Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design Examples 1 2 of Circular Silo 1 PDF
Design Examples 1 2 of Circular Silo 1 PDF
Uploaded by
Shita AlemieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design Examples 1 2 of Circular Silo 1 PDF
Design Examples 1 2 of Circular Silo 1 PDF
Uploaded by
Shita AlemieCopyright:
Available Formats
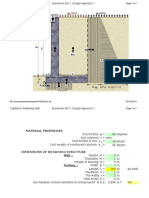
Design Example 1
Design the wall and hopper of a wheat silo with an internal diameter of 10 meter and with
the height of cylindrical portion of 40 m. The central hopper is supported by eight
columns monolithic with the lower walls. The Roof load ( DL = 150 kg/m2 and LL= 100
kg/m2)
Use the following parameter
f c' 350 kg / cm 2
f y 4200 kg / cm 2
800 kg / m 3
25o
' 0.444
1.5m
D= 10m
40m
60m
20m
10m
1.5m
ENGC6353 Dr. Mohammed Arafa Page 1
Solution
Assume angle of response = =25
2
hs 5 tan 25 2.33 hs 1.5m
3
k 1 sin 25 0.577
R
4D 2
D 4 10 / 4 2.5m
D
H / D 40 /10 4
Overpressure Factor Cd
H / D 40 /10 4
From Table 1
upper H1 cd 1.5
lower 2/3 H cd 1.85
Hooper use cd 1.5
ACI313-4.4.3.2 allows to use cd =1.35 for the Hooper
At the bottom of the silos
At the bottom of the silos Y=40-1.5=38.5m
R
1e
R
q
' kY
7.65 t/m 2
'k
P kq 4.42 t/m 2
Ring Tension
C d Pu D 1.85 1.7 4.42 10
T 69.5 ton
2 2
T 69.5
A st 18.4 cm 2 /m ie. 9.2 cm 2 /m for each side
f y 0.9 4200
use 12@12.5cm
If slip forming will be used:
T 69.5
A st 19.4 cm 2 /m ie. 9.7 cm 2 /m for each side
0.95 f y 0.95 0.9 4200
Minimum Thickness
t=
ε sh E s f s nfct
T
0.0003 200 104 1680 8 35 4.42 10
=7.5 cm
100f s fct 100 1680 35 2
ENGC6353 Dr. Mohammed Arafa Page 2
The thickness of silo walls shall be not less than 150 mm for cast-in-place concrete.
Use Wall thickness t=20cm
Vertical Loads
Weight of the wall Wt 2.5 0.2 60 30 ton / m
Friction V Y q R
atY 38.5 V 0.8 38.5 7.65 2.5 57.9 ton/m
0.15 D 2 / 4
Roff DL= =0.15 10 4 0.375 ton / m
D
LL 0.10 10 / 4 0.25 ton / m
Pver 1.7 57.9 0.375 1.4 30 0.25 141.4 ton
Check for Buckling
141.4
f c ,vert 101 kg/cm 2
0.7 20 100
Pnw 0.55 f c' 0.55 0.7 350 134.75 f c ,vert
The buckling does not control
A st 0.002 20 100 4 cm 2 /m 5.0m
Design for the Hopper
q y q0 hy
at h y 1.0 m
4.1
q y 7.65 0.8 1 8.45 t/m 2
W L = weight of the material in hopper 5.8m
0.8
4.1 0.75 5.8 84.4 ton
2 2
WL=
3
2.5 0.75
Wg= 2 4.1 0.2 2 0.75 0.2 5.8 29.5 ton
3
Merdional forces and required reinforcing
qy D WL Wg
Fmu 1.7 1.4
4sin D sin D sin
1.5 8.45 2 4.1 84.4 29.5
Fmu 1.7 1.4 59.2 ton/m
4sin 60 2 4.1 sin 60 2 4.1 sin 60
59.2
A st 16.5cm 2 /m
0.9 4200
ENGC6353 Dr. Mohammed Arafa Page 3
Hoop Reinforcement
1.5 q D
Ftu 1.7
2sin
q P sin 2 q cos 2
where P kq 0.577 8.45 4.87 t/m 2
q 4.87 sin 2 60 8.45cos 2 60 5.765t/m 2
assume ' 25
q y tan 8.45 tan 30
or q p n 4.67t/m 2
tan tan ' tan 30 tan 25
use q p n 4.67t/m 2
1.5 5.765 2 4.1
Ftu 1.7 59.6 ton/m
2sin 60
69.6
A st, hopper 19.4 cm 2 /m
0.9 4200
ENGC6353 Dr. Mohammed Arafa Page 4
Design of the Circular Beam
a1 100
33cm
b1 90
33 a2 100
28.5 b 2 57
100cm
28.5
r=467cm
100 R=4.67m
A r 6150
32.9
32.9
x 32.9cm , y 42.3cm
a 87.2cm
90 90cm
b 74.5cm
M t 0.285 684 19.5 t .m
R 5 32.9 /100 4.67m
q y 7.65 0.8 100 42.3 /100 8.1 t / m 2
W L 0.8
3
4.67 2
0.752 6.24 116.5ton
W g 2.5 2 4.1 0.2 2 0.75 0.2 5.8 29.5ton
3
q D WL Wg
Fmu 1.7 y 1.4 D sin
4sin D sin
1.5 8.1 10 116.5 29.5
Fmu 1.7 1.4 68.4 ton
4sin 60 10 sin 60 10 sin 60
Fx Fmu cos 68.4 cos 60 34.2ton
Fy 0.615 2.5 1.4 68.4sin 60 61.5ton
Location Shear Comp. Force Bending Moment Mt due
due to Fx due to Mt Due to Fy to Fy
Support 112.5 159.4 91 69.4 0
Midspan 0 159.4 91 34.86 0
9 33 form support 64.7 159.4 91 0 5.34
ENGC6353 Dr. Mohammed Arafa Page 5
Example 2
If the silo’s bottom in Example 1 is a circular slab with central opening on the lower walls
and carrying hopper forming concrete fill.
Load on the slab
a) Load from wheat in Hopper (assume uniform)
3 5 5 0.8
2
WL 1.3 t/m 2
5
2
at y=38.5 m ie. h=40m
q=7.65 t/m2 10m
p=kq=4.42 t/m2 40m
Total LL=7.65+1.3=9 t/m2
b) Dead Load
5m
Weight of Hopper forming fill
50cm
2 3 5 5 2.5
2
Wg 8.33 t/m 2 7m
5
2
Slab weight assume 40 cm slab thickness
W slab 0.4 2.5 1.0 t/m 2
DLtotal 8.33 1.0 9.33 t/m 2
W u 1.7 9 1.4 9.33 28.4 t/m 2
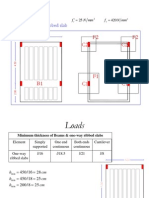
Design of the slab Holes
Slabs with holes may be designed in two ways
By computing bending moments for slabs with no holes and reinforcing with a
steel member with adequate strength and of stiffness equal to that of removed slab.
By considering the hole and reinforcing for bending moments obtained using
tables or Timoshenko equations.
ENGC6353 Dr. Mohammed Arafa Page 6
Check for shear on slab
28.4 5 0.35
2
Vu 66 ton
2 5 0.35
V c 0.53 0.85 300 35 2 5 0.35 798 ton V u
Total reaction at the bottom wall must includes
From Roof, Material above the Hopper, Material in the Hopper, Hopper filling form,
Bottom Slab, Upper Wall, and Lower Wall
ENGC6353 Dr. Mohammed Arafa Page 7
You might also like
- 2.4L PSI Engine Parts ManualDocument45 pages2.4L PSI Engine Parts ManualErin Davila100% (1)
- Structural Design of Steel Bins and SilosDocument36 pagesStructural Design of Steel Bins and Silosyoussefayay92% (12)
- Design Examples 1 2 of Circular Silo 1 PDFDocument7 pagesDesign Examples 1 2 of Circular Silo 1 PDFlahlou_d921650% (2)
- Project Management Plan ExampleDocument10 pagesProject Management Plan Example1094No ratings yet
- Calculation For D12m SiloDocument3 pagesCalculation For D12m SiloHaftamu Tekle80% (10)
- Silo Design CementDocument4 pagesSilo Design Cementkvamshi_1971100% (7)
- Concrete Silo Design According To EuroCodeDocument14 pagesConcrete Silo Design According To EuroCodeJay Ryan Santos50% (2)
- Design of Counterfort Retaining WallDocument14 pagesDesign of Counterfort Retaining WallMonjit Gogoi100% (5)
- General NotesDocument3 pagesGeneral NotesElline Ivy Calitis88% (8)
- Silo Design Final For Mombasa Is NiladriDocument18 pagesSilo Design Final For Mombasa Is NiladrijnmanivannanmechNo ratings yet
- Silo Design WebDocument1 pageSilo Design Weblecongdinh100% (1)
- Design of Hopper BottomDocument1 pageDesign of Hopper Bottomamir1911411No ratings yet
- Prestressed Silo DesignDocument11 pagesPrestressed Silo DesignmahakNo ratings yet
- Design of Silos 2010Document21 pagesDesign of Silos 2010Topaca Paec100% (3)
- IS Code For Steel Bin Design - 9178Document29 pagesIS Code For Steel Bin Design - 9178krishna kumar50% (2)
- Conc Silos 20101Document53 pagesConc Silos 20101cdvreugd100% (1)
- Retain Wall Counter FortDocument48 pagesRetain Wall Counter FortSWADES RANJAN PAIRANo ratings yet
- Technical Drawings PDFDocument3 pagesTechnical Drawings PDFAnicet Vincent33% (3)
- Euclidean ZoningDocument1 pageEuclidean Zoningneda1388No ratings yet
- 1.elements of Landscape DesignDocument33 pages1.elements of Landscape DesignshelmiNo ratings yet
- Example 3 Rectangular SiloDocument7 pagesExample 3 Rectangular SiloAhmed Said50% (2)
- RM Silo Ocp3Document7 pagesRM Silo Ocp3Mahata Priyabrata50% (2)
- Silos DesignDocument7 pagesSilos Designaloyssberg100% (4)
- Silo WallDocument5 pagesSilo WallMunish GaurNo ratings yet
- Silo Design Final For Mombasa - Is - NiladriDocument9 pagesSilo Design Final For Mombasa - Is - NiladriMahata Priyabrata100% (1)
- Silo Structure Rev 3Document176 pagesSilo Structure Rev 3saadyamin2821100% (3)
- Silo VoDocument2 pagesSilo Vosuntoshsalvi4859No ratings yet
- Silo and Hopper Design For StrengthDocument36 pagesSilo and Hopper Design For Strengthazouin59100% (4)
- Calc. Shell Thickness SiloDocument29 pagesCalc. Shell Thickness SiloJunaid MateenNo ratings yet
- Tel: (978) 649-3300 Fax: (978) 649-3399 Tel: (805) 541-0901 Fax: (805) 541-4680Document48 pagesTel: (978) 649-3300 Fax: (978) 649-3399 Tel: (805) 541-0901 Fax: (805) 541-4680gkdora57489% (9)
- Silo Data SheetDocument4 pagesSilo Data SheetZoran Danilov100% (1)
- Silo SizeDocument1 pageSilo Sizeuvarajmecheri100% (1)
- IS 9178 (Part 1) - 1978Document39 pagesIS 9178 (Part 1) - 1978bhustlero0o100% (2)
- DIN-1055-6 2005silosDocument195 pagesDIN-1055-6 2005silosTunisian Mentalist75% (4)
- Design of BinsDocument37 pagesDesign of BinsAgarry Emmanuel100% (1)
- 1000 m3 Ash Silo Calculation ReportDocument15 pages1000 m3 Ash Silo Calculation Reporttranceintt0% (1)
- Steel Silo's DesignDocument2 pagesSteel Silo's Designemad sabri100% (1)
- Standard Design of SilosDocument12 pagesStandard Design of SilosTarun VermaNo ratings yet
- Central Cone Silos StructuralDocument28 pagesCentral Cone Silos StructuralMayMST100% (2)
- Silo Design Kit PP013Document42 pagesSilo Design Kit PP013cris_2010100% (4)
- Example Design of Circular Beam ACI 1999Document5 pagesExample Design of Circular Beam ACI 1999José Pablo Rosales Sánchez100% (3)
- Slab DesignDocument96 pagesSlab Designdilrangi100% (2)
- Concrete Design14 Analysis Design Torsion 2Document7 pagesConcrete Design14 Analysis Design Torsion 2cocococo1100% (1)
- Analysis and Design For Torsion 2Document13 pagesAnalysis and Design For Torsion 2cjcute91No ratings yet
- Time Saving DesignDocument22 pagesTime Saving DesignViswanadh OngoluNo ratings yet
- Design of SyphonDocument7 pagesDesign of SyphonraghurmiNo ratings yet
- WR401 01 Design of SyphonDocument7 pagesWR401 01 Design of Syphonale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban PlanningDocument22 pagesFaculty of Applied Engineering and Urban PlanningHazem Almasry100% (1)
- Diseño de ColumnasDocument9 pagesDiseño de ColumnasSovich82No ratings yet
- Site Civil Works:: Footing FTBDocument21 pagesSite Civil Works:: Footing FTBChelzey Jhoy BautistaNo ratings yet
- Proiect Constructii Din Lemn Tema 2Document9 pagesProiect Constructii Din Lemn Tema 2Mihai Alexandru TuțuNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallDocument18 pagesRetaining WallMonirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - SolutionDocument25 pagesAssignment 2 - Solutionblasticinc100% (1)
- Mathcad CMU WallDocument23 pagesMathcad CMU WallqimingzengNo ratings yet
- Example From CH 1 To CH 6Document21 pagesExample From CH 1 To CH 6SteveNo ratings yet
- Minor-1 QP Section - 1 SolutionsDocument3 pagesMinor-1 QP Section - 1 SolutionsAshok (B20CI015)No ratings yet
- 12 M High Retaining Wall Design For Seismic LoadingDocument27 pages12 M High Retaining Wall Design For Seismic Loadingaminjoles0% (1)
- Design of Pressed Steel Tank Using IS CodesDocument5 pagesDesign of Pressed Steel Tank Using IS CodesISFAQUL AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Lecture Material - WatermarkDocument57 pagesWeek 11 Lecture Material - WatermarkVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Automotive Science and Mathematics AnswersDocument14 pagesAutomotive Science and Mathematics AnswersBig FloresNo ratings yet
- Example 3.4 - Continuous One Way Slab-Updated 080812Document12 pagesExample 3.4 - Continuous One Way Slab-Updated 080812Muhammad Farhan Gul86% (7)
- Testbeams For Ver Pile CapacityDocument13 pagesTestbeams For Ver Pile CapacitytmssorinNo ratings yet
- Vibration Serviceability of Composite SlabsDocument8 pagesVibration Serviceability of Composite SlabsDelahan AbatyoughNo ratings yet
- Eccentric FootingsDocument34 pagesEccentric FootingsMelaku Seyoum0% (1)
- Laboratory Exercises in Astronomy: Solutions and AnswersFrom EverandLaboratory Exercises in Astronomy: Solutions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Substation Construction ManualDocument63 pagesSubstation Construction ManualAnicet VincentNo ratings yet
- Safety Health Book 2019 VfinalDocument15 pagesSafety Health Book 2019 VfinalAnicet VincentNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting DrawingsDocument6 pagesFire Fighting DrawingsAnicet Vincent0% (1)
- NORPLAN Tanzania BrochureDocument20 pagesNORPLAN Tanzania BrochureAnicet VincentNo ratings yet
- NORPLAN Tanzania Geotechnical EngineerigDocument20 pagesNORPLAN Tanzania Geotechnical EngineerigAnicet VincentNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Installation Standards HandbookDocument80 pagesNatural Gas Installation Standards HandbookAnicet Vincent100% (1)
- Basics of DialysisDocument32 pagesBasics of DialysisAnicet Vincent100% (1)
- Dehumidification of Fertilizer - Storage PDFDocument2 pagesDehumidification of Fertilizer - Storage PDFAnicet VincentNo ratings yet
- Tujenge 2012Document1 pageTujenge 2012Anicet VincentNo ratings yet
- EGR2206Document5 pagesEGR2206plaxisplax255No ratings yet
- Retrofitting Strengthening of Permanent Bridges - Maris Dam Br.Document19 pagesRetrofitting Strengthening of Permanent Bridges - Maris Dam Br.John Rheynor MayoNo ratings yet
- W6 Notes - Spatial OrderDocument18 pagesW6 Notes - Spatial OrderEricka MayNo ratings yet
- BMP Software Developer Business Plan 1Document43 pagesBMP Software Developer Business Plan 1msamala09No ratings yet
- Flareless Bite Type FittingsDocument24 pagesFlareless Bite Type FittingsRickson Viahul Rayan CNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall With PilesDocument7 pagesRetaining Wall With PilesEngineering KaizenNo ratings yet
- AASHTO ASTM CODE NameDocument2 pagesAASHTO ASTM CODE NamekashifNo ratings yet
- Form Inspection For Rebar Pilecap and ColumnDocument4 pagesForm Inspection For Rebar Pilecap and ColumnHary Anugrah100% (1)
- Boq 4Document3 pagesBoq 4China AlemayehouNo ratings yet
- Coz 1Document4 pagesCoz 1kevsiNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Behaviour of Tall BuildingDocument22 pages1.0 Behaviour of Tall BuildingOne The100% (1)
- Project: Model: CHK'D: DateDocument55 pagesProject: Model: CHK'D: DateFarhsa Dhom Eemihahs DhomNo ratings yet
- Posisi KendaraanDocument4 pagesPosisi Kendaraanary fauzi rahmanNo ratings yet
- Dodge - Bearing Ingineering Catalog PDFDocument708 pagesDodge - Bearing Ingineering Catalog PDFJose Laiza50% (2)
- DS Flex Rev7 0309 PDFDocument2 pagesDS Flex Rev7 0309 PDFDavid GonzaloNo ratings yet
- Monolithic DomesDocument22 pagesMonolithic DomesNaveen Revanna67% (3)
- MRL Template Before Drawing (Print Only)Document5 pagesMRL Template Before Drawing (Print Only)Syahmie DaudNo ratings yet
- AB. Habieb - PaperDocument4 pagesAB. Habieb - PaperAhmad Basshofi HabiebNo ratings yet
- Proposed Warehouse ConstructionDocument14 pagesProposed Warehouse Constructionorode franklynNo ratings yet
- คู่มือซ่อมเครื่องยนต์นิสสันYD25คอมม่อนเรลDocument80 pagesคู่มือซ่อมเครื่องยนต์นิสสันYD25คอมม่อนเรลtataeNo ratings yet
- Satip Q 001 03Document10 pagesSatip Q 001 03munnaNo ratings yet
- StressDocument158 pagesStressSapana Malla100% (1)
- Vol 1 1Document137 pagesVol 1 1Mudit Mehra0% (1)
- Estimate Road Safety 14-15Document36 pagesEstimate Road Safety 14-15Bilal Ahmed Barbhuiya100% (1)
- Week 2 - Highway Development and PlanningDocument10 pagesWeek 2 - Highway Development and PlanningADRIAN FRAGATANo ratings yet
- Concept Folding 77: Invite Nature Into Your BuildingDocument4 pagesConcept Folding 77: Invite Nature Into Your BuildingStefan PavalutaNo ratings yet