Professional Documents
Culture Documents
17 Photosynthesis PDF
Uploaded by
Silibaziso MasukuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
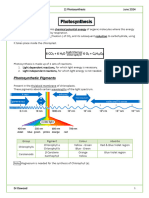
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
17 Photosynthesis PDF
Uploaded by
Silibaziso MasukuCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary
17 Photosynthesis
1 In photosynthesis, light energy is absorbed by 6C compound splits to give two molecules of a
chlorophyll pigments and converted to chemical 3C compound, GP (also known as PGA). GP is
energy, which is used to produce complex organic reduced to carbohydrate, using ATP and reduced
molecules. NADP from the light-dependent reactions.
This carbohydrate can be converted into other
2 In the light-dependent reactions, water is split by
carbohydrates, amino acids and lipids or used to
photolysis to give hydrogen ions, electrons and
regenerate RuBP. This sequence of light-independent
oxygen. The hydrogen ions and electrons are used to
events is called the Calvin cycle.
reduce the carrier molecule, NADP, and the oxygen
is given off as a waste product. 6 Chloroplasts, palisade mesophyll cells and whole
leaves are all adapted for the efficient absorption of
3 ATP is synthesised in the light-dependent reactions
light for the process of photosynthesis.
of cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
During these reactions the photosynthetic pigments 7 When a process is affected by more than one factor,
of the chloroplast absorb light energy and give out the rate of the process will be limited by the factor
excited electrons. Energy from the electrons is used closest to its lowest value. The rate of photosynthesis
to synthesise ATP. is subject to various such limiting factors, including
light intensity and wavelength, carbon dioxide
4 ATP and reduced NADP are the two main products
concentration and temperature.
of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis,
and they then pass to the light-independent 8 A graph of the particular wavelengths of light that
reactions. are absorbed by a photosynthetic pigment is called
an absorption spectrum, and a graph of the rate of
5 In the light-independent reactions, carbon dioxide
photosynthesis at different wavelengths of light is
is trapped by combination with a 5C compound,
called an action spectrum.
RuBP, which acts as an acceptor molecule. This
reaction is catalysed by the enzyme ribulose 9 The different pigments present in a chloroplast can
bisphosphate carboxylase (rubisco), which is the be separated by paper chromatography.
most common enzyme in the world. The resulting
© Cambridge University Press 2013 Summary: Chapter 17 11
You might also like
- IAL Biology SB2 AnswersDocument77 pagesIAL Biology SB2 AnswersChryssa Economou100% (7)
- Edexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFDocument120 pagesEdexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFMaha NaserNo ratings yet
- Pathology, Chapter 3, Inflammation (Slides)Document187 pagesPathology, Chapter 3, Inflammation (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi97% (33)
- Photosynthesis EllaDocument42 pagesPhotosynthesis EllaElla AgyeiNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Bio Topic 5Document6 pagesEdexcel Bio Topic 5quesntinmoorsNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE9, Second Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesSCIENCE9, Second Quarter ReviewerkinzyItchNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 5.2.1Document5 pagesPhotosynthesis 5.2.1bexNo ratings yet
- 5.2. Energy For Biological ProcessesDocument5 pages5.2. Energy For Biological ProcessesAdwaar HassanNo ratings yet
- Light Reactions and The Calvin CycleDocument24 pagesLight Reactions and The Calvin CycleMay NisperosNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesisalyaainsyirah04No ratings yet
- 13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument9 pages13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsAarushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 6.0 2024Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 6.0 2024jagartidubey5842No ratings yet
- Q2 Reviewer in General BiologyDocument7 pagesQ2 Reviewer in General BiologyariannealzagaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument22 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISAhmad albabNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1melc 5 Light Independent ReactionDocument22 pagesScience 9 Q1melc 5 Light Independent ReactionMenchie YabaNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes Topic 5 Energy Flow Ecosystems and The Environment Edexcel (IAL) Biology A LevelDocument9 pagesSummary Notes Topic 5 Energy Flow Ecosystems and The Environment Edexcel (IAL) Biology A LevelLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesisVivien LancinNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisSokuntheary SrunNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis T5-1Document9 pagesPhotosynthesis T5-1Kyile FernandoNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent RXNDocument10 pagesLight Dependent RXNChristoPher TorioNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 9700 CieDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis 9700 CietrinhcloverNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Consists of Light-Dependent and Light-Independent ReactionsDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Consists of Light-Dependent and Light-Independent Reactionsaby251188No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4ElariaNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 5 Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The Environment - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-Level PDFDocument9 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 5 Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The Environment - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-Level PDFsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument3 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISgods2169No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PDFDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis PDFHayamMohamedNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviwerDocument7 pagesBiology Reviwerapi-709918261No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesissteven7 IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Dark and Light ReactionDocument12 pagesDark and Light ReactionRobie Elliz TizonNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Exploration Guide - Cell Metabolism #3Document6 pagesAP Biology Exploration Guide - Cell Metabolism #3Gunnar OlsonNo ratings yet
- CSIR Unit 6@lifescience - BiotechDocument164 pagesCSIR Unit 6@lifescience - BiotechJigyasu bNo ratings yet
- Division of Cebu Lilo-An National High School - Senior High: Department of Education (Deped)Document5 pagesDivision of Cebu Lilo-An National High School - Senior High: Department of Education (Deped)Jeston Mar BayogNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 9700 Biology A-Level RevisionDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis 9700 Biology A-Level RevisionMehreen SyedNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent Reaction QuestionsDocument14 pagesLight Dependent Reaction QuestionsSevilay CaferogluNo ratings yet
- 06photosynthesis 12Document35 pages06photosynthesis 12Anne CuadernoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 2020 Paet 2Document6 pagesPhotosynthesis 2020 Paet 2yashandaluNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsAditya VenkatNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Part I: Overview & The Light-Dependent ReactionsDocument51 pagesPhotosynthesis Part I: Overview & The Light-Dependent ReactionsZ. Miller07No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics: Is The Study of How Energy Flows Through Living CellsDocument49 pagesBioenergetics: Is The Study of How Energy Flows Through Living CellsRy CyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in PlantsDocument64 pagesPhotosynthesis in PlantsBianca CapadociaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document32 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Allihannah PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Unveiling The Light Reaction Event in PhotosynthesisDocument18 pagesUnveiling The Light Reaction Event in Photosynthesiszbplayer8No ratings yet
- CHP 5 PhotosynthesisDocument43 pagesCHP 5 PhotosynthesisSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesGroup 4 - Photosynthesisditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- Genbio Study GuideDocument2 pagesGenbio Study GuideMaria Athinen AstorgaNo ratings yet
- Wa0009Document9 pagesWa0009law fullNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Photosynthesis, ATP and ADPDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology - Photosynthesis, ATP and ADPAnnalee MacarayaNo ratings yet
- 1 PhotosynthesisDocument22 pages1 PhotosynthesisLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- 5A Photosynthesis 5A Checkpoint: 5A.1 The Importance of ATPDocument4 pages5A Photosynthesis 5A Checkpoint: 5A.1 The Importance of ATPsalmaNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The EnvironmentDocument9 pagesEnergy Flow, Ecosystems and The EnvironmentafeefaNo ratings yet
- Significant Events of The Calvin CycleDocument4 pagesSignificant Events of The Calvin CycleBernadette PasionNo ratings yet
- Lec. 19 PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesLec. 19 PhotosynthesisChinar BuddyNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument10 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISNur SafirahNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsDocument67 pagesBiology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsWill AndyNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesCH 2 - PhotosynthesisnawarakanNo ratings yet
- 28 PhotosynthesisDocument20 pages28 PhotosynthesisAngelNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 101 Module 5Document5 pagesGen Bio 101 Module 5Kyne GasesNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesPhotosynthesisEla PatriciaNo ratings yet
- 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Jerusalem, Israel 6–11 July 1975From Everand25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Jerusalem, Israel 6–11 July 1975Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 4.31-40From EverandTetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 4.31-40Derek BartonNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Metabolism PDFDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To Metabolism PDFVidanes, Earl JosephNo ratings yet
- First Aid Revised (Easiest Edition On Earth) @mueen - AhmadDocument2,144 pagesFirst Aid Revised (Easiest Edition On Earth) @mueen - AhmadAyub SadiqNo ratings yet
- Bio 30 2nd Long TestDocument5 pagesBio 30 2nd Long TestAira GamboaNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster 2020v2Document1 pageFrac Moa Poster 2020v2NGUYỄN HỮU THÀNHNo ratings yet
- Biol 309 Question Bank Cell CommunicationDocument6 pagesBiol 309 Question Bank Cell CommunicationWalaa abo fool100% (1)
- RnaiDocument13 pagesRnaiIrah Jane BadeNo ratings yet
- pET-41a-c (+) VectorDocument2 pagespET-41a-c (+) VectorsimpleemailNo ratings yet
- 5 Cell Division p1Document9 pages5 Cell Division p1Sharifah NurainNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 KSSM: Chapter 6 CellDocument19 pagesBiology Form 4 KSSM: Chapter 6 CellPrithika Shankar100% (1)
- Glycogen Metabolism.Document49 pagesGlycogen Metabolism.Santino MajokNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Materials and Energy Cycle in The EcosystemDocument28 pagesLesson 4 Materials and Energy Cycle in The EcosystemBelle JariolneNo ratings yet
- 10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDocument26 pages10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDayne Ocampo-Soliman100% (1)
- MeiosisDocument34 pagesMeiosisapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Botanica Lab Virtual 1Document8 pagesBotanica Lab Virtual 1Equalis SantosNo ratings yet
- Tema 2. Control HormonalDocument3 pagesTema 2. Control HormonalAnaili DuránNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA MCQDocument6 pagesRecombinant DNA MCQChaze WaldenNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Genetics 3rd Edition Brooker Test BankDocument22 pagesConcepts of Genetics 3rd Edition Brooker Test BankChristianBrownxmstk100% (16)
- Fast Fed Cycle 2016 MJHDocument11 pagesFast Fed Cycle 2016 MJHGoran MaliNo ratings yet
- The Cell Quiz L 9Document2 pagesThe Cell Quiz L 9moutaz bedeweyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReceptorsDocument28 pagesNuclear ReceptorsDr. Lehrasip AliNo ratings yet
- Module 5 CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesModule 5 CarbohydratesSpongebob SquarepantsNo ratings yet
- How Genes WorkDocument47 pagesHow Genes WorkJelly Joy CampomayorNo ratings yet
- Modern and Convensional Wound Dressing To Interleukin 1 and Interleukin 6 in Diabetic WoundDocument2 pagesModern and Convensional Wound Dressing To Interleukin 1 and Interleukin 6 in Diabetic WoundGilang yuanggaNo ratings yet
- Bio Synthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument15 pagesBio Synthesis of Fatty Acidspriya19866No ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyDocument2 pagesMicrobial PhysiologyRizwanul IslamNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manualantheagian4p4y4100% (32)
- DNA Translation Written ReportDocument5 pagesDNA Translation Written ReportHerlene SeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Classifieds Final 2023 (2) 2Document11 pagesUnit 5 Classifieds Final 2023 (2) 2MNRNo ratings yet
- Antioxidants: Lipid Peroxidation-Derived Aldehydes, 4-Hydroxynonenal and Malondialdehyde in Aging-Related DisordersDocument17 pagesAntioxidants: Lipid Peroxidation-Derived Aldehydes, 4-Hydroxynonenal and Malondialdehyde in Aging-Related DisordersffwasitoNo ratings yet