Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sperm Release Pathway
Sperm Release Pathway
Uploaded by
Octerley Love BlancoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sperm Release Pathway
Sperm Release Pathway
Uploaded by
Octerley Love BlancoCopyright:
Available Formats
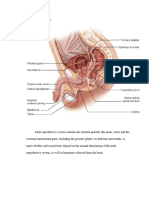
Sperm release pathway
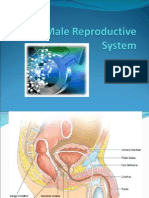
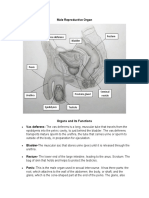
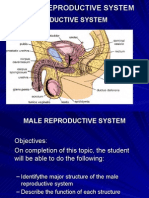
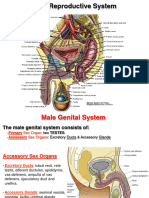
The key male reproductive organs include the testes, epididymis, urethra, vas deferens,
prostate gland, seminal vesicle, and penis.
The testes are composed of coiled structures called seminiferous tubules, which are the
sites of sperm production. The structure on top of the seminiferous tubules in the testes
is the epididymis. The sperm migrate from of the seminiferous tubules to the
epididymis. Within the epididymis, the sperm mature while they are stored in this
structure.
The ejaculation process begins as the penis fills with blood and becomes erect. With
sufficient stimulation, mature sperm travel from the epididymis through the vas
deferens, a muscular tube, which propels sperm forward through smooth muscle
contractions. The sperm arrive first at the ampulla, where secretions from the seminal
vesicle are added.
From the ampulla, seminal fluid is propelled forward through the ejaculatory ducts
toward the urethra, passing first by the prostate gland, where a milky fluid is added to
form semen. Finally, the semen is ejaculated through the far end of the urethra.
You might also like
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument49 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRinkish Dalliah50% (2)
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument47 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument14 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemmarkkkkkkkheeessNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemkcNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesReproductive SystembokkNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 WPS Office1Document11 pagesPresentation1 WPS Office1Maryjenica DaligdigNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageHuman Reproductive SystemMjlen B. ReyesNo ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Science Presentation: By: Beam BorachoDocument33 pagesScience Presentation: By: Beam BorachoPEMAR ACOSTANo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument6 pagesHistologyarezoo bahramiNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewDocument3 pagesScience ReviewAinieNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document158 pagesWeek 4Qossay WaxNo ratings yet
- The Path Sperm-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageThe Path Sperm-WPS OfficeBryan Reufrir CortezanoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemSejuta AdaNo ratings yet
- 3Q W1 Reproductive Systems 1Document41 pages3Q W1 Reproductive Systems 1chikmxzcNo ratings yet
- Human Male Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesHuman Male Reproductive Systemmilviepaz100% (1)
- Parenthood and Family RelationsDocument2 pagesParenthood and Family RelationsSakshi TyagiNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemHoney MalabuteNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Basic Concept of DRRRDocument44 pages3.1 Basic Concept of DRRRCharmine MendezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesReproductive SystemMatt MasilonganNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesThe Reproductive SystemKem Marian MauricioNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemEunimae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument71 pagesReproductive SystemDEBORAH JUBILEE MABAYAGNo ratings yet
- Oleza Cannery S. Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesOleza Cannery S. Reproductive SystemCannery OlezaNo ratings yet
- Male Repro SystemDocument21 pagesMale Repro Systemdoreen03No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemAbbasi KahumaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Science 10Document22 pagesReproductive Science 10palicpicbea50No ratings yet
- Ovaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeDocument2 pagesOvaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeCyril AlngogNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive SystemRiaz siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument70 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDaniel HikaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive ReportDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive ReportLeilla Mae PataNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System 1Document56 pagesReproductive System 1zekesergmanuedenina08No ratings yet
- Bio MalesDocument2 pagesBio MalesTrann TtuyetNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive OrganDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive OrganLawren Ira LanonNo ratings yet
- 4 Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument26 pages4 Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentEGUIA, MARY SHENIETH M.No ratings yet
- Biomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument29 pagesBiomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionBrian CastañedaNo ratings yet
- 295 Overview of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pages295 Overview of The Male Reproductive SystemDesvira PoetriNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Anatomy - KWDocument26 pagesMale Reproductive Anatomy - KWabyannaybaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 M&Freprod 2304Document55 pagesChapter 26 M&Freprod 2304sairahhannahNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument58 pagesMale Reproductive Systemtropakoto5No ratings yet
- 5a. Male & Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument119 pages5a. Male & Female Reproductive AnatomyvictorNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument71 pagesMale Reproductive Systemאילן גרינולדNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive System Includes The PenisDocument3 pagesThe Male Reproductive System Includes The PenisLYRA GUEVARRANo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument45 pagesMale Reproductive SystemAl AmosNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 8Document7 pagesReproductive System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 8Agustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Developmental Aspect of Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Aspect of Reproductive SystemFrancis ArceoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document2 pagesQuiz 3sitti marwa baraNo ratings yet
- Development of The Urogenital System: Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesDevelopment of The Urogenital System: Learning ObjectivesKingNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument5 pagesReproductiveMaryrose MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Sem4 2008-2Document16 pagesKuliah Sem4 2008-2cathencloxNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System 2023-2024Document16 pagesMale Reproductive System 2023-2024michaelsoncole410No ratings yet
- Task 4Document20 pagesTask 4maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Male Reproductive Systemmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemaynNo ratings yet
- Bio InfoDocument5 pagesBio InfoSoham MultaniNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesParts of The Male Reproductive SystemEris MolenoNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesThe Reproductive SystemAries BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapt28 LectureDocument44 pagesChapt28 Lecturemelissa_sunNo ratings yet
- Rerproduction NotesDocument16 pagesRerproduction NotesSheryl Lou AngelesNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Average 4th GradingDocument11 pagesGrade 10 Average 4th GradingOcterley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School Id School YearDocument18 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School Id School YearOcterley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Letter of Intent 2021Document1 pageLetter of Intent 2021Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document8 pagesGrade 8Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9Document6 pagesGrade 9Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10Document6 pagesGrade 10Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- G8Document2 pagesG8Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Saint Michael Institute of Leadership and Excellence Centro 02, Sanchez Mira, Cagayan Second Quarter 2 Periodical Test Science 9Document4 pagesSaint Michael Institute of Leadership and Excellence Centro 02, Sanchez Mira, Cagayan Second Quarter 2 Periodical Test Science 9Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Saint Michael Institute of Leadership and Excellence Centro 02, Sanchez Mira, Cagayan Second Quarter 2 Periodical Test Science 10Document7 pagesSaint Michael Institute of Leadership and Excellence Centro 02, Sanchez Mira, Cagayan Second Quarter 2 Periodical Test Science 10Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Saint Michael Institute of Leadership and Excellence Centro 02, Sanchez Mira, Cagayan Second Quarter 2 Periodical Test Science 9Document4 pagesSaint Michael Institute of Leadership and Excellence Centro 02, Sanchez Mira, Cagayan Second Quarter 2 Periodical Test Science 9Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Sci10 - 9Document4 pagesSci10 - 9Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- A Molecule Which Breaks and Gives Off Hydrogen and Oxygen. Water Carbon Dioxide Air Sodium ChlorideDocument3 pagesA Molecule Which Breaks and Gives Off Hydrogen and Oxygen. Water Carbon Dioxide Air Sodium ChlorideOcterley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Q2 Grade 10Document42 pagesQ2 Grade 10Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet
- Sci 8Document3 pagesSci 8Octerley Love BlancoNo ratings yet