Professional Documents
Culture Documents
William Perry David Kolb Benjamin Bloom Richard Paul and Linda Elder
William Perry David Kolb Benjamin Bloom Richard Paul and Linda Elder
Uploaded by
Robert Aquino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagetaxonomy
Original Title
Reimers Taxonomy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttaxonomy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageWilliam Perry David Kolb Benjamin Bloom Richard Paul and Linda Elder
William Perry David Kolb Benjamin Bloom Richard Paul and Linda Elder
Uploaded by
Robert Aquinotaxonomy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
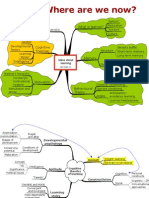
Taxonomy of [some] Critical Thinking Theories
Learning Styles/Bio-Neurological Processes of Self (in Culture &
Models Developmental Categories of Cognitive Skills
Modes of Thought Society)
William Perry David Kolb Benjamin Bloom Richard Paul and Linda Elder
o Dualism o Concrete Experience o Knowledge o Information and belief-generating
o Multiplism o Observation and Reflection o Comprehension and processing skills
o Relativism o Abstract Concepts o Application o Habits of intellectual commitment
o Commitment in Relativism o Testing o Analysis guiding behavior
o Synthesis
o Evaluation
Belenky et. al. James Zull Diane Halpern Donald Schön
o Silence o Sensory cortex o Retrieval of Knowledge o Reflective practice
o Received Knowledge o Back integrative cortex o Drawing Conclusions § Knowing-in-action
o Subjective Knowledge o Front integrative cortex o Argument Analysis § Reflection-in-action
o Procedural Knowledge o Motor cortex o Understanding Probabilities § Reflection-on-reflection-in-
o Constructed Knowledge o Decision Making action
o Problem Solving o Predicament of learning
o Hypothesis Testing § Self education
o Creative Thinking § Doing before understanding
§ Risk
Susan Wolcott Jerome Bruner Dee Fink Stephen Brookfield
o Confused Fact Finder o Paradigmatic (scientific, logical) o Significant Learning o Productive, positive, lived
o Biased Jumper construction of reality § Learning how to Learn o Process
o Perpetual Analyzer o Narrative construction of reality § Foundational Knowledge o Context-specific
o Pragmatic Performer § Enactive § Application o Emotive and rational
o Strategic Revisioner § Iconic § Integration
§ Symbolic § Human Dimension Critical reflection
• § Caring o Challenging assumptions
• § Contextual awareness
o Imagining/exploring alternatives
§ Reflective skepticism
Giants Piaget/Vygotsky/Dewey Maslow/Dewey/Late Bruner
What holds them together = Compiled by Tine Reimers, University at Albany
1) Judgment of evidence leading to new behavior (narrative with consequences) creimers@albany.edu
2) Self-appropriation of knowledge that makes #1 possible (attitude)
You might also like
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasNo ratings yet
- Autism: The PositivesDocument1 pageAutism: The PositivesHarriet CannonNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, Kohlberg Theories: Developmental PhenomenaDocument3 pagesComparison of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, Kohlberg Theories: Developmental PhenomenaNorashia MacabandingNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument402 pagesPhilosophythvstm95No ratings yet
- Beyond Imagination: Spiritual Interpretation of NumbersDocument172 pagesBeyond Imagination: Spiritual Interpretation of NumbersWayne Hartman100% (2)
- Feist Theories of Personality Chapter 1Document2 pagesFeist Theories of Personality Chapter 1Rashia LubuguinNo ratings yet
- Language, Memory, and Cognition in Infancy and Early ChildhoodFrom EverandLanguage, Memory, and Cognition in Infancy and Early ChildhoodNo ratings yet
- Kalmar PDFDocument8 pagesKalmar PDFSimion PetruNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design 1 - Lecture 13 - Design SynthesisDocument22 pagesArchitectural Design 1 - Lecture 13 - Design SynthesisAL HAYUDININo ratings yet
- Intro To AdlerDocument15 pagesIntro To AdlerRae DoroteoNo ratings yet
- We Don'T See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are.Document27 pagesWe Don'T See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are.shankyshine0072861No ratings yet
- Perception: " We Don't See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are."Document27 pagesPerception: " We Don't See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are."Viji Venky100% (1)
- We Don'T See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are.Document50 pagesWe Don'T See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are.nalleconfidentialNo ratings yet
- Psychology For BSC GNM Chapter 6Document30 pagesPsychology For BSC GNM Chapter 6Athena MagistrateNo ratings yet
- Topic Two: Knowledge Representation, Reasoning and InferenceDocument72 pagesTopic Two: Knowledge Representation, Reasoning and InferenceVisnu ManimaranNo ratings yet
- L01 Human BeDocument3 pagesL01 Human Bemelodyleung999No ratings yet
- Piaget 2023Document16 pagesPiaget 2023shiv mahatoNo ratings yet
- GSI - PerceptionDocument21 pagesGSI - PerceptionMallika NawalNo ratings yet
- ES 102-Act-Domains-of-Learning-Odi, John Harold T.-BEED 2ADocument2 pagesES 102-Act-Domains-of-Learning-Odi, John Harold T.-BEED 2AJoseph StalinNo ratings yet
- Psych Assessment Trans Lec1Document3 pagesPsych Assessment Trans Lec1ALYANAH DALE MAGNONo ratings yet
- Cognitive FormulationDocument24 pagesCognitive FormulationLeidy PinillaNo ratings yet
- IBO - Session 3 4 - Perception and AttributionDocument9 pagesIBO - Session 3 4 - Perception and AttributionAshwani RathourNo ratings yet
- Cognition FlashcardsDocument92 pagesCognition FlashcardsLoraNo ratings yet
- Cognition Through The Lifespan Cognitive Functions: Individual-Developmental Stage - EnvironmentDocument15 pagesCognition Through The Lifespan Cognitive Functions: Individual-Developmental Stage - EnvironmentGayathri sundarajanNo ratings yet
- Psychology Lecture 9 Intelligence 2022Document6 pagesPsychology Lecture 9 Intelligence 2022Hannah Florenz TanNo ratings yet
- Teaching The Student in Front of YouDocument124 pagesTeaching The Student in Front of YouArianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- Khan 2017 - PersonalityDocument6 pagesKhan 2017 - PersonalityfraNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Cognitive Stage TheoryDocument8 pagesPiaget's Cognitive Stage TheoryTamamaNo ratings yet
- Perception PersonalityDocument62 pagesPerception PersonalityGagan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Psychological Foundation Sociological FoundationDocument3 pagesPsychological Foundation Sociological FoundationVallada, FebroseNo ratings yet
- Perdev PTDocument3 pagesPerdev PTCamylia CocjinNo ratings yet
- Development Psychology - Chapter 5 (Santrock)Document88 pagesDevelopment Psychology - Chapter 5 (Santrock)Shaine C.No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson Planjega84mNo ratings yet
- FP Hand OutDocument2 pagesFP Hand OutKatherine DahangNo ratings yet
- Module 2-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesModule 2-WPS OfficeRosalie A. GuiananNo ratings yet
- Module 3. Early ChildhoodDocument7 pagesModule 3. Early ChildhoodMicaNo ratings yet
- COGPSYCH-MT ReviewerDocument8 pagesCOGPSYCH-MT ReviewerTrixia LoveNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 119 LEC 1 - Requisites - For - Successful - L - M PDFDocument4 pagesWEEK 3 119 LEC 1 - Requisites - For - Successful - L - M PDFclaire yowsNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document26 pagesModule 2Ana Andreea HorbencoNo ratings yet
- 1-2 因果表述学习技术进展Document34 pages1-2 因果表述学习技术进展Ke TianNo ratings yet
- DEVPSYCH 5 - Cognitive Development During The First 3 YearsDocument3 pagesDEVPSYCH 5 - Cognitive Development During The First 3 YearsRedgie G. GabaneNo ratings yet
- Cognitive PsychologyDocument19 pagesCognitive PsychologyyoucanseemarizflyNo ratings yet
- We Don'T See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are.Document42 pagesWe Don'T See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are.RiyaNo ratings yet
- Legal Technique Midterm NotesDocument7 pagesLegal Technique Midterm NotesChristia Sandee SuanNo ratings yet
- Perceptionpersonality 120110025836 Phpapp02Document32 pagesPerceptionpersonality 120110025836 Phpapp02harshadampgdmNo ratings yet
- L02 - Knowledge-Rep - Part 1Document47 pagesL02 - Knowledge-Rep - Part 1jl289173No ratings yet
- The Scientific Investigation of Phenomena: ResearchDocument3 pagesThe Scientific Investigation of Phenomena: ResearchlibbyNo ratings yet
- PerceptionDocument25 pagesPerceptionadidas14388% (16)
- 0rganizational Learning: Tuesday Class Week 6 Ph.D. Jesper DoeppingDocument14 pages0rganizational Learning: Tuesday Class Week 6 Ph.D. Jesper DoeppingaunpunnNo ratings yet
- Note Ebpmog - Organization Behavior - Chapter 5Document12 pagesNote Ebpmog - Organization Behavior - Chapter 5fikri bistami yahyaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Piaget's Developmental StagesDocument1 pageSummary of Piaget's Developmental StagesAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- CHUA - PHILO 1 - Concept MapDocument1 pageCHUA - PHILO 1 - Concept MapElinette ChuaNo ratings yet
- SHDH 2039 Topic 3 - Part - ADocument22 pagesSHDH 2039 Topic 3 - Part - AdaisysintszwaiNo ratings yet
- Biological and Environmental Factors.": Perdev'T ExamDocument1 pageBiological and Environmental Factors.": Perdev'T ExamMikka RoqueNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology Prelim and Finals Reviewer - CompressDocument31 pagesDevelopmental Psychology Prelim and Finals Reviewer - CompressGlory Mae ProllesNo ratings yet
- El 115 Midterm Module 2Document18 pagesEl 115 Midterm Module 2Ella Marie Gamayon PoloNo ratings yet
- 4286-1680525111712-HND MSCP W15 Reflection Performance of ProjectDocument15 pages4286-1680525111712-HND MSCP W15 Reflection Performance of ProjectDulanja OmeshNo ratings yet
- CB W3 Consumers KnowledgeDocument38 pagesCB W3 Consumers Knowledgefajar dugi prasetyaNo ratings yet
- Gestalt 26 Feb 07Document22 pagesGestalt 26 Feb 07api-3732338100% (1)
- Materi Toefl 01 JanDocument60 pagesMateri Toefl 01 JanfaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7.Document6 pagesLesson 7.Janna Mae L. DeliguerNo ratings yet
- Negotiation TopicsDocument3 pagesNegotiation TopicsKhushi BhansaliNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Design User Guide: Cadds 5i Release 12Document528 pagesSheet Metal Design User Guide: Cadds 5i Release 12kadam_nitsi2046No ratings yet
- Gas TurbinesDocument11 pagesGas Turbinesmustafa benzer67% (3)
- Research Methodology AssignmentDocument15 pagesResearch Methodology AssignmentSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument73 pagesEnglishaaaber6No ratings yet
- Raft Modeling in Etabs - Foundation Design - Structural Engineering Forum of Pakistan PDFDocument1 pageRaft Modeling in Etabs - Foundation Design - Structural Engineering Forum of Pakistan PDFKenny Manuel Vettoor100% (1)
- 1017U757-2002056-MM150 - 00 Mobile Motorized Transfer PumpDocument257 pages1017U757-2002056-MM150 - 00 Mobile Motorized Transfer PumpFRANCISCONo ratings yet
- Cat 02 13 2009Document51 pagesCat 02 13 2009Freddy YánezNo ratings yet
- BoeingDocument27 pagesBoeingpotdarmanviNo ratings yet
- BCC MicroprojectDocument25 pagesBCC Microprojectvedantdeshmukh950No ratings yet
- Analog IDocument48 pagesAnalog Isheeron20No ratings yet
- GEA1000 Tutorial ClementDocument3 pagesGEA1000 Tutorial ClementClement LimNo ratings yet
- Quadcopter Body Frame Model and Analysis: ArticleDocument5 pagesQuadcopter Body Frame Model and Analysis: ArticleDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Briefcase BrowserDocument64 pagesBriefcase BrowserAmol KolheNo ratings yet
- Central Virginia Training Center Site Redevelopment PlanDocument216 pagesCentral Virginia Training Center Site Redevelopment PlanDavid CrossNo ratings yet
- Manual HtpicDocument390 pagesManual Htpicioana ilieNo ratings yet
- Peter Drucker Entrepreneurship Summary Ch-1 and CH - 2Document3 pagesPeter Drucker Entrepreneurship Summary Ch-1 and CH - 2prajwalkhanal0% (1)
- Class List Be I Year I Semeater 2013-14Document94 pagesClass List Be I Year I Semeater 2013-14Ajayvidyanand SharmaNo ratings yet
- Teneo, Sinius: Maintenance LogDocument14 pagesTeneo, Sinius: Maintenance LogAwdan MailNo ratings yet
- History of The CellphoneDocument16 pagesHistory of The Cellphonedzireyes94No ratings yet
- Family Health HistoryDocument5 pagesFamily Health Historyapi-512912034No ratings yet
- 2 - Extensions of The Parallel Design - Factorial and Large Simple DesignsDocument10 pages2 - Extensions of The Parallel Design - Factorial and Large Simple DesignsNataliaNo ratings yet
- Gold First Unit 2Document10 pagesGold First Unit 2SamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Physics Grade 8Document2 pagesLesson Plan in Physics Grade 8Camille Derecho83% (6)
- MODULE 1 UNIT 1 SUPPLEMENT - Schumacher - The Historian's Task in The PhilippinescDocument18 pagesMODULE 1 UNIT 1 SUPPLEMENT - Schumacher - The Historian's Task in The PhilippinescFEBEE ANGAGKANo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Crisis CommunicationDocument28 pagesFundamentals of Crisis CommunicationMinh Cong NGUYENNo ratings yet