Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscle Cell Comparison PDF
Muscle Cell Comparison PDF
Uploaded by
Rio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
muscle cell comparison.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageMuscle Cell Comparison PDF
Muscle Cell Comparison PDF
Uploaded by
RioCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
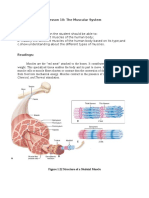
Comparative Physiology
of
Skeletal, Smooth & Cardiac Muscle Fibers
Ziser, 2001
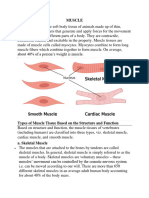
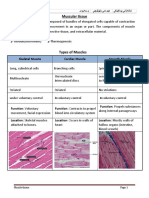
Striated Muscle Cells Smooth Muscle Cells Cardiac Muscle Cells
Voluntary Involuntary Involuntary
Attached to bones or skin Line walls of most internal organs Found only in the Heart
Very long, cylindrical, multnucleate, Single, tapering, cells with Branching chains of cells connected
cells a single nucleus by porous intercalated discs, with single
nucleus and striations
Striated: packed with orderly arrangement Not Striated: Fewer myofibrils of varying Striated: many myofibrils in orderly
of myofibrils lengths arrangement
Not self stimulating: each fiber innervated Self stimulating: not individually Self stimulating: impulse spreads from
by branch of somatic motor neuron as innervated, impulse spreads from cell to cell
part of motor unit cell to cell
Under control of nervous system Under control of nervous and endocrine Under control of nervous and endocrine
systems and various chemicals and systems and various chemicals
stretching
High energy requirement: lots of Lower energy requirement: fewer Intermediate energy requirement
mitochondria, creatine phosphate, mitochondria, etc.
myoglobin
Fast Contracting Slower contracting and rhythmic Intermediate speed of contraction yet
in some organs producing peristaltic contraction spreads quickly through
waves along organ tissue due to intercalated discs
No rhythmic contractions Rhythmic contractions Rhythmic contractions
Strength increases with stretching Stress - Relaxation Response Strength increases with stretchiing
Fatigues Easily Doesn’t fatigue Doesn’t fatigue
You might also like
- NASM-CPT Study Guide: Domain 1: Basic and Applied Sciences andDocument49 pagesNASM-CPT Study Guide: Domain 1: Basic and Applied Sciences andsonia100% (3)
- Gyrokinesis BeginnerDocument11 pagesGyrokinesis BeginnerSF Wong100% (2)
- NASM-CPT6 Exam Study GuideDocument52 pagesNASM-CPT6 Exam Study Guidedw3541100% (11)
- OSTEOARTHRITISDocument53 pagesOSTEOARTHRITISRiza Umami100% (1)
- Cardiac and Smooth MusclesDocument15 pagesCardiac and Smooth MusclesDr Muhammad Abdul QadirNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE B.Sc-IIDocument13 pagesMUSCLE B.Sc-IIAjinkya BansodeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesClinical Case: Anatomy and PhysiologyGeorge KoNo ratings yet
- 副本 - Classification of musclesDocument31 pages副本 - Classification of musclesTan Ting WeiNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument16 pagesMuscular Systemjgabiran02No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument101 pagesMuscular Systemsheryl dungogNo ratings yet
- 7B Muscles, Movement and The Heart 7B CheckpointDocument8 pages7B Muscles, Movement and The Heart 7B CheckpointsalmaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument21 pagesMuscular System ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument10 pagesChapter 7 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Structure of Muscles DR - Dilrukshi ThavinDocument26 pagesMicroscopic Structure of Muscles DR - Dilrukshi ThavinOmar Ali AyoubkhanNo ratings yet
- Types of MusclesDocument8 pagesTypes of MusclesJoan Vito CruzNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Muscular SystemDocument76 pages6.0 Muscular System[R2A] Khadijah AzlanNo ratings yet
- Assignment of PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAssignment of PhysiologySalman aliNo ratings yet
- Histology Week 4 Assignment Muscle Tissue: Srdongre5520val@student - Fatima.edu - PHDocument1 pageHistology Week 4 Assignment Muscle Tissue: Srdongre5520val@student - Fatima.edu - PHShreyasi DongreNo ratings yet
- Zoology PPT Muscular SystemDocument68 pagesZoology PPT Muscular SystemDian O. Velasquez100% (1)
- Muscular TissueDocument37 pagesMuscular Tissueمؤمل عدنان الشمخيNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 (Muscular System)Document7 pagesUNIT 3 (Muscular System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Muscular SystemRodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Lab 08 Muscle TissueDocument16 pagesLab 08 Muscle TissueSarwar JafarNo ratings yet
- D.muscular System PDFDocument8 pagesD.muscular System PDFJohn Lawrence YbanezNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue - HistologyDocument35 pagesMuscle Tissue - HistologyjabirNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Myo and Mys - Muscle Sarco - FleshDocument4 pagesThe Muscular System: Myo and Mys - Muscle Sarco - FleshDCRUZNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument7 pagesPhysiologyLe Maurice CiminiNo ratings yet
- 11J - Caybot - Jash Jovian - Task10Document11 pages11J - Caybot - Jash Jovian - Task10JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- Zoo 102 Compilation - Scalps.Document305 pagesZoo 102 Compilation - Scalps.adepegbaadebisi05No ratings yet
- Classification of MusclesDocument30 pagesClassification of MusclesAreej SadruddinNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument20 pagesMuscular SystemAltaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Smooth and Cardiac MuscleDocument19 pagesSmooth and Cardiac Musclezahra nabilaNo ratings yet
- Report in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesReport in Anatomy and Physiologydowngrade840No ratings yet
- Muscles:: Types & FunctionDocument19 pagesMuscles:: Types & FunctionAmna Fatima GhayoorNo ratings yet
- 5 MuscleDocument3 pages5 MuscleNicolePorsueloNo ratings yet
- Muskuloskeletal DisordersDocument15 pagesMuskuloskeletal DisordersLienyPerasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of MuscleDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Musclenandhini raguNo ratings yet
- Muscular System - Part 1 (BSN - 1F)Document5 pagesMuscular System - Part 1 (BSN - 1F)yulo.jhoselleanne.bsnNo ratings yet
- 3 Topic 3 MascleDocument62 pages3 Topic 3 Masclesamuel mergaNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscle TissuesDocument2 pagesTypes of Muscle TissueswatermelonNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Functional Anatomy, Excitation-Contraction CouplingDocument46 pagesMuscles and Muscle Tissue: Functional Anatomy, Excitation-Contraction CouplingRevanth VejjuNo ratings yet
- Muscular System - Part 1 (BSN - 1F)Document5 pagesMuscular System - Part 1 (BSN - 1F)yulo.jhoselleanne.bsnNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtDocument9 pagesActivity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtAMEER MUHMIEN JALMAANI. LERIOSNo ratings yet
- Eme 1Document20 pagesEme 1Tara LingatingNo ratings yet
- Muscle 1Document53 pagesMuscle 1mem734094No ratings yet
- 5 Muscular SystemDocument55 pages5 Muscular SystemFareez HamidNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument17 pagesAnimal TissuesLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- 20201027-20201103-1149-Muscular SystemDocument21 pages20201027-20201103-1149-Muscular Systemdrin zekaNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument23 pagesMuscle PhysiologyAnna HarunNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth Muscle Cells-Myasthenia Gravis, Muscular Dystrophy and MyotoniaDocument51 pagesDisorders of Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth Muscle Cells-Myasthenia Gravis, Muscular Dystrophy and MyotoniaCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- 2 Cytology and Histology BriefDocument37 pages2 Cytology and Histology BriefBekalu EndaleNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument64 pagesMuscle Physiologylynn.dargham2No ratings yet
- Compact Bone and Spongy Bone: OsteocytesDocument27 pagesCompact Bone and Spongy Bone: OsteocytesMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Nerve and Muscle TissueDocument26 pages1 - Nerve and Muscle TissueupbandaraNo ratings yet
- Muscular tissue: یکیتکارپ ینازەناش ىجۆلۆياب ىمەوود .م رەورەس Lab 8: Muscle TDocument2 pagesMuscular tissue: یکیتکارپ ینازەناش ىجۆلۆياب ىمەوود .م رەورەس Lab 8: Muscle TSarwar JafarNo ratings yet
- 04 Muscle 2022Document39 pages04 Muscle 2022AlkadafeNo ratings yet
- Updated Notes On PhysiologyDocument39 pagesUpdated Notes On PhysiologyRoscelie KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10: The Muscular System Lesson Objectives:: Chemical, and Thermal StimulationDocument3 pagesLesson 10: The Muscular System Lesson Objectives:: Chemical, and Thermal StimulationRichee LunnayNo ratings yet
- Histology Muscle and Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesHistology Muscle and Nervous Tissuejosh100% (1)
- Chapter 6 (Anaphy)Document8 pagesChapter 6 (Anaphy)Gerald SouribioNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement 1Document34 pagesAcknowledgement 1Raihanur KiranNo ratings yet
- Group C PDFDocument1 pageGroup C PDFRaihanur KiranNo ratings yet
- Intermediatepagedocument 11082017 PDFDocument1 pageIntermediatepagedocument 11082017 PDFRaihanur KiranNo ratings yet
- North 24 Parganas NT Rlst3Document2 pagesNorth 24 Parganas NT Rlst3Raihanur KiranNo ratings yet
- Shuttle Vectors and Expression VectorsDocument2 pagesShuttle Vectors and Expression VectorsRaihanur Kiran100% (2)
- Schistosoma Haematobium: Dr. Shatarupa ChakrabortyDocument30 pagesSchistosoma Haematobium: Dr. Shatarupa ChakrabortyRaihanur KiranNo ratings yet
- Cloning VectorsDocument1 pageCloning VectorsRaihanur KiranNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Hamstring Strains: Phase I: Acute PhaseDocument3 pagesRehabilitation of Hamstring Strains: Phase I: Acute PhaseariyatiNo ratings yet
- Large Medium ExternalfixatorsDocument42 pagesLarge Medium ExternalfixatorsZulfadli Salleh0% (1)
- Peroneal Tendon InjuriesDocument12 pagesPeroneal Tendon InjuriesSamuel LauNo ratings yet
- Biodex System ProDocument102 pagesBiodex System ProJose MarioNo ratings yet
- A Study of The Effects of Mulligan's Mobilization With Movement Treatment ofDocument7 pagesA Study of The Effects of Mulligan's Mobilization With Movement Treatment ofManuel OlarteNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Origins, Current Practice, and Views of Wide Awake Hand SurgeryDocument10 pagesConceptual Origins, Current Practice, and Views of Wide Awake Hand SurgeryLorenyaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Structure of The Human Foot Herbert and ElftmanDocument10 pagesDynamic Structure of The Human Foot Herbert and ElftmantriptykhannaNo ratings yet
- Daily Report On Injuries and Illnesses: - ExampleDocument2 pagesDaily Report On Injuries and Illnesses: - Examplevalle93No ratings yet
- Speech and Hearing Science-Anotomy and Physiology ZemlinDocument622 pagesSpeech and Hearing Science-Anotomy and Physiology ZemlinelkkrotNo ratings yet
- Minimal Imvasive AC Joint RecontructionDocument15 pagesMinimal Imvasive AC Joint RecontructionAmri NawiNo ratings yet
- Elbow and Sport 1st Ed (BUKU)Document263 pagesElbow and Sport 1st Ed (BUKU)Tri Waluyo100% (1)
- Laporan Kegiatan IGD: Bagian BedahDocument24 pagesLaporan Kegiatan IGD: Bagian Bedahbagus arisNo ratings yet
- A Modified Boytchev Procedure For Recurrent Anterior Dislocation of The Shoulder Khaled M Mostafa and Kamal El-GafaryDocument9 pagesA Modified Boytchev Procedure For Recurrent Anterior Dislocation of The Shoulder Khaled M Mostafa and Kamal El-GafaryDebangshu KumarNo ratings yet
- 17 Inguinal CanalDocument17 pages17 Inguinal CanalgeorgefrombaNo ratings yet
- Knee Dry NeedlingDocument24 pagesKnee Dry NeedlingJavi EgeaNo ratings yet
- MiscellaneousDocument487 pagesMiscellaneoussalah subbahNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Nerve Conduction Studies and Electromyography (2 Ed.)Document10 pagesAtlas of Nerve Conduction Studies and Electromyography (2 Ed.)rodrigocorcino899959No ratings yet
- Delta XtendDocument60 pagesDelta XtendMarcelo KrauseNo ratings yet
- TMJ Anatomy and Biomechanics-14Document67 pagesTMJ Anatomy and Biomechanics-14erfan mohammadiNo ratings yet
- RHC 2 TrainingDocument6 pagesRHC 2 TrainingcookiekhanhNo ratings yet
- Why These 10 Exercises Will Rock Your BodyDocument4 pagesWhy These 10 Exercises Will Rock Your BodyWelkin SkyNo ratings yet
- Urn NBN No Ntnu Diva-560-1 Fulltext PDFDocument66 pagesUrn NBN No Ntnu Diva-560-1 Fulltext PDFMohammed AlkhafajiNo ratings yet
- 1.postural Assessment - CHECKLISTDocument3 pages1.postural Assessment - CHECKLISTMohammad FoudaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2. Skeletal System PowerPointDocument51 pagesGeneral Biology 2. Skeletal System PowerPointMetal ManNo ratings yet
- 338 Stretching PDFDocument7 pages338 Stretching PDFsage porterNo ratings yet
- HEAD NECK BACK SPINE SPECIAL TESTS December 2022Document5 pagesHEAD NECK BACK SPINE SPECIAL TESTS December 2022Ted Lawrence CiscarNo ratings yet
- Surface AnatomyDocument63 pagesSurface AnatomyCodie SimoneauxNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Chapter Quiz Skeletal and Muscular System Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Midterm Chapter Quiz Skeletal and Muscular System Skeletal SystemMartin ManuelNo ratings yet