Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motherboard Components and Their Functions
Uploaded by
Herwin Capiñanes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views20 pagesMotherboard
Original Title
Motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctions 150518115051 Lva1 App6891 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMotherboard
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views20 pagesMotherboard Components and Their Functions
Uploaded by
Herwin CapiñanesMotherboard
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
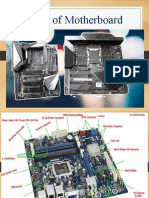
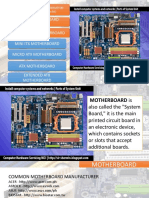
Motherboard Components
and Their Functions
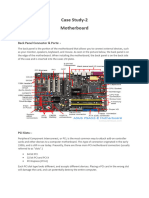
1- Back Panel Connectors & Ports
Connectors and ports for connecting
the computer to external devices such
as display ports, audio ports, USB
ports, Ethernet ports, PS/2 ports etc.
2. PCI Slots PCI: Peripheral Component Interconnect
Slot for older expansion cards such as
sound cards, network cards, connector
cards. See image below for a close-up
view.
3. PCI Express x1 Slots
Slot for modern expansion cards such as sound
cards, network cards (Wi-Fi, Ethernet,
Bluetooth), connector cards (USB, FireWire,
eSATA) and certain low-end graphics cards. See
image below for a close-up view
4. PCI Express x16 Slot
Slot for discrete graphic cards and high
bandwidth devices such as top-end solid
state drives. See image below for a close-
up view
5. Northbridge
Also known as Memory Controller Hub (MCH).
Chipset that allows the CPU to communicate
with the RAM and graphics card.
Beginning from Intel Sandy Bridge in 2011, this
motherboard component is no longer present as
it has been integrated within the CPU itself.
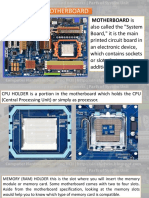
6. CPU Socket
A CPU socket or CPU slot is a mechanical
component(s) that provides mechanical and
electrical connections between a microprocessor
and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows the
CPU to be placed and replaced without soldering.
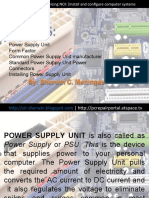
7. ATX 12V Power Connector
Connects to the 4-pin power cable of a
power supply unit which supplies power to
the CPU.
8. Front Panel USB 2.0 Connectors
Connects to USB 2.0 ports at the front or top of
a computer case. See image above for a close-
up view.
9. Front Panel Connectors
Connects to the power switch, reset switch,
power LED, hard drive LED and front audio ports
of a computer case. See image above for a
close-up view.
10. IDE Connector
Connects to older hard drive disks and optical
drives for data transfer. See image above for a
close-up view. Have been replaced over by SATA
connectors (see motherboard component #13
below).
11. CMOS Battery
Supplies power to store BIOS settings and keep
the real-time clock running. See image above for
a close-up view. The CMOS battery found on
most motherboards is the CR2032 lithium coin
cell.
12. Southbridge
Also known as the Input/output Controller Hub
(ICH).Chipset that allows the CPU to communicate
with PCI slots, PCI-Express x 1 slots (expansion
cards), SATA connectors (hard drives, optical
drives), USB ports (USB devices), Ethernet ports and
on-board audio.
13. SATA Connectors
Connects to modern hard disk drives, solid
state drives and optical drives for data
transfer. See image above for a close-up
view.
14. Fan Header
Supplies power to the CPU heat sink fan
and computer case fans. See image above
for a close-up view.
15. RAM Slots
A memory slot, memory socket, or RAM slot is what
allows computer memory (RAM) to be inserted into the
computer. Depending on the motherboard, there may be
2 to 4 memory slots (sometimes more on high-end
motherboards) and are what determine the type of RAM
used with the computer.
16. mSATA Connector
Connects to a mSATA solid state drive. In most
cases, this SSD is used as cache to speed up hard
disk drives, but it's possible to re-purpose it as a
regular hard drive.
17. Power & Reset Button
he reset button could be an actual button or concept.
The reset button would typically kick off a soft boot,
instructing the computer to go through the process of
shutting down, which would clear memory and reset
devices to their initialized state. Contrary to the 'Power
Button', which would simply remove power immediately.
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument20 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsavinmanzanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctionsDocument20 pagesLesson 5motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctionsJason BaloroNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionCherrisNo ratings yet
- Back Panel & Ports, PCI Slots, CPU Socket GuideDocument2 pagesBack Panel & Ports, PCI Slots, CPU Socket GuideThomas James P. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Guide: Components and Functions Explained in 40 CharactersDocument29 pagesMotherboard Guide: Components and Functions Explained in 40 CharactersChristian Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components Functions GuideDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components Functions GuideDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functions PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functions PDFMaria Norberta MandacNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument39 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsJamer AmpongNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsErwin BenitezNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument5 pagesMotherboardRichard Melvin GarciaNo ratings yet
- A Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataDocument11 pagesA Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataPenchalaiah NarasapuramNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.6 Motherboard: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesInformation Sheet 1.6 Motherboard: Learning Objectivesjezreel csNo ratings yet
- ITP421 WEEK 2 - MotherboardsDocument29 pagesITP421 WEEK 2 - MotherboardsJaira Mae DiazNo ratings yet
- Computer MotherboardDocument15 pagesComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument14 pagesParts of MotherboardNoelyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Parts GuideDocument17 pagesMotherboard Parts GuiderommelNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functionsjoel lacayNo ratings yet
- M2 Yash AllabadiDocument7 pagesM2 Yash Allabadidegijon661No ratings yet
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryDocument8 pagesMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462No ratings yet
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER MOTHERBOARD: Main PC Circuit Board ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOMPUTER MOTHERBOARD: Main PC Circuit Board ExplainedStar Boy DavieNo ratings yet
- What Is A MotherboardDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MotherboardManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- CMN Lab Expt-1Document3 pagesCMN Lab Expt-1Aaryan SinghNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument30 pagesSeminarShweta Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Computer ComponentsDocument53 pagesComputer ComponentsAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of The MotherboardDocument2 pagesParts and Function of The MotherboardTorreja JonjiNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument12 pagesClass NotesHeart WeyganNo ratings yet
- PartsandFunctions 302911981992807Document1 pagePartsandFunctions 302911981992807lotusvanhardt0099No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardKurk DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- Motherboard components and portsDocument32 pagesMotherboard components and portsAnanduNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Module 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Essential Motherboard Parts GuideDocument28 pagesEssential Motherboard Parts GuideJohn Adams Budomo100% (2)
- Final Notes of Second Yr 2022Document269 pagesFinal Notes of Second Yr 2022RAM KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Description of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Document4 pagesDescription of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Nain khanNo ratings yet
- Motherboard SlidesDocument21 pagesMotherboard Slidesmubiru mosesNo ratings yet
- Hardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519Document46 pagesHardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519crecbhoomi21No ratings yet
- Understanding Motherboard ComponentsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Motherboard ComponentsallamNo ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- MotherboardDocument15 pagesMotherboardDragoon GamingNo ratings yet
- A MotherboardDocument4 pagesA MotherboardOttonniel BenNo ratings yet
- CahmDocument3 pagesCahmakkivish37No ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- PC TroubleshootingDocument112 pagesPC TroubleshootingMosul VictoriaNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument20 pagesMotherboardJeyc RapperNo ratings yet
- Is The Enclosure For All The Other Main Interior Components of A Computer. It Is Also Called The Computer Case, Computer Chassis, or Computer TowerDocument5 pagesIs The Enclosure For All The Other Main Interior Components of A Computer. It Is Also Called The Computer Case, Computer Chassis, or Computer TowerAlfredo DimaanoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Motherboard ?Document13 pagesWhat Is A Motherboard ?Ian OffemariaNo ratings yet
- Configure Computer SystemsDocument17 pagesConfigure Computer SystemsRyuNo ratings yet
- Aim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)Document15 pagesAim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)VanessaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Board or Logic BoardDocument9 pagesMotherboard: Board or Logic BoardappatujuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemSohum VenkatadriNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument2 pagesParts of MotherboardMarklawrence DucenaNo ratings yet
- 2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardDocument3 pages2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardAashish KandelNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionsCheryl Dumaguit BelaloNo ratings yet
- 1.pci Peripheral Component Interconnected 2.what Is Troubleshooting?Document6 pages1.pci Peripheral Component Interconnected 2.what Is Troubleshooting?no fake NewsNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to MotherboardsDocument5 pagesThe Essential Guide to MotherboardsElleera RemorerasNo ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Environmental Management Practices: Greener Management International December 2002Document24 pagesEnvironmental Management Practices: Greener Management International December 2002Herwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- 2a. THREE KEY WORDS IN THE COURSE TITLE - PHILOSOPHY, CULTURE, ETHICSDocument11 pages2a. THREE KEY WORDS IN THE COURSE TITLE - PHILOSOPHY, CULTURE, ETHICSHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- PMD 302 - Course OutlineDocument8 pagesPMD 302 - Course OutlineHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Persuasion Map Powerpoint TemplateDocument8 pagesPersuasion Map Powerpoint TemplateHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- PMD 302 - Course PortfolioDocument14 pagesPMD 302 - Course PortfolioHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Consuklting ReferecensDocument1 pageConsuklting ReferecensHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- PDF Real Estate Brokerage Version 1pauline XLSB CompressDocument4 pagesPDF Real Estate Brokerage Version 1pauline XLSB CompressHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3Herwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- 0b. CV of DR. SOPHREMIANO B. ANTIPOLODocument4 pages0b. CV of DR. SOPHREMIANO B. ANTIPOLOHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- PDF Real Estate Brokerage Version 1pauline XLSB CompressDocument4 pagesPDF Real Estate Brokerage Version 1pauline XLSB CompressHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2Herwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Permit To Teach For School PersonnelDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Permit To Teach For School PersonnelHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Parts of System Unit QuestionsDocument19 pagesParts of System Unit QuestionsHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Project Name: Class Name, Number Instructor Group Member NamesDocument20 pagesProject Name: Class Name, Number Instructor Group Member NamesHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- PDF Real Estate Brokerage Version 1pauline XLSB CompressDocument4 pagesPDF Real Estate Brokerage Version 1pauline XLSB CompressHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- PDF Real Estate Principles 5th Edition DDDocument8 pagesPDF Real Estate Principles 5th Edition DDHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- PDF Real Estate Brokerage Version 1pauline XLSB CompressDocument4 pagesPDF Real Estate Brokerage Version 1pauline XLSB CompressHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Parts of System UnitDocument49 pagesParts of System UnitHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Desktop Computer SetupDocument18 pagesDesktop Computer SetupEdz Libre GayamoNo ratings yet
- Parts of System Unit NewDocument12 pagesParts of System Unit NewGladystarucanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Mobo For SharingDocument13 pagesParts of Mobo For SharingHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Installing Window Server 2008Document27 pagesInstalling Window Server 2008Herwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Parts of the Motherboard ExplainedDocument17 pagesParts of the Motherboard ExplainedAnnika Orillaneda HabloNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Unit Form Factor Common Power Supply Unit Manufacturer Standard Power Supply Unit Power Connectors Installing Power Supply UnitDocument41 pagesPower Supply Unit Form Factor Common Power Supply Unit Manufacturer Standard Power Supply Unit Power Connectors Installing Power Supply UnitHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Installing Window Server 2008r2Document27 pagesInstalling Window Server 2008r2Herwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Parts of Mobo For SharingDocument13 pagesParts of Mobo For SharingHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Installing Microsoft Office 2003Document10 pagesInstalling Microsoft Office 2003Herwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Installing Window Server 2008r2 First TaskDocument27 pagesInstalling Window Server 2008r2 First TaskHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Installing Video CardDocument8 pagesInstalling Video CardHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Installing PowersuplyDocument41 pagesInstalling PowersuplyHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Generic 6-Panel Brochure TemplateDocument4 pagesGeneric 6-Panel Brochure Templateapi-459387854No ratings yet
- Daily Drilling Report: Bha Tally Bit Record Mud Report Mud Pump Drilling InformationDocument25 pagesDaily Drilling Report: Bha Tally Bit Record Mud Report Mud Pump Drilling InformationHamed NazariNo ratings yet
- Turbo RamjetDocument16 pagesTurbo RamjetDhana JayanNo ratings yet
- 8 - CONTINUOUS MINER SpecificationsDocument4 pages8 - CONTINUOUS MINER Specificationsisnindian100% (1)
- Faculty Recruitment Test: Mental Ability Test (MAT) Paper - BDocument4 pagesFaculty Recruitment Test: Mental Ability Test (MAT) Paper - BN C NAGESH PRASAD KOTINo ratings yet
- Ch01 Opr Supply ChainDocument44 pagesCh01 Opr Supply ChainAyudya Rizky Budi UtamiNo ratings yet
- Junior Resume EEDocument1 pageJunior Resume EESudeep AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PDFDocument55 pagesModule 3 PDFSandeep VermaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Typesetting FactorsDocument57 pagesModule 4 Typesetting FactorsMirajane StraussNo ratings yet
- 09 IGV SystemDocument5 pages09 IGV Systemnabil160874100% (1)
- Project With Header Spring 2015 PDFDocument111 pagesProject With Header Spring 2015 PDFPavan Sandeep V VNo ratings yet
- EMI Vs Veris ECDocument11 pagesEMI Vs Veris ECEzrin Mohd Husin100% (2)
- Detroit Ds Pf12v149tDocument2 pagesDetroit Ds Pf12v149tMuhammad rizkiNo ratings yet
- Tia s7 1500 Programming 2 (Tia Pro2)Document2 pagesTia s7 1500 Programming 2 (Tia Pro2)osto720% (2)
- 24 Useful Excel Macro Examples For VBA Beginners (Ready-To-use)Document24 pages24 Useful Excel Macro Examples For VBA Beginners (Ready-To-use)Shrinivasan ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Gearing BSNL for NGN ServicesDocument27 pagesGearing BSNL for NGN ServicesAlandNo ratings yet
- Application of A Li-Ion Battery in The Frequency Containment Reserve MarketDocument20 pagesApplication of A Li-Ion Battery in The Frequency Containment Reserve MarketClaysius DewanataNo ratings yet
- Chladni Patterns in Variable ShapesDocument28 pagesChladni Patterns in Variable ShapesMarcel KoslabNo ratings yet
- Clean Technology HubDocument14 pagesClean Technology HubAdedimeji FredNo ratings yet
- CS Pipe Metric Dimensions As Per Asme B36-10Document20 pagesCS Pipe Metric Dimensions As Per Asme B36-10havocs havenNo ratings yet
- AMSOIL 10W-40 Advanced Synthetic Motorcycle OilDocument2 pagesAMSOIL 10W-40 Advanced Synthetic Motorcycle OilBruce WappmanNo ratings yet
- Grand Impianti Washer ExtractorDocument124 pagesGrand Impianti Washer ExtractorredvalorNo ratings yet
- Visual Studio & C# Lecture 5: Understanding ADO.NET and Entity FrameworkDocument21 pagesVisual Studio & C# Lecture 5: Understanding ADO.NET and Entity FrameworkFarrukh zamanNo ratings yet
- UAP Grading Policy Numeric Grade Letter Grade Grade PointDocument2 pagesUAP Grading Policy Numeric Grade Letter Grade Grade Pointshahnewaz.eeeNo ratings yet
- AxSEAM - Scanner-User ManualDocument116 pagesAxSEAM - Scanner-User ManualGhaithNo ratings yet
- P DrivDocument441 pagesP DrivptslabNo ratings yet
- ME96NSR Power MeterDocument11 pagesME96NSR Power MeterAndrew MaverickNo ratings yet
- Gas Appliance Pressure Regulators with Integrated FilterDocument8 pagesGas Appliance Pressure Regulators with Integrated FilterAlEjAnDrO CoNtReRaSNo ratings yet
- Identificación de RoscasDocument7 pagesIdentificación de RoscasEduNo ratings yet