Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING BULLETS
Uploaded by
Jaezee RamosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING BULLETS
Uploaded by
Jaezee RamosCopyright:
Available Formats
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING BULLETS
Prepared by: Omar Brian Yu
March 24, 2007 (Saturday)
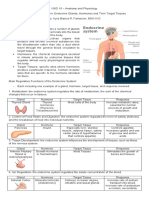
ENDOCRINE
IDENTIFICATION
1. It is a hormone that promotes development of mammary gland and secretion of milk.
2. Which hormone of thyroid gland that regulates serum Ca levels?
3. It is a drug used to inhibit release of stored thyroid hormone and retard hormone synthesis.
4. It is a drug used to inhibit synthesis of thyroid hormones
5. common side effect of number (4)
ENUMERATION
6.7. identify the two hormones secreted by Posterior Pituitary gland (neurophypophysis)
8.10 identify the three hormones secreted by the Adrenal Cortex
GASTROINTESTINAL
IDENTIFICATION
11. What is the best post-op position for patient (especially infants) who has Cleft palate?
12. What is the best post-op position for patient (especially infants) who has Cleft lip?
13. It is a type of peptic ulcer that is relieved by eating?
14. What is the most common microorganism that causes peptic ulcer?
ENUMERATION
15-20 What are the 3 enzymes secreted by the pancreas (exocrine cells) and its corresponding nutrients digested
ANSWERS
1. Prolactin
2. thyrocalcitonin
T3 (triiodothyronine) metabolism
T4 (Thyroxine) body heal production/ catabolism
3. SSKI/ KISS (Lugol’s Solution) – Saturated Solution of Potassium iodide
Nursing intervention: administer with a juice and straw
4. Thioamides: PTU (Propylthiouracil) and Tapazole (Methimazole)
5. Agranulocytosis/ neutropenia
6. ADH (antidiuretic Hormone/ Vasopressin) – retains water in the renal tubules
7. Oxytocin – uterine contraction
8. Salt Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
increase Na reabsorption and K loss through renal tubules
response to angiotensin II and ACTH
9. Sugar Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
Increase blood glucose by stimulating gluconeogenesis and lipolysis
Response to ACTH
10. Sex hormones androgens and estrogen
Development of certain secondary sex characteristics
Controlled by ACTH
11. prone
12. supine/ side-lying
13. duodenal ulcers – hypersecretion of acid
gastric ulcer – damaged mucosa
14. helicobacter pylori
15-20. amylase – starch
lipase – fats
trypsin – protein
GAMES:
Mouth (Oral Cavity)
*frenelum
Pharynx
Esophagus (gullet)
(Diaphragmatic hiatus)
(Esophagogastric junction)
Stomach
3 sections:
(1) *Fundus
(2) *Body/ corpus
(3) *Antrum/ pylorus
Small intestine
3 sections:
(1) Duodenum
Duodenal papilla – entry duct for bile (liver common hepatic duct gallbladder/cystic duct bile duct duodenal papilla)
and pancreatic enzymes (pancreas)
(2) Jejunum
(3) Ileum
(Cecum – junction) appendix – collects lymphoid tissue
*Ileocecal valve
Large intestine (colon)
3 sections:
(1) Ascending
(2) transverse
(3) descending
Sigmoid
Rectum
Anus
2 Sphincters:
internal sphincter - involuntary control
external sphincter - voluntary control
You might also like
- Group 9 (Module 22)Document24 pagesGroup 9 (Module 22)maba.zuniga.sjcNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Hormones and DiseasesDocument24 pagesThe Endocrine System: Hormones and DiseasesMd Nasir Uddin Mahmood100% (2)
- Pharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingDocument58 pagesPharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingRaveenmayiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands GuideDocument38 pagesEndocrine Glands GuideSajeev S Chadayamangalam SajNo ratings yet
- ICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)Document14 pagesICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)TAHMEENA ZAFARNo ratings yet
- 3rd BSC Endocrinology NotesDocument25 pages3rd BSC Endocrinology NotesPratyashaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesEndocrine SystemPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesAssignment For Endocrine SystemMoheeddin KababNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument124 pagesHormonesMr T KillworthNo ratings yet
- CPAC Nursing Course Syllabus for Competency Appraisal IIDocument10 pagesCPAC Nursing Course Syllabus for Competency Appraisal IIMary Janet Pinili100% (2)
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFDocument8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFSaurav SoniNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System (Notes)Document4 pagesThe Endocrine System (Notes)Wasim HakimNo ratings yet
- Endocrine system and Excretion wordDocument10 pagesEndocrine system and Excretion wordJoachim “Jayrz” MwambireNo ratings yet
- X ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFDocument9 pagesX ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemLen Len Ochinang OchinangNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReviewDocument9 pagesEndocrine ReviewSpencer ThomasNo ratings yet
- NURS 3103 GI Pathophysiology NotesDocument4 pagesNURS 3103 GI Pathophysiology NotesjuliafinnNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI EndocrineDocument8 pagesChapter VI EndocrineTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- BIOS5130 Week 9 Slides W - o AnswersDocument47 pagesBIOS5130 Week 9 Slides W - o AnswersOkikiola JohnsonNo ratings yet
- My FinalDocument33 pagesMy FinalBhoj RajNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument8 pagesClinical Chemistryleizej29No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Endocrine and Metabolic SystemDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of The Endocrine and Metabolic Systemcoy008No ratings yet
- Endocrine Case StudyDocument3 pagesEndocrine Case StudyJenny ViNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 085347 PDFDocument30 pagesEndocrine System 085347 PDFClyde ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hormon ReproDocument36 pagesHormon Reproalvinrinaldi1101No ratings yet
- Endo Pathology Lect1Document11 pagesEndo Pathology Lect1ALi AL-kwafiNo ratings yet
- OT Endocrine SystemDocument53 pagesOT Endocrine SystemJei CorbesNo ratings yet
- Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Susannah Nelson Longenbaker Solutions ManualDocument4 pagesMaders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Susannah Nelson Longenbaker Solutions Manualadelaideoanhnqr1v100% (21)
- Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesClass 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine SystemDXN LUDHIANANo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Review NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System Review Notesjeshema100% (1)
- Ch45 EndocrineSystemDocument3 pagesCh45 EndocrineSystemCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine SystemKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Chronic Constipation PharmacologyDocument37 pagesChronic Constipation PharmacologyBishal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- SLP Hypothalamus and Pituitary IIDocument6 pagesSLP Hypothalamus and Pituitary IIMuhd ArsyadNo ratings yet
- Physiology of the Pancreas (Lecture 6Document4 pagesPhysiology of the Pancreas (Lecture 6Ketan PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit IXDocument10 pagesUnit IXPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Short Review Original PDFDocument13 pagesEndocrine System Short Review Original PDFBijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Hormone Regulation & Endocrine StructuresDocument28 pagesHormone Regulation & Endocrine StructuresFujoshiNo ratings yet
- Main GIT Processes and GALT FunctionDocument5 pagesMain GIT Processes and GALT FunctionantoonieNo ratings yet
- Ms - Anu Sebastian: B.Pharm M.Pharm Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Nirmala College of Pharmacy Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam, KeralaDocument18 pagesMs - Anu Sebastian: B.Pharm M.Pharm Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Nirmala College of Pharmacy Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam, KeralaZzeba KhanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNo ratings yet
- GROUP 11 Problem 1-2Document85 pagesGROUP 11 Problem 1-2Shitta InayahNo ratings yet
- Hema, Onco, Cardiology Review NotesDocument9 pagesHema, Onco, Cardiology Review Notesjeshema100% (1)
- Insuline HormoneDocument36 pagesInsuline HormoneF ParikhNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PharmaDocument10 pagesReviewer in Pharmark24zsyfmxNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesEndocrine Gland - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediakbhattacNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Gi AnaphysioDocument13 pagesMedsurg Gi AnaphysioNermeen Mudsol100% (1)
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Document8 pagesOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Jhason John J. CabigonNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument24 pagesPancreasJeanette RiosNo ratings yet
- SISTIM PENCERNAKANDocument30 pagesSISTIM PENCERNAKANDesi Dwi CahyantiNo ratings yet
- Biology Endocrine System Notes Compiled by Srikrshna p1 PDFDocument8 pagesBiology Endocrine System Notes Compiled by Srikrshna p1 PDFKazi AslamNo ratings yet
- Development Team: Zoology Animal Physiology Gastrointestinal HormonesDocument36 pagesDevelopment Team: Zoology Animal Physiology Gastrointestinal HormonesIrfan Pathan KakarNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics-01 AssignmentDocument14 pagesBiopharmaceutics-01 AssignmentRA TanvirNo ratings yet
- E. A. D. A.: Gastrointestinal SystemDocument9 pagesE. A. D. A.: Gastrointestinal SystemDominic ReambonanzaNo ratings yet
- Progesterone and Estrogen Thyroid GlandDocument3 pagesProgesterone and Estrogen Thyroid GlandReymark VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument34 pagesEndocrineBahareh SanabakhshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. The Endocrine System: Short QuestionsDocument24 pagesChapter 9. The Endocrine System: Short QuestionsParardha DharNo ratings yet
- Unit Qualification and Learning OutcomesDocument2 pagesUnit Qualification and Learning OutcomesJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- 1.data Gathering InstrumentsDocument2 pages1.data Gathering InstrumentsJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- MOI-TemplateDocument3 pagesMOI-TemplateJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Plan Session SampleDocument3 pagesPlan Session SampleJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Waste Segregation PlanDocument7 pagesWaste Segregation PlanJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- How To Use This Document: About The Information SheetDocument4 pagesHow To Use This Document: About The Information SheetMien TiangcoNo ratings yet
- High Risk Pediatric Conditions and DisordersDocument80 pagesHigh Risk Pediatric Conditions and DisordersJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Pedia Penta NotesDocument73 pagesPedia Penta Notesstuffednurse100% (1)
- Utilize Electronic Media 2 2012noDocument151 pagesUtilize Electronic Media 2 2012noRam-tech Jackolito FernandezNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument21 pagesPediatricsJo Anne75% (8)
- 03 (1) .21.07 MSDocument1 page03 (1) .21.07 MSJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- How to Use Performance Criteria ChecklistDocument2 pagesHow to Use Performance Criteria ChecklistJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument2 pagesCHNJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing BulletsDocument2 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing BulletsJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Health IndicesDocument27 pagesHealth IndicesJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Bullets: By: Omar Brian YuDocument1 pageMedical-Surgical Bullets: By: Omar Brian YuJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- GenitoUrinary Tract PresentationDocument60 pagesGenitoUrinary Tract PresentationJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nuirsing Bullets: By: Omar Brian YuDocument1 pageMedical-Surgical Nuirsing Bullets: By: Omar Brian YuJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Bullets: By: Omar Brian YuDocument1 pageCommunity Health Nursing Bullets: By: Omar Brian YuJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Management GuideDocument8 pagesPerioperative Management GuideJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Bullets: By: Omar Brian YuDocument1 pageCommunity Health Nursing Bullets: By: Omar Brian YuJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Childcare 2 - Communicable DiseasesDocument31 pagesChildcare 2 - Communicable DiseasesJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Health IndicesDocument27 pagesHealth IndicesJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- GenitoUrinary Tract PresentationDocument60 pagesGenitoUrinary Tract PresentationJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Immediate Care of The Newborn and Newborn AssessmentDocument105 pagesImmediate Care of The Newborn and Newborn AssessmentAngela BautistaNo ratings yet
- Complete Communicable Disease TrainingDocument7 pagesComplete Communicable Disease TrainingJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Professional Regulation Commission Board of Nursing Nursing Practice 1 (One)Document7 pagesProfessional Regulation Commission Board of Nursing Nursing Practice 1 (One)Jaezee Ramos100% (1)
- Communicable Diseases QuizDocument2 pagesCommunicable Diseases QuizJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Anthropometric MeasurementsDocument18 pagesAnthropometric MeasurementsJaezee Ramos50% (2)
- Endocrine System CH 9Document57 pagesEndocrine System CH 9Gibraluve Barbado PonceNo ratings yet
- Eplerenone As A Treatment For Resistant Hypertension in PregnancyDocument4 pagesEplerenone As A Treatment For Resistant Hypertension in PregnancyLabontu IustinaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antithyroid PharmaDocument31 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid PharmaxaviermargaridaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Assessment.Document30 pagesEndocrine System Assessment.ramoli1988100% (2)
- Chemical Coordination and Integration by - Dr. Sunita SaxenaDocument66 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration by - Dr. Sunita SaxenaDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Mst-Case Management - (3) p2nm, 2023Document51 pagesMst-Case Management - (3) p2nm, 2023metria riza sativaNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismfinalpptDocument91 pagesHypothyroidismfinalpptswathi bsNo ratings yet
- Negative FeedbackDocument2 pagesNegative FeedbackCharlene ElioNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY FFGDocument32 pagesDRUG STUDY FFGElenor May Chantal MessakaraengNo ratings yet
- ANP 120 TEST 2 KEY POINTSDocument22 pagesANP 120 TEST 2 KEY POINTSJoseph A MwitupaNo ratings yet
- 11 Foods That Can Affect Your Thyroid HealthDocument6 pages11 Foods That Can Affect Your Thyroid HealthSchumarcinaNo ratings yet
- EANM Practice Guideline SNMMI Procedure Standard For RAIU and Thyroid ScintigraphyDocument12 pagesEANM Practice Guideline SNMMI Procedure Standard For RAIU and Thyroid ScintigraphyArif SatriaNo ratings yet
- R3Document1 pageR3Asif ButtNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Thermoregulation in ELBW InfantsDocument6 pagesNeonatal Thermoregulation in ELBW InfantsHaikal Ambri RosleNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease: Presentation By: Pimundu Vicent Audo Ritah Tutor: Dr. Fualal JaneDocument41 pagesThyroid Disease: Presentation By: Pimundu Vicent Audo Ritah Tutor: Dr. Fualal JaneEsther AumaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Guidelines For The Management of Thyroid Storm From Japan Thyroid AssociationDocument40 pages2016 Guidelines For The Management of Thyroid Storm From Japan Thyroid AssociationMartha RosanaNo ratings yet
- Iodine Summaryupdate 2016Document26 pagesIodine Summaryupdate 2016FrankNo ratings yet
- ThyroidectomyDocument5 pagesThyroidectomyJennelyn LumbreNo ratings yet
- Lab 6td5tbyyvtc1920 RevDocument15 pagesLab 6td5tbyyvtc1920 RevrinidinanNo ratings yet
- First Vita Plus Healing Testimony - LelayDocument16 pagesFirst Vita Plus Healing Testimony - LelayArnulfo Yu LanibaNo ratings yet
- Uman Hysiology: Endocrine Control of Growth and MetabolismDocument24 pagesUman Hysiology: Endocrine Control of Growth and Metabolismpanairina03026273No ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Problem Set SolutionsDocument15 pagesWork, Energy and Power Problem Set Solutionsdeomonhunter1No ratings yet
- Izabella WentzDocument20 pagesIzabella Wentzharmziie100% (3)
- Lange Endocrine Physiology Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument19 pagesLange Endocrine Physiology Self-Assessment QuestionsDimsy Flora KpaiNo ratings yet
- Thresiakutty PappuDocument2 pagesThresiakutty PappuAnson vargheseNo ratings yet
- Activating AutophagyDocument59 pagesActivating Autophagynomedacerniauskaite6600100% (19)
- Diagnostic TestDocument57 pagesDiagnostic TestPam ArauneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Abbreviations - Flash CardsDocument78 pagesNursing Abbreviations - Flash Cardsɹǝʍdןnos100% (4)
- Endocrine Glands and Their FunctionsDocument31 pagesEndocrine Glands and Their FunctionsAfrina Asmi MINo ratings yet