Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Moment Distribution Beam
Uploaded by
MAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Moment Distribution Beam
Uploaded by
MAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMCopyright:
Available Formats
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Moment Distribution Method
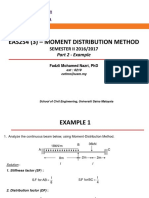
Example 1:
Analyse the continuous beam shown Bellow using the moment distribution method. Draw the
bending moment diagram and shear force diagram. Assume constant EI throughout the beam.
Solution
Step 1: The distribution factors at joint B are evaluated as follows.
Joint Member Relative Stiffness (k) Sum k Distribution Factor ( k k )
1
BA 0.47
6 17
B
3 1 3 48
BC = 0.53
4 4 16
Step 2: Fixed end moments.
WL2 (10 )( 6 )
2
FEM AB = = = 30kNm
12 12
WL2 (10 )( 6 )
2
FEM BA =− = = − 30kNm
12 12
WL2 ( 30 )( 4 )
2
FEM BC = = = 40kNm
12 12
WL2 ( 30 )( 4 )
2
FEM BA =− = = − 40kNm
12 12
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 1
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Step 3: Moment Distribution table.
Joint A B C
Member AB BA BC CB
DF 0 0.47 0.53 1
FEM +30 -30 +40 -40
Bal. - 4.7 -5.3 40
C.O. -2.35 20
Bal -9.4 -10.6
CO -4.7
Final 22.95 - 44.1 44.1 0
Bending moment diagram of the beam is drawn as shown below.
10(6)2 ( 22.96 + 44.1) 30(4) 2 ( 22.96 + 0 )
MC = − = 11.37 kNm, M D = − = 37.95kNm
8 2 8 2
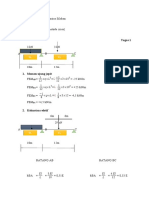
Step 4: shear force and bending moment diagram
Segment AB
Fy = 0 VAB + VBA − 60 = 0
M B = 0 22.96 − 6VAB + 180 − 44.1 = 0
VAB = 26.5 kN & VBA = 33.5 kN
Segment BC
Fy = 0 VBC + VCB − 120 = 0
M C = 0 44.1 − 4VBC + 240 = 0
VBC = 71 kN & VCB = 49 kN
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 2
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
The shear force of the beam is shown below.
Based on similar triangle x1 and x2 can be determined as follow.
x1 26.5 159
= 33.5 x1 = 159 − 26.5 x1 x1 = = 2.65 m
6 − x1 33.5 (33.5 + 26.5)
x2 49 196
= 71x2 = 196 − 49 x2 x2 = = 1.63m
4 − x2 71 (71 + 49 )
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 3
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Example 2:
Analyse the following beam using moment distribution method. Assume constant EI throughout
the beam.
Solution:
Step 1: Distribution Factor
K BC : K CD DFBC : DFCD
3 1 1 1 1
: :
4 6 8 1+1 1+1
1 1 0.5 : 0.5
8 : 8
1 1
Step 2: Fixed end moments
Assume counterclockwise is positive and clockwise is negative.
Segment BC
WL2 ( 20 )( 6 )
2
FEM BC = + = = +60 kNm
12 12
( 20 )( 6 ) = − 60 kNm
2
WL2
FEM CB =− =−
12 12
Segment CD
PL (120 )( 8 )
FEM CD = + = = +120 kNm
8 8
FEM DC =−
PL
=−
(120 )(8 ) = −120kNm
8 8
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 4
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Step 3: Moment Distribution Table
B C D
Member BA BC CB CD DC
D.F. 1 1 0.5 0.5 0
FEM –100 +60 –60 +120 – 120
+40 +20 0
FEM –100 +100 – 40 +120 – 120
D.M. 0 0 – 40 – 40 0
C.O. 0 0 – 20
D.F. 0 0 0
Final M –100 +100 – 80 +80 – 140
The bending moment can be drawn as shown below.
Step 3: Shear forces and shear force diagram
Segment AB
Fy = 0 VBA − 50 = 0
VBA = 50kN
Segment BC
Fy = 0 VBC + VCB − 120 = 0
20 62
M C = 0 60 − 6VBC + − 60 = 0
2
VBC = 60 kN , VCB = 60 kN
Segment CD
VCD = VDC = 60 kN
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 5
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Example 3:
Analyse the continuous beam shown in Figure below. The support B settles down by 10 mm. E=
200 GN/m2 and I=8000 cm4. The MI of span AB is I and of span BC is 2I.
Solution:
Step 1: Distribution Factor
K AB : K BC DFBA : DFBC
1 3 2 1 1.125
: :
6 4 8 1 + 1.125 1 + 1.125
1 3 8 9
: :
6 16 17 17
1 : 1.125
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 6
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Step 2: Fixed end moments
Segment AB
Fixed end moment due to load
Fixed end moment due to settelment at B
FEM AB = FEM 'AB +FEM ''AB
FEM 'AB :Fixed end moment due to load
FEM"AB :Fixed end moment due to settlment
WL2 (15 )( 6 )
2
FEM = '
AB = = 45 kNm ,
12 12
6 EI B 6 EI B 6 200 106 8000 10−8 0.01
FEM ''AB = − − = 2 = = 26.67 kNm
LAB LAB LAB 62
FEM AB = 45 +26.67 = 71.67 kNm
FEM BA = FEM 'BA +FEM ''BA
WL2 6 EI B
FEM BA = − + 2
12 LAB
FEM BA = − 45 +26.67 = −18.67 kNm
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 7
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Segment BC
Fixed end moment due to load one
Fixed end moment due to load two
Fixed end moment due to settelment at B
FEM BC = FEM 'BC +FEM ''BC FEM '''BC
Pab 2 Pa 2b 6 E ( 2 I ) B
FEM BC = + 2 −
L2BC LBC L2BC
80 2 62 80 32 5 6 200 10 ( 2 8000 ) 10 0.01
6 −8
= + −
82 82 82
=90 + 56.25 − 30 =116.25 kNm
FEM CB = FEM 'CB +FEM CB
''
FEM '''CB
Pa 2b Pab 2 6 E ( 2 I ) B
FEM CB = − − 2 −
L2BC LBC L2BC
80 22 6 80 3 52 6 200 10 ( 2 8000 ) 10 0.01
6 −8
=− − −
82 82 82
= − 30 − 93.75 − 30 = − 153.75 kNm
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 8
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Step 3: Moment Distribution Table
A B C
Member AB BA BC DC
D.F. 0 0.47 0.53 1
FEM +71.67 –18.67 116.25 – 153.75
D.M 0 -45.863 -51.717 153.75
C.O -22.93 0 76.875 0
D.M 0 -36.131 -40.741
C.O -18.07 0 0
D.M. 0 0 0
Final M +30.67 – 100.667 +100.667 0
Step 3: Shear force and moment diagram
Segment AB
Segment BC
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 9
Moment distribution Method- Beam Examples
Shear force and moment diagram
Prepared by Maged Mohammed (mm.almaged@gmail.com)
Structural Analysis III (BCE 3123) Page 10
You might also like
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- The Structure of Groups with a Quasiconvex Hierarchy: (AMS-209)From EverandThe Structure of Groups with a Quasiconvex Hierarchy: (AMS-209)No ratings yet
- Samabungan Topic 1 (Slope Deflection Method)Document24 pagesSamabungan Topic 1 (Slope Deflection Method)Azhar SabriNo ratings yet
- 9e. Re - Tambahan Contoh Soal - Slopde Deflection Dan Moment DistributionDocument11 pages9e. Re - Tambahan Contoh Soal - Slopde Deflection Dan Moment Distributionvincent.siswajiNo ratings yet
- ConstructionDocument13 pagesConstructionasoomlayNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 03 - Solution - Slope DeflectionDocument9 pagesTutorial - 03 - Solution - Slope DeflectionkikiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures 2 Chapter 4.1 - Analysis of Frames: No SideswayDocument11 pagesTheory of Structures 2 Chapter 4.1 - Analysis of Frames: No SideswayBone SnowNo ratings yet
- Rohini 49671255834Document8 pagesRohini 49671255834Bibi AyeeshaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Road Bridges: Prof. Nirjhar DhangDocument101 pagesReinforced Concrete Road Bridges: Prof. Nirjhar DhangAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Flexibility & Stiffness Matrix MethodDocument19 pagesFlexibility & Stiffness Matrix MethodKrishnaChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Problems On SFD & BMDDocument43 pagesProblems On SFD & BMDmal201182% (11)
- Penyelesaian Tugas I Analisis Struktur I: Soal No. 1Document6 pagesPenyelesaian Tugas I Analisis Struktur I: Soal No. 1lindaNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory 2Document12 pagesStructural Theory 2GinoOcampo100% (1)
- Analysis of Indeterminate MethodsDocument36 pagesAnalysis of Indeterminate MethodsRenu RathodNo ratings yet
- Contoh 1 Analisis Balok-Kontinu Berikut Dengan Metode Distribusi MomenDocument6 pagesContoh 1 Analisis Balok-Kontinu Berikut Dengan Metode Distribusi MomenGege LimbersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Analysis of Indeterminate Beam & Frames: Section 4.2Document48 pagesChapter 4: Analysis of Indeterminate Beam & Frames: Section 4.2MaheshNo ratings yet
- Stranalysis SD METHODDocument78 pagesStranalysis SD METHODNaveen RevannaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document38 pagesTopic 5LIK HENG LAUNo ratings yet
- Definition of A BeamDocument47 pagesDefinition of A BeamJack PresadoNo ratings yet
- PDF 4 Mechanics of DBDocument16 pagesPDF 4 Mechanics of DBRizette PaloganNo ratings yet
- Capid, Angelicka Joy M. Bsar-3G: FEB 17,2021 SM313 Activity No. 4Document2 pagesCapid, Angelicka Joy M. Bsar-3G: FEB 17,2021 SM313 Activity No. 4Angelicka Joy CapidNo ratings yet
- AIS VTUPulse - Com ModDocument10 pagesAIS VTUPulse - Com Modnaga rajNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Luctures - Part 4Document10 pagesStrength of Material Luctures - Part 4mohaiman566No ratings yet
- Tugas 1: XQXL X3X10 XQXL X3X10 XPXL X 3 X 12 - 4,5 KN/MDocument6 pagesTugas 1: XQXL X3X10 XQXL X3X10 XPXL X 3 X 12 - 4,5 KN/Mgilbert novensiusNo ratings yet
- BLD 401 - Module 4Document15 pagesBLD 401 - Module 4Ijadunola John BelovedNo ratings yet
- Analysis Sem 1 (08-09) AnswerDocument23 pagesAnalysis Sem 1 (08-09) Answersyah123100% (1)
- Eas254 MDM Part 2 - ExampleDocument8 pagesEas254 MDM Part 2 - ExampleNasrulNo ratings yet
- From The Load Diagram:: Click Here To Show or Hide The SolutionDocument19 pagesFrom The Load Diagram:: Click Here To Show or Hide The SolutionChibi Maou-ChanNo ratings yet
- 404 To 410Document22 pages404 To 410Muhammad Jhangeer KhanNo ratings yet
- E3Document300 pagesE3JuinNo ratings yet
- Basics of Stability Hand Calculation Vs FEM 1599738959Document11 pagesBasics of Stability Hand Calculation Vs FEM 1599738959Ahsan KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit2-HPS Structural Analysis IIDocument89 pagesUnit2-HPS Structural Analysis IISmr OnlyNo ratings yet
- Define Positions As Positive Downward From A Fixed Level. Constraint of CableDocument1 pageDefine Positions As Positive Downward From A Fixed Level. Constraint of CableLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection Method 3rd DamDocument19 pagesSlope Deflection Method 3rd DamAyad SlabyNo ratings yet
- Non-Sway Frame Example: SolutionDocument5 pagesNon-Sway Frame Example: SolutionRoif SamsulNo ratings yet
- Design of Cantilever Beam 1Document18 pagesDesign of Cantilever Beam 1Rogen Graciano DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution MethodDocument11 pagesMoment Distribution MethodKenneth Onwuegbuchu0% (1)
- Second Mid-Term Examination (23%) Vii Sem, 2018 - 19Document2 pagesSecond Mid-Term Examination (23%) Vii Sem, 2018 - 19Kartik ModiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 2013Document97 pagesChapter 4 2013Enes YavuzNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Problems and SolutioDocument22 pagesStructural Analysis Problems and SolutioAlexander Appiah OkoreNo ratings yet
- Segment ABDocument4 pagesSegment ABTonyang CruzNo ratings yet
- By Prof. A.B.Harwalkar PDA College of Engineering, Gulbarga: Chapter-4: Kani's MethodDocument34 pagesBy Prof. A.B.Harwalkar PDA College of Engineering, Gulbarga: Chapter-4: Kani's MethodmahakNo ratings yet
- Shear and Moment in Beams CH No 4Document48 pagesShear and Moment in Beams CH No 4Maqsood86% (7)
- Lecture 7Document27 pagesLecture 7Tayyab ZafarNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Problems and Solutio PDFDocument22 pagesStructural Analysis Problems and Solutio PDFjay balagotNo ratings yet
- Engr. A Umar CVE 512Document12 pagesEngr. A Umar CVE 512Chinonso OrjiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Shear and Moment in Beams Cest 412: Theory of Structures 1 Engr. S. OlarteDocument7 pages1 - Shear and Moment in Beams Cest 412: Theory of Structures 1 Engr. S. OlarteSam OlarteNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection MethodDocument6 pagesSlope Deflection MethodRaja RajanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 (Slope Deflection Method)Document38 pagesTopic 1 (Slope Deflection Method)koxxjemNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problems On SFD and BMDocument21 pagesNumerical Problems On SFD and BMbalajigandhirajan100% (4)
- Cve10004 L07Document30 pagesCve10004 L07Evena FungNo ratings yet
- Analisis Struktur C4Document47 pagesAnalisis Struktur C4Hazyema HarunNo ratings yet
- Statics 13esi Solutions-Manual Chapter 6Document152 pagesStatics 13esi Solutions-Manual Chapter 6Kavinesh AnanthanNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution MethodDocument7 pagesMoment Distribution MethodAnju KlNo ratings yet
- Theory-STATICALLY DETERMINATE BEAMDocument15 pagesTheory-STATICALLY DETERMINATE BEAMMariel De VeraNo ratings yet
- A B C B: 12.3. Example ProblemsDocument1 pageA B C B: 12.3. Example ProblemsmanmathkNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution MethodDocument5 pagesMoment Distribution MethodDezzalyn D. GabrielNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Computation of Electric and Magnetic Field Problems: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesFrom EverandAnalysis and Computation of Electric and Magnetic Field Problems: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Modular Forms and Special Cycles on Shimura Curves. (AM-161)From EverandModular Forms and Special Cycles on Shimura Curves. (AM-161)No ratings yet
- Comparing Carbon Emissions of Precast and Cast-In-Situ Construction MethodsDocument32 pagesComparing Carbon Emissions of Precast and Cast-In-Situ Construction MethodsMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- C-TRF H2 400x1200 TORSIONDocument2 pagesC-TRF H2 400x1200 TORSIONMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Chp.12.Elasticity and Plasticity 2019Document17 pagesChp.12.Elasticity and Plasticity 2019MAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Comparing Carbon Emissions of Precast and Cast-In-Situ Construction MethodsDocument32 pagesComparing Carbon Emissions of Precast and Cast-In-Situ Construction MethodsMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Precast StructureDocument11 pagesPrecast StructureMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Link Abaqus To FortranDocument1 pageLink Abaqus To FortranMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Modelling Structural Concrete - KotsovosDocument189 pagesFinite Element Modelling Structural Concrete - KotsovosAdolfo Gálvez Villacorta100% (2)
- Surface-Based Cohesive Behaviour: Damage InitiationDocument11 pagesSurface-Based Cohesive Behaviour: Damage InitiationMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Theory of Plasticity-FLRF00132Document1 pageTheory of Plasticity-FLRF00132MAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- 46910: PHD Course in Advanced Finite Element Simulations Using AbaqusDocument11 pages46910: PHD Course in Advanced Finite Element Simulations Using AbaqusMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Advance Solid MechanicsDocument156 pagesAdvance Solid MechanicsMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- 46910: PHD Course in Advanced Finite Element Simulations Using AbaqusDocument44 pages46910: PHD Course in Advanced Finite Element Simulations Using AbaqusMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- UMAT Subroutine Implementation: Michael Wenani NielsenDocument13 pagesUMAT Subroutine Implementation: Michael Wenani NielsenMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- En0175 02Document7 pagesEn0175 02Sanjay KabraNo ratings yet
- Continuum PlasticityDocument44 pagesContinuum PlasticityPrantik Adhar SamantaNo ratings yet
- Cohesive ElementDocument6 pagesCohesive ElementMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Surface-Based Cohesive Behaviour: Damage InitiationDocument11 pagesSurface-Based Cohesive Behaviour: Damage InitiationMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Generalized Hookes LawDocument14 pagesGeneralized Hookes LawtamizhanNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmeMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Ch.8. Plasticity: Continuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPCDocument88 pagesCh.8. Plasticity: Continuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPCMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Generalized Hookes LawDocument14 pagesGeneralized Hookes LawtamizhanNo ratings yet
- Zheng 2012Document10 pagesZheng 2012MAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Stress Trans Full PageDocument39 pagesStress Trans Full PageIfiokobong AkpanNo ratings yet
- Amendments PDFDocument1 pageAmendments PDFMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Lab 14 PDFDocument13 pagesLab 14 PDFMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Ch.8. Plasticity: Continuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPCDocument88 pagesCh.8. Plasticity: Continuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPCMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Reduced and Full Integaratiin StiffnessDocument1 pageReduced and Full Integaratiin StiffnessMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- UncertaintyDocument1 pageUncertaintyMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- M. Rades - Finite Element AnalysisDocument274 pagesM. Rades - Finite Element AnalysisMircea Rades100% (12)
- Test 4Document11 pagesTest 4MAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Sentence Structure TypesDocument44 pagesSentence Structure TypesGanak SahniNo ratings yet
- 3 C FamilyIImoot2015Document3 pages3 C FamilyIImoot2015ApoorvaChandraNo ratings yet
- PHD 2020 21 List of Shortlisted Candidates For InterviewDocument6 pagesPHD 2020 21 List of Shortlisted Candidates For InterviewAnkesh Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Wedding Salmo Ii PDFDocument2 pagesWedding Salmo Ii PDFJoel PotencianoNo ratings yet
- Complete Wedding With DJ Worksheets.4pgsDocument4 pagesComplete Wedding With DJ Worksheets.4pgsDanniNo ratings yet
- Girls, Gangs and Crime-The Profile of The Female OffenderDocument16 pagesGirls, Gangs and Crime-The Profile of The Female OffenderLiLiThBLaCkNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Final OkDocument43 pagesCHAPTER 1 Final Okroneldayo62No ratings yet
- Zambian Open University: School of Social Science and HumanitiesDocument9 pagesZambian Open University: School of Social Science and HumanitiesEvangelist Kabaso SydneyNo ratings yet
- 330A 2018docDocument20 pages330A 2018docDavid MendozaNo ratings yet
- Buad 306 HW 2Document4 pagesBuad 306 HW 2AustinNo ratings yet
- EDEL453 Spring2013 MelanieHADJES Unit 4 Economic Day1Document6 pagesEDEL453 Spring2013 MelanieHADJES Unit 4 Economic Day1Melanie HadjesNo ratings yet
- Jury Assessment FormDocument2 pagesJury Assessment FormMatias CANo ratings yet
- MarketingplanmiltonDocument4 pagesMarketingplanmiltonapi-385455349No ratings yet
- Evaluation of UNHCR's Leadership of The Global Protection Cluster and Field Protection Clusters, 2017Document101 pagesEvaluation of UNHCR's Leadership of The Global Protection Cluster and Field Protection Clusters, 2017andyfeatherstoneNo ratings yet
- Sagittarius The HeroDocument2 pagesSagittarius The HeroСтеди Транслейшънс0% (1)
- Applied Optimization For Wireless, Machine Learning, Big DataDocument1 pageApplied Optimization For Wireless, Machine Learning, Big DataSumaNo ratings yet
- 30 Feet: High Elf MediumDocument10 pages30 Feet: High Elf MediumAli Kaan (Uyau)No ratings yet
- Kutub PDFDocument12 pagesKutub PDFMs RawatNo ratings yet
- Powerful Hero Dpa Rtsal Protective DeityDocument50 pagesPowerful Hero Dpa Rtsal Protective DeityjinpaNo ratings yet
- President Uhuru Kenyatta's Speech During The Kenya@50 Celebrations at Uhuru Gardens, Nairobi On The Mid-Night of 12th December, 2013Document3 pagesPresident Uhuru Kenyatta's Speech During The Kenya@50 Celebrations at Uhuru Gardens, Nairobi On The Mid-Night of 12th December, 2013State House KenyaNo ratings yet
- Problems and Answer Key: - 1 (A) 70 (B) 97 (C) 127 (D) 159 (E) 729 2Document9 pagesProblems and Answer Key: - 1 (A) 70 (B) 97 (C) 127 (D) 159 (E) 729 2alice24134No ratings yet
- Jurnal Teori Pertukaran SosialDocument11 pagesJurnal Teori Pertukaran SosialRhama PutraNo ratings yet
- After The Banquet - Yukio MishimaDocument171 pagesAfter The Banquet - Yukio Mishimalazar10plusNo ratings yet
- Corrective Action Report (CAR) : Form1001 CAR-KMR - e Page 1 of 1 Revision: 6 Reference: Organizational Instruction 8.5.01Document1 pageCorrective Action Report (CAR) : Form1001 CAR-KMR - e Page 1 of 1 Revision: 6 Reference: Organizational Instruction 8.5.01JOECOOL67No ratings yet
- The Importance of Instructional MaterialDocument3 pagesThe Importance of Instructional MaterialJheramae SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Ieo Sample Paper Class-10Document2 pagesIeo Sample Paper Class-10jairusr100% (1)
- Upholding Malay Language Strengthening Command English LanguageDocument12 pagesUpholding Malay Language Strengthening Command English LanguagemucheliaNo ratings yet
- Activateroom HLDZDocument11 pagesActivateroom HLDZPerinorte100% (2)
- Tourism Signs & Symbols Published by World Tourism OrganizationDocument244 pagesTourism Signs & Symbols Published by World Tourism OrganizationJemima Pontino0% (1)
- Cold Calls Excerpt by Charles BenoitDocument25 pagesCold Calls Excerpt by Charles BenoitHoughton Mifflin HarcourtNo ratings yet