Professional Documents
Culture Documents
B. Weak Bonds Dynamic and Reversible
Uploaded by
Fareeda BhattiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
B. Weak Bonds Dynamic and Reversible
Uploaded by
Fareeda BhattiCopyright:
Available Formats
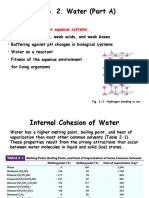
Lecture 1 1/6/2015
Weak Forces
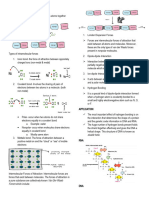
Types of Weak Bonds
Hydrogen bonds – a weak chemical bond between an electronegative atom, such as fluorine,
oxygen, or nitrogen, and a hydrogen atom bound to another electronegative atom.
Ionic (charge) interactions (in aqueous environment)
o Attraction of opposite charges
o Repulsion of similar charges
Hydrophobic interactions – the association of nonpolar groups or compounds with each other in
aqueous systems, driven by the tendency of the surrounding water molecules to seek their most
stable (disordered) state
o Hydrophobic molecules are uncharged (unlike partial charges on water)
Clump together to avoid charges of water
Van Der Waals – weak intermolecular forces between molecules as a result of each inducing
polarization in the other
o Includes dipole-dipole interactions and London dispersion forces
o When two uncharged atoms are brought very close together, variations in the position
of electrons in their surrounding electron clouds induces a transient dipole in each other
What are the important characteristics of weak bonds that are important for life?
Additive
o Although individual bonds are weak, added together they make strong connection
o E.g. gecko’s feet allow gecko to walk up walls due to additive nature of weak Van Der
Waals interactions between feet and wall
Reversibility (Dynamic)
Some of them are spontaneous (don’t need enzymes)
Clicker Question: What is the most important reason that life requires weak chemical bonds?
A. Many weak bonds = One strong bond
B. Weak bonds = Dynamic and reversible
C. Strong bonds = Need enzymes to break
D. Weak bonds = Additive effect
E. Weak bonds = hydrophobic
Explanation; the most important factor is the reversibility of weak bonds, even though the other
answer choices may also be correct.
Examples of Why Bonds Must Be Dynamic
DNA; bases are connected via hydrogen bonds
o Because hydrogen bonds are reversible, DNA can be separated and replication can occur
Soap and hydrophobic interactions
o Charged soap causes dirt/grease to undergo hydrophobic interactions, clump, and be
washed away
Lecture 1 1/6/2015
Weak Forces
Enzyme substrate binding site
o Needs to be reversible to allow finished product to leave and continue process with
another substrate
Friction and Van Dar Waals
o Allows for movement
Capillary action in plants
o Allows water to be pulled up in plants
o Also occurs in human blood vessels
Flexion and extension of muscles
o Needs to occur both ways
Cell-cell signaling
o Needs to be able to start and stop (e.g. in neurons)
Water tension
o Allows “Jesus bugs” to walk on water
You might also like
- Toddle - (A1 2Document44 pagesToddle - (A1 2Youssef SamehNo ratings yet
- Acosta, Niel Task 5Document3 pagesAcosta, Niel Task 5Algrin AcostaNo ratings yet
- 6 Water-MoleculeDocument39 pages6 Water-MoleculeVanna AmarilloNo ratings yet
- A 1.1 SLHL WaterDocument47 pagesA 1.1 SLHL WaterKumutha ChelliahNo ratings yet
- 2.bonds in BiomoleculesDocument32 pages2.bonds in Biomoleculesmnouma1612No ratings yet
- TBA 1013 Assignment 1 SEM 2 2010/2011Document3 pagesTBA 1013 Assignment 1 SEM 2 2010/2011Zafiera ZukriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Water: The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsDocument6 pagesChapter 2: Water: The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsMariam EidNo ratings yet
- A1.1 WaterDocument42 pagesA1.1 WaterKumutha ChelliahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Water ChemistryDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Water ChemistryKathy Del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of WaterDocument17 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of Watershubham debNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CompleteDocument149 pagesUnit 1 CompleteValine Cysteine MethionineNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 6th Edition Karp Test BankDocument36 pagesCell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 6th Edition Karp Test Bankhesperidspalela3l3e100% (39)
- Chem400 2Document36 pagesChem400 2Ramces Soliman100% (1)
- Physical Science Quarter 3 Week 4Document5 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 Week 4Rogeilyn CalimpongNo ratings yet
- BSC 450 CH 2 NotesDocument15 pagesBSC 450 CH 2 NotesMaddie NNo ratings yet
- Transcript For Water LectureDocument5 pagesTranscript For Water Lecturestanly sotoNo ratings yet
- Multicellular Organsisms - ChemicalBondsDocument25 pagesMulticellular Organsisms - ChemicalBondsValine Cysteine MethionineNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 1Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 1blackmage016No ratings yet
- Water Wps OfficeDocument6 pagesWater Wps OfficeJobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- HGC1201 MODULE 1 (Week2-3)Document12 pagesHGC1201 MODULE 1 (Week2-3)Tommy Franco DavidNo ratings yet
- Nursing Study Guide On BIOCHEMISTRY (CHAPTER 2 WATER)Document10 pagesNursing Study Guide On BIOCHEMISTRY (CHAPTER 2 WATER)Arvin Kim QuibingcoNo ratings yet
- Water: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, Fourth EditionDocument40 pagesWater: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, Fourth EditionDita SipayungNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Outline Mark AtesDocument7 pagesPhysical Science Outline Mark Atesryanreyserbas99No ratings yet
- Types of Intermolecular ForcesDocument7 pagesTypes of Intermolecular ForcesRhenczell Angela VelascoNo ratings yet
- ch1 .ST - Medical - WaterDocument55 pagesch1 .ST - Medical - Watersultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and Genetics 16-08-17Document4 pagesCell Biology and Genetics 16-08-17Huda HalaneNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of Life 1 3Document30 pagesChemicals of Life 1 3kitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Bio 112 - Activity 4Document3 pagesBio 112 - Activity 4LAGMAY, Daniel Scott G.No ratings yet
- IntermolecularDocument13 pagesIntermolecularRowena FloresNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument60 pagesBiology Noteskiler2314No ratings yet
- Biology 101 NotesDocument60 pagesBiology 101 Noteskiler2314No ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Water - ApplicationDocument4 pagesBiomolecules and Water - ApplicationPercival Castro CarpioNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - WaterDocument14 pagesModule 2 - Waterjanmariefernandez0No ratings yet
- Inorganic Biological Molecules - Water 0 MineralsDocument40 pagesInorganic Biological Molecules - Water 0 MineralsjonNo ratings yet
- Learning Task2-Lec BiochemDocument2 pagesLearning Task2-Lec BiochemMaria Dolores MallariNo ratings yet
- Biological ChemistryDocument65 pagesBiological Chemistrynyrayasin13No ratings yet
- Physical Science - Module 5 (Assignment)Document1 pagePhysical Science - Module 5 (Assignment)CharlesNo ratings yet
- The Main Types of Intermolecular ForcesDocument44 pagesThe Main Types of Intermolecular ForcesHumms B Lyka Jenny Alterado BangugNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Intermolecular ForcesDocument49 pagesLesson 3 Intermolecular ForcesAira Mae PeñaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manual PDFnopalsmuggler8wa100% (8)
- Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesCell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manualpoorly.germuleo6bv100% (30)
- Chapter 1 Lesson 1Document24 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 1PhoenixNo ratings yet
- WATERDocument5 pagesWATERKyle ManaloNo ratings yet
- Water IBDocument33 pagesWater IBIsadora PereiraNo ratings yet
- 1A 1 The Chemistry of LifeDocument15 pages1A 1 The Chemistry of Lifemuhammad naufalNo ratings yet
- 2.2 WaterDocument38 pages2.2 Wateralina blueNo ratings yet
- L9.intermolecular Forces of Attraction and Physical Properties of Matter - GorgonioDocument3 pagesL9.intermolecular Forces of Attraction and Physical Properties of Matter - GorgonioHarley MabaybayNo ratings yet
- s15 Miller Chap 2a LectureDocument19 pagess15 Miller Chap 2a LectureYannis ZoldenbergNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - 18.11.2022Document18 pagesLecture 4 - 18.11.2022Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatNo ratings yet
- 1.2 IntermolecularDocument6 pages1.2 IntermolecularJade RanteNo ratings yet
- 2water TheSolventForBIOCHEMICALReactionsDocument9 pages2water TheSolventForBIOCHEMICALReactionsMae RabariaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument35 pagesIntermolecular ForcesMikee Fernandez TangubNo ratings yet
- 450 F17 Lect 02 PostDocument59 pages450 F17 Lect 02 PostJason WangNo ratings yet
- Cohesion (Chemistry) - WikipediaDocument9 pagesCohesion (Chemistry) - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Alan M - Guía Bio 1Document34 pagesAlan M - Guía Bio 1PaulinaNo ratings yet
- James L, General Biology I (MF009) Foundation in ScienceDocument22 pagesJames L, General Biology I (MF009) Foundation in ScienceHorng Ke GoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument387 pagesBiologyAaron Wong100% (1)
- A1.1.4 Adhesion of Water To Materials That Are Polar or Charged and Impacts For Organisms.Document10 pagesA1.1.4 Adhesion of Water To Materials That Are Polar or Charged and Impacts For Organisms.taiga.aisaka14404No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of LifeDocument7 pagesThe Chemistry of LifeprimalNo ratings yet
- K LP - All ItemsDocument11 pagesK LP - All ItemsRumesh RoshanNo ratings yet
- Edi Patit Paban Das DetailsDocument11 pagesEdi Patit Paban Das DetailsAnik ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Iste Certification Alignment MapDocument12 pagesIste Certification Alignment Mapapi-665015818No ratings yet
- ITCE419 - Final ExamDocument5 pagesITCE419 - Final ExamKANSNNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyor Pulley DesignDocument11 pagesBelt Conveyor Pulley Designthakur_raghab100% (1)
- IMGS Individual CW2 - 2024Document3 pagesIMGS Individual CW2 - 2024AqsaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 06 Questions With Possible Solutions: IS333: Project Management - Semester I 2021Document5 pagesTutorial 06 Questions With Possible Solutions: IS333: Project Management - Semester I 2021Chand DivneshNo ratings yet
- DM - Basic SPoken ENglishDocument4 pagesDM - Basic SPoken ENglishFeriyanto MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Rein Control: From Daisyworld To Active PerceptionDocument6 pagesHomeostasis and Rein Control: From Daisyworld To Active PerceptionVeronique PoenelleNo ratings yet
- Cbiemasu 05Document5 pagesCbiemasu 05Shalini MishraNo ratings yet
- TUV SUD CE Certificate (1500V New Standard)Document3 pagesTUV SUD CE Certificate (1500V New Standard)iszlaitundeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Kinematics and MechanismsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Kinematics and Mechanismsdhilip_sacetNo ratings yet
- JBL PRX815W ServiceManual VADocument23 pagesJBL PRX815W ServiceManual VAJeimyng Dahinys100% (1)
- Our Town October 11, 1929Document34 pagesOur Town October 11, 1929narberthcivicNo ratings yet
- Amanda Sephiroth: Amanda Sephiroth - Aasimar/half-Celestial/half-Dragon (Gold) Class: Monk 10/clericDocument7 pagesAmanda Sephiroth: Amanda Sephiroth - Aasimar/half-Celestial/half-Dragon (Gold) Class: Monk 10/clericDaniel MarinhoNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior and The Social Environment I 1590508065Document1,310 pagesHuman Behavior and The Social Environment I 1590508065prim100% (1)
- Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument27 pagesFinite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madrasnataraj deshpandeNo ratings yet
- Character Personality ClothesDocument3 pagesCharacter Personality ClothesMelania AnghelusNo ratings yet
- Fred David - Strategic Management - A Competitive Advantage Approach, Concepts and Cases (Team-IRA) - Pearson (2023)Document681 pagesFred David - Strategic Management - A Competitive Advantage Approach, Concepts and Cases (Team-IRA) - Pearson (2023)Soad Daawoh100% (4)
- Concept of Statistical Quality ControlDocument51 pagesConcept of Statistical Quality ControlTehmeena BegumNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy, Properties, and Uses of FerrousDocument37 pagesMetallurgy, Properties, and Uses of FerrousAl DrinNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module - Surveying (Earthworks) : Methods of Calculating VolumeDocument2 pagesRefresher Module - Surveying (Earthworks) : Methods of Calculating VolumeOctavia BlakeNo ratings yet
- Paper - 8: Financial Management and Economics For Finance Section - A: Financial ManagementDocument31 pagesPaper - 8: Financial Management and Economics For Finance Section - A: Financial ManagementRonak ChhabriaNo ratings yet
- Mini Shear ManualDocument39 pagesMini Shear Manualhenry vegaNo ratings yet
- The Forbidden Equation I QC, by Miles MathisDocument5 pagesThe Forbidden Equation I QC, by Miles MathisBaba YagaNo ratings yet
- Signaling Server: Installation and ConfigurationDocument118 pagesSignaling Server: Installation and Configurationwanriz1971No ratings yet
- Year Date Year Date Discharge (M /S) Gauge Height (M) Discharge (M /S) Gauge Height (M)Document3 pagesYear Date Year Date Discharge (M /S) Gauge Height (M) Discharge (M /S) Gauge Height (M)Rajib MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Fs1-Episode 11Document22 pagesFs1-Episode 11Jamille Nympha C. BalasiNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Weekly UpdateDocument12 pagesNatural Gas Weekly Updateapi-212233479No ratings yet
- Monsters of Hyrule For D&D 5e: Master Cycle ZeroDocument33 pagesMonsters of Hyrule For D&D 5e: Master Cycle ZeroNihl ArtsNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Practical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationFrom EverandPractical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Integrating Management Systems and Metrics to Improve Process Safety PerformanceFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Management Systems and Metrics to Improve Process Safety PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Troubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesFrom EverandTroubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyFrom EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- Dust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesFrom EverandDust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyFrom EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet