Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hand Outs 3rd Grading
Hand Outs 3rd Grading
Uploaded by
Raymond Reyes Curibang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
233 views13 pagesTLE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTLE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
233 views13 pagesHand Outs 3rd Grading
Hand Outs 3rd Grading
Uploaded by
Raymond Reyes CuribangTLE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
EsP 9-Modyul 9 10.
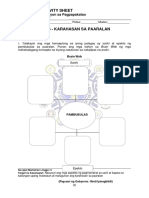
Katarungang Panlipunan • Ito ang namamahala sa
kaayusan ng ugnayan ng tao sa kaniyang kapwa at sa
Aralin 9 KATARUNGANG ugnayan ng tao sa lipunan. • Inilalagay nito sa ayos ang
PANLIPUNAN panlipunang ugnayan ayon sa kraytirya ng pagsunod sa
batas
2. Balik-aral: • Ang pakikilahok ay isang tungkulin na
kailangang isakatuparan ng lahat na mayroong 11. Katangian ng Katarungang Panlipunan • Paggalang
kamalayan at pananagutan tungo sa kabutihang sa karapatan ng bawat tao • Pagpapaliban sa
panlahat. • Ang bolunterismo ay isang paraan ng pansariling interest • Pagsusuri sa kabuuang sitwasyon
paglilingkod at pagpapakita ng pagmamahal sa kapwa at • Pagsasaalang sa kabutihang panlahat
sa lipunan na hindi naghahangad ng anumang kapalit. •
Hindi lahat ng pakikilahok ay may aspekto ng 12. Katarungang Panlipunan at Dignidad ng tao • Ang
bolunterismo pero lahat ng bolunterismo ay may katarungang panlipunan ay kumikilala sa dignidad ng
aspekto ng pakikilahok. tao. • Ang bawat tao ay may dignidad dahil sa kanyang
pagkatao. • May dignidad ang tao dahil mahalaga siya. •
3. Panimula • Bilang panlipunang nilalang, tayo ay may Dahil mahalaga ang tao, makatarungan na ibigay ang
likas na pangangailangan sa kapwa lalo na sa panahon nararapat sa kanya.
ng kagipitan. • Ito ay dahil ang tao ay umiiral na kasama
ang ibang tao; isang ugnayan na dapat na
pinagyayaman ng katarungan. Sagutin at Ipaliwanag ang sumusunod
• Paano magiging makatarungan ang tao? Ipaliwanag
4. Ano ang katarungan? • Ito ang pagbibigay sa kapwa • Paano nagsisimula sa pamilya ang pagiging
ng nararapat sa kanya. • Ang tuon ng katarungan ay ang makatarungan?
labas ng sarili. Ito ay ang pagpapahalaga sa kaniyang
dignidad bilang tao. • Ang pagkatao ay isang _____________________________________________
katotohanang nangangailangan ng ating pagkilala at _____________________________________________
paggalang. (Dr. Manuel B. Dy Jr.) _____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
5. Ano ang katarungan? • Ang katarungan ay batay sa _____________________________________________
pagkatao ng tao. • Ang pagiging makatarungan ay _____________________________________________
pagpapakita ng pagmamahal bilang tao na namumuhay _____________________________________________
kasama ang iba. • Ang paninira sa ibang tao ay isa ring _____________________________________________
paglapastangan sa iyong sariling pagkatao. _____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
6. Ano ang katarungan? • Ang katarungan ay isang gawi _____________________________________________
na gumagamit lagi ng kilos-loob sa pagbibigay ng _____________________________________________
nararapat sa isang idibidwal. • Ang kilos-loob ay _____________________________________________
magpapatatag sa iyong pagiging makatarungang tao. _____________________________________________
(Sto. Tomas de Aquino) _____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
7. Makatarungang Tao • Makatarungan ang isang tao _____________________________________________
kung ginagamit nito ang kanyang lakas sa paggalang sa _____________________________________________
batas at sa karapatan ng kapwa. • Isinasaalang-alang din _____________________________________________
nito ang pagiging patas sa lahat ng tao. • Kailangan _____________________________________________
mong salungatin ang iyong mismong sarili, ang ibang _____________________________________________
tao at ang mundo sa hindi pagiging patas ng mga ito. _____________________________________________
(Andre Comte-Sponville, 2003) _____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
8. Pangunahing Prinsipyo ng Katarungan • Ang _____________________________________________
makatarungang ugnayan ay umiiral kung walang nang- _____________________________________________
aagrabyado sa isa’t isa. • Bilang tao, karapatan ng bawat _____________________________________________
isa na mamuhay nang hindi hinahadlangan ng iba. Kung _____________________________________________
nilalabag ang karapatang ito, mawawalan ng _____________________________________________
katarungan. Maari itong magbunga ng gulo sa buhay ng _____________________________________________
mga nasasangkot. _____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
9. Nagsisimula sa Pamilya ang Katarungan • Ang _____________________________________________
pamilya ang unang nagbibigay sa iyo ng kamalayan _____________________________________________
tungkol sa katarungan. • Dahan-dahang nahuhubog ang _____________________________________________
iyong pagkatao sa paggabay ng iyong mga mahal sa _____________________________________________
buhay. • Nauunawaan mo na kapag iginagalang mo ang _____________________________________________
mga karapatan ng iba isinasaalang- alang mo ang _____________________________________________
kabutihang panlahat. _____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
EsP 9-Modyul 10 • Nagagamit ba ang mga talento at kasanayang
ipinagkaloob ng Diyos?
Aralin 10 KAGALINGAN SA • Nagamit ba ang aral ng buhay na natutuhan mula sa
PAGGAWA karanasan?
Sagutin at Ipaliwanag ang sumusunod:
• Ano-anong kasanayan ang kailangan sa paggawa ng
2. Balik-aral: • Ang katarungan ay ang pagbibigay sa
may kalidad?
kapwa ng nararapat sa kanya.
• Bakit mahalaga ang kalidad o kagalingan sa paggawa?
• Makatarungan ang isang tao kung ginagamit nito ang
kanyang lakas sa paggalang sa batas at sa karapatan ng
_____________________________________________
kapwa.
_____________________________________________
• Ang pamilya ang unang nagbibigay sa tao ng
_____________________________________________
kamalayan tungkol sa katarungan.
_____________________________________________
• Ang katarungang panlipunan ay namamahala sa
_____________________________________________
kaayusan ng ugnayan ng tao sa kaniyang kapwa at sa
_____________________________________________
ugnayan ng tao sa lipunan.
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
3. Panimula • Ang pagsasagawa ng isang gawain o
_____________________________________________
paglikha ng produkto ay nangangailangan ng sapat na
_____________________________________________
kasanayan at kahusayan. • May mga partikular na
_____________________________________________
kakayahan at kasanayan na kailangan sa paggawa.
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
4. Kabutihan ng Paggawa
_____________________________________________
• Ang paggawa ay mabuti sa tao sapagkat
_____________________________________________
naisasakatuparan niya ang kanyang tungkulin sa sarili,
_____________________________________________
kapwa at sa Diyos.
_____________________________________________
• Ang kagustuhang maisabuhay ang layuning ito ang
_____________________________________________
nagtutulak sa kaniya upang magkaroon ng kagalingan sa
_____________________________________________
paggawa. (Laborem Exercens)
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
5. Katangian ng Kagalingang Paggawa
_____________________________________________
a. Nagsasabuhay ng mga pagpapahalaga
_____________________________________________
b. Nagtataglay ng kakailanging kasanayan
_____________________________________________
c. Nagpupuri at nagpapasalamat sa Diyos
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
6. Nagsasabuhay ng mga pagpapahalaga
_____________________________________________
• Ang mga pagpapahalagang ito ang nagsisilbing gabay
_____________________________________________
niya upang gumawa ng mga dekalidad na produkto o
_____________________________________________
serbisyo:
_____________________________________________
1. Kasipagan
_____________________________________________
2. Tiyaga
_____________________________________________
3. Masigasig
_____________________________________________
4. Malikhain
_____________________________________________
5. Disiplina sa Sarili
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
7. Nagtataglay ng kakailanging kasanayan
_____________________________________________
• Siya ay bukas at handang matutuo upang lalong
_____________________________________________
mapabuti ang kagalingan sa paggawa.
_____________________________________________
1. Pagkatuto Bago ang Paggawa
_____________________________________________
2. Pagkatuto Habang Ginagawa
_____________________________________________
3. Pagkatuto Pagkatapos ng Gawain
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
8. Nagpupuri at nagpapasalamat sa Diyos
_____________________________________________
• Ang kagalingan ay naaayon sa kalooban ng Diyos at
_____________________________________________
iniaalay bilang paraan ng papuri at pasasalamat sa
_____________________________________________
Kanya. Ang paggawa ng mabuti at may kahusayan ay
_____________________________________________
may balik na pagpapala mula sa Diyos.
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
9. Batayang tanong tungkol sa Kagalingang Paggawa
_____________________________________________
• Ito ba ay pinag-isipang mabuti?
_____________________________________________
• Nasunod ba ang mga hakbang na dapat gawin?
_____________________________________________
• Bunga ba ito ng malalim na pag-iisip?
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
Modyul 11: Kasipagan, Pagpupunyagi, Pagtitipid at 15. Nasasayang ang kasipagan at pagpupunyagi ng isang
Wastong Pamamahala ng Naimpok tao kung hindi niya napapamahalaan ng wasto ang
kaniyang mga pinaghirapan.
MODYUL 11: KASIPAGAN,
PAGPUPUNYAGI, PAGTITIPID 16. Sapagkat hindi napupulot ang pera, hindi ito
mapipitas sa mga puno, o di kaya hindi ito nalalaglag
AT WASTONG PAMAMAHALA mula sa langit. Ang pera ay pinagpapaguran upang
kitain ito. Kaya kinakailangan lamang na gastusin sa
SA NAIMPOK tama upang huwag itong mawala.
2. KASIPAGAN: ay tumutukoy sa pagsisikap na gawin o
tapusin ang isang gawain na mayroong kalidad. 17. Ang Pag-iimpok ay paraan upang makapag “save” o
makapag ipon ng salapi, na siyang magagamit sa ating
3. Ito ay tumutulong sa tao na malinang ang iba pang pangangailangan sa takdang panahon.
mabubuting katangian tulad ng tiwala sa sarili,
mahabang pasensya, katapatan, integridad, disiplina at 18. Mayroong tatlong dahilan kung bakit kailangan na
kahusayan mag-impok Ayon kay Francisco Colayco, ang tao.
1. Para sa proteksyon sa buhay.
4. na kung saan malaki ang maitutulong nito sa tao sa 2. Para sa mga hangarin sa buhay.
kaniyang relasyon sa kaniyang gawain, sa kaniyang 3. Para sa pagreretiro.
kapwa at sa kaniyang lipunan.
5. Narito ang ilang palatandaan ng taong nagtataglay ng
kasipagan. 1. Nagbibigay ng buong kakayahan sa
paggawa.
6. Ang taong masipag ay hindi nagmamadali sa kaniyang
ginagawa. Sinisiguro niya na magiging maayos ang
kalalabasan ng kaniyang gawain.
7. 2. Ginagawa ang gawain ng may pagmamahal.
Ibinibigay niya ang kaniyang puso sa kaniyang ginagawa
ibig sabihin naroroon ang kaniyang malasakit.
8. 3. Hindi umiiwas sa anumang gawain. Ito ay ginagawa
niya ng maayos at kung minsan ay higit pa na maging
ang gawain ng iba ay kaniyang ginagawa.
9. Ang kabaligtaran ng kasipagan ay katamaran. Ang
katamaran ang pumapatay sa isang gawain,
hanapbuhay o trabaho. Ito ang pumipigil sa tao upang
siya ay magtagumpay.
10. PAGPUPUNYAGI: Ang pagpapatuloy sa gawain kahit
na ikaw ay nahihirapan, ang pagpatuloy kahit minsan
ikaw ay nasasaktan o nagdurusa,
11. ang pagpapatuloy kahit maraming natatanggap na
mga puna mula sa iba, at ang pagpapatuloy sa kabila ng
matinding pagod at hirap makamit mo lamang ang
iyong minimithi sa buhay
12. Ang pagpupunyagi ay pagtitiyaga na maaabot o
makukuha ang iyong layunin o mithiin sa buhay. Ito ay
may kalakip na pagtitiyaga, pagtitiis, kasipagan at
determinasyon.
13. Ito ay pagtanggap sa mga hamon o pagsubok ng
may kahinahunan at hindi nagrereklamo. Ito ay patuloy
na pagsubok ng mga gawain hanggat hindi nakakamit
ang mithiin.
14. PAGTITIPID: kailangan na maging mapagkumbaba at
matutong makuntento sa kung ano ang meron ka. Ito
ang pinakamahalagang paraan ng pagtitipid.
EsP 9-Modyul 12 • Pagsisimula sa Tamang Oras – ang bawat gawain ay
kailangang simulan sa itinakdang oras.
Aralin 12 PAMAMAHALA • Pamamahala sa Pagpapabukas (Mañana habit) – ang
mañana habit ay ang puwang mula sa oras na binabalak
SA PAGGAMIT NG ORAS mong gawin ang isang bagay at sa aktuwal na oras ng
2. Balik-aral: • Ang kasipagan ang tumutulong sa isang paggawa. Makabubuting alamin ang mga
tao upang mapaunlad niya ang kanyang pagkatao. sirkumstansiya at mga dahilan ng iyong pagpapabukas
• Ang katamaran ang pumapatay sa isang gawain, at nang sa gayun ay mapamahalaan mo ito.
pumipigil sa tao upang siya ay magtagumpay.
• Ang pagpupunyagi ay pagtitiyaga na maabot o 11. Pangangasiwa o Pamamahala ng Oras
makuha ang iyong layunin at mithiin sa buhay. • Prayoritasyon – ito ang pagtatakda kung anong mga
• Kailangan na tratuhin ang pag-iimpok na isang gawain ang dapat gawin at tapusin sa takdang oras. Sa
obligasyon at hindi opsiyonal ayon kay Francisco pamamagitan nito, mapamahalaan mo ang paggamit ng
Colayco. iyong oras at matupad ang iyong mga tunguhin.
3. Panimula 12. Mga Hakbang sa Pangangasiwa ng Oras
• “Time is gold” sabi nila. • Pagtukoy sa iyong layunin na magbibigay ng
• Ano ang oras para sa iyo? Ano ang pananaw mo sa direksiyon sa nais mong matupad. Magplano para sa
paggamit ng oras? Bakit kaya nasabi ng karamihan na iyong buhay.
time is gold? • Pagtukoy sa kung ano ang iyong pangangailangan sa
kinahaharap na gawain.
4. Pamamahala sa Paggamit ng Oras • Pagtasa sa mga gawain. Kung ito ay malawak, simulan
• Ang oras ay kaloob na ipinagkakatiwala sa tao. Tayo ay sa pinakamaliit na gawain. Ang pagsisimula sa
ginawang katiwala ng Diyos sa maraming bagay - isa na pinakapayak at madaling gawain ay makapagdudulot ng
rito ang oras. kasiyahan o sense of achievement.
• Bilang katiwala, may tungkulin tayo na gamitin ang
oras na may pananagutan sapagkat ito ay HINDI na 13. Mga Hakbang sa Pangangasiwa ng Oras
maibabalik kailanman. • Pag-aayos ng mga kongkretong hakbang o plano ng
pagkilos upang matapos nang maayos. Magtakda ng
5. Pamamahala sa Paggamit ng Oras araw kung kailan tatapusin ang gawain. Iwasang malihis
• Ang oras ay di tulad ng salapi na maaring ipunin. sa ibang gawain. Mag-focus.
• Ang pamamahala sa oras ay ang kakayahan sa • Gumawa. Itakda ang oras. Gantimpalaan ang sarili sa
epektibo at produktibong paggamit nito sa paggawa. Ito tuwing may natatapos na gawain.
ang pagkontrol sa dami ng oras na gugugulin sa isang • Tasahin kung nagawa ang nararapat gawin. Maging
tiyak na gawain. matiyaga at kapaki-pakinabang.Huwag susuko.
• Sa pamamagitan ng pamamahala sa paggamit ng oras
tataas ang produktibidad, pagkamabisa at kagalingan sa 14. Pamamahinga at Paglilibang
paggawa. • Ang paglalaan ng oras para sa pamamahinga at
paglilibang pagkatapos ng iyong paggawa ay magbibigay
6. Pagtatakda ng Tunguhin sa Paggawa SPECIFIC balanse sa iyong buhay.
MEASURABLE ATTAINABLE REALISTIC TIME BOUND
15. Pagbubuod: Ang pagsasapuso mo sa kahalagahan ng
7. Pagtatakda ng Tunguhin sa Paggawa pamamahala sa paggamit ng iyong oras ay nakaaapekto
1. Specific (Tiyak). Tiyak ang iyong tunguhin kung ikaw sa iyong sariling pag-unlad, sa iyong kapwa, sa lipunan
ay nakasisiguro na ito ang iyong nais na mangyari sa at sa iyong ugnayan sa Diyos na Siyang nagkaloob ng
iyong paggawa. lahat ng bagay kabilang na ng oras.
2. Measurable (Nasusukat). Dapat pagnilayan kung ito
ba ay tumutugma sa iyong mga kakayahan sapagkat 16. • Magbigay ng mga dahilanan ng nakakapag-aksaya
kung hindi ay HINDI mo rin ito maisasakatuparan. ng oras at panahon mo? Paano mo ito nalalabanan?
8. Pagtatakda ng Tunguhin sa Paggawa _____________________________________________
3. Attainable (Naaabot). Ang tunguhin mo ay _____________________________________________
makatotohanan, maabot at mapanghamon. _____________________________________________
4. Realistic (Makatotohanan). Mahalagang tignan ang _____________________________________________
kaangkupan ng iyong gawain sa pagtugon sa _____________________________________________
pangangailangan ng iyong kapwa at timbangin kung ito _____________________________________________
ay higit na makakabuti. _____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
9. Pagtatakda ng Tunguhin sa Paggawa _____________________________________________
5. Time Bound (Nasusukat ng Panahon). Kailangan na _____________________________________________
magbigay ng takdang panahon kung kailan mo _____________________________________________
maisasakatuparan ang iyong tunguhin. _____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
10. Pangangasiwa o Pamamahala ng Oras _____________________________________________
MAPEH 8 - Health 3rd Quarter 20. 2. RESERVOIR It is a place within which
1. Objectives: explain the chain of infection; discuss microorganisms can thrive and reproduce. “The most
the stages of infection; create a short presentation common reservoir is the human body.”
showing the chain/stages of infection; realize the 21. 3. PORTAL OF EXIT It provides a way for a
importance of knowing the chain and stages of infection microorganism to leave the reservoir. “through the
for prevention. nose, mouth, body feces”
2. TAMA MALI Activity: Tanggal ang Magkamali! 22. 4. MODE OF TRANSMISSION It is the method by
3. Instructions: You will be answering TAMA or MALI which the organism moves from one host to another.
statements. After I say “GO”, you have 10 seconds to “direct contact, indirect contact, air- borne, food-borne,
stand behind the word of your answer. The student water-borne, vector-borne”
who will get the wrong answer will be eliminated from 23. 5. PORTAL OF ENTRY It is an opening allowing the
the game. The remaining students who will get the microorganism enter the host. “body orifices, mucus
correct answer up to the last question will be awarded membranes, breaks in the skin”
with additional points. 24. They may enter through: Respiratory System
4. Statement No. 1 Communicable Diseases are diseases (inhalation) Gastrointestinal System (ingestion)
that do not transfer from one person to another. TAMA 25. They may enter through: Urinary and Reproductive
MALI Tracts (sexual contact) Breaks in the skin
5. Statement No. 2 Infectious Diseases are also called as 26. 6. THE SUSCEPTIBLE HOST It is a person who cannot
Communicable Diseases. TAMA MALI resists a microorganism invading its body.
6. Statement No. 3 Bacteria, fungi, and virus are 27. There are six links in the chain of infection
pathogens which cause diseases to the host. TAMA PATHOGEN RESERVOIR PORTAL OF EXIT MODE OF
MALI TRANSMISSIO N SUSCEPTIBL E HOST PORTAL OF ENTRY
7. Statement No. 4 The most common reservoir of CHAIN OF INFECTION
pathogens is the human body. TAMA MALI 28. STAGES OF INFECTION INCUBATION STAGE
8. Statement No. 5 The links of the chain of infection PRODROMAL STAGE ILLNESS STAGE RECOVERY STAGE
are cannot be broken. TAMA MALI 29. 1. INCUBATION STAGE It is when a person acquires
9. Statement No. 6 Coughing and sneezing are direct the pathogen until the appearance of the first sign.
modes of transmission that causes infection. TAMA “silent stage”
MALI 30. 2. PRODROMAL STAGE It is when there are non-
10. Statement No. 7 Tiredness, slight fever, and runny specific signs and symptoms appearing. “headache,
nose are some of the indications of Illness stage. TAMA runny nose, slight fever”
MALI 31. 3. ILLNESS or CLINICAL STAGE It is the time when
11. Statement No. 8 The diseases or infection is still illness reaches its highest point of development.
communicable in the recovery stage. TAMA MALI “severe aches, vomiting, high fever, sore throat, sinus
12. Statement No. 9 HIV is a communicable disease congestion”
which can be transferred by needle pricking. TAMA 32. 4. RECOVERY or CONVALESCENCE STAGE This is the
MALI time when recovery seems complete although the
13. Statement No. 10 You cannot be infected again with disease is still communicable. “pathogen has mostly
chicken pox if you have been infected already before. eliminated”
TAMA MALI 33. APPLICATION Group Presentation
14. Analysis: How did you find the activity? Most of 34. Instructions: You will be grouped into 3 groups.
the questions are all about what? Were you able to You will create a short presentation based on the task
get the correct answers honestly? How? Why have you have picked. Each group will be given 5 to 10
you eliminated from the game for the first three minutes to prepare for the presentation.
questions? Out of the activity, were you able to draw 35. Instructions: You will be rated according to the
out the topic for today? following criteria: Content – 10 pts. Presentation –
15. Analysis: How did you find the activity? Most of 10 pts. Creativity – 5 pts. Member’s participation – 5
the questions are all about what? Were you able to pts. TOTAL = 30 points
get the correct answers honestly? How? Why have 36. TASK: ROLE PLAYING You will be portraying how a
you eliminated from the game for the first three certain disease transfers from one person to other.
questions? Out of the activity, were you able to draw You will be following the links of the chain of infection.
out the topic for today? After the presentation, there will be a group
16. CHAIN OF INFECTION representative to explain what you have presented in
17. Infection An invasion of microorganisms into the front. All members should have a role to portray.
body that are capable of producing a disease. 37. TASK: POSTER MAKING You will be making a
18. There are six links in the chain of infection poster about the chain of infection. You substitute the
PATHOGEN RESERVOIR PORTAL OF EXIT MODE OF names of the links of the chain of infection with
TRANSMISSIO N SUSCEPTIBL E HOST PORTAL OF ENTRY symbols. There should have a group representative to
CHAIN OF INFECTION present your output.
19. 1. PATHOGEN It is an organism with the ability to 38. TASK: NEWS CASTING There will be students who
cause disease. “bacteria, virus, fungi, protozoa, parasitic will act as news reporters in front of the class.
worms, rickettsiae” Members of the group should make a simple script to
report by the reporters. The script should be about
the stages of infection.
39. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ 1. These are each number. (A is 1st step, B 2nd step, so on..)
diseases which are transferred from one person to EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ
another. 59. _____ 6. Convalescence stage is recovery stage.
40. 2. What is the disease- causing microorganism that _____ 7. Illness stage is when specific severe signs and
attack the body and infect cells? EVALUATION: PEN AND symptoms appear. _____ 8. Incubation stage is when a
PAPER QUIZ person acquires the pathogen. _____ 9. Prodromal
41. 3. This is the interval between entrance of pathogen stage is when there are non-specific signs and
into the body to the appearance of first symptoms. symptoms appearing. _____ 10. Decline stage time
EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ when the signs and symptoms of the sick person slowly
42. 4. It is the route of escape of the pathogen from the go down. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ
reservoir. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ 60. _____ 6. Convalescence stage is recovery stage.
43. 5. The stage of infection wherein the illness reaches _____ 7. Illness stage is when specific severe signs and
its highest point of development. EVALUATION: PEN symptoms appear. _____ 8. Incubation stage is when a
AND PAPER QUIZ person acquires the pathogen. _____ 9. Prodromal
44. Arrange the following processes in chronological stage is when there are non-specific signs and
order. Write letters A to E on the space provided before symptoms appearing. _____ 10. Decline stage time
each number. (A is 1st step, B 2nd step, so on..) when the signs and symptoms of the sick person slowly
EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ go down. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ E C A B D
45. _____ 6. Convalescence stage is recovery stage. 61. _____ 11. passed through a direct or indirect Mode
_____ 7. Illness stage is when specific severe signs and of Transmission. _____ 12. reservoir which can be a
symptoms appear. _____ 8. Incubation stage is when a living or non-living object. When the pathogen _____
person acquires the pathogen. _____ 9. Prodromal 13. Susceptible Host if one who has a low immunity
stage is when there are non-specific signs and resistance is the next victim. _____ 14. leaves the
symptoms appearing. _____ 10. Decline stage time reservoir through a Portal of Exit, the pathogen is _____
when the signs and symptoms of the sick person slowly 15. The organism enters then the body through a Portal
go down. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ of Entry and the The chain of infection starts when a
46. _____ 11. passed through a direct or indirect Mode pathogen lives in …
of Transmission. _____ 12. reservoir which can be a 62. _____ 11. passed through a direct or indirect Mode
living or non-living object. When the pathogen _____ of Transmission. _____ 12. reservoir which can be a
13. Susceptible Host if one who has a low immunity living or non-living object. When the pathogen _____
resistance is the next victim. _____ 14. leaves the 13. Susceptible Host if one who has a low immunity
reservoir through a Portal of Exit, the pathogen is _____ resistance is the next victim. _____ 14. leaves the
15. The organism enters then the body through a Portal reservoir through a Portal of Exit, the pathogen is _____
of Entry and the The chain of infection starts when a 15. The organism enters then the body through a Portal
pathogen lives in … of Entry and the The chain of infection starts when a
47. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ Let’s check! pathogen lives in … C A E B D
48. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ 1. These are 63. ASSIGNMENT Now that you have understood the
diseases which are transferred from one person to stages of infection, choose the stage where you think is
another. the best stage to CUT from the flow of infection and
49. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ Correct explain why you chose that stage. Write your answer in
Answer: 1. Communicable Diseases or Infectious a ¼ sheet of paper. Research also on the internet the 6
Diseases kinds of pathogens and list 3 examples of diseases that
50. 2. What is the disease- causing microorganism that are caused by those pathogens.
attack the body and infect cells? EVALUATION: PEN AND
PAPER QUIZ
51. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ Correct
Answer: 2. Pathogen (Causative Agent)
52. 3. This is the interval between entrance of pathogen
into the body to the appearance of first symptoms.
EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ
53. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ Correct
Answer: 3. Incubation Stage
54. 4. It is the route of escape of the pathogen from the
reservoir. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ
55. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ Correct
Answer: 4. Portal of Exit
56. 5. The stage of infection wherein the illness reaches
its highest point of development. EVALUATION: PEN
AND PAPER QUIZ
57. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ Correct
Answer: 5. Illness Stage or Clinical Stage
58. Arrange the following processes in chronological
order. Write letters A to E on the space provided before
MAPEH 8 - Health 3rd Quarter MAPEH 8 – PE 3rd Quarter
16. CHAIN OF INFECTION SCRABBLE - MAPEH 8 (Physical Education 3rd Quarter)
17. Infection An invasion of microorganisms into the 1. SCRABBLE® MR. CARLO JUSTINO J. LUNA Malabanias
body that are capable of producing a disease. Integrated School Angeles City PHYSICAL EDUCATION
18. There are six links in the chain of infection PATHOGEN Unit 3 – Indoor Recreational Activities
RESERVOIR PORTAL OF EXIT MODE OF TRANSMISSIO N 2. SCRABBLE • An internationally popular word game
SUSCEPTIBL E HOST PORTAL OF ENTRY CHAIN OF where word power, strategy and luck are equally
INFECTION important • A word game in which two to four players
19. 1. PATHOGEN It is an organism with the ability to score points by placing tiles onto a game board which is
cause disease. “bacteria, virus, fungi, protozoa, parasitic divided into a 15×15 grid of squares
worms, rickettsiae” 3. SCRABBLE • Recognized as an excellent means for
20. 2. RESERVOIR It is a place within which increasing vocabulary and word power • Helps improve
microorganisms can thrive and reproduce. “The most analytical skills and sharpens mathematical ability • The
common reservoir is the human body.” benefits will develop more if you directly engage in the
21. 3. PORTAL OF EXIT It provides a way for a game with your family and friends.
microorganism to leave the reservoir. “through the nose, 4. History
mouth, body feces” 5. ➜In 1931, Alfred Mosher Butts translated his lifelong
22. 4. MODE OF TRANSMISSION It is the method by love of crossword puzzles into a board game. ➜A key to
which the organism moves from one host to another. the game was Butts' analysis of the English language.
“direct contact, indirect contact, air- borne, food-borne, Butts studied the front page of The New York Times to
water-borne, vector-borne” calculate how frequently each letter of the alphabet was
23. 5. PORTAL OF ENTRY It is an opening allowing the used. HISTORY
microorganism enter the host. “body orifices, mucus 6. ➜He then used each letter's frequency to determine
membranes, breaks in the skin” how many of each letter he would include in the game.
24. They may enter through: Respiratory System
➜He included only four "S" tiles so that the ability to
(inhalation) Gastrointestinal System (ingestion)
make words plural would not make the game too easy.
25. They may enter through: Urinary and Reproductive HISTORY
Tracts (sexual contact) Breaks in the skin
7. ➜Butts initially called the game "Lexiko", but later
26. 6. THE SUSCEPTIBLE HOST It is a person who cannot
changed the name to "Criss Cross Words", after
resists a microorganism invading its body.
27. There are six links in the chain of infection PATHOGEN considering "It", and began to look for a buyer. ➜The
RESERVOIR PORTAL OF EXIT MODE OF TRANSMISSIO N game makers he originally contacted rejected the idea,
SUSCEPTIBL E HOST PORTAL OF ENTRY CHAIN OF but Butts was tenacious. HISTORY
INFECTION 8. ➜Eventually, in 1948, he sold the rights to
28. STAGES OF INFECTION INCUBATION STAGE entrepreneur and game-lover James Brunot, who made
PRODROMAL STAGE ILLNESS STAGE RECOVERY STAGE a few minor adjustments to the design and renamed the
29. 1. INCUBATION STAGE It is when a person acquires game "Scrabble", a word meaning "to grope frantically"
the pathogen until the appearance of the first sign. (from the Dutch "Schrabben", to scrape or scratch)
“silent stage” HISTORY
30. 2. PRODROMAL STAGE It is when there are non- 9. The HARDWARE
specific signs and symptoms appearing. “headache, 10. The Hardware • The Scrabble Board • Tile Bag with
runny nose, slight fever” 100 Tiles • Tile Racks • Timers or Clocks
31. 3. ILLNESS or CLINICAL STAGE It is the time when 11. The Scrabble® Board • The board has a 15x15 grid. •
illness reaches its highest point of development. “severe The board is composed of 225 squares and 100 tiles. • It
aches, vomiting, high fever, sore throat, sinus can be played by two to four players.
congestion” 12. The Scrabble® Board Double Word Score Triple Word
32. 4. RECOVERY or CONVALESCENCE STAGE This is the Score Double Letter Score Triple Letter Score • Some of
time when recovery seems complete although the the squares are premium.
disease is still communicable. “pathogen has mostly 13. Points Per Letter 1 point: A, E, I, O, U, L, N, R, S, T 2
eliminated” points: D, G 3 points: B, C, M, P 4 points: F, H, V, W, Y 5
41. 3. This is the interval between entrance of pathogen points: K 8 points: J, X 10 points: Q, Z
into the body to the appearance of first symptoms. 14. Scrabble®: Fun with Words The idea of the game is to
EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ score points making words.
42. 4. It is the route of escape of the pathogen from the 15. Player’s Turns Put all letter tiles into the tile bag or
reservoir. EVALUATION: PEN AND PAPER QUIZ any suitable container. Draw for the first play. The player
43. 5. The stage of infection wherein the illness reaches drawing the letter nearest the beginning of the alphabet
its highest point of development plays first. A blank supersedes all other tiles. Return the
tiles into the bag and reshuffle. Each player draws 7 tiles
and places them on his/her track. Turn of players follow
clockwise. BEFORE THE GAME
16. Word Judge To decide word challenges, a word judge
is elected by the players who may be one of them. He or
she may also act as the scorekeeper who keeps a tally of
each player’s score, entering it after each turn. BEFORE 28. Premium Word Squares The premium square
THE GAME “DOUBLE WORD SCORE” doubles the score of the word
17. Dictionary Before the game begins, the players must when one of the letters is placed on it, and “TRIPLE
first agree on the dictionary to be used in settling WORD SCORE” triples the score of the word when one of
challenges on what words to allow or not to allow. its letters is placed on it. Count LETTER premiums if any,
BEFORE THE GAME before doubling or tripling the WORD score. If a word is
18. Start of Play The first player forms a word with two formed that covers TWO double word squares, the score
or more of his/her letters and positions it on the board is doubled then redoubled (4 times word score). If a word
to read across or down with one letter on the center is formed that covers TWO triple word squares, the score
(MB) square. Placing a word diagonally on the board is is triple then retripled (9 times word score). SCORING
not allowed. BEFORE THE GAME THE GAME
19. Completing a Turn A player completes a turn by 29. Pearly Twins The two blanks by themselves have no
counting and announcing the score for the turn. The score value but when a blank is played on a premium
player then draws as many letter tiles as played, thus, word square, the value of the word is doubled or tripled
always keeping 7 letters on his/her track. BEFORE THE as indicated. SCORING THE GAME
GAME 30. Multiple Score When two or more words are formed
20. Subsequent Turns Play proceeds to the left. The in the same play, each is scored. The common letter is
second player, and then each in turn, adds one or more counted with full premium value, if any, for each word.
letters to those already played to form new words. All SCORING THE GAME
letters played on a turn must be placed in one row across 31. Bingo Score Any player who plays 7 tiles on a turn,
or down the board to form one complete word. PLAYING scores a bonus of 50 points added to the total of his/her
THE GAME score for the turn. SCORING THE GAME
21. Forming New Words New words may be formed by: 32. ENDING THE GAME The game ends when all the tiles
➜ Adding one or more letters to a word or letters have been drawn and one of the players has used all the
already on the board ➜ Placing a word at right angles to tiles in his/her rack. The game also ends when all possible
word already on the board. The new word must use one plays have been made or all players have passed twice in
of the letters already on the board or add a letter to it ➜ a consecutive turns.
Placing a complete word parallel to a word already 33. ENDING THE GAME At game’s end, each player’s
played so that adjacent letters also form complete words score is reduced by the sum of his/her rack unplayed
PLAYING THE GAME letters. In addition, if a player used all tiles on his/her
22. Blank Tiles The two blank tiles may be used as any rack, the sum of the other players’ unplayed letters is
letters. When playing a blank, the player must state added to that player’s score.
which letter it represents. It remains that latter for the 34. ENDING THE GAME The player with the highest final
rest of the game. PLAYING THE GAME score WINS the game. Players who tie for the highest
23. Replacing Tiles Any player may use his or her turn to final score shall equally be considered as winners
replace any or all of the tiles in his/her rack, discarding (DRAW).
them face down, drawing the same number of new tiles 35. BASIC MOVES
from the bag, and mixing the discarding tiles with those 36. BASIC MOVES 1. To play through an existing letter 2.
remaining in the bag. Replacing tiles is considered a turn Hooking a letter to the front or back of an existing word
and the score is zero. PLAYING THE GAME to create new words 3. Extension play – extending a pre-
24. Passing A player may voluntarily miss a turn. Instead existing word 4. Parallel play – placing a word parallel to
of placing tiles on the board or replacing tiles, a player an existing word such that more than one word is formed
may also decide to pass whether or not he/she is able to A BINGO is a move in which all seven tiles are used. a
make a word or words. Passing a turn scores zero. bonus of 50 points is added to the score for scoring a
PLAYING THE GAME bingo.
25. Challenge Any word may be a challenged before the 37. BASIC MOVES Example with “A R M” already played
next player starts a turn. If the word challenged is on the board and the 7 tiles on your rack being “U B D N
unacceptable, the challenged player takes back his/her A H S” A¹ R¹ M³
letter tiles, loses that turn and scores zero. If the word 38. BASIC MOVES Playing through an existing letter A¹ R¹
challenged is acceptable, the score is entered and the M³ B³ A¹ N¹ D²
game continues with no penalty to the challenger. 39. BASIC MOVES Hooking a letter to the front or back of
PLAYING THE GAME an existing word to create new words A¹ R¹ M³ B³ A¹ N¹ D²
26. Turn Score The score of each turn is the sum of the S¹Hч A¹ N¹ D²
letter values in each word formed or modified on that 40. BASIC MOVES Extension Play Extending a pre-existing
turn plus the additional points obtained from placing word A¹ R¹ M³ B³ A¹ N¹ D² S¹
letters on premium squares. The score value of each 41. BASIC MOVES Parallel Play Placing a word parallel to
letter is indicated by the number at the bottom of the an existing word such that more than one word is
tile. The score value of a blank is zero. SCORING THE formedA¹ R¹ M³ B³ A¹ H4
GAME 42. BASIC MOVES BINGO All seven tiles are used +50
27. Premium Letter Squares The premium letter square points A¹ R¹ M³ Hч U¹ S¹ B³ A¹ N¹ D² Hч U¹ S¹ B³ A¹ N¹ D²
“DOUBLE LETTER SCORE” doubles the value of the letter
placed on it, and “TRIPLE LETTER SCORE” triples the value
of the letter placed on it. SCORING THE GAME
20. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 2.
Music of India - MAPEH 8 (Music Avanaddh Daf (Duf, Daphu) Tabla Dhol
3rd Quarter) 21. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 3. Sushir
1. INDIA also known as blown air is characterized by the use of
2. FLAG air to excite the various resonators
3. Capital: New Delhi Largest City: Mumbai Official 22. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 3. Sushir
Language: Hindi Bansuri Shehnai Shankh Surpeti
4. Demonym: Indian Currency: Indian Rupee (INR) 23. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 4. Tat
Religion: Hinduism (79.8%) referred to as vina during the old civilization
5. India is the largest country in South Asia. The music Instruments in this class are plucked (stringed
of India reflects different aspects of Asian culture instruments)
through its timbre, rhythm, melody, texture, form, and 24. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 4. Tat
style. Sitar Gottuvadyam Ektar GopichandRabab
6. Vocal Music of India includes Carnatic and Hindustani 25. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 5. Vitat
music, and several types of folk and popular music uses described as bowed stringed instruments is of the
melismatic singing with nasal vocal quality oldest classifications of instruments and yet did not
7. Samagana singing based on a set of pitches popular occupy a place in classical Indian music until the last few
during the Vedic times centuries
8. Sama Veda a sacred text, were sung as Samagana 26. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 5. Vitat
and not chanted is the third of the four Vedas of Banam Esraj Chikara Sarangi
Hinduism but ranks next to Rig Veda (Rigveda) in terms
of its sanctity and liturgical importance
9. Rig Veda is also sung in the Samagana traditional
Grade 8 Arts - 3rd Quarter
singing style is counted as first among the four 1. Lesson 3: Pakistan
canonical sacred texts of Hinduism known as Vedas 2. Four recognized periods in Pakistani architecture:
10. Rig Veda is an ancient Indian sacred collection of •Pre-Islamic •Islamic •Colonial •Post-Colonial
Vedic Sanskrit hymns 3. Around 3rd millennium BCE: •Advanced urban culture
11. Characteristics of Traditional Indian Music Carnatic was developed •Large Buildings were Built
Music refers to music from South India directed to a 4. Mohenjo Daro •means “mound of the dead men”
Hindu god, which is why it is called “temple music” •built around 2500 BCE •one of the world’s earliest
Music pieces are mainly set for the voice and with lyrics. major urban settlements
Compositions called krti are devotional songs. 5. Ancient City of Harappa • believed to have as many as
12. Characteristics of Traditional Indian Music Carnatic 23,500 residents • both Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa are
Music is unified where schools are based on the: generally characterized as having "differentiated living
same ragas same solo instruments (veena, flute, violin) quarters, flat-roofed brick houses, and fortified
same rhythm instruments (mridangam and ghatam) administrative or religious centers.
13. Characteristics of Traditional Indian Music Hindustani 6. Kot Diji • it is a fortress • the forerunner of the Indus
Music goes back to Vedic period times around 1000 BC Civilization. • Located about 22 kilometers south of
further developed in the 13th and 14th centuries AD Khairpur in the province of Sindh, Pakistan.
with Persian influences and from existing religious and 7. •Brightly colored flamboyant trucks •Painted with
folk music predominantly found in the northern and images of: •idealized landscapes •Famous personalities
central regions •Flowers •Trees •Turns village lanes, city streets, and
14. Characteristics of Traditional Indian Music Hindustani long- distance highways into gallery without walls •A
Music influenced by ancient Hindu musical traditions, free-form, kaleidoscopic exhibition in motion
historical Vedic religion / Vedic philosophy, native Indian 8. Other arts of Pakistan •Painted chests and jars
sounds and enriched by the Persian performance 9. Lesson 4: UZBEKISTAN, KAZAKHSTAN, AND TAJIKISTAN
practices of the Mughal area nasal singing is observed 10. Printed Cloth of Uzbekistan •People who lived there
in their vocal music are known for making printed cloth. •Printed tablecloths,
15. Characteristics of Traditional Indian Music Hindustani curtains, bedspreads, shawls, and various coverlets were
Music In North India, the most common style of singing used and served as a daily-round ornament as well
is called khyal, a word which means “imagination” 11. Artistic Ceramics and Clothing of Uzbekistan
16. Instrumental Music of India Hindustani Sangeet – 12. The Pearl of Asia: Uzbekistan
instruments used in North Indian music Carnatic 13. Visual Arts of Kazakhstan •In ancient times, nomads
Sangeet – instruments used in South Indian music used to draw on rocks (petroglyphs)
17. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 1. Ghan 14. •Fine art in Kazakhstan varies in style, direction, and
described as a non-membranous percussive genre •The most captivating work by Kazakhstan artists
instrument but with solid resonators is one of the can be seen in their museums
oldest classes of instrument in India may also be a 15. Feel the Beauty of Kazakhstan
melodic instrument or instruments to keep tal 16. The Art of Decorative Carvings of Tajikistan •For
18. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 1. Ghan many centuries, Tajiks have been making fabrics,
Ghatam Kartal Manjira Nout utensils, musical instruments, carpets, furniture, and
19. Classification of Indian Musical Instruments 2. jewelries •Carving is mostly present in architectural
Avanaddh described as a membranous percussive monuments, household structures and objects, musical
instrument typically comprise the drums instruments, and souvenirs.
17. Discover Tajikistan
18. Lesson 5: TURKEMINISTAN and KYRGYSTAN
19. TURKMENISTAN •Carpet weaving is an ancient art,
and each tribe developed its own pattern. •Turkmen
carpets have been traditionally woven out of wool,
cotton, and silk by women using horizintal looms.
20. •The traditional arts include felt manufacture,
jewelry making, woodwork, ceramics, and silverwork.
21. The country is also the source of keteni. Used for
beautiful dresses worn by Turkmen women on special
occasions.
22. Kyrgystan Kyrgyz women produce a wide range of
textiles, mostly from the felt of their sheep. Nowadays
ancient patterns are adapted to the tourist and export
market, but it is still a living tradition and that all yurts
and most houses contain hand- made carpets or rugs
called shirdaks.
23. •Tush kyiz, large elaborately embroidered wall
hangings, made by women to commemorate the
marriage of a son or daughter. •Flowers, plants, animals,
stylized horns, national designs, and emblems of Kyrgyz
life are often found in these ornate and colorful
embroideries.
24. Flat cushions called xxx, are usually made in shadow-
pairs. These are seen on every chair, padding the seat.
25. LESSON 6: ARTS AND CRAFTS OF THE MIDDLE EAST
26. •The Middle East is rich in cultural heritage, and this
is clearly evident in the 14 variety and quality of regional
arts and crafts.
27. Typical artistic forms from the region include:
•embroidery •ceramics •wood carving •inlaid wood
designs •Calligraphy •hammered metalwork •blown
glassworks
28. Although these are some of the most acclaimed art
forms contributed by the Middle East, the Middle
Eastern aesthetic can be seen in almost any product from
the region even including such things as handmade soap
from Syria or Lebanon.
Grade 10 Health UNIT 3 health trends issues and concern Prevention and Control of Non- Communicable Diseases.
Global level Global Health Initiatives
1. QUARTER III – MODULE HEALTH TRENDS, ISSUES AND 14. These are goals set by the United Nations for its
CONCERN (GLOBAL LEVEL) MAPEH 10 –Teacher member- nations to be fulfilled on an agreed span of
MONREAL NHS, Monreal, Masbate time (2015) to be evaluated and counter-checked under
2. This module aims to help you: • learn about different world standards. UN created MDG in 2000 in effort to
global health issues and the initiatives made to help improve life in developing regions by 2015
address these problems. • Improve understanding of 15. 1. ERADICATE EXTREME POVERTY AND HUNGER –
health concerns and how these are treated or Developing countries particularly in Africa and Asia suffer
implemented around the world and locally. At the end of from extreme poverty and hunger. Poverty and hunger
each lesson, a transfer activity will help evaluate your leads to severe malnutrition which leads to lifelong
understanding of the different topics. • You will also be physical and cognitive (learning and reasoning) damage
assessed prior to answering the different activities and and affects health, well-being and the economy. Some
again at the end of the lesson to check for knowledge, key suggestions to eradicate poverty and hunger are :
understanding, attitudes and skills learned. Education Promoting gender equality Producing
3. Todays lesson: • Definition/meaning of global health • more jobs Investing more in agriculture Strengthened
8 Millennium development goals (MDG) • UNDP’s Quick nutrition programs for children and infants
Wins to answer achieve the 8 MDG 16. 2. ACHIEVE UNIVERSAL PRIMARY EDUCATION –
4. Activity: Word Hunt With your group spot the word Persons, particularly women who are educated, are
Use whiteboard marker pen and write the answers in more likely to seek medical care especially during
your activity white pad. Procedure: 1. Look for pregnancy, ensuring proper nutrition for their family,
words/terms related global health issues and concerns adopting healthy sanitary practices and ensuring
that the World Health Organization and member-nations immunization of children. As an effect, infants and
are facing. childrenhave better survival rates, are healthier and
5. 3 M I N U T E S better nourished. If these are attained, children who
6. Guide questions: 1.List down different health, trends receive primary education are more likely to: Marry
and issues problem cited on the video you are going to and have their own families at a later stage in life
watch? 2. What are the different health services Practice family planning and have fewer children Know
mentioned in the video? Video clip viewing: WHO rights, responsibilities and civic obligations Seek
Bringing Health to life employment and sustain personal and family needs
7. The term “global health” rose in popularity along with Have decreased risk of getting sexually transmitted
the rise of globalization. Both terms improved public infections like HIV/AIDS
awareness of vulnerabilities and shared responsibilities 17. 3. PROMOTE GENDER EQUALITY & EMPOWER
among people for the different injustices in the world. WOMEN – Gender equality means equal representation
8. Global Health - pertains to various health issues, of men and women. It implies that all gender should have
concerns, and trends which go beyond national equal value and treatment. Equal gender treatment
boundaries and call for global initiatives for the empowers women and other groups creating
protection and promotion of peoples’ health across the opportunities in education, work, finances, and other
world. - Ilona Kickbush (2006) Global Health is an area for aspects which improves the economy and lessen effects
study, research and practice that prioritizes health of financial crises. Gender equality can be achieved
improvement and achieving impartiality in healthcare through: Early childhood development intervention
and wellness worldwide. - Koplan and Associates (2009) Promotion of women’s political rights and involvement
9. GLOBAL HEALTH - Diverse health issues, concerns and Improved reproductive health programs and policies
trends which call for all nations to address and act on to Education and integrating gender equality in school
promote and protect health of individuals and groups curriculum
across boundaries. 18. 4. REDUCE CHILD MORTALITY - Programs and policies
10. The primary international body responsible for which help reduce child mortality like improving
developing leadership in health, setting norms and nutritional intake, healthcare facilities and
standards and providing health support among nations infrastructure, and other fields which improve children’s
around the world. WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION lives. Strengthening local and national health programs
(WHO): and policies is one way to reduce child mortality. This
11. These are programs and projects which help address includes: Immunization programs Assuring the
global health issues, concerns and trends. Global Health survival and better health of mothers Improving
Initiatives reproductive health programs and policies Better
12. QUICK WINS -- UNDP intervention program which nutrition program for infants, children and
refers to actions that can be immediately used within the 19. 5. IMPROVED MATERNAL HEALTH - is not only about
community or locale to produce effective results. (See mother’s health but also involves the health and wellness
page 272-273) *UNDP – United Nations Development of the family. Maternal health also helps eradicate other
Program problems like poverty, gender inequality, decreased
13. Stop TB Roll Back Malaria Global Fund to Fight workforce, lower birth deaths, and disability of women.
HIV/AIDS Malariaand otherdiseases, Framework Some ways to improve maternal health include:
Convention on Tobacco Control Comprehensive Mental Improved and proper nutrition of mothers Teaching
Health Action Plan Global Strategy to Reduce the the benefits of birth spacing and small family size
Harmful Use of Alcohol Global Strategy for the Educating young boys and girls about the importance of
maternal health Better and improved access to hospital methods which are harmful to themselves or others. 2.
care especially obstetric- gynecology, prenatal and DRUG USE & ABUSE
postnatal care 30. 3. HIV / AIDS
20. 6. COMBAT HIV/AIDS MALARIA AND OTHER DISEASES 31. It is transmitted primarily via unprotected sexual
– Emerging and re-emerging diseases like HIV/AIDS, intercourse, contaminated blood transfusions,
malaria, influenza and other diseases affect productivity hypodermic needles, and from mother to child during
and growth of nations. Some of the effects of disease pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding. 3. HIV / AIDS
outbreak are loss of jobs, shortage in professional 32. NON-COMMUNICABLE DISEASE NCD, can refer to
workers, and creating social crises. Children are the most chronic diseases which last for long periods of time and
vulnerable and are exposed to exploitation and abuse progress slowly.
undermining their normal growth and development. 33. COMMUNICABLE DISEASE - Also known as infectious
Some ways to combat diseases include effective disease or transmissible diseases. - These are illnesses
prevention, treatment and care Like: Improved housing that result from the infection, presence and growth of
conditions Increased access to anti-malarial medicines pathogenic biologic agents in humans.
Promoting safer sex behavior and preventive education 34. CLIMATE CHANGE A change in global or regional
for all Promoting Tuberculosis (TB) screening of climate patterns attributed directly or indirectly to
HIV/AIDS persons and TB - Directly Observed human activity. • “Global Warming” in sheep’s clothing.
Treatment Short (TB-DOTS) Course therapy Promoting A long-term change in the Earth’s climate. • A long-term
the use of insecticide-treated nets to fight mosquito- change in the Earth’s climate.
borne diseases 35. MENTAL HEALTH -It is a level of psychological well-
21. 7. ENSURE ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY - being and the absence of a mental disorder.
Investing and supporting sustainable energy like solar, 36. IMMUNIZATION & VACCINES - It is the safe and
wind and water energy help support jobs, create effective use of a small amount of a weakened and killed
business opportunities, and save remaining non- virus or bacteria or bits of lab made protein that imitate
renewable energy sources. Environmental sustainability the virus in order to prevent infection by the same virus
assures peoples to live healthier and enjoy a clean and or bacteria. When you get an immunization, you’re
green environment. Some of the benefits of a injected with the weakened form or a disease. This
sustainable environment are: Cleaner air and triggers your body’s immune response, causing it to
environment Clean, environment-friendly, and either produce antibodies and the like.
renewable energy New and aspiring jobs and business 37. ALCOHOL & TOBACCO ABUSE/ADDICTION The
in energy Increased access to sanitation excessive consumption of alcohol and tobacco. - Causes
22. 8. GLOBAL PARTNERSHIP FOR DEVELOPMENT - The communicable and non communicable diseases.
United Nations, World Health Organization, World Bank 38. MALARIA / OTHER VECTOR-BORNE MALARIA causes
and governments work together to make sure there is symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue, vomiting
fair trade and that heavily indebted countries obtain and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause yellow skin,
relief and funds to combat poverty, malnutrition and seizures, coma or death. VECTORS are living organisms
funds for education and social projects. Some benefits of that can transmit infectious diseases between humans or
global partnership are: Expanded international trade from animals to
agreements Improved access to affordable medicine 39. There are 195 countries in the world today. This total
Reduced poverty through government debt relief grant comprises 193 countries that are member states of the
Developed information and communication technology United Nations and 2 countries that are non-member
(ICT) observer states: the Holy See and the State of Palestine.
23. Activity: NAME THAT ICON
24. Video Clip Viewing Guide Questions: 1. How much
portion was cut in extreme poverty? 2. How Many
Percent was increased or added in universal primary
education? 3. Was gender equality has been met? Yes or
no? 4. How many children are still dying below 5 years
old? 5. How many of the women get prenatal care? 6.
How many young women are infected by HIV every
Hour? 7. How many people don’t have basic sanitation
like toilet? 8. Was the Global partnership fully achieved?
Yes/no?
25. THE 10 GLOBAL HEALTH TRENDS, ISSUES, AND
CONCERNS
26. 1.TUBERCULOS IS
27. 1.TUBERCULOSIS Commonly known as TB (Tubercle
Bacillus, is a bacterial infection that can spread through
the lymph nodes and bloodstream to any organ in your
body. It is often most found in the lungs.
28. 2. DRUG USE & ABUSE
29. It is patterned use of a drug in which the user
consumes the drug substance in amounts or with
You might also like
- Dignidad at Sekswalidad Pangalagaan NatinDocument44 pagesDignidad at Sekswalidad Pangalagaan NatinJessa C. Ramos89% (9)
- Hybrid - EsP9 Q3 Week No.2Document9 pagesHybrid - EsP9 Q3 Week No.2SirNick DiazNo ratings yet
- EsP 9 Modyul 7 Activy SheetsDocument12 pagesEsP 9 Modyul 7 Activy SheetsDangay National High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Ap 10 Q3 Week 3 4Document4 pagesAp 10 Q3 Week 3 4JOHN WAYNE CARL AGUIONo ratings yet
- DyornalDocument5 pagesDyornalanon_462259979No ratings yet
- PIVOT-EsPAPEL-G10 Q3 W4Document4 pagesPIVOT-EsPAPEL-G10 Q3 W4EUNICE PORTONo ratings yet
- LAS-EsP10 Q1 WEEK7Document3 pagesLAS-EsP10 Q1 WEEK7KimNo ratings yet
- Esp 3RDDocument8 pagesEsp 3RDKalia SharNo ratings yet
- EsP9 - Q4LAS Week 1.2Document5 pagesEsP9 - Q4LAS Week 1.2Paul Romano Benavides RoyoNo ratings yet
- HGP5 Q4 Week4 Carmela-M.-santosDocument8 pagesHGP5 Q4 Week4 Carmela-M.-santosdeonel dan moyanoNo ratings yet
- LS4 Magtagumpay Sa NegosyoDocument2 pagesLS4 Magtagumpay Sa NegosyoMK Dizon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Modyul & Journals 5-8Document5 pagesModyul & Journals 5-8Ritchel San Mateo MendozaNo ratings yet
- MAHABANG PAGSUSULIT SA EsP VII (3rd Quarter)Document2 pagesMAHABANG PAGSUSULIT SA EsP VII (3rd Quarter)UnissNo ratings yet
- Esp7 q2 w4 Srudentsversion v4Document10 pagesEsp7 q2 w4 Srudentsversion v4Albert Ian CasugaNo ratings yet
- Esp 3rd Quarter Parallel and Activity SheetDocument7 pagesEsp 3rd Quarter Parallel and Activity SheetCycris Bungabong Unggoy MadinoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 ESP 7 3rd QRTRDocument27 pagesWeek 3 ESP 7 3rd QRTRTan JelynNo ratings yet
- EsP 10 UNANG MARKAHAN - MODYUL 7Document11 pagesEsP 10 UNANG MARKAHAN - MODYUL 7Carra MelaNo ratings yet
- Activity No.2Document1 pageActivity No.2Mayen FetalveroNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Worksheets 1 Araling Panlipunan 9Document6 pagesLearning Activity Worksheets 1 Araling Panlipunan 9Mathewgabriel MolatoNo ratings yet
- Katapatan Sa Salita at Gawa: Mga InaasahanDocument10 pagesKatapatan Sa Salita at Gawa: Mga InaasahanadamcabasNo ratings yet
- AS Q2 Week 7 8Document2 pagesAS Q2 Week 7 8gutierrezdanica20No ratings yet
- HARMONIZED-TASK-2nd-Quarter For PhotoDocument8 pagesHARMONIZED-TASK-2nd-Quarter For PhotoMARY ANN PEREZ MANALONo ratings yet
- Quiz PananawDocument2 pagesQuiz PananawClydylyn Jane Pastor (Clyd)No ratings yet
- Quiz EspDocument2 pagesQuiz EspDuke Noah WynknightNo ratings yet
- Smile-G8 LP5-Q1 3.1Document7 pagesSmile-G8 LP5-Q1 3.1Romeo jr RamirezNo ratings yet
- EsP7 Q3 MOD1 Birtud at PagpapahalagaDocument18 pagesEsP7 Q3 MOD1 Birtud at PagpapahalagaDionyLisingGonzalesNo ratings yet
- Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao: Kaibigan Ko! Kilalanin MoDocument16 pagesEdukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao: Kaibigan Ko! Kilalanin MoHoney pil OmandamNo ratings yet
- Esp 9 Week 3Document2 pagesEsp 9 Week 3Brige SimeonNo ratings yet
- Esp 9 Q - 2 Module 16Document10 pagesEsp 9 Q - 2 Module 16Raymart NaagNo ratings yet
- ESP 8 2nd QUARTERDocument8 pagesESP 8 2nd QUARTERARVIN TABIO100% (1)
- 1st Periodical Test ESP 10Document3 pages1st Periodical Test ESP 10Marie Antonette Dacanay LaraNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips - 3rd Quarter Exam Esp G 9docxDocument3 pagesQdoc - Tips - 3rd Quarter Exam Esp G 9docxKaren BlythNo ratings yet
- 1.3-Moral Na Pagpapahalaga Nagpapatatag Sa LipunanDocument1 page1.3-Moral Na Pagpapahalaga Nagpapatatag Sa LipunanHazel Torres BadayosNo ratings yet
- Araling Panlipunan Lm2 q2 Grade10Document9 pagesAraling Panlipunan Lm2 q2 Grade10Jovi AbabanNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Week 5-6 - Quarter1Document3 pagesActivity Sheet Week 5-6 - Quarter1RECEL PILASPILASNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2LINDSY MAE SULA-SULANo ratings yet
- Las Esp6 Q1 Week7Document7 pagesLas Esp6 Q1 Week7Laiza AlabadoNo ratings yet
- EsP 7 Modyul 5 QuizDocument1 pageEsP 7 Modyul 5 QuizMitzie OsabelNo ratings yet
- LeaP ESP G6 Week 6 Q4Document3 pagesLeaP ESP G6 Week 6 Q4Glydel Eveth EnriquezNo ratings yet
- ESP Q2 Week 3Document3 pagesESP Q2 Week 3ronaldlumapac28No ratings yet
- Grade 6 - Learning Activities 1-8Document2 pagesGrade 6 - Learning Activities 1-8heart angel payawalNo ratings yet
- Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao 3.1 AbDocument4 pagesEdukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao 3.1 AbRomeo jr RamirezNo ratings yet
- Esp7 q2 w7 Studentsversion v2Document9 pagesEsp7 q2 w7 Studentsversion v2Albert Ian CasugaNo ratings yet
- Values Enhancement HandoutsDocument24 pagesValues Enhancement HandoutsCherry AldayNo ratings yet
- ESP 8-RemedialDocument3 pagesESP 8-RemedialAmelinda ManigosNo ratings yet
- ESP8 Q2 - Remedial ActivitiesDocument9 pagesESP8 Q2 - Remedial ActivitiesEileen Nucum CunananNo ratings yet
- Q3 Val7 Lesson6Document3 pagesQ3 Val7 Lesson6mark jay legoNo ratings yet
- ESPQ3W4Document3 pagesESPQ3W4Ynnej GemNo ratings yet
- PAGSASABUHAYinterviewDocument1 pagePAGSASABUHAYinterviewGeojanni PangibitanNo ratings yet
- EsP 8 - Q4 - LAS 3 RTPDocument4 pagesEsP 8 - Q4 - LAS 3 RTPFlor Valencia100% (1)
- Ap8 Week 2-3 Activity SheetDocument8 pagesAp8 Week 2-3 Activity SheetAnna Mary Devilla Castillo100% (1)
- Activity Sheet RemedialDocument5 pagesActivity Sheet RemedialJaycarlo AbaigarNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY SHEETS Quarter 1 Week 1Document9 pagesACTIVITY SHEETS Quarter 1 Week 1Rojanie EstuitaNo ratings yet
- Modyul 4Document3 pagesModyul 4Eden BayaniNo ratings yet
- EsP SLM 3.1Document10 pagesEsP SLM 3.1Nhean DawiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Sa PakikipagkapwaDocument2 pagesWorksheet Sa PakikipagkapwaDionyLisingGonzales67% (3)
- Comprehensive Nursing Health History QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesComprehensive Nursing Health History QuestionnaireNicole Faith L. NacarioNo ratings yet
- MUDYUL 2 ESP 9 WebinarDocument21 pagesMUDYUL 2 ESP 9 WebinarJossie Laquio BatbatanNo ratings yet