Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Science - Module 5 (Assignment)
Uploaded by
CharlesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science - Module 5 (Assignment)
Uploaded by
CharlesCopyright:
Available Formats
LAMBINO, CHARLES JAY B.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE │MODULE 5
ABM 12B MARCH 17, 2021
ASSIGNMENT:
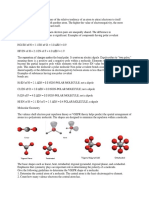
1. Why do some solids dissolve in water but others do not?
Many solids do not dissolve in water and that is because they are non-polar and do not interact
well with water molecules. A common example is oil and water. Oil contains molecules that are
non-polar, thus they do not dissolve in water. And when a solid does not dissolve in water; that
means the attraction between the ions in ionic compound is greater than the one between ions
and molecules of water.
2. Why some substances gases at room temperature, but others are liquid or solid?
The state a given substance exhibits is also a physical property. Some substances exist as
gases at room temperature; oxygen and carbon dioxide, while others, like water and mercury
metal, exist as liquids. Most metals exist as solids at room temperature. All substances can exist
in any of these three states. And it is because a solid has definite volume and shape, a liquid has
a definite volume but no definite shape, and a gas has neither a definite volume nor shape.
3. How the atoms of a molecule are gained a partially negative or a partially positive charge?
Partial charge is a way of explaining the bond polarity of bonds between atoms of different
electro negativities, nuclear shielding. So when the two atoms involved in a covalent bond both
have equal affinity for electrons, the electrons in the bond are evenly shared between them. In this
case, the more electronegative atom gains a partial negative charge, while the less
electronegative atom becomes partially positive.
4. What do you call the weak forces of attraction that exists in the molecule?
I’ve heard it simply called molecular attraction but it is still the attraction that occurs between
atoms. Molecules are just combinations of two or more dissimilar atoms that are able to work
together. Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction or repulsion which act between
neighboring particles; atoms, molecules, or ions. These forces are weak compared to the intra-
molecular forces, such as the covalent or ionic bonds between atoms in a molecule.
5. What are Intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are electrostatic in nature; that is, they arise from the interaction between
positively and negatively charged species. Like covalent and ionic bonds, intermolecular
interactions are the sum of both attractive and repulsive components. And these are its four types:
ion-dipole, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole, and Van der Waals forces.
You might also like
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument4 pagesIntermolecular ForcesglennNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 Intermolecular ForcesDocument14 pagesLesson2 Intermolecular ForcesJenny Rose Butac Ocden100% (1)
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument4 pagesIntermolecular ForcesAgathaNo ratings yet
- Solving HNMR ProblemsDocument7 pagesSolving HNMR ProblemsJorge Eneas DosoliNo ratings yet
- Week 1 4 Chemistry 2Document46 pagesWeek 1 4 Chemistry 2Sheena Glen100% (2)
- Beer-Lambert Law: Concentration (G/ML) x10 AbsorbanceDocument3 pagesBeer-Lambert Law: Concentration (G/ML) x10 AbsorbanceCaleb LiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report On Bonding and StructureDocument9 pagesLab Report On Bonding and StructureOdongo Tonny100% (1)
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesIntermolecular ForcesAngelNo ratings yet
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Study GuideDocument9 pagesPhysical Chemistry Study Guidekrymxen100% (2)
- 1.2 IntermolecularDocument6 pages1.2 IntermolecularJade RanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document11 pagesChapter 6Eubin Choi100% (1)
- The Impact of Internet Use For StudentsDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Internet Use For StudentsCharlesNo ratings yet
- Learning Task2-Lec BiochemDocument2 pagesLearning Task2-Lec BiochemMaria Dolores MallariNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 Chemistry of LifeDocument5 pagesQuiz 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 Chemistry of LifenadiaNo ratings yet
- Transcript For Water LectureDocument5 pagesTranscript For Water Lecturestanly sotoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BruceNo ratings yet
- Ejara Zge4301 M2act1Document4 pagesEjara Zge4301 M2act1JAMAICA EJARANo ratings yet
- Open TAKS 1Document1 pageOpen TAKS 1goldnretrieverrNo ratings yet
- Open TAKS 1Document1 pageOpen TAKS 1goldnretrieverrNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesCell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manualpoorly.germuleo6bv100% (30)
- Dwnload Full Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manual PDFnopalsmuggler8wa100% (8)
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument35 pagesIntermolecular ForcesMikee Fernandez TangubNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 & 2 Chemical BiologyDocument11 pagesLecture 1 & 2 Chemical BiologyParth MehraNo ratings yet
- Semester 2 Chem NotesDocument10 pagesSemester 2 Chem NotesClayton FengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1:the Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument36 pagesLesson 1:the Kinetic Molecular TheoryKarylle MorlaNo ratings yet
- Acosta, Niel Task 5Document3 pagesAcosta, Niel Task 5Algrin AcostaNo ratings yet
- Water Notes: Syllabus Dot Point Notes/InformationDocument9 pagesWater Notes: Syllabus Dot Point Notes/InformationClayton FengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument12 pagesLesson 5 Intermolecular Forces of AttractionJames BagsikNo ratings yet
- Science Notes q2Document8 pagesScience Notes q2itohtomoka017No ratings yet
- Chemicals of LifeDocument4 pagesChemicals of LifeZoeNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity of An AtomDocument4 pagesElectronegativity of An AtomLindsay AgabasNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Intermolecular Forces of Attraction: Engr. Anthony V. AbesadoDocument28 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Intermolecular Forces of Attraction: Engr. Anthony V. AbesadoAnthony AbesadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - 18.11.2022Document18 pagesLecture 4 - 18.11.2022Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatNo ratings yet
- How To Teach Intermolecular ForcesDocument6 pagesHow To Teach Intermolecular ForcesMSHYDERABAD4334No ratings yet
- Module-4 ScienceDocument6 pagesModule-4 ScienceErnie Rosemarie T. BucalenNo ratings yet
- 1-Chemistry of Life Part Two StudentDocument21 pages1-Chemistry of Life Part Two StudentteniNo ratings yet
- 3 Bio ChemistryDocument7 pages3 Bio ChemistryartichokeyNo ratings yet
- Admmodule s11 12ps Iiic 16Document12 pagesAdmmodule s11 12ps Iiic 16Lebz RicaramNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document9 pagesLecture 2hfzyahmd613No ratings yet
- 7 Intermolecular ForcesDocument17 pages7 Intermolecular ForcesfathmathfaiherNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Honors - Lesson 3 Molecular Biology/BiochemistryDocument5 pagesChemistry Honors - Lesson 3 Molecular Biology/BiochemistryCamilo Narvaez NuñezNo ratings yet
- Local Media8644807033659826232Document23 pagesLocal Media8644807033659826232Gwend MemoracionNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document2 pagesModule 4Christopher Agustin Tambogon LptNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document18 pagesModule 1Lore Isabel Mendoza PaclebNo ratings yet
- Las Week03 Physci-2Document5 pagesLas Week03 Physci-2quilangroleo555No ratings yet
- 09/098 Bio NotesDocument3 pages09/098 Bio NotesNaomi SmithNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 6th Edition Karp Test BankDocument36 pagesCell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 6th Edition Karp Test Bankhesperidspalela3l3e100% (39)
- Lesson 3. INTERMOLECULAR FORCESDocument2 pagesLesson 3. INTERMOLECULAR FORCESmariaisabelmatala22No ratings yet
- CHM130LL (Experiment 10)Document8 pagesCHM130LL (Experiment 10)sandraNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2Document13 pagesUNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2KARTIKAY LADDHANo ratings yet
- Liquid Solution and InterDocument1 pageLiquid Solution and Intersalaandeska2015No ratings yet
- Polarity NotesDocument5 pagesPolarity NotesShailesh GhediyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Week 1 Gen Chem 2 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument30 pagesLesson 1 Week 1 Gen Chem 2 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsTwilightNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3Document9 pagesPhysical Science Week 3Rona Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Week 1Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Week 1Wayne AngeloNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Part 1Document24 pagesChapter 4. Part 1aly.darghouthNo ratings yet
- Notes Chemistry - ch4 - 11Document17 pagesNotes Chemistry - ch4 - 11VikramNo ratings yet
- A Chemistry ReviewDocument4 pagesA Chemistry ReviewPaul ShimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Small Molecules Chemical Bonds: BIOL 112 Notes Jan 11th-Jan 13thDocument10 pagesChapter 2: Small Molecules Chemical Bonds: BIOL 112 Notes Jan 11th-Jan 13thCaroline DonovanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Properties of Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesDocument23 pages2.1 Properties of Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesmckhiandivinoNo ratings yet
- Chem 12Document15 pagesChem 12Glenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Nelson Biology 1.1-1.4 Notes Grade 12Document16 pagesNelson Biology 1.1-1.4 Notes Grade 12Kahoot GroupNo ratings yet
- Carbon Is of Immense Significance To Us in Both Its Elemental Form and in The Combined FormDocument2 pagesCarbon Is of Immense Significance To Us in Both Its Elemental Form and in The Combined FormkalloliNo ratings yet
- Lambino, Charles Jay B. Physical Education 2 Final Exams Abm 12B JANUARY 21, 2021 EssayDocument1 pageLambino, Charles Jay B. Physical Education 2 Final Exams Abm 12B JANUARY 21, 2021 EssayCharlesNo ratings yet
- Physical Education - Module 5 (Activity 3)Document1 pagePhysical Education - Module 5 (Activity 3)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Module 11 and 12 (Activities)Document2 pagesApplied Economics - Module 11 and 12 (Activities)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Module 9 and 10 (Activities)Document2 pagesApplied Economics - Module 9 and 10 (Activities)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Module 3 (Assignment)Document1 pagePhysical Science - Module 3 (Assignment)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Module 4 (Assignment)Document1 pagePhysical Science - Module 4 (Assignment)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Module 6 (Assignment)Document1 pageApplied Economics - Module 6 (Assignment)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Module 8 (Activity)Document1 pageApplied Economics - Module 8 (Activity)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Module 9 (Activity)Document1 pageApplied Economics - Module 9 (Activity)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Intro To The Philo - Module 4 (Activity)Document1 pageIntro To The Philo - Module 4 (Activity)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Module 11 and 12 (Activities)Document2 pagesApplied Economics - Module 11 and 12 (Activities)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Organizational ChartDocument1 pageOrganizational ChartCharlesNo ratings yet
- Color Fun Run TixDocument1 pageColor Fun Run TixCharlesNo ratings yet
- Requesting Security For Special EventsDocument2 pagesRequesting Security For Special EventsCharlesNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONNAIREDocument3 pagesQUESTIONNAIRECharlesNo ratings yet
- Jeasel V. Ramos: CIT Colleges of Paniqui Foundation, IncDocument4 pagesJeasel V. Ramos: CIT Colleges of Paniqui Foundation, IncCharlesNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument3 pagesCommunicationCharles100% (1)
- 21st Century of Philippine LiteratureDocument5 pages21st Century of Philippine LiteratureCharlesNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1. Universe and Solar System Our SolarDocument2 pagesAssignment: 1. Universe and Solar System Our SolarCharlesNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Content of Meat: Republic of The Philippines Region III Province of Tarlac CIT Colleges Foundation IncDocument4 pagesNutrient Content of Meat: Republic of The Philippines Region III Province of Tarlac CIT Colleges Foundation IncCharlesNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1. Universe and Solar System Our SolarDocument2 pagesAssignment: 1. Universe and Solar System Our SolarCharlesNo ratings yet
- Intro.2 SpectrosDocument185 pagesIntro.2 SpectrosBerhanu LimenewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Organic Spectroscopy.Document118 pagesChapter 5 Organic Spectroscopy.Dr. Dhondiba Vishwanath60% (5)
- 2D and 3D Coordination PolymersDocument12 pages2D and 3D Coordination PolymersTHARIK ANWARNo ratings yet
- 3D Electron Microscopy and FIB-Nanotomography: Learning OutcomesDocument1 page3D Electron Microscopy and FIB-Nanotomography: Learning OutcomesMuraleetharan_BNo ratings yet
- Spandan Prasad Sahu: AlpineDocument9 pagesSpandan Prasad Sahu: AlpineSpandan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Module-3: Recombination in SemiconductorsDocument13 pagesModule-3: Recombination in SemiconductorsKARUTURI AKASH 17BEC0396No ratings yet
- 597 - Semiconductor in Equilibrium&Pn Junction1Document65 pages597 - Semiconductor in Equilibrium&Pn Junction1dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- MSC Final Chemistry p1 Application of Spectroscopy Photochemistry 2017 18Document4 pagesMSC Final Chemistry p1 Application of Spectroscopy Photochemistry 2017 18vnbmNo ratings yet
- Spotting Isomers Spotting Isomers: C C C C C C C CDocument1 pageSpotting Isomers Spotting Isomers: C C C C C C C Ccharlesma123No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of SpectrosDocument10 pagesBasic Principles of SpectrosAlexiss Chavez-De la MoraNo ratings yet
- Post-Laboratory Questions: 2. Bathophenanthroline Is A Compound That FormsDocument2 pagesPost-Laboratory Questions: 2. Bathophenanthroline Is A Compound That FormsJenny PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Generation of A Molecular Network From Electron Ionization Masa Spectrometry Data by Combining MZmine2 and MetGem SoftwareDocument4 pagesGeneration of A Molecular Network From Electron Ionization Masa Spectrometry Data by Combining MZmine2 and MetGem Softwaremuhamad daffa putraNo ratings yet
- Group 9 Assignment Determination of KMnO4Document6 pagesGroup 9 Assignment Determination of KMnO4UsmanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry QuestionsDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry QuestionsSagar JainNo ratings yet
- LO-RAY-LIGH® Diffraction Gratings in UV-VIS SpectrosDocument4 pagesLO-RAY-LIGH® Diffraction Gratings in UV-VIS SpectrosChemistrydavidNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 pageGujarat Technological UniversityRishita ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Q2 Molecular Geometry and PolarityDocument50 pagesQ2 Molecular Geometry and PolarityTosee istoseeNo ratings yet
- 1Q - Week 2 Physical ScienceDocument19 pages1Q - Week 2 Physical ScienceJEBONIE TUBICENo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements Hand Written NotesDocument10 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements Hand Written NotesAvi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Baran 2005Document16 pagesBaran 2005Jose Leal RodriguesNo ratings yet
- 13 C NMRDocument10 pages13 C NMRJamal SharifNo ratings yet
- TEM Characterization of Dislocation ImageDocument11 pagesTEM Characterization of Dislocation ImagerahmatsaptonoNo ratings yet
- IR SpectrosDocument41 pagesIR SpectrosKD LoteyNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecule WaterDocument18 pagesBiological Molecule WaterLaila MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Beh H: Localized Bonding Delocalized BondingDocument33 pagesBeh H: Localized Bonding Delocalized Bondingimad IftikharNo ratings yet
- Acidity, Basicity and PkaDocument39 pagesAcidity, Basicity and PkaZubaydah Abdullah100% (1)