Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Education and Health Grade 12 1st Semester
Uploaded by
Franzcine100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
2K views4 pagesPhysical Education and Health Grade 12 1st Semester
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhysical Education and Health Grade 12 1st Semester
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
2K views4 pagesPhysical Education and Health Grade 12 1st Semester
Uploaded by
FranzcinePhysical Education and Health Grade 12 1st Semester
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Modern Dance 1) Altitude
- a broad genre of western concert or theatrical 2) Force
dance 3) Motion
-primarily arising out of Germany and the United 4) Sequence
States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries 5) Direction
-often considered to have emerged as a rejection of, 6) Form
or rebellion against, classical ballet. 7) Velocity
8) Reaction
CREATORS OF A NEW IDEA 9) Extension
- Movement education in the 1800’s to early Liselott Diem
1900’s -She and her husband founded an internationally
- The early pioneers of movement education were known college in Germany, Deutsche
influenced by the idea of the body being an Sporthochschule Koln, to train teachers in sport
expression of movement. and physical education.
-The college taught a “natural approach to teaching
3 of the Most Historically Influential children to move effectively in all kinds of
Individuals situations”
○ Francois Delsarte -The teacher’s role was to provide an environment
○ Liselott Diem that would encourage children to explore
○ Rudolf von Laban movement freely in their own way.
Teachers Equipment
Francois Delsarte (France, 1811-1871) 1. Balls
-French man 2. Ropes
-Developed what he termed applied aesthetics and 3. Wands
focused his work in the arts. 4. Boxes
-Contributed critical ideas of connections among 5. Benches
the mind, body, and spirit. -Allow children to develop a wide variety of
-Also saw movement as a union of time, space and movement responses individually, with partners, or
motion within small groups.
-Believed the expressive movement should relate to -Teachers were encouraged to challenge children
the emotion that inspired that movement. by asking questions such as Who can do this? and
-Introduced the idea of parallelism in movements – How can this be done differently?
the simultaneous motion of two body parts in the
same direction and in succession
9 Laws of Motion Rudolf von Laban
-Considered by most as the true pioneer of - A common Horton move seen in many
movement education. modern classes: the arms straight
-Critical contribution: Theory of Movement- above the heads and a flat back
focusing specially on the concept of effort. INTRODUCTION TO TRADITIONAL
-He believed that the body was an instrument of DANCES
expression. Dancing is Good for Mind and Body
-Made a distinction between: 1. Improved fitness levels
Dancing has a wide range of physical
○ Expressive movement
benefits. These include improved muscular
○ Functional movement strength, coordination, flexibility, increased
Expressive movement aerobic fitness and spatial awareness, to name
a few. Many types of dancing are full body
-Communicates ideas in dance or other forms of
workouts, where you utilize majority of your
artistic expression. muscle groups, unlike when you’re working
Functional Movement out at the gym. This is a great way to effectively
manage weight and improve cardiovascular
Movements that serve as a purpose in everyday life, health. Regular dancing as part of your exercise
such as sports and games. regime will also result in a boost in energy
levels, allowing you to perform better at work.
Identified 4 factors of movement
1. Weight 2. Improved mood and mental health
2. Space The psychological benefits of dancing are
numerous. This includes improved mood,
3. Time
greater self-confidence and self-esteem, as
4. Flow well as improved social skills.
Martha Graham The complex mental and physical
coordination helps to boost memory and
-Is considered the “Mother of Modern dance,” brain function, which may guard your
-Wanted dancers to focus on “feeling.” Feeling the mind against developing dementia as you
age
floor beneath them, contracting and releasing the
The act of dancing itself also induces the
core of the body (the center of the body, as contrast production of natural antidepressants such
to ballet’s emphasis on the limbs,) coordinating as endorphins in your body that aids in
stress relief, which helps keep
breathing and movement.
psychological illnesses such as depression
Lester Horton and anxiety at bay.
- developed his own approach that
Dancing can also be particularly helpful in
incorporated Native American dances improving social skills as it is usually
and modern jazz. performed in a group setting or with a
partner.
- His technique is the most
Seeing others overcome their shyness or
demanding: focusing on the whole- insecurities can aid in you overcoming
body: Flexibility, strength, your own issues.
Dancing in a group or with a partner where
coordination.
physical contact is made enhances the
experience of fellowship and helps people
forge deeper ties with one another.
celebrate their foreigners
Dancing is a great way to kick start or add stepped daily lives
to your exercise regime, but remember to Bontoc, Ifugao, Benguet,
perform adequate warm up and cool Apayao, & Kalinga tribes
down exercises to prevent injury, muscle A people whose way of life
strain or soreness. If you haven’t exercised existed long before any
in a long time or have previous injuries, it A good foot on the harvest,
may be wise to get your doctor’s advice on health, peace, Philippine war,
your physical limitations before and other
commencing on any exercise regime. Gongs, ganza symbols of living
2. Spanish Influenced Dances
Traditional dancing Dances reflects socialities to the
can be another term for folk dance, or Christianitym and stringed
sometimes even for ceremonial dance. music of European art and the
The term “traditional”- more frequently rondalla culture
used when the emphasis is on the cultural Philippine aristocrats created
roots of the dance however, dances that Filipino adaptations of
have a ritual origin or purpose are not European dances
usually considered to be traditional dances.
Jotas, fandangos, mazurakas,
waltes
FOLK DANCE
Dances by the young
a dance that originates as ritual among and
3. Muslim Dances
is characteristics of the common people of
Influenced by Malay, Javanese
a country and that is transmitted from
& Middle Eastern Traders
generation to generation.
(Islam)
the oldest form of dance and the earliest
form of communication. Mysticism, royalty, and beauty
Traditional dance of a given country which Uses intricate hand & arm
evolved naturally and spontaneously with movement
everyday activities The fingers express feelings &
emotions
Characteristics of Philippine Folk Dances in Uses shimmering costumes
general 4. Tribal Dances
The dancers are apart in order to move Animal sounds found in
freely their hands and feet. different parts of human
To execute the dance moves properly. singing, the Philippines (T’boli,
Most dances are done by pairs it is Bilaan, Manobo, Bangobo,
because the theme mainly express indigenous materials etc.)
courtship dance. Intricate craftsmanship in
metal, clothing, and jewelry
Reflects rituals & animals,
belief in “spirits” & shamans
Also known as Ethnic nature –
“anito” dances; Ethnic
Minorities
5 Major Classifications of Philippine Folk 5. Rural Dances
Dances Reflects the simple life of the
1. Cordillera Dances people in the barrio
Dances reflects rituals Depicts common work, daily
Spaniards or other which activities of the peasants
Shows gaiety & laughterm bridegroom offers the bride the
festivities protection and comfort of his
Performed in fiestas to honor blanket. He simulates the
patron saints movements of a rooster at love play,
Give homage to the barrios aspiring to attract and seize his love.
namesake for a good harvest, The bride’s friends are ready to help
health & perseverance prepare the bride by offering
Indigenous materials, clapping, “bangas” (earthen pots) filled with
rondalla, percussion fresh water from the mountain
instrukments spring,
ETHNIC DANCE • Binasuan (Pangasinan) – Filipino
• define as expressive movement, folk dance that involves dancers
incidental movement as from balancing glasses of wine on their
excitement or emotion, movement to heads and the palms of their hands.
rhythm, movement to music, 3. Occupational Dance
movement for its own sake, movement • Mananagat (Cebu) – occupational
outside the normal movements of life. dance which originated from Bogo,
Characteristics of Ethnic Dances in general: Cebu. This dance imitates the work
• Ethnic dances tell a story. of a fisherman and his companions.
• Many are agricultural in origin, and Importance and value of folk dance and ethnic
many convey male-female dances:
relationships. Value
• There are usually costumes, often • Philippine folk dance helps keep the
flowing colorful skirts. Also, traditional people connected to their ancestry and
instruments are used. their traditions. Folk dance helps to
Examples Of Ethnic Dances preserve the cultural unity of the people
1. Ritual Dance
• Dugso (bukidnon) – shows the Importance
Higaonon performing the ritual of • People think folk dances are important
hinaklaran wherein the men and because they help keep a culture alive.
women hold hands while moving People have been doing folk dances for
around in measured steps named hundreds of years, and there is value
after a peculiar body movement. keeping that tradition alive.
The women are also dressed in • Folk dances are important because they
colorful dresses and oanikas or preserve the Philippine culture and pass
feathered combs full of colorful it on to the next generation. They are a
yarns, mirrors, beads, and gold uniting force to the Philippine people.
spangles.
• Pagdiwata (Palawan) – pagdiwata
is a dance originating from
Tagbanua tribe of Palawan which
depicts rituals after a rice harvest.
These rites are held as part of thanks
giving and part an appeal for
continued protection.
2. Life-Cycle Dance
• Salip (Apayao) – celebrate
important events in life such
wedding. A kalinga wedding dance
is an important celebration. The
You might also like
- Q1-L2-Managing Stress Through DanceDocument19 pagesQ1-L2-Managing Stress Through DanceJaysonMananquilLabsan100% (2)
- Prosperidad National High School Health TestDocument3 pagesProsperidad National High School Health TestLeeJane May As GasconNo ratings yet
- TEST Peh11Document3 pagesTEST Peh11Jerwin SamsonNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Test in HOPE 3Document2 pages1st Quarter Test in HOPE 3Chad Ballon100% (2)
- PE 12 QuizDocument2 pagesPE 12 Quizcindy juntongNo ratings yet
- Pretest Pe11 1st SemDocument2 pagesPretest Pe11 1st SemElyzee S ColumbresNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - PE and Health 3Document6 pagesGrade 12 - PE and Health 3Robert Coloma100% (1)
- Diagnostic Test Grade 12Document3 pagesDiagnostic Test Grade 12Fayee Mae Hyacinth Meca100% (4)
- 1st Examination of Pe 12Document4 pages1st Examination of Pe 12Ian Santiago ParagguaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Hope 1: 2 Quarter - Week 5-8Document3 pagesSummative Test in Hope 1: 2 Quarter - Week 5-8Mylyn Mina67% (3)
- ORMOC CITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY: Dance Module on Health-Related FitnessDocument22 pagesORMOC CITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY: Dance Module on Health-Related FitnessStephanie Dillo67% (3)
- Physical Education and Health 12 Q2 Module 1 2Document13 pagesPhysical Education and Health 12 Q2 Module 1 2Benedict LumagueNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 DISTRICT UNIFIED SUMMATIVE TEST IN HOPE TQ 1Document2 pagesGrade 12 DISTRICT UNIFIED SUMMATIVE TEST IN HOPE TQ 1Kaye AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physical Education and Health 3rd QuarterDocument2 pagesGrade 12 Physical Education and Health 3rd QuarterJonathan Cerezo100% (3)
- HOPE 3 Module 4 Physiological Indicators EditedDocument21 pagesHOPE 3 Module 4 Physiological Indicators EditedFrancine FlorandaNo ratings yet
- Hope 11 Module 1 Q2Document20 pagesHope 11 Module 1 Q2Jimar EsmeriaNo ratings yet
- I. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Space ProvidedDocument2 pagesI. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Space ProvidedAnonymous fnrqeJ88nNo ratings yet
- 2019 Grade 12 Pe and Health 3 Nature of DanceDocument13 pages2019 Grade 12 Pe and Health 3 Nature of DanceJonah Angeles100% (2)
- Hope - 3 Grade 12: Energy Systems Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Document15 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12: Energy Systems Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Alvin Sinel Belejerdo100% (2)
- Hope 2 DLLDocument6 pagesHope 2 DLLNahida TakiriNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Hope 2Document4 pagesSummative Test in Hope 2Aian Villanueva100% (1)
- HOPE 1 - Q1 - W9 - Mod9Document12 pagesHOPE 1 - Q1 - W9 - Mod9Donajei RicaNo ratings yet
- Cheerdance HandoutDocument6 pagesCheerdance HandoutMarkjan S. AlmoginoNo ratings yet
- Ade 11 Pe 2nd SemDocument2 pagesAde 11 Pe 2nd SemivonneNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Health 12Document5 pagesPhysical Education and Health 12Mike GuerzonNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physical Education and Health Handouts 1st Quarter 1 PDF FreeDocument2 pagesGrade 12 Physical Education and Health Handouts 1st Quarter 1 PDF FreeCarmela Estrada100% (1)
- G11 PEH1 Module 1Document19 pagesG11 PEH1 Module 1Junar AlarconNo ratings yet
- Sabang National High School PE TestDocument3 pagesSabang National High School PE TestElias Q. de MesaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Festivals PEH ExamDocument6 pagesPhilippine Festivals PEH ExamJonathan Laurito Adrales100% (1)
- Quarter 3 - 1 Summative Test in Pe & Health 12: Godwino Integrated SchoolDocument3 pagesQuarter 3 - 1 Summative Test in Pe & Health 12: Godwino Integrated SchoolChariza L. Pacurib100% (1)
- Assessment Test - Hope 1Document5 pagesAssessment Test - Hope 1Queenie Gamboa100% (2)
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 3: 1 Quarter - Grade 12Document20 pagesHealth Optimizing Physical Education 3: 1 Quarter - Grade 12Angelo LumbaNo ratings yet
- P.E 2nd Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesP.E 2nd Quarter ExamCherry Vhim Flores Lanurias100% (3)
- Quarter 1 - Summative Test in Pe and Health 12Document2 pagesQuarter 1 - Summative Test in Pe and Health 12JESSA SUMAYANG100% (11)
- Grade 12 ExamDocument3 pagesGrade 12 ExamMark M Pi100% (1)
- Physical Education and Health 3Document15 pagesPhysical Education and Health 3Christian PacotNo ratings yet
- Summative Test: 2 Quarter/Subject: Q1-H.O.P.E.12Document3 pagesSummative Test: 2 Quarter/Subject: Q1-H.O.P.E.12John QuidulitNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Physical Education and HealthDocument5 pagesLearning Module: Physical Education and Healthmaxene jade100% (1)
- K to 12 PEH Curriculum Optimizes Health through FitnessDocument11 pagesK to 12 PEH Curriculum Optimizes Health through FitnessTrishia Bon100% (1)
- Kamapehmilya: Fitness Through Traditional DancesDocument21 pagesKamapehmilya: Fitness Through Traditional DancesValerieNo ratings yet
- Hope 1 2ND Summative TestDocument5 pagesHope 1 2ND Summative TestJohn Rahzl NaradaNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Examination in PEH 12Document1 pageSecond Periodical Examination in PEH 12Mersha Mengote Caspe100% (1)
- ATHS Module 1 for P.E. and Health 12: Philippine Folk DancesDocument28 pagesATHS Module 1 for P.E. and Health 12: Philippine Folk DancesMikaella Tiangson100% (1)
- Nat-Physical EducationDocument8 pagesNat-Physical EducationArnel LomocsoNo ratings yet
- Hope 12 4th QuarterDocument6 pagesHope 12 4th QuarterCatherineNo ratings yet
- New Exam Grade 11Document6 pagesNew Exam Grade 11Jessieann Balmaceda CabanganNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Exam Quarter 2Document2 pagesPhysical Education Exam Quarter 2Otenciano100% (3)
- 4th Quarter Exam P.EDocument3 pages4th Quarter Exam P.EKim Reyes Balen100% (3)
- Module Pe and Health 12 Second SemesterDocument13 pagesModule Pe and Health 12 Second SemesterMark Laurence FernandoNo ratings yet
- SHS PEH3 Quarter 2 Week 1 4Document36 pagesSHS PEH3 Quarter 2 Week 1 4Marc Morris Bautista Mancenido100% (1)
- Self Learning Module in Grade 12 P.E. and HealthDocument15 pagesSelf Learning Module in Grade 12 P.E. and Healthserry gupitNo ratings yet
- Hope 3 Module 6 Quarter 2Document16 pagesHope 3 Module 6 Quarter 2Marchan Dalapo-Llacuna CorowanNo ratings yet
- Philippine High School Exam on PE and Health TopicsDocument2 pagesPhilippine High School Exam on PE and Health TopicsMARLON MARTINEZ100% (2)
- HOPE 3 Module 1Document39 pagesHOPE 3 Module 1Lei Dulay100% (4)
- PE & HEALTH 3 Summative 1st Quarter With Answer KeyDocument1 pagePE & HEALTH 3 Summative 1st Quarter With Answer KeyTessa Kaye - Rumol AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Hope Grade 11 Second QuarterDocument3 pagesHope Grade 11 Second QuarterJoylass Pasac100% (3)
- Reviewer in PEDocument4 pagesReviewer in PEAndrew CruzNo ratings yet
- Swimming P.E 1Document6 pagesSwimming P.E 1Rhea Anne NuñezNo ratings yet
- Spec Pe 09 Movement Education Module 1Document12 pagesSpec Pe 09 Movement Education Module 1Joas Refil100% (1)
- Rhythmic Activities 28 First Grading Coverage 29Document11 pagesRhythmic Activities 28 First Grading Coverage 29Kevin Shane ReyesNo ratings yet
- Details Location in Article (Section/Subsection) : HHLT1RAE Research and Evidence in Practice - Article Summary TemplateDocument5 pagesDetails Location in Article (Section/Subsection) : HHLT1RAE Research and Evidence in Practice - Article Summary TemplateThanh ThảoNo ratings yet
- MemoDocument2 pagesMemoAboubakr SoultanNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Government - Certificate of Physical Fitness For Executive PostsDocument2 pagesTamil Nadu Government - Certificate of Physical Fitness For Executive PostsDr.Sagindar86% (7)
- 3rd Quarter Grade 9 Pe Learning Activity Sheets Week 1 4 FinalDocument17 pages3rd Quarter Grade 9 Pe Learning Activity Sheets Week 1 4 FinalCristilyn Saagundo100% (3)
- DLL Hope 2 Co1 Olea TuazonDocument4 pagesDLL Hope 2 Co1 Olea TuazonDandref ReyesNo ratings yet
- Circuit Training Part 2Document7 pagesCircuit Training Part 2Cultural Council [OLD], IIT KanpurNo ratings yet
- Gymnastic Intervals TrainingDocument7 pagesGymnastic Intervals TrainingAnonymous BEEeTPqiNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 7 1st Quarter ExamDocument7 pagesMAPEH 7 1st Quarter ExamJoyce SollestaNo ratings yet
- Iron Clad CardioDocument6 pagesIron Clad Cardiorajkumarvpost6508No ratings yet
- Done - OBE Syllabus - PathFit 2 - Fitness ExercisesDocument5 pagesDone - OBE Syllabus - PathFit 2 - Fitness ExercisesJoseph Mazo100% (1)
- Personal Trainer TextDocument97 pagesPersonal Trainer Textwuddafren100% (1)
- Mechanical Properties and Testing of MaterialsDocument67 pagesMechanical Properties and Testing of Materialsgalati12345No ratings yet
- CA Physical Education IA 2020 Credit 4 FF PDFDocument20 pagesCA Physical Education IA 2020 Credit 4 FF PDFKeara MosesNo ratings yet
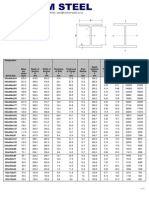
- Universal steel columns technical specificationsDocument2 pagesUniversal steel columns technical specificationsdenyfateNo ratings yet
- P.E November 13 PassDocument3 pagesP.E November 13 PassJhodenn Lorenzo LucilaNo ratings yet
- Tests For Anaerobic CapacityDocument32 pagesTests For Anaerobic CapacityshurentharNo ratings yet
- Athletics Sport Drill Book Updated August 2012Document17 pagesAthletics Sport Drill Book Updated August 2012MalekNo ratings yet
- 36 Pictures Show Which Muscles You're StretchingDocument13 pages36 Pictures Show Which Muscles You're StretchingMarco TorreNo ratings yet
- Gross Ana Functions of Skeletal Ms 09BDocument44 pagesGross Ana Functions of Skeletal Ms 09BKyra Gayle H. PaudNo ratings yet
- Curso 6 UNIT 6 Calusac Level 6Document80 pagesCurso 6 UNIT 6 Calusac Level 6dessireechuy199310No ratings yet
- Tle Agriculture 9 3RD Quarter 3 and 4Document3 pagesTle Agriculture 9 3RD Quarter 3 and 4Mark Jim Torero100% (2)
- Research ProposalDocument5 pagesResearch Proposalapi-632214019No ratings yet
- Transformation GuideDocument16 pagesTransformation GuideToni-MarieNo ratings yet
- 2021 New Years Home Workout Guide: Tag @lillysabri On Instagram To Be Reposted & Featured On The Videos!Document2 pages2021 New Years Home Workout Guide: Tag @lillysabri On Instagram To Be Reposted & Featured On The Videos!Joyce SouzaNo ratings yet
- Mastering Handstands and Beyond by Lee WeilandDocument74 pagesMastering Handstands and Beyond by Lee WeilandRayen HamrouniNo ratings yet
- ROB 2020 Training Plan IntermediateDocument6 pagesROB 2020 Training Plan Intermediatewiligton oswaldo uribe rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Q3 Pe WorksheetDocument7 pagesQ3 Pe WorksheetApr CelestialNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology Labs StudentDocument2 pagesCSEC Biology Labs Studentxy4msvdy46No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Pe and Health 11 H.O.P.E. 3 N6VE0BER 3-6, 2018Document2 pagesLesson Plan in Pe and Health 11 H.O.P.E. 3 N6VE0BER 3-6, 2018Hearty Fajagutana RiveraNo ratings yet
- Benefits of SportDocument2 pagesBenefits of SportJacque Landrito ZurbitoNo ratings yet