transmission LineDocument1 pagePlanar Transmission LineMaxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Distributed-Element Circuit PDFDocument16 pagesDistributed-Element Circuit PDFahmedNo ratings yet
- 12eDocument33 pages12eDan Farris100% (1)
- Design Techniques of Microwave Cavity and Waveguide Filters: A Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesDesign Techniques of Microwave Cavity and Waveguide Filters: A Literature ReviewTanko SuleNo ratings yet
- Microstrip FilterDocument16 pagesMicrostrip FiltermariyambuttNo ratings yet
- Coplanar Waveguide - WikipediaDocument2 pagesCoplanar Waveguide - Wikipediaalvipin001No ratings yet
- Microstrip LineDocument2 pagesMicrostrip LineMedo KassabNo ratings yet
- Wave GuidesDocument21 pagesWave GuidesJerryNo ratings yet
- Intro To MICDocument37 pagesIntro To MICHari HaranNo ratings yet
- Waveguide Principles in Microwave TechnologyDocument3 pagesWaveguide Principles in Microwave TechnologySayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Analysis On The State-Of-The-Artdevelopments in Reflectarray, Transmitarray, and Transmit-Reflectarray AntennasDocument22 pagesA Comprehensive Analysis On The State-Of-The-Artdevelopments in Reflectarray, Transmitarray, and Transmit-Reflectarray AntennasZohre NoamadeNo ratings yet
- Following Are The Main Properties of MicrowavesDocument31 pagesFollowing Are The Main Properties of MicrowavesSanju SahuNo ratings yet
- Properties of MicrowavesDocument31 pagesProperties of MicrowavesSanju SahuNo ratings yet
- Microwaves Lesson Transmission LinesDocument35 pagesMicrowaves Lesson Transmission LinesulseceNo ratings yet
- 08cDocument78 pages08cDan FarrisNo ratings yet
- Microstrip FilterDocument16 pagesMicrostrip FiltermariyambuttNo ratings yet
- Planar Transmission Lines PDFDocument12 pagesPlanar Transmission Lines PDFGECM85No ratings yet
- 529 - Microwave Circuit Design by PrashanthDocument38 pages529 - Microwave Circuit Design by PrashanthHarshaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Quasi-Planar Transmission Lines: FinlinesDocument6 pagesOverview of Quasi-Planar Transmission Lines: FinlinesVimalNo ratings yet
- Microwave Devices and Systems: Introduction To Microwave EngineeringDocument58 pagesMicrowave Devices and Systems: Introduction To Microwave EngineeringTolera GudisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction To Antenna Systems PDFDocument64 pagesChapter One Introduction To Antenna Systems PDFAmare KassawNo ratings yet
- Types of Transmission Lines - TutorialspointDocument5 pagesTypes of Transmission Lines - TutorialspointHari SNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Common Printed Circuit Transmission Lines: Guiding The WaveDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Common Printed Circuit Transmission Lines: Guiding The WaveHabib Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Trends in Antennas For Wireless CommunicationDocument32 pages1.1 Trends in Antennas For Wireless CommunicationbabuNo ratings yet
- A Planar UWB Antenna With Tripple Notched Bands: Muhammad Irfan Khattak Muhammad Irshad Khan Ali Imran NajamDocument5 pagesA Planar UWB Antenna With Tripple Notched Bands: Muhammad Irfan Khattak Muhammad Irshad Khan Ali Imran NajamMuhammad Irshad Khan Lab Engineer Kohat CampusNo ratings yet
- Designing and Analysis of Microwave Hairpin Filter by Sanjay SinghDocument5 pagesDesigning and Analysis of Microwave Hairpin Filter by Sanjay SinghmagicecstaticNo ratings yet
- Microwave Filters-Applications and TechnologyDocument12 pagesMicrowave Filters-Applications and Technologyalokcena007No ratings yet
- MstripDocument2 pagesMstripFaise JanNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@mop 32199Document5 pages10 1002@mop 32199Sanjib MandalNo ratings yet
- Microwave Devices and Systems: Introduction To Microwave EngineeringDocument66 pagesMicrowave Devices and Systems: Introduction To Microwave Engineeringwarke abayNo ratings yet
- TestDocument2 pagesTestAlfred BalamadNo ratings yet
- EEE 1287-Fall 2019-Topic 10Document18 pagesEEE 1287-Fall 2019-Topic 10Ahnaf AmerNo ratings yet
- H-Shaped Fractal Slots Based Highly Miniaturized Substrate Integrated Waveguide Metamaterial Bandpass Filters For C-Band ApplicationsDocument20 pagesH-Shaped Fractal Slots Based Highly Miniaturized Substrate Integrated Waveguide Metamaterial Bandpass Filters For C-Band ApplicationsThierno Amadou Mouctar BaldeNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Pabba Mahanth - 08bec230 K Prudvi Teja Reddy - 08bec149Document27 pagesSubmitted By: Pabba Mahanth - 08bec230 K Prudvi Teja Reddy - 08bec149Mahanth PabbaNo ratings yet
- Network CH 2Document27 pagesNetwork CH 2Aashutosh VyasNo ratings yet
- Nguyen 1998Document13 pagesNguyen 1998joslinNo ratings yet
- AME - 3.5 Microstrip AntennaDocument30 pagesAME - 3.5 Microstrip Antennanandini.chakraborty2021No ratings yet
- Itu Recommendations For Leaky Feeder SystemsDocument9 pagesItu Recommendations For Leaky Feeder SystemsMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- ACircuit Modelina Wide Frequency Rangefor Power Transformerand Analysisofits CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesACircuit Modelina Wide Frequency Rangefor Power Transformerand Analysisofits CharacteristicslimanNo ratings yet
- Types of Antenna (Sir)Document9 pagesTypes of Antenna (Sir)Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 3 Transmission LinesDocument19 pages3 Transmission Linesfathin noorshafirahNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Transmission Line Measurement: Danvdw@engr - Wisc.eduDocument24 pagesHigh Frequency Transmission Line Measurement: Danvdw@engr - Wisc.eduAbishek PonrajNo ratings yet
- Microwave & MM Wave Planar Transmission Lines-III PDFDocument125 pagesMicrowave & MM Wave Planar Transmission Lines-III PDFGhfrt JhuyNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering-IntroductionDocument35 pagesMicrowave Engineering-IntroductionKobid Karkee100% (1)
- Ee2303 Transmission and DistributionDocument16 pagesEe2303 Transmission and Distributionfpttmm100% (2)
- Microwave Components Waveguides - Comparison With RF LinesDocument4 pagesMicrowave Components Waveguides - Comparison With RF LineslvsaruNo ratings yet
- Antenna Theory and Design: Associate Professor: WANG Junjun 王珺珺Document41 pagesAntenna Theory and Design: Associate Professor: WANG Junjun 王珺珺JUAN MARCELO CEVALLOS DURAN100% (1)
- Chapter 16Document106 pagesChapter 16Michael CatolosNo ratings yet
- Single Element Beam Steerable AntennasDocument2 pagesSingle Element Beam Steerable AntennasDr-Gurpreet KumarNo ratings yet
- Circularly Polarized Circular Patch Antenna With Coplanar Parasitic ElementsDocument4 pagesCircularly Polarized Circular Patch Antenna With Coplanar Parasitic ElementseditorinchiefijcsNo ratings yet
- Couplings of Microstrip Square Open-Loop Resonators For Cross-Coupled Planar Microwave FiltersDocument11 pagesCouplings of Microstrip Square Open-Loop Resonators For Cross-Coupled Planar Microwave FiltersbluewolfNo ratings yet
- An Ten ADocument13 pagesAn Ten At.sin48No ratings yet
- Communication 3 MidtermDocument12 pagesCommunication 3 MidtermSumangil, Maria Margarita P.No ratings yet
- Special Considerations PLCDocument32 pagesSpecial Considerations PLCdilipelineNo ratings yet
- BrittneyDocument13 pagesBrittneyMaxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 20Document1 pageIzsrael 20Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 11Document1 pageIzsrael 11Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 19Document1 pageIzsrael 19Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 17Document1 pageIzsrael 17Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 16Document1 pageIzsrael 16Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 14Document1 pageIzsrael 14Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 12Document1 pageIzsrael 12Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 18Document1 pageIzsrael 18Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 13Document1 pageIzsrael 13Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 10Document1 pageIzsrael 10Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 15Document1 pageIzsrael 15Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 7Document1 pageIzsrael 7Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 2Document1 pageIzsrael 2Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 4Document1 pageIzsrael 4Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 3Document1 pageIzsrael 3Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 8Document1 pageIzsrael 8Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Match: Mandatory Palestine 5-1 LebanonDocument1 pageMatch: Mandatory Palestine 5-1 LebanonMaxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 9Document1 pageIzsrael 9Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 6Document1 pageIzsrael 6Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 1Document1 pageIzsrael 1Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Izsrael 5Document1 pageIzsrael 5Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Match: Mandatory Palestine 5-1 LebanonDocument1 pageMatch: Mandatory Palestine 5-1 LebanonMaxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- C3Document1 pageC3Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- History: Urban RevolutionDocument1 pageHistory: Urban RevolutionMaxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- 1940 - Page 1Document1 page1940 - Page 1Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- 1940 - Page 2Document5 pages1940 - Page 2Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Cultural Identity: A Study of HistoryDocument1 pageCultural Identity: A Study of HistoryMaxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Fall of Civilizations: - Berkleycenter - Georgetown.edu. Retrieved 1 September 2020Document1 pageFall of Civilizations: - Berkleycenter - Georgetown.edu. Retrieved 1 September 2020Maxwell_RhodeszNo ratings yet
- Low Power Wireless Technologies: Roman Budek - NXP APEC 2013 EH Forum Industry SessionDocument26 pagesLow Power Wireless Technologies: Roman Budek - NXP APEC 2013 EH Forum Industry SessionMimiEdreesNo ratings yet
- IC-V80 V80E ManualDocument64 pagesIC-V80 V80E Manualrzkyln100% (1)
- Gereja GMIT PNIEL Oebobo NTT 25 KWPDocument8 pagesGereja GMIT PNIEL Oebobo NTT 25 KWPViadolorosa Ell Kaba100% (1)
- ComPact NSX - LV429435Document2 pagesComPact NSX - LV429435REN JTNNo ratings yet
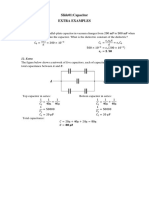
- Slide01 Capacitor - Extra Examples SolutionsDocument3 pagesSlide01 Capacitor - Extra Examples Solutions王施甯No ratings yet
- Dragonwave Product GuideDocument8 pagesDragonwave Product GuidejlmompriveNo ratings yet
- Listing Program ArduinoDocument15 pagesListing Program ArduinoRizky SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Price List Asus - Dealer - 4 NovDocument213 pagesPrice List Asus - Dealer - 4 Novari anggaraNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 16F1938 PDFDocument488 pagesDatasheet 16F1938 PDFAnonymous ZMx8heNo ratings yet
- AFP-2800-2802 Manual V5 - 08Document158 pagesAFP-2800-2802 Manual V5 - 08Victor ChuaNo ratings yet
- Kenwood Kac-529s (2sc5099lb 2sa1907lb Irfiz44n Upc494c)Document8 pagesKenwood Kac-529s (2sc5099lb 2sa1907lb Irfiz44n Upc494c)Luis Tellez CedeñoNo ratings yet
- UK List Pricelist August 2019Document29 pagesUK List Pricelist August 2019Eimantas ČiurinskasNo ratings yet
- Company ProfileDocument5 pagesCompany Profileapi-3852546No ratings yet
- 4 Channel Power Amplifier: Front PanelDocument2 pages4 Channel Power Amplifier: Front PanelAngel BacaNo ratings yet
- Bule Hora University Department of Ece Eceg 4222 Power Electronics & Electric DrivesDocument14 pagesBule Hora University Department of Ece Eceg 4222 Power Electronics & Electric DrivesBilisuma DamiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document5 pagesChapter 16Luqman Hakim ShihabudinNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications: Version 1.4 February 2006Document5 pagesTechnical Specifications: Version 1.4 February 2006László AmbrusNo ratings yet
- NA2750-usermanual Y 20130403Document20 pagesNA2750-usermanual Y 20130403Fendy KristiawanNo ratings yet
- OSS0501 SDH Principle PDFDocument89 pagesOSS0501 SDH Principle PDFjmezatapiaNo ratings yet
- Hai1000 UG VL740 03 UsermanualDocument246 pagesHai1000 UG VL740 03 UsermanualRobertNo ratings yet
- Bandpass Filter TutorialDocument7 pagesBandpass Filter TutorialJaideep BoseNo ratings yet
- Multi - Link ECG Care Cable: Explanation of SymbolsDocument1 pageMulti - Link ECG Care Cable: Explanation of SymbolsKiky Indah SariNo ratings yet
- BA E MASTER - LED1 INVIDIA - v1 0Document26 pagesBA E MASTER - LED1 INVIDIA - v1 0Axl RamirezNo ratings yet