Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rupture. Excessive Elongation of Tension Member Is Undesirable in That It Normally
Uploaded by
sereOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rupture. Excessive Elongation of Tension Member Is Undesirable in That It Normally
Uploaded by
sereCopyright:
Available Formats
STRUCTURAL STEEL DESIGN
Dr. Ammar A. Ali
yielding and stress distribution. This will result in a uniform stress distribution at ultimate
load.
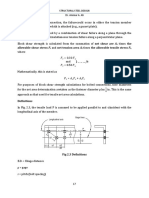
The allowable tensile stress Ft takes into consideration two types of failure:
1. The mamber may rupture on the least net area. This is the classical and historical
approach to tension member analysis.
2. The tension member may undergo uncontrolled yielding of its gross area without
rupture. Excessive elongation of tension member is undesirable in that it normally
results in deformation of the structure and can lead to failure in other parts of the
structural system.
The types of failure above may be predicted using the following formulas:
1. 𝐹𝐹𝑡𝑡 = 0.50𝐹𝐹𝑢𝑢 … … … (on the net area)
D1
2. 𝐹𝐹𝑡𝑡 = 0.60𝐹𝐹𝑦𝑦 … … … (on the gross area)
These allowable stresses do not apply to pin-connected members (such as eye bars or
plates connected with relatively large pins), threaded steel rods, or flexible tension
members such as cables and wire ropes.
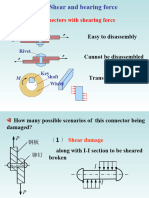
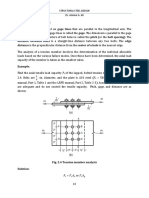
Block Shear
A tearing failure that can occure at end connections along the perimeter of welds or
along the perimeter of a group of bolt holes (Fig 2.2).
Tension area
Tension area
Pt
Pt
Shear area Shear area
(a) Bolted angle (b) Bolted plate
Pt Shear area
Shear area
Tension
area
Pt
(c) Bolted W shape
Tension area
(d) Welded angles
Fig.2.2 Block shear in end connections
16
You might also like
- 剪切与挤压实用计算 EnglishDocument21 pages剪切与挤压实用计算 EnglishMilkiNo ratings yet
- Ch5 RevDocument30 pagesCh5 RevPratik PoriyaNo ratings yet
- Ch5 RevDocument30 pagesCh5 Revkomalthawrani.ideaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Design of Steel Structure: Civil Engineering Department, NUCES, Lahore PakistanDocument23 pagesAdvanced Design of Steel Structure: Civil Engineering Department, NUCES, Lahore Pakistansyed muneeb haiderNo ratings yet
- Design of Tension Members: Arijit GuhaDocument30 pagesDesign of Tension Members: Arijit GuhaSEKARNo ratings yet
- Block Shear AISC 20005Document15 pagesBlock Shear AISC 20005bisagantiNo ratings yet
- BoltDocument26 pagesBoltsixramesh123No ratings yet
- Total Strength Assessment: Buckling and Ultimate StrengthDocument30 pagesTotal Strength Assessment: Buckling and Ultimate Strengthding liuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Steel 23-24Document66 pagesChapter 3 Steel 23-24nyankyalps5No ratings yet
- Connections 1 - Ch.4 Tension Members Notes (154-187)Document12 pagesConnections 1 - Ch.4 Tension Members Notes (154-187)travis8zimmermannNo ratings yet
- Bending: The Bend Radius Is Measured To The Inner Surface of The Bent PartDocument32 pagesBending: The Bend Radius Is Measured To The Inner Surface of The Bent Partjim clarkNo ratings yet
- EndPl MomConn LSDDocument54 pagesEndPl MomConn LSDTony RoseNo ratings yet
- De Chiffre 1977Document10 pagesDe Chiffre 1977Murilo BertoNo ratings yet
- Min Max Steel Reinforcement For SlabDocument1 pageMin Max Steel Reinforcement For SlabRodel, Jr. NatividadNo ratings yet
- EndPl MomConn LSDDocument54 pagesEndPl MomConn LSDsilroy d'saNo ratings yet
- ستيل ستركشرDocument73 pagesستيل ستركشرAws SamaNo ratings yet
- Tension MemDocument19 pagesTension MemNick AvisNo ratings yet
- Steel Column Design (EN1993)Document8 pagesSteel Column Design (EN1993)Bernard KiruiNo ratings yet
- Bolts Non-Structural (A-307) A325 A449 A490 Rivets (Obsolete)Document40 pagesBolts Non-Structural (A-307) A325 A449 A490 Rivets (Obsolete)claudio perez prietoNo ratings yet
- Design Tension Members: Allowable Tensile Stress of Structural Steel According To AISC As FollowDocument5 pagesDesign Tension Members: Allowable Tensile Stress of Structural Steel According To AISC As FollowHaftom GebreegziabiherNo ratings yet
- Branch RF CalcDocument6 pagesBranch RF CalcHarish Harish0% (1)
- Behaviour of Block Shear Failure in Different Connections: Jagdish R. Dhanuskar & Laxmikant M. GuptaDocument15 pagesBehaviour of Block Shear Failure in Different Connections: Jagdish R. Dhanuskar & Laxmikant M. GuptaJagdish DhanuskarNo ratings yet
- Tension Members1Document11 pagesTension Members1erwin sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Brackets and Corbels ACI 318 L # 1Document7 pagesBrackets and Corbels ACI 318 L # 1soran azizNo ratings yet
- Session 11 - Design of Steel ConnectionsDocument32 pagesSession 11 - Design of Steel Connectionsshan kumarNo ratings yet
- API 650 RF Pad Calculation PDFDocument1 pageAPI 650 RF Pad Calculation PDFRakeshNo ratings yet
- API 650 RF Pad Calculation PDFDocument1 pageAPI 650 RF Pad Calculation PDFBimal DeyNo ratings yet
- Causes of Welding Cracks and Their AvoidanceDocument28 pagesCauses of Welding Cracks and Their AvoidanceMiguel HermosaNo ratings yet
- Torsion PDFDocument40 pagesTorsion PDFHongVuthyNo ratings yet
- Div Syd Detailing of Reinforcement in Concrete StructuresDocument82 pagesDiv Syd Detailing of Reinforcement in Concrete Structuresتقوى طهNo ratings yet
- Connection Design Steel Base Plate Bs5950 v2015 01Document4 pagesConnection Design Steel Base Plate Bs5950 v2015 01Anonymous j9PxwnoNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Report For High Lift Pump StationDocument195 pagesStructural Design Report For High Lift Pump StationEphrem GalNo ratings yet
- Module-39A: Beams and Beam-Columns, Column BasesDocument6 pagesModule-39A: Beams and Beam-Columns, Column BasesAjay MalikNo ratings yet
- Design of Tension Members: Rafter Suspenders Sag Rod PurlinDocument15 pagesDesign of Tension Members: Rafter Suspenders Sag Rod PurlinMohammed Junaid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument2 pagesBeam DesignBilal A BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- RCC Lecture Series 2 2018-19 PDFDocument41 pagesRCC Lecture Series 2 2018-19 PDFMansa ArthurNo ratings yet
- Member Design - Reinforced Concrete Beam BS8110Document37 pagesMember Design - Reinforced Concrete Beam BS8110sanusi69No ratings yet
- Beam Basic Data Pb1Document14 pagesBeam Basic Data Pb1acchanduNo ratings yet
- Design of JointsDocument39 pagesDesign of JointsHari NaniNo ratings yet
- Angle Starred Angle Round Bar Flat Bar Double Angle S-Sectio N (America N Built-Up Box Sections Standard)Document7 pagesAngle Starred Angle Round Bar Flat Bar Double Angle S-Sectio N (America N Built-Up Box Sections Standard)erwin sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Calculation Sheet Consulting EngineersDocument11 pagesEngineering Calculation Sheet Consulting EngineersJONAS NGNo ratings yet
- The Interaction Between Shield, Ground and Tunnel Support in TBM Tunnelling Through Squeezing GroundDocument25 pagesThe Interaction Between Shield, Ground and Tunnel Support in TBM Tunnelling Through Squeezing GroundFederico MalteseNo ratings yet
- Bending in Beam 2: Reinforced Concrete Design IDocument53 pagesBending in Beam 2: Reinforced Concrete Design IMongkol JirawacharadetNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structure Module 4Document61 pagesDesign of Steel Structure Module 4ShazNo ratings yet
- T Fillet WeldsDocument26 pagesT Fillet WeldssereNo ratings yet
- Pile Horizontal CheckDocument8 pagesPile Horizontal CheckDINESHNo ratings yet
- 7023exq Lecture 3 Bolted Steel ConnectionsDocument17 pages7023exq Lecture 3 Bolted Steel ConnectionsAkhil SurendranNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Major Component: 1. Main PumpDocument10 pagesGroup 2 Major Component: 1. Main PumpDavidNo ratings yet
- EndPl MomConn LSDDocument73 pagesEndPl MomConn LSDNguyen Duc CuongNo ratings yet
- Tension MembersDocument21 pagesTension Membersshuja2008No ratings yet
- TorsionDocument36 pagesTorsiondixn__No ratings yet
- Design of Shear Connection Between Beam To Beam:: As Per AISC 13 Edition (ASD)Document13 pagesDesign of Shear Connection Between Beam To Beam:: As Per AISC 13 Edition (ASD)rohitnrg0% (1)
- Minggu Ke 3 TORSIONDocument32 pagesMinggu Ke 3 TORSIONMuhamad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Body Flange .PVDB FlangeDocument1 pageBody Flange .PVDB FlangeAnonymous aBg51lbe18No ratings yet
- Lewis and Buckingam EquationDocument13 pagesLewis and Buckingam EquationVishak ReguNo ratings yet
- Drilling GeomechanicsDocument32 pagesDrilling Geomechanicsjsever1No ratings yet
- SteelDesign Tension FuDocument24 pagesSteelDesign Tension FuAr Agner O. BatuigasNo ratings yet
- Lecture Development of Reinforcement 24 November 2017Document40 pagesLecture Development of Reinforcement 24 November 2017valentina ayu100% (1)
- Lecture 3Document46 pagesLecture 3mooNo ratings yet
- (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) : Fig. 3.1 Compression Member Cross Sections. Ideal ColumnsDocument1 page(A) (B) (C) (D) (E) : Fig. 3.1 Compression Member Cross Sections. Ideal ColumnssereNo ratings yet
- Flowchart 1: Tension Member Analysis: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageFlowchart 1: Tension Member Analysis: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageStructural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Use 4 Bolts.: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageUse 4 Bolts.: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageStructural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Length Effects: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageLength Effects: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Example:: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageExample:: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageStructural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Fig. 2.13 Bolt in Single Shear.: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageFig. 2.13 Bolt in Single Shear.: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageStructural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. Ali: Fig. 2.10 Flange Block Shear ExampleDocument1 pageStructural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. Ali: Fig. 2.10 Flange Block Shear ExamplesereNo ratings yet
- Necessary To Revise The Selection.: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageNecessary To Revise The Selection.: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- A U Reduction Coefficient (Table 2.1) U 0.9Document1 pageA U Reduction Coefficient (Table 2.1) U 0.9sereNo ratings yet
- Gusset Plates PT: Fig. 2.9 Truss Connection. SolutionDocument1 pageGusset Plates PT: Fig. 2.9 Truss Connection. SolutionsereNo ratings yet
- Fig. 2.11 Double-Angle Tension Member Welded End Connection SolutionDocument1 pageFig. 2.11 Double-Angle Tension Member Welded End Connection SolutionsereNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageStructural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Pages22 PDFDocument1 pagePages22 PDFsereNo ratings yet
- Effective Net Area: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageEffective Net Area: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Table 2.2 Value of U (Longitudinal Welds On A Flat Bar or Plate)Document1 pageTable 2.2 Value of U (Longitudinal Welds On A Flat Bar or Plate)sereNo ratings yet
- Example:: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageExample:: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Allowable Shear Stress F: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageAllowable Shear Stress F: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageStructural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Design Considerations: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageDesign Considerations: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- D Distance Between BoltsDocument1 pageD Distance Between BoltssereNo ratings yet
- Common Torsional Properties of Fillet Welds (Table 9-1) : Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignDocument1 pageCommon Torsional Properties of Fillet Welds (Table 9-1) : Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignsereNo ratings yet
- B Width of Plate T Thickness of Plate A: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageB Width of Plate T Thickness of Plate A: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Ages13 PDFDocument1 pageAges13 PDFsereNo ratings yet
- Tension Members: Tension Member Analysis StressDocument1 pageTension Members: Tension Member Analysis StresssereNo ratings yet
- (A) Pipe and Round HSS (B) Square HSS (C) Rectangular HSSDocument1 page(A) Pipe and Round HSS (B) Square HSS (C) Rectangular HSSsereNo ratings yet