Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Time Base Generators
Uploaded by
raman yarramilli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views14 pagesTIME BASE GENERATORS
Original Title
Typesoftimebasegenerators 150714175023 Lva1 App6892
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTIME BASE GENERATORS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views14 pagesTypes of Time Base Generators
Uploaded by
raman yarramilliTIME BASE GENERATORS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
TYPES OF
TIME BASE GENERATORS
1) UJT as RELAXATION OSCILLATOR.
2) MILLER SWEEP GENERATOR.
3) BOOTSTRAP RAMP GENERATOR.
4) CURRENT TIME BASE
GENERATOR.
UJT as RELAXATION OSCILLATOR
Equivalent circuit.
Discharging of capacitor through UJT generates saw-
tooth waveform.
When VBB is connected, it will start charging the
capacitor through R1.
The capacitor keeps on charging until the voltage
across it becomes equal to 0.7V .
We take output across the capacitor ‘C’.
During the charging process, the voltage across
capacitor increases until it reaches its peak value.
At the peak value the UJT is switched ON and it
starts conducting.
When the UJT starts conducting , the capacitor
starts discharging between emitter and B1.
When the capacitor voltage become zero, the
capacitor again starts charging.
The frequency of the o/p saw-tooth waveform can
be varied by changing the value of R1 resistor, since
this controls the time constant(R1C) of the
capacitor charging circuit.
FORMULA
t=2.3R1Clog10(1/1-ŋ)
t=R1Cloge(1/1-ŋ)
VC=VBB[1-e^(-t/R1C)]
MILLER SWEEP GENERATOR
Q1 acts as a switch and Q2 acts as a CE configuration
high gain amplifier.
When Q1 is ON, Q2 is OFF.
At this instance o/p voltage across capacitor is
equal to VCC.
If a pulse of negative polarity is applied, then Q1 is
reverse biased and it is switched OFF. Q2 then is
switched ON.
Since Q2 conducts, o/p voltage begins to decrease
towards zero.
When the i/p pulse is removed the capacitor again
begins to charge.
FORMULA
tS=CRC(β+1)
where tS=sweep time(rising time).
BOOTSTRAP RAMP GENERATOR
The transistor Q1 acts as a switch and Q2 as an unity
gain amplifier.
Suppose the transistor Q1 is ON and Q2 is OFF.
The capacitor C1 begins to charge to VCC through the
diode forward resistance RE.
At this instant, the output voltage Vo is zero.
When negative pulse is applied to the base of transistor
Q1, it turns OFF.
The output voltage (Vo) is the same as the base voltage
of transistor Q2.
Diode is reversed biased. Capacitor ‘C’ starts charging.
Output voltage begins to increase from zero.
Since the value of capacitor C1 is much larger than that
of capacitor C, therefore the voltage across capacitor
C1 practically remains constant.
Thus the voltage drop across the resistor R also remains
constant because of this, the current iR through the
resistor also remains constant.
This causes the voltage across the capacitor C (and
hence the output voltage) to increase linearly with time.
CURRENT TIME BASE GENERATOR
There are 3 important blocks-constant current source,
capacitor and a switch.
During the sweep interval, the capacitor ‘C’ is charged by
the constant current.
When the sweep waveform reaches to its maximum
value VS the switch opens and does not allow the current
to flow further.
The capacitor ‘C’ starts discharging.
The o/p voltage waveform is measured across the
capacitor.
You might also like
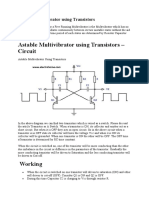
- Astable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocument10 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using TransistorsGangireddy SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Time Base GeneratorsDocument29 pagesTime Base GeneratorsPrasad100% (1)
- Dual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.Document3 pagesDual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.sbpatel123No ratings yet
- Answers of Power Electronics NewDocument9 pagesAnswers of Power Electronics NewSyed ZabiullahNo ratings yet
- Multi VibratorDocument10 pagesMulti VibratorKeith BoltonNo ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument5 pagesAstable Multivibratorbhanuka2009No ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document10 pagesLecture 10zaidNo ratings yet
- Bistable Mono StableDocument30 pagesBistable Mono StableTurkish GatxyNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 3 - HemakeshDocument13 pagesASSIGNMENT 3 - HemakeshHemkeshNo ratings yet
- Fpe QB 23Document7 pagesFpe QB 23manishchalke65No ratings yet
- Multi Vibrators WikipediaDocument13 pagesMulti Vibrators Wikipediasreedhar_vk280No ratings yet
- MultivibratorDocument4 pagesMultivibratorsakibNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv - Multivibrator CircuitsDocument29 pagesUnit Iv - Multivibrator CircuitsAshwini SaravannavarNo ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesAstable MultivibratorWaldo PulancoNo ratings yet
- What Are Astable Multi-Vibrator, Its Wave Form, Saturated Point, Cutoff Point and Application? Astable MultivibratorDocument7 pagesWhat Are Astable Multi-Vibrator, Its Wave Form, Saturated Point, Cutoff Point and Application? Astable MultivibratorwilliamNo ratings yet
- Multivibrators OverviewDocument15 pagesMultivibrators OverviewAchuilNo ratings yet
- Aim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsDocument6 pagesAim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsShahrukh PinjariNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document22 pagesModule 2canusha820No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Astable Blocking OscillatorDocument1 pageUnit 5 Astable Blocking Oscillatordev_mathanNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - SCR Triggering and CommutationDocument14 pagesUNIT I - SCR Triggering and CommutationmalathynarayaniNo ratings yet
- Current Commutated Chopper Through SimulinkDocument54 pagesCurrent Commutated Chopper Through SimulinkAbhijeetSinha100% (1)
- Power ElectronicsDocument15 pagesPower ElectronicsSatya Sudhakar RasamsettiNo ratings yet
- Inverter and ChopperDocument92 pagesInverter and ChopperGnanaseharan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- MC Murray InverterDocument92 pagesMC Murray InverterGnanaseharan Arunachalam100% (5)
- Clipper and ClamperDocument11 pagesClipper and ClamperPoorni Jayaraman100% (1)
- Phase-Controlled Converters: Unit IiDocument29 pagesPhase-Controlled Converters: Unit IiChinnaGurappaNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument2 pagesColpitts Oscillatorkristalclear100% (2)
- Multi VibratorDocument4 pagesMulti VibratorAna Josefina BeltranNo ratings yet
- Multi VibratorsDocument3 pagesMulti VibratorsShameer Sr S RNo ratings yet
- Monostable MultivibratorDocument2 pagesMonostable MultivibratorsNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Demo NADocument155 pagesPower Electronics Lab Demo NAsoumyaNo ratings yet
- Charging and DischargingDocument14 pagesCharging and DischargingRavi GargNo ratings yet
- Unit - V InvertersDocument11 pagesUnit - V InvertersSukhpal SinghNo ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - Multi PhaseDocument39 pagesAC-DC Converter - Multi Phasebishnu prasad muniNo ratings yet
- On InverterDocument49 pagesOn InverterSahil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Voltage Controlled OscillatorDocument7 pagesVoltage Controlled Oscillatorjonesy5000No ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - DDocument39 pagesAC-DC Converter - DBishnu100% (1)
- InverterDocument93 pagesInverterABCDNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronics IV Assignment 1Document6 pagesAnalogue Electronics IV Assignment 1Phelix PheloNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics L2 ConvertersDocument6 pagesPower Electronics L2 ConvertersBakri BugaNo ratings yet
- Tan Kien Hau (01Dem16F1004) ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006) Lee Zhi Shern (01Dem16F1038) Zulhilmi (01Dem16F1007)Document18 pagesTan Kien Hau (01Dem16F1004) ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006) Lee Zhi Shern (01Dem16F1038) Zulhilmi (01Dem16F1007)Eden HazardNo ratings yet
- Phase Controlled RectifiersDocument59 pagesPhase Controlled RectifiersAravindh EnggNo ratings yet
- Commutation Circuits - IsraDocument23 pagesCommutation Circuits - IsraAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument37 pagesRectifiersSukhpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Effect of Source InductanceDocument10 pagesEffect of Source Inductancemeeravali_snNo ratings yet
- Thyrister Based InverterDocument31 pagesThyrister Based InverterAbdul HudaifNo ratings yet
- Abert AinoDocument12 pagesAbert AinoAINOMUGISHA ABERTNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2016-17 ECE1013 ETH 1601 24-APR-2017 RM001 9 Opamp 555timerDocument16 pagesWINSEM2016-17 ECE1013 ETH 1601 24-APR-2017 RM001 9 Opamp 555timerMassSomeshNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Application & Photosensitive Control Circuits: Chapter No.5Document28 pagesThyristor Application & Photosensitive Control Circuits: Chapter No.5Kim ManaloNo ratings yet
- Pe 42 Ee17Document16 pagesPe 42 Ee17Knight knightNo ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument146 pagesAstable Multivibratorsantovaron123No ratings yet
- 6.1 IC555 TIMER: Circuit ComponentsDocument8 pages6.1 IC555 TIMER: Circuit ComponentsManish PradhanNo ratings yet
- IntegratorDocument2 pagesIntegratorlabdownloadNo ratings yet
- 2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiDocument59 pages2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiSaranya. M SNSNo ratings yet
- Unit 05: Single Phase DC-AC Converter (Transistor Based)Document20 pagesUnit 05: Single Phase DC-AC Converter (Transistor Based)vaibhav bodkheNo ratings yet
- Unijunction Transistor: T.Y.B.Sc - Eletronics Power EletronicsDocument10 pagesUnijunction Transistor: T.Y.B.Sc - Eletronics Power EletronicsAvinash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Waveform GeneratorsDocument26 pagesLesson 4 Waveform GeneratorsOdoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- B64 CDD12 D 01Document28 pagesB64 CDD12 D 01mannokhNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument15 pagesAmplitude Shift Keyingraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Variables and Operators - ProgrammingDocument21 pagesVariables and Operators - Programmingraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Prototyping With A Team: Acting Machines Support Shared UnderstandingDocument6 pagesPrototyping With A Team: Acting Machines Support Shared Understandingraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- 1 - Io StatementsDocument16 pages1 - Io Statementsraman yarramilli100% (1)
- Communication Systems 2019-20 Course HandoutDocument6 pagesCommunication Systems 2019-20 Course Handoutraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- 17D06207 System On Chip Design - OrderDocument5 pages17D06207 System On Chip Design - Orderraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Account Statement From 16 Jun 2020 To 16 Dec 2020Document1 pageAccount Statement From 16 Jun 2020 To 16 Dec 2020raman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument1 pageDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineeringraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- B.Tech IV Sem AC Quiz 1-2019ABDocument2 pagesB.Tech IV Sem AC Quiz 1-2019ABraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument41 pagesUnit IvSoundararajan RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document3 pagesPresentation 1raman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada Kakinada - 533 001, Andhra PradeshDocument69 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada Kakinada - 533 001, Andhra PradeshAndreansyahNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio Propagation - Small Scale FadingDocument60 pagesMobile Radio Propagation - Small Scale Fadingraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Probability 120904030152 Phpapp01Document25 pagesProbability 120904030152 Phpapp01raman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Ece PDFDocument157 pagesEce PDFrafi skNo ratings yet
- A Vision of 6G Wireless Systems Applications, Trends, Technologies, and Open Research ProblemsDocument10 pagesA Vision of 6G Wireless Systems Applications, Trends, Technologies, and Open Research ProblemsAndro Elnatan HarianjaNo ratings yet
- (Proakis J.G.) Digital Signal Processing. PrinciplDocument60 pages(Proakis J.G.) Digital Signal Processing. Principllhslhin100% (1)
- Co1 3 2 2 - 1 3 - Co2 3 2 2 - 1 - 1 3 - Co3 3 2 2 - 1 - 1 3Document2 pagesCo1 3 2 2 - 1 3 - Co2 3 2 2 - 1 - 1 3 - Co3 3 2 2 - 1 - 1 3raman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Cellular CommunicationDocument48 pagesCellular CommunicationFaim HasanNo ratings yet
- K L E F (Deemed To Be UNIVERSITY) : Code: 15 EC 305Document2 pagesK L E F (Deemed To Be UNIVERSITY) : Code: 15 EC 305raman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 (PDC) PDFDocument32 pagesUnit 5 (PDC) PDFraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Lakireddy Bali Reddy College of Engineering (Document9 pagesLakireddy Bali Reddy College of Engineering (raman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- PSC Important Questions For Mid-IIDocument2 pagesPSC Important Questions For Mid-IIraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Chapter1: Introduction: Poker Card Game Using PythonDocument5 pagesChapter1: Introduction: Poker Card Game Using Pythonraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Unijunction TransistorDocument13 pagesUnijunction Transistorraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Unijunction TransistorDocument13 pagesUnijunction Transistorraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Outcome-Based Education (Obe) : Knowledge Comprehension Application AnalysisDocument2 pagesOutcome-Based Education (Obe) : Knowledge Comprehension Application AnalysissivakumarNo ratings yet
- Multi VibratorDocument20 pagesMulti VibratorNitin RananavareNo ratings yet
- Digital ElectronicsDocument102 pagesDigital Electronicsdurga0% (1)
- Amplificadores Automotivos PyramidDocument13 pagesAmplificadores Automotivos Pyramidedusf1000No ratings yet
- Subsea Pipeline Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesSubsea Pipeline Job DescriptionVijay_DamamNo ratings yet
- Munchies BrochureDocument28 pagesMunchies BrochureIbrahim Diaz LazoNo ratings yet
- Bill of Quantity: Supply of Pipes and FittingsDocument3 pagesBill of Quantity: Supply of Pipes and FittingssubxaanalahNo ratings yet
- Architecture of Neural NWDocument79 pagesArchitecture of Neural NWapi-3798769No ratings yet
- R35 Credit Analysis Models - AnswersDocument13 pagesR35 Credit Analysis Models - AnswersSakshiNo ratings yet
- 7273X 47 ITOW Mozart PDFDocument3 pages7273X 47 ITOW Mozart PDFAdrian KranjcevicNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Math 7 Curriculum Guide PDFDocument15 pagesK To 12 Math 7 Curriculum Guide PDFEdmar Tan Fabi100% (1)
- Definition Nature and Scope of Urban GeographyDocument4 pagesDefinition Nature and Scope of Urban Geographysamim akhtarNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter SUMMATIVE TEST in MAPEHDocument3 pages3rd Quarter SUMMATIVE TEST in MAPEHzaile felineNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physiotherapy PracticeDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Physiotherapy PracticejNo ratings yet
- Impeller Velocity TrianglesDocument2 pagesImpeller Velocity TrianglesLorettaMayNo ratings yet
- Corporate Profile of Multimode GroupDocument6 pagesCorporate Profile of Multimode GroupShaheen RahmanNo ratings yet
- 88 Year Old Man Missing in SC - Please ShareDocument1 page88 Year Old Man Missing in SC - Please ShareAmy WoodNo ratings yet
- KPI's Troubleshooting GuideDocument27 pagesKPI's Troubleshooting GuideMohamed SayedNo ratings yet
- 95 935 Dowsil Acp 3990 Antifoam CompDocument2 pages95 935 Dowsil Acp 3990 Antifoam CompZhan FangNo ratings yet
- A Dessertation Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocument65 pagesA Dessertation Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofMadhavpokale100% (1)
- Grade 8 Mathematics Checkpoint Booklet AY 23-24Document270 pagesGrade 8 Mathematics Checkpoint Booklet AY 23-24Arta riaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7odeDocument29 pagesChapter 7odeRoberto NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Q1. What Is JDBC? Explain Different Types JDBC Drivers With Suitable DiagramDocument64 pagesQ1. What Is JDBC? Explain Different Types JDBC Drivers With Suitable DiagramjyebbwycqmfkuxNo ratings yet
- APS PresentationDocument32 pagesAPS PresentationRozack Ya ZhackNo ratings yet
- 10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupDocument4 pages10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupArvin ArmojallasNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal DraftDocument1 pageProject Proposal DraftCarl Axel M. FajardoNo ratings yet
- Bell Single-Sleeve Shrug Crochet PatternDocument2 pagesBell Single-Sleeve Shrug Crochet PatternsicksoxNo ratings yet
- Case Study Presentation - CGDocument37 pagesCase Study Presentation - CGapi-290866384No ratings yet
- Letter of Intent Date: 18-Feb-2019 Mr. Ravi Mishra,: For Multiplier Brand Solutions PVT LTDDocument2 pagesLetter of Intent Date: 18-Feb-2019 Mr. Ravi Mishra,: For Multiplier Brand Solutions PVT LTDRavi MishraNo ratings yet
- WHITE TOWN GROUP-4 FinalDocument112 pagesWHITE TOWN GROUP-4 Finalaswath manojNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson MF7600 Technician Workshop ManualDocument798 pagesMassey Ferguson MF7600 Technician Workshop Manualgavcin100% (5)
- C305 - QTO Workshop PDFDocument90 pagesC305 - QTO Workshop PDFJason SecretNo ratings yet
- DRUGPDocument371 pagesDRUGPPolarogramaNo ratings yet