Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Population and Migration - Revision Placemat
Uploaded by
Gaming TriadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Population and Migration - Revision Placemat
Uploaded by
Gaming TriadCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Population and migration – Revision Placemat
Knowledge tick list: Global population explosion (p4-5) Overpopulation and underpopulation (p6-11) Key Words and definitions
Describe and suggest reasons for the world’s a. Annotated diagram Definitions Birth rate
‘population explosion’. Death rate
Describe the main components influencing Consequences of:
Natural increase
population growth – birth rate, death rate and a. Over-population
migration Immigration
b. Under-population
Describe the main components influencing emigration
population growth – birth rate, death rate and
Nigeria – four facts: Net migration
migration
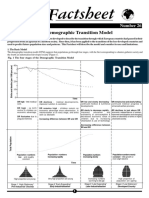
The Demographic Transition Model – five
Push and pull factors
stages Overpopulation
Describe the relationship between population
b. Reasons for the rapid growth after 1800 Under-population
and resources and explain why problems such Australia – four facts:
LIC, MIC, HIC
as over-population and under-population may
arise in some areas. Dependency ratio
Population structure and age-sex pyramids Population distribution
(and the way they link into DTM) Population density
The impacts of varying types of dependent
populations (youthful and ageing).
Describe and account for (using physical,
Causes of a change in population size (p12-13) Variation in population growth rates (p14-15) Population growth/decline case studies (p16-17)
human and economic factors) the global
distribution of population. How do each of the following affect growth rate? Niger – four facts Russia – four facts
Describe and account for the main patterns of a. Annotated sketch of the DTM
migration. Rural- urban (internal) and
a. GDP
international migrations must be included, as
well as voluntary/ involuntary.
Case studies of: b. cost of living
o High/low natural increase
o Over/underpopulation
c. disease (HIV/AIDS) Migration case study: Qatar – four facts (p26-27)
o Aging and youthful population
o migration
d. religion
e. government policy
b. Falling birth rates – three reasons:
High dependence case study: Italy (ageing) – four facts (p30-31)
c. Falling death rates – three reasons:
Population policies (20-21) Population migration (p22-25) Population structure (p28-29) Distribution and density (p32-37)
a. Annotated youthful pyramid (LIC)
a. Why governments create population policies a. Push-pull model diagram a. Factors causing concentration
b. Singapore (pro-natalist policy) – four facts b. Factors causing dispersal (sparse)
b. Push factors – three examples:
c. Pull factors – three examples:
b. Annotated aged (post-mature) pyramid (HIC)
c. Japan: high density – four facts
d. Impacts of migration
c. China (anti-natalist policy) – four facts
Origin Destination
+ve -ve +ve -ve
d. Namibia: low density – four facts
You might also like
- 1 - Population iGCSEDocument5 pages1 - Population iGCSEAndy FunnellNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesContemporary Finals ReviewerFina TorresNo ratings yet
- IB Geography - CORE - Populations in Transition Knowledge AuditDocument2 pagesIB Geography - CORE - Populations in Transition Knowledge Auditapi-26186088No ratings yet
- Health StatisticsDocument2 pagesHealth StatisticsACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.No ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 Population Growth in Organisms and HumansDocument51 pagesTOPIC 3 Population Growth in Organisms and HumansChamie Azuela LagamayoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Current Issues and Importance 18 Dec 2021Document17 pagesUnit 4 Current Issues and Importance 18 Dec 2021Ankit RajNo ratings yet
- Population Unit: Natural Increase MigrationDocument6 pagesPopulation Unit: Natural Increase MigrationAndy FunnellNo ratings yet
- DemographyDocument4 pagesDemographyAlexis BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Soc GeoDocument10 pagesSoc GeoJananya PetlaNo ratings yet
- Population and Demographic TransitionDocument51 pagesPopulation and Demographic TransitionMaheen HayatNo ratings yet
- Demographic Dividends Revisited: Effrey IlliamsonDocument25 pagesDemographic Dividends Revisited: Effrey IlliamsonSaira BalochNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-We21-22Document53 pagesLesson 3-We21-22Beatriz MachadoNo ratings yet
- CPH LEC Demography and Pop Estimates ReviewerDocument4 pagesCPH LEC Demography and Pop Estimates ReviewerCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Cattaneo & Robinson (2020) - Multiple Moves and Return Migration Within Developing CountriesDocument21 pagesCattaneo & Robinson (2020) - Multiple Moves and Return Migration Within Developing Countriesd.benitessanchezNo ratings yet
- GLOBALIZATION and DEMOGRAPHYDocument37 pagesGLOBALIZATION and DEMOGRAPHYMeca FernandezNo ratings yet
- Demography Hotel ManagementDocument39 pagesDemography Hotel ManagementShairyn AbacajenNo ratings yet
- Relation of Demographic Transition Model With MigrationDocument8 pagesRelation of Demographic Transition Model With MigrationMashrup HasanNo ratings yet
- The Demographic Transition Model: September 1997Document5 pagesThe Demographic Transition Model: September 1997Takunda GundumuraNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Block 1 Unit 5 Demography, Surveillance & Interpretation of DataDocument15 pagesIGNOU Block 1 Unit 5 Demography, Surveillance & Interpretation of Dataerice.research100% (1)
- Population Growth Rate and Its Determinants - An OverviewDocument18 pagesPopulation Growth Rate and Its Determinants - An Overviewzhao.liangfengNo ratings yet
- Pee RevDocument7 pagesPee RevAeiaNo ratings yet
- Topic Presentation 7Document58 pagesTopic Presentation 7Mary ThereseNo ratings yet
- Nsci 111Document7 pagesNsci 111Hiroshi MatsushimaNo ratings yet
- NEWS0 REP10 Box 317447 B01 PUBLIC1Document3 pagesNEWS0 REP10 Box 317447 B01 PUBLIC1retro glitchyNo ratings yet
- 5 Deblij - Human7e - ch04 PopulationDocument13 pages5 Deblij - Human7e - ch04 PopulationEdward Tamayo DuqueNo ratings yet
- Cohen (2003)Document4 pagesCohen (2003)Rosalba PeñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Global Demography SUPPLEMENT New RevisedDocument56 pagesChapter 11 Global Demography SUPPLEMENT New RevisedKathleen Hazel AndresNo ratings yet
- Population and Migration Patterns PDFDocument1 pagePopulation and Migration Patterns PDFRuryk KowaNo ratings yet
- Change in Demographics: BY: Steve Magdaong and Therese Angelu L. AbionDocument30 pagesChange in Demographics: BY: Steve Magdaong and Therese Angelu L. AbionTherese Angelu Lubiano AbionNo ratings yet
- Pointers in EconDevDocument2 pagesPointers in EconDevValmonte CaitNo ratings yet
- Changing Demographics and Economic Growth BloomDocument6 pagesChanging Demographics and Economic Growth BloomMehul GuptaNo ratings yet
- PAEE Reviewer FinalsDocument24 pagesPAEE Reviewer FinalsBea MercadoNo ratings yet
- Population and Society Essential Readings 2Nd Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesPopulation and Society Essential Readings 2Nd Edition Full Chapterallison.deans127100% (24)
- Ge 3 Global Demography FinalDocument21 pagesGe 3 Global Demography FinalFerlyn del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Population and Settlement StudiesDocument8 pagesPopulation and Settlement StudiesMolly majezaNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id1898868Document15 pagesSSRN Id1898868Coca LoloNo ratings yet
- CHN DemographyDocument9 pagesCHN DemographyISHI REIGN PEJENo ratings yet
- 4.2 Demographic Transition ModelDocument29 pages4.2 Demographic Transition ModelRuxandra ZahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document29 pagesUnit 5114 Wais RazaNo ratings yet
- Dinamics of Human Population, &population GrowthDocument14 pagesDinamics of Human Population, &population GrowthMahdiyani fadhilahNo ratings yet
- Global Demography G 1Document27 pagesGlobal Demography G 1Jemuel Luc JavierNo ratings yet
- Population Growth and Earth's Human Carrying Capacity: Joel E. CohenDocument10 pagesPopulation Growth and Earth's Human Carrying Capacity: Joel E. Cohenapi-281790046No ratings yet
- CONTEMPORARY WORLD REVIEWER (1st Year-2nd Sem)Document3 pagesCONTEMPORARY WORLD REVIEWER (1st Year-2nd Sem)Deborah AquinoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: 6. The Human Population and Its Impact?Document28 pagesEnvironmental Science: 6. The Human Population and Its Impact?Nguyễn Quỳnh HươngNo ratings yet
- Demography Structure TypesDocument3 pagesDemography Structure TypesChuchulate MamanaoNo ratings yet
- AQA A Tourism Revision GuideDocument40 pagesAQA A Tourism Revision Guideprincess2011No ratings yet
- PopulationDocument23 pagesPopulationAman SinghNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Human Population Dynamic - IssuesDocument8 pagesLESSON 2 - Human Population Dynamic - IssuesDalupire, Jhonryl A.No ratings yet
- Lesson TwoDocument22 pagesLesson TwoPaulo Victor SazonNo ratings yet
- Principles Population Demography Moazzam Ali 2016Document59 pagesPrinciples Population Demography Moazzam Ali 2016InextLive PrayagrajNo ratings yet
- Trends in International MigrationDocument15 pagesTrends in International MigrationtzorbatzakisNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesHuman ReproductionDELA TORRE, SHENANORNo ratings yet
- Policy Brief Demographic DividendDocument8 pagesPolicy Brief Demographic DividendHarry Hernandez ZaballeroNo ratings yet
- Soc U2 2010 PDFDocument8 pagesSoc U2 2010 PDFCrystel AgardNo ratings yet
- P A Popu and E Latio Emplo On, La Oyme Abour Ent R For Rce: Chapte Er No. 12Document31 pagesP A Popu and E Latio Emplo On, La Oyme Abour Ent R For Rce: Chapte Er No. 12BilalNumanNo ratings yet
- Demography and Health Services StatisticsDocument74 pagesDemography and Health Services StatisticsHamse AdenNo ratings yet
- DemographyDocument8 pagesDemographyprashant guptaNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Chapter 9Document3 pagesEconomic Development Chapter 9Ara Mae WañaNo ratings yet
- Global Population and MobilityDocument61 pagesGlobal Population and MobilityFrancisco PizarroNo ratings yet
- Postwar Fertility Trends and Differentials in the United StatesFrom EverandPostwar Fertility Trends and Differentials in the United StatesNo ratings yet
- Atom Bonding - Revise HWK AnsDocument1 pageAtom Bonding - Revise HWK AnsGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- 2c. Empirical Formula A WorkDocument1 page2c. Empirical Formula A WorkGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Atom Bonding - Revise HWK AnsDocument1 pageAtom Bonding - Revise HWK AnsGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- 7.-WRITING-and-Balancing HWK LWi NaDocument1 page7.-WRITING-and-Balancing HWK LWi NaGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- 2 MG + O 2 Mgo 3. Cu + S Cus 4. Cubr Cu + BR 5. Ext: KBR + Agno Agbr + Kno 2 MG + O 2 Mgo Cu + S Cus Cubr Cu + BR Ext: KBR + Agno Agbr + KnoDocument1 page2 MG + O 2 Mgo 3. Cu + S Cus 4. Cubr Cu + BR 5. Ext: KBR + Agno Agbr + Kno 2 MG + O 2 Mgo Cu + S Cus Cubr Cu + BR Ext: KBR + Agno Agbr + KnoGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Writing Equations Worksheet HWKDocument1 pageWriting Equations Worksheet HWKGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Writing Equations Worksheet Answers HWKDocument1 pageWriting Equations Worksheet Answers HWKGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Balancing Equations - Level 4: - NaclDocument1 pageYear 10 Balancing Equations - Level 4: - NaclGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Masses - : in Each Case The First One Has Been Done For YouDocument1 pageMasses - : in Each Case The First One Has Been Done For YouGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations - LWiDocument2 pagesBalancing Equations - LWiGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Masses - : in Each Case The First One Has Been Done For YouDocument1 pageMasses - : in Each Case The First One Has Been Done For YouGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Balancing Equations - Level 3: - NaclDocument1 pageYear 10 Balancing Equations - Level 3: - NaclGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Masses - : in Each Case The First One Has Been Done For YouDocument1 pageMasses - : in Each Case The First One Has Been Done For YouGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Molecular and Empirical Formula Molecular and Empirical FormulaDocument1 pageMolecular and Empirical Formula Molecular and Empirical FormulaGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Balancing Equations - Level 1 Year 10 Balancing Equations - Level 1Document2 pagesYear 10 Balancing Equations - Level 1 Year 10 Balancing Equations - Level 1Gaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition C.T.Document8 pagesAnimal Nutrition C.T.Gaming TriadNo ratings yet
- 1b. RED - RFM WksDocument1 page1b. RED - RFM WksGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Masses - Empirical Formula: Find The Empirical Formula of Each of The Following Substances. 1) - C 1.24 G H 0.26 GDocument1 pageMasses - Empirical Formula: Find The Empirical Formula of Each of The Following Substances. 1) - C 1.24 G H 0.26 GGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- RFM HWKDocument1 pageRFM HWKGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageRevision Questions Revision QuestionsGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- 1b. RED - RFM Answer SheetDocument1 page1b. RED - RFM Answer SheetGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Balancing Equations - Level 2 Year 10 Balancing Equations - Level 2Document2 pagesYear 10 Balancing Equations - Level 2 Year 10 Balancing Equations - Level 2Gaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - ChemistryDocument13 pagesTerm 1 - ChemistryGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - Physics Part 2Document11 pagesTerm 1 - Physics Part 2Gaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - Physics Part 1Document10 pagesTerm 1 - Physics Part 1Gaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - MathsDocument10 pagesTerm 1 - MathsGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Extract Based Essay PracticeDocument136 pagesExtract Based Essay PracticeGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - BiologyDocument17 pagesTerm 1 - BiologyGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - Engineering PDFDocument8 pagesTerm 1 - Engineering PDFGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Pre-Q Human Nutrition and DigestionDocument33 pagesPre-Q Human Nutrition and DigestionGaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Do You Have Some Ideas About These Industries?: Mportance OF AnufacturingDocument22 pagesDo You Have Some Ideas About These Industries?: Mportance OF Anufacturing30 sec any movieNo ratings yet
- LearningDocument2 pagesLearningaldira bilaNo ratings yet
- Lansang vs. Garcia (G.R. No. L-33964 - December 11, 1971)Document10 pagesLansang vs. Garcia (G.R. No. L-33964 - December 11, 1971)Lecdiee Nhojiezz Tacissea SalnackyiNo ratings yet
- ENR 5.1 - Proh - Rest - DangerareasDocument32 pagesENR 5.1 - Proh - Rest - DangerareasNoob GamingNo ratings yet
- EASA Essay Paper Mod 7,9,10Document5 pagesEASA Essay Paper Mod 7,9,10Anthony Hcs80% (15)
- Lead Engineer - Civil (JD)Document1 pageLead Engineer - Civil (JD)sandeep wNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PMP StudyDocument24 pagesChapter 4 PMP StudyAbdülhamit KayyaliNo ratings yet
- Change MasteryDocument24 pagesChange MasteryGeta WalelignNo ratings yet
- What Is A BadmintonDocument5 pagesWhat Is A BadmintonRuru Uwu0% (1)
- Exceptional Leadership SlidesDocument8 pagesExceptional Leadership SlidesENNYNo ratings yet
- Ipr in Fashion DesignDocument6 pagesIpr in Fashion DesignMuskan KashyapNo ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Learning ItalianDocument50 pagesBeginners Guide To Learning Italianannie.nikol75% (4)
- Sociolinguistics and Gender: Traditional Sociolinguistic InterviewDocument80 pagesSociolinguistics and Gender: Traditional Sociolinguistic InterviewSeptiyan Adi Purwanto100% (1)
- Vocational Centre at Khurja: Sunderdeep College of Architecture (Dasna, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh)Document45 pagesVocational Centre at Khurja: Sunderdeep College of Architecture (Dasna, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh)NAZEEF KHANNo ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 20204Document32 pagesMPRA Paper 20204thotosthoNo ratings yet
- AUD 1206 Case Analysis Number 1Document1 pageAUD 1206 Case Analysis Number 1Brian GoNo ratings yet
- Evaluating SOWsDocument1 pageEvaluating SOWsAnonymous M9MZInTVNo ratings yet
- Luigi Russolo S Imagination of Sound MusicDocument292 pagesLuigi Russolo S Imagination of Sound MusicMaría Jiménez100% (1)
- Chapter One: 1.1. Introduction of Internship Report:: Kashf Micro-Finance Bank LimitedDocument56 pagesChapter One: 1.1. Introduction of Internship Report:: Kashf Micro-Finance Bank Limitedmunna_bhai_tk7534No ratings yet
- Procedure For Preparation of Dry Chemical Wheeled Extinguishers Data SheetDocument5 pagesProcedure For Preparation of Dry Chemical Wheeled Extinguishers Data SheetmNo ratings yet
- ADocument4 pagesAGanuke PereraNo ratings yet
- Follow - Up Services DefinedDocument2 pagesFollow - Up Services DefinedBon Sawyer100% (1)
- 2010 Metrobank Foundation Outstanding TeachersDocument10 pages2010 Metrobank Foundation Outstanding Teachersproffsg100% (1)
- Prototyping: The Best Way To Have A Good Idea Is To Have Lots of Ideas - Linus PaulingDocument33 pagesPrototyping: The Best Way To Have A Good Idea Is To Have Lots of Ideas - Linus PaulingHassan AsgharNo ratings yet
- Control of AirDocument71 pagesControl of Airajay ahlawatNo ratings yet
- Ethics in MarketingDocument23 pagesEthics in MarketingVijyata SinghNo ratings yet
- Strategic Brand Management ProcessDocument6 pagesStrategic Brand Management ProcessRaghav BansalNo ratings yet
- WORK STUDY (WORK MEASUREMENT & METHOD STUDY) of PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGYDocument72 pagesWORK STUDY (WORK MEASUREMENT & METHOD STUDY) of PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGYvvns451988885% (131)
- Assignment of PragmaticsDocument8 pagesAssignment of PragmaticsFatima QadeerNo ratings yet
- Collector of Internal Revenue vs. University of Santo Tomas and The Court of Tax Appeals, 104 Phil 1062, November 28, 1958Document3 pagesCollector of Internal Revenue vs. University of Santo Tomas and The Court of Tax Appeals, 104 Phil 1062, November 28, 1958Jane Bandoja100% (5)