Professional Documents
Culture Documents
p-1 Split 13
Uploaded by
LokendraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
p-1 Split 13
Uploaded by
LokendraCopyright:
Available Formats
RATIONAL NUMBERS 13
−3 −5 5 Distributivity of Multi-
And × =
4 6 8 plication over Addition
−3 2 −3 −5 −1 5 1 and Subtraction.
Therefore × + × = + = For all rational numbers a, b
4 3 4 6 2 8 8
and c,
−3 2 −5 −3 2 −3 −5 a (b + c) = ab + ac
Thus, × + = × + ×
4 3 6 4 3 4 6 a (b – c) = ab – ac
TRY THESE
7 −3 7 5 9 4 9 −3
Find using distributivity. (i) × + × (ii) × + ×
5 12 5 12 16 12 16 9
Example 3: Write the additive inverse of the following:
When you use distributivity, you
−7 21 split a product as a sum or
(i) (ii) difference of two products.
19 112
Solution:
7 −7 −7 7 −7+7 0
(i) is the additive inverse of because + = = =0
19 19 19 19 19 19
21 − 21
(ii) The additive inverse of is (Check!)
112 112
Example 4: Verify that – (– x) is the same as x for
13 −21
(i) x = (ii) x =
17 31
13
Solution: (i) We have, x =
17
13 −13 13 −13
The additive inverse of x = is – x = since + = 0.
17 17 17 17
13 −13 −13 13
The same equality + = 0 , shows that the additive inverse of is
17 17 17 17
−13 13
or −
17 17
= , i.e., – (– x) = x.
−21 21 −21 21
(ii) Additive inverse of x = is – x = since + = 0.
31 31 31 31
−21 21 21 −21
The same equality + = 0 , shows that the additive inverse of is ,
31 31 31 31
i.e., – (– x) = x.
You might also like
- CBSE Grade 8 Maths NotesDocument161 pagesCBSE Grade 8 Maths NotesGovindNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Maths All ChaptersDocument331 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 8 Maths All ChaptersShazrah BaigNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 1: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument9 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 1: Back of Chapter Questionssangdeep waldeNo ratings yet
- Integers Worksheets For 8th Grade Worksheet 1Document12 pagesIntegers Worksheets For 8th Grade Worksheet 1Thousand SunnyNo ratings yet
- 8 Math Rational NumbersDocument8 pages8 Math Rational NumbersAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Examples and ExercisesDocument1 pageMathematics Examples and ExercisesLokendraNo ratings yet
- Solve Simple Linear EquationsDocument2 pagesSolve Simple Linear EquationsNics GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ab Means A × B A A: AlgerbraDocument9 pagesAb Means A × B A A: AlgerbraNoor NoorNo ratings yet
- Math Science Helper SheetDocument2 pagesMath Science Helper SheetmarshaNo ratings yet
- EeDocument33 pagesEeAhtide OtiuqNo ratings yet
- c11 Set1 AnsDocument6 pagesc11 Set1 Ansbhumigehlot77No ratings yet
- Class VIII PDFDocument7 pagesClass VIII PDFManthan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- V1663930820koswaal CBSE Class-9 Mathematics - Self Assessment Paper-3Document6 pagesV1663930820koswaal CBSE Class-9 Mathematics - Self Assessment Paper-3Ryan TakkarNo ratings yet
- SIMULTANEOUSEQUATIONS - Elimination12Document7 pagesSIMULTANEOUSEQUATIONS - Elimination12Zacariah SaadiehNo ratings yet
- Class VII Foundation OlympiadDocument20 pagesClass VII Foundation OlympiadDraksha ChimurkarNo ratings yet
- MST124 SyllabusDocument7 pagesMST124 SyllabusskateboarddeeNo ratings yet
- 1.2.7 Reciprocal: A B A B A B A BDocument1 page1.2.7 Reciprocal: A B A B A B A BLokendraNo ratings yet
- Essential math solutions for VC 10&10A 2edDocument14 pagesEssential math solutions for VC 10&10A 2edzenifyy dasdawNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition Tobey Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition Tobey Solutions Manual PDFvoleryremurmur560v5100% (10)
- Full Download Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition Tobey Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition Tobey Solutions Manualtieberrodsn100% (37)
- Teoremas de La Potenciacion para Sexto Grado de PrimariaDocument4 pagesTeoremas de La Potenciacion para Sexto Grado de PrimariaAUGUSTO CESPEDES ORTEGANo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.2Document23 pagesExercise 1.2sarbjit73No ratings yet
- CSU - ITU 07104 Lecture 4Document20 pagesCSU - ITU 07104 Lecture 4MAWAZO KADAMHINo ratings yet
- Deepak Revision Model Test Paper 8 Maths Class 12 Section A SolvedDocument20 pagesDeepak Revision Model Test Paper 8 Maths Class 12 Section A SolvedYogender RawatNo ratings yet
- Notes_1Document6 pagesNotes_1kv8nrv5kdzNo ratings yet
- Integration by Substitution: SolutionDocument3 pagesIntegration by Substitution: SolutionVape DrugNo ratings yet
- 4 3 EliminationDocument7 pages4 3 Eliminationapi-314809600No ratings yet
- Linear Equation in One VariableDocument2 pagesLinear Equation in One VariableDanilo de MesaNo ratings yet
- Algebra worksheet preparation for statisticsDocument13 pagesAlgebra worksheet preparation for statisticsTaya LewendonNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition Tobey Solutions ManualDocument30 pagesIntermediate Algebra 8th Edition Tobey Solutions ManualJamesGrantfzdmo100% (14)
- Linear equation systems solved by elimination and substitution methodsDocument6 pagesLinear equation systems solved by elimination and substitution methodsNurull 11No ratings yet
- Solutions For JMET Quant Paper-1Document4 pagesSolutions For JMET Quant Paper-1divya1850% (1)
- Chap 06Document42 pagesChap 06nicolas_urdanetaNo ratings yet
- College and Advance Algebra MODULE 4Document6 pagesCollege and Advance Algebra MODULE 4Jefferson SociasNo ratings yet
- Algebra - Expanding: "Expanding" Means Removing The ... But You Have To Do It The Right Way!Document6 pagesAlgebra - Expanding: "Expanding" Means Removing The ... But You Have To Do It The Right Way!Annisa RohmahNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.5Document15 pagesExercise 1.5sarbjit73No ratings yet
- S1 Review Exercise 2Document29 pagesS1 Review Exercise 2Mustufa KhalilNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ExponentsDocument20 pagesGrade 8 ExponentsSarthak TiwariNo ratings yet
- Linear Inequalities WS ASDocument11 pagesLinear Inequalities WS ASAditi JaniNo ratings yet
- 2020 G. C 4 Quarter M Lesson Note FOR Grade 11Document10 pages2020 G. C 4 Quarter M Lesson Note FOR Grade 11zenusamriNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Equations SolutionsDocument8 pagesSimultaneous Equations SolutionsEsio TrotNo ratings yet
- Equations in one variableDocument14 pagesEquations in one variableJane PadillaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations: in One VariableDocument31 pagesLinear Equations: in One VariablePradhosh On AirNo ratings yet
- Calculus II ReviewerDocument4 pagesCalculus II ReviewerJhon Mar BencionNo ratings yet
- 01 Solving Basic Equations and Inequalities (One Variable, Linear)Document15 pages01 Solving Basic Equations and Inequalities (One Variable, Linear)Yeri KimNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 Holiday Homework PDFDocument66 pages2022-2023 Holiday Homework PDFAlfred SandersNo ratings yet
- 1543411700-0llmath-Workbook8 Answers-With-Cover PDFDocument149 pages1543411700-0llmath-Workbook8 Answers-With-Cover PDFsuchitra mishraNo ratings yet
- SAT Algebraic FractionsDocument10 pagesSAT Algebraic FractionsYb Andik Adi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- Appendix C Complex Number 2021 A Modern Introduction To Differential EquatDocument4 pagesAppendix C Complex Number 2021 A Modern Introduction To Differential EquatLJ AuNo ratings yet
- Sigma Complex3 2009 1Document2 pagesSigma Complex3 2009 1Kwentohan TimeNo ratings yet
- 19th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad key insightsDocument9 pages19th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad key insightsChantelle EstarisNo ratings yet
- University of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadDocument24 pagesUniversity of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadHazem AlmasryNo ratings yet
- Parabola SolutionsDocument2 pagesParabola SolutionsPreethi VictorNo ratings yet
- Ex 5 3 FSC Part1Document6 pagesEx 5 3 FSC Part1Omer Muneer QaziNo ratings yet
- Algebra IGCSE GuideDocument41 pagesAlgebra IGCSE GuideMariam ShehabNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Solving Linear EquationsDocument6 pages1.3 Solving Linear Equationsrad58No ratings yet
- Algebraic Forms & Linear EquationsDocument9 pagesAlgebraic Forms & Linear Equationsgiarpuji UtamiNo ratings yet
- 9th Chapter FiksDocument156 pages9th Chapter Fikstikafebriani52No ratings yet
- 20 ExpandingDocument2 pages20 Expandingapi-299265916No ratings yet
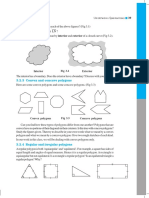
- 3.2.3 Convex and Concave Polygons: Interior Exterior Fig 3.2Document1 page3.2.3 Convex and Concave Polygons: Interior Exterior Fig 3.2LokendraNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3.1: Nderstanding UadrilateralsDocument1 pageExercise 3.1: Nderstanding UadrilateralsLokendraNo ratings yet
- Do This: 3.2.5 Angle Sum PropertyDocument1 pageDo This: 3.2.5 Angle Sum PropertyLokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 12Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 12LokendraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Quadrilaterals: Nderstanding UadrilateralsDocument1 pageUnderstanding Quadrilaterals: Nderstanding UadrilateralsLokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 8Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 8LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 13Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 13LokendraNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1 Classification of Polygons: Number of Sides Classification Sample Figure or VerticesDocument1 page3.2.1 Classification of Polygons: Number of Sides Classification Sample Figure or VerticesLokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 7Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 7LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 14Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 14LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 6Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 6LokendraNo ratings yet
- (Iii) Rational Numbers: Ational UmbersDocument1 page(Iii) Rational Numbers: Ational UmbersLokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 5Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 5LokendraNo ratings yet
- Solve equations and find a two-digit number from number interchange and sum propertiesDocument1 pageSolve equations and find a two-digit number from number interchange and sum propertiesLokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 9Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 9LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 2Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 2LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 1Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 1LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 4Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 4LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 16Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 16LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 15Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 15LokendraNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Representation of Rational Numbers On The Number Line: 10. WriteDocument1 page1.3 Representation of Rational Numbers On The Number Line: 10. WriteLokendraNo ratings yet
- Rational numbers between any two rational numbersDocument1 pageRational numbers between any two rational numbersLokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 11Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 11LokendraNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 3Document1 page8 Maths NCERT Chapter 2 Split 3LokendraNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers: Example 6: SolutionDocument1 pageRational Numbers: Example 6: SolutionLokendraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Examples and ExercisesDocument1 pageMathematics Examples and ExercisesLokendraNo ratings yet
- p-1 Split 13Document1 pagep-1 Split 13LokendraNo ratings yet
- Example 2: Solution:: Find We HaveDocument1 pageExample 2: Solution:: Find We HaveLokendraNo ratings yet
- p-1 Split 16Document1 pagep-1 Split 16LokendraNo ratings yet
- Peter-Linz-Automata BUET Download PDFDocument2 pagesPeter-Linz-Automata BUET Download PDFmalang0% (2)
- Cswip 3.1 Practice QuestionDocument22 pagesCswip 3.1 Practice QuestionKoya ThangalNo ratings yet
- 2012 Vcaa Physics Exam 2 SolutionsDocument2 pages2012 Vcaa Physics Exam 2 SolutionspappadutNo ratings yet
- Phylogenetic studies of Mammillaria provide new insightsDocument13 pagesPhylogenetic studies of Mammillaria provide new insightsA Man ZedNo ratings yet
- Drainage DesignDocument21 pagesDrainage Designronaldnyirenda2230100% (1)
- On The Quantum Well and Multi DimensionaDocument19 pagesOn The Quantum Well and Multi DimensionaGianna Barcelli FantappieNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse and Data Mining: Lab ManualDocument69 pagesData Warehouse and Data Mining: Lab ManualFfdgsffNo ratings yet
- Hysteretic Energy DissipationDocument22 pagesHysteretic Energy Dissipationdharma raj upadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Process AnalysisDocument10 pagesProcess AnalysisNikeshKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Plumbing and Fire Fighting Sample BoqDocument30 pagesPlumbing and Fire Fighting Sample BoqNajeeb Ahmad Khan100% (2)
- Mech 2 Module 1 Unit 3 (Position, Velocity and Acceleration)Document8 pagesMech 2 Module 1 Unit 3 (Position, Velocity and Acceleration)Zamantha DomingoNo ratings yet
- 고체역학 문제집Document41 pages고체역학 문제집Michael MeashoNo ratings yet
- GCB HVR BrochureDocument8 pagesGCB HVR BrochureHan HuangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3b - MP DSBDocument32 pagesChapter 3b - MP DSBsheham ihjamNo ratings yet
- Saas 1000Document69 pagesSaas 1000rjnemoNo ratings yet
- SOLO/UNISON/POLY/Octave Shift/Portamento: Settings Panel DescriptionsDocument1 pageSOLO/UNISON/POLY/Octave Shift/Portamento: Settings Panel Descriptionsanon_713757213No ratings yet
- 4-4 - Electrical Works SpecsDocument39 pages4-4 - Electrical Works SpecsTarek TarekNo ratings yet
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument12 pagesDownloaded From Manuals Search EngineWilly WakkerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Mengulhounuo Keretsu Class: 12 (Science) School: Maple Tree SchoolDocument23 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Mengulhounuo Keretsu Class: 12 (Science) School: Maple Tree SchoolmengulhounuoNo ratings yet
- Excel 2003 Bible PDF RapidshareDocument2 pagesExcel 2003 Bible PDF RapidshareUrsulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document44 pagesChapter 4Ping LeungNo ratings yet
- Readings: Decision AnalysisDocument44 pagesReadings: Decision AnalysisPierre Moreno SotoNo ratings yet
- Icd Aidc Ver3Document95 pagesIcd Aidc Ver3Alvin Guillermo Rodriguez ArguelloNo ratings yet
- 21 WordPress Interview Questions and Answers (II) For ExperiencedDocument8 pages21 WordPress Interview Questions and Answers (II) For Experiencedjatinkant123No ratings yet
- Profibus-Gateway v3 Eng 2Document64 pagesProfibus-Gateway v3 Eng 2Bob YahyaNo ratings yet
- Release Notes 15.1SY PDFDocument208 pagesRelease Notes 15.1SY PDFCsim MiscNo ratings yet
- InfoPLC Net PowerFlex 525 AC DrivesDocument34 pagesInfoPLC Net PowerFlex 525 AC DrivesgodoyunipNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Conversations To Transform Algebra ClassDocument9 pagesMathematical Conversations To Transform Algebra ClassSyamil AlliyusNo ratings yet
- A L L Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) : P Code Charts P0315Document2 pagesA L L Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) : P Code Charts P0315Jose GarciaNo ratings yet
- MCGB - Data Sheet For Suppliers Old MAT Nos.: Weldox 700 EDocument3 pagesMCGB - Data Sheet For Suppliers Old MAT Nos.: Weldox 700 Ebaskaran ayyapparajNo ratings yet