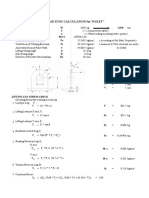
Pad-Eye Calculations and Frame Stress Verification
W-Industries, Inc.
Subsea Control Project: 14035 - BLIND FAITH UPS PANEL
11500 Charles Road Engineer: Haider Kazzaz
Houston, TX 77041 Date: April 10, 2007
Revision: 0B, (ECN: 14035-08)
Height (H) 1.75 inches
Padeye Width (W) 5 inches
Padeye Thickness (t) 0.5 inches
Hole Diameter (D) 1.125 inches
Padeye Radius (R) 2.5 inches
Shackle Pin Diamter (Dp) 1 inches
Load per Lug (F) 789.5 lbs
%Out of Plane (%OOP) 5 %
Design Factor (I) 3
Vertical Load (Fv=FxI) 2,369 lbs
Horizontal Load (Fh) 1,367 lbs
Sling Angle (θ) 60 degrees from horizontal
Sling Load (Fr) 2,735 lbs
Weld Metal tensile strength (Wt) 69,610 psi
Figure - 1 Lug Material 316L
Lug Material Yield Stress (Fy) 24,650 psi
Case -1 : Pad-eye Shear Stress
Fr
Actual Shear Stress (fv)= = 1,412 psi
D
2 × t × R −
2
Allowable Shear Stress (fv) =0.4xFy 9,860 psi
Shear stress case pass (safe) when the actual shear stress is lower than the allowable shear stress
Checking
Shear stress is OK
Case-2 : Pad-eye Combined stress
Fh × H F %OOP × Fr × H
Actual Combined Bending, Tension and Out of Plane Stress: = + v + = 3,245 psi
W 2 t ×W t2
t × W ×
6 6
Allowable Combined Stress =0.6xFy 14,790 psi
Combined stress case pass (safe) when the actual combined stress is lower than the allowable combined stress
Checking
Combined stress is OK
Case-3 : Pad-eye Bearing stress
F
Bearing Stress =
r
= 5,470 psi
t × D p
Allowable Bearing Stress =0.9xFy 22,185 psi
Bearing stress case pass (safe) when the actual combined stress is lower than the allowable combined stress
Checking
Bearing stress is OK
Page 1 of 5
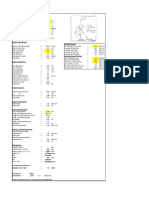
�Case-4 : Pad-eye FEA
Material Steel : Structural ( SS 316L)
Young Modulus 2.751e+007psi
Poisson Ratio 0.27
Density 0.289lb_in3
Thermal Expansion 0.0000117
Applied sling load (4619 lb)
Yield Strength 24656.4psi
Figure - 2
Results
Figure - 3
Criteria of checking the FEA results
The loading is safe when Von Mises Stress (Figure-3) is lower than the yield stress: σ V .M ises< σ Yield
σ V .Mises =
1
2
(
[ (σ x − σ y ) 2 + (σ x − σ z ) 2 + (σ y − σ z ) 2 + 6 τ 2 xy +τ 2 xz +τ 2 yz ] ) = 7840 psi
Allowable Stress =0.85xFy= 20,953
Checking
Loading Stress OK
Page 2 of 5
�Pad-eye Weld Calculations:
Weld Modulus
Total Weld Length Wl: 2 ×W + 2 × t = 11 inches
W2
Sx = W ×t + =
2
Weld Section Modulus 11 in (Treated as a line)
3
Combined Stress Calculation
Fh × H
Weld Bending fb = = 221 lb/in
Sx
Fh
Weld Shear fv = = 124 lb/in
L
Fv
Weld Tension ft = = 215 lb/in
L
= ( fb+ft) +fv =
2 2
Combineded stress
factual 454 lb/in
Allowable stress and force per in of leg
Allowable force per in of leg = .707*.47*yield stress= 8190.9 (lb/in)/(1 in leg)
Allowable Weld Stress (0.47xWt) Weld Allowable 11,586 psi
Weld Fillet Calculation
f actual f actual
= =ω = Minimum Fillet Weld Size (ω) = 0.0554 inch
f allowable allowable f orce per in of leg
Applied Fillet Weld Size Used (ωa)= 0.25 inch
2
Actual Effective Weld Throat Area (wa)= 1.94 in
Transverse Load Capability= 22,525 lbs
Criteria of checking the weld length
Each stress (Twisting, Bending, Shear, Tension and Combined) should be less than the allowable porce per in of leg
Checking
Weld length and stresses are OK
Criteria of checking the Weld Fillet
The actual applied weld fillet should be greater than the calculated minimum fillet size (w)
Checking
Applied Fillet Weld size (W a) OK
Page 3 of 5
�FEA for Frame
Material Steel : Structural ( SS 316L)
Young Modulus 2.751e+007psi
Poisson Ratio 0.27
Density 0.289lb_in3
Thermal Expansion 0.0000117
Yield Strength 24656.4psi
Self Weight + Applied load =
(7900 lb)
Figure - 4
Results
Figure - 5
Criteria of checking the FEA results
The loading is safe when Von Mises Stress (Figure-5) is lower than the yield stress: σ V .M ises< σ Yield
σ V .Mises =
1
2
(
[ (σ x − σ y ) 2 + (σ x − σ z ) 2 + (σ y − σ z ) 2 + 6 τ 2 xy +τ 2 xz +τ 2 yz ] ) = 16800 psi
Allowable Stress =0.85xFy= 20,953
Checking
Loading Stress OK
Page 4 of 5
�Summary and Conclusion
A) Pad-eye design verification
Actual Allowable Fail if Actual Stress >= Allowable stress
Case # and Description Stress PSI Stress PSI Ok / Fail
Case -1 : Pad-eye Shear Stress 1,412 9,860 OK
Case-2 : Pad-eye Combined stress 3,245 14,790 OK
Case-3 : Pad-eye Bearing stress 5,470 22,185 OK
Case-4 : Pad-eye FEA 7840 20952.5 OK
B) Pad-eye Weld length Verification
Actual Allowable Fail if Actual Stress >= Allowable stress
Case # and Description Stress lb/in Stress (force per in of leg) lb/in Ok / Fail
Weld Bending 221 8190.9 OK
Weld Shear 124 8190.9 OK
Weld Tension 215 8190.9 OK
Combineded stress 454 8190.9 OK
C) Pad-eye Weld Fillet Verification
Applied Minimum Calculated Fail if Applied fillet <= Minimum Fillet
Case # and Description Fillet (in) Fillet (in) Ok / Fail
Weld Fillet Calculation 0.25 0.0554 OK
D) FEA for Frame
Actual Allowable Fail if Actual Stress >= Allowable stress
Stress lb/in Stress PSI Ok / Fail
16800 20952.5 OK
Conclusion
The pad-eye is designed using 1/2” SS 316L @ 3 SWL. The pad-eye shape and dimensions were determined using engineering
analysis, geometry constrains as well as FMC guidelines G03.33.
All the above mentioned items for the pad-eye part and weldment show a safe operation under the 3 SWL applied load.
The stresses generated in the Frame were verified using FEA method @ 2.5 SWL and the maximum octahedral shear stress found to be
lower than allowable shear stress indicating a safe operation condition
Page 5 of 5