0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views7 pagesLesson Plan Angle
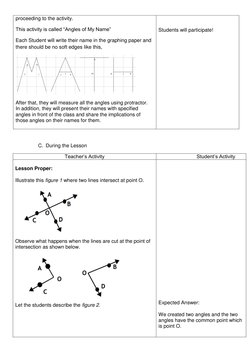
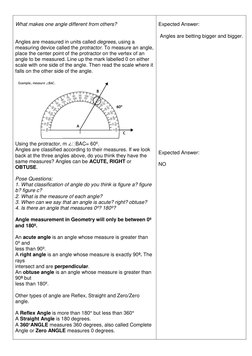
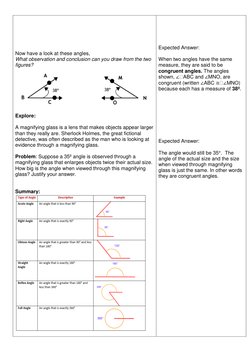
The document provides a lesson plan for teaching 7th grade students about geometry and different types of angles, including objectives, materials, procedures for motivation, teaching the lesson, and assessment. It defines an angle, identifies the parts of an angle, and teaches how to name, identify characteristics of, and illustrate acute, right, obtuse, and reflex angles. Students are asked to measure angles in their names, draw and classify examples, and state the type of angle for given measures in an assignment.
Uploaded by
Joven De AsisCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views7 pagesLesson Plan Angle
The document provides a lesson plan for teaching 7th grade students about geometry and different types of angles, including objectives, materials, procedures for motivation, teaching the lesson, and assessment. It defines an angle, identifies the parts of an angle, and teaches how to name, identify characteristics of, and illustrate acute, right, obtuse, and reflex angles. Students are asked to measure angles in their names, draw and classify examples, and state the type of angle for given measures in an assignment.
Uploaded by
Joven De AsisCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd