Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Well Design - 2D: Process Flowchart
Uploaded by
Slim.BOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Well Design - 2D: Process Flowchart
Uploaded by
Slim.BCopyright:
Available Formats
Well Design – 2D
ENM210 Drilling Technology
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 1
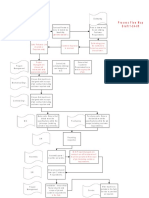
Process flowchart
C e m e n t in g
C e m e n t in g p ro g ra m m e
Th is p h a s e o f t h e D e s ig n
Obta in spa c ia l p ro c e s s is d a t a
da ta for fie ld D a t a t r a n s f e r p ro c e d u r e Input & a c q u is it io n a n d G e t s p e c ia lis t
va lida te da ta v a lid a t io n f ro m t h e S e le c t TO C f o r c o n t ra c t o r t o
c lie n t . Th e re m u s t e a c h h o le f o rm u la t e
se ts b e a r e c o rd re c ip e s
s e c t io n f r o m
m a in t a in e d o f t h is L O F b a s is
Obta in lithology, t ra n s f e rt o D e t e rm in e
S c h lu m b e r g e r v o lu m e s p re f lu s h ,
fra c ture a nd C o m p le t e d W e ll
D a t a t ra n s f e r p ro c e d u re Input & D e t e rm in e TO TC s p a c e ra n d
pore pre ssure D e s ig n f o r is o la t io n c em ents then
da ta va lida te da ta
p u rp o s e s p ro d u c e p u m p in g
se ts s c h e d u le
Y es
Obta in w e ll
re quire me nts D a t a t r a n s f e r p ro c e d u r e D rillin g D rills t rin g
Input & T& D , C a s in g W e a r a n d sy stem and BH A
va lida te H y d ra u lic s t u d y O K ? d e s ig n
S e le c t b it a n d B it / B H A s t ra t e g y
No
sy stem w it h d rills t rin g
c o m b in a t io n
T h e re m u s t b e d e s ig n D e s ig n B H A
s t a n d a rd s f o r: S u rv e y d e t a ils t o g iv e D e s ig n D r ills t r in g
D e s ig n T ra je c t o ry
C onduc tor P ro g ra m m e r e q u ire d D L S
C a s in g D e s ig n
S u r f a c e C a s in g D e s ig n
I n t e rm e d ia t e C a s in g s Y es
No P ro d u c t io n C a s in g
P ro d u c t io n L in e r s
P re s s u re S e le c t H o le S u rf a c e
S ize s t o Y es
c o n t a in m e n t ? N o C o llis io n R is k ?
d e liv e r C a s in g
D e s ig n No No
Y es D r illin g F lu id
C an
No b e t t e r S u rv e y
W e ll lif e P ro g ra m m e
D e t e rm in e p ro f ile
c o n s id e ra t io n s ? r e m o v e ris k ?
c o n s t ra in t s : MW and
s u rf a c e C o n f irm F r ic t io n
A re
re s e rv o ir le g is la t io n F a c t o rs
a ll w e ll p o s it io n a l
Y es w e llb o re s t a b ilit y re q u ire m e n t s re q u ire m e n t s
m et?
Tra je c t o ry S e le c t M W
D e s ig n W e ll P la n D rillin g F lu id
W e ll d rillin g p la n f ro m p o r e
W e ll P lo t s p ro g ra m m e
p re s s u re a n d
w e llb o r e s t a b ilit y
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 2
Casing
• Good indication of
competent formations
• Hard enough to allow
deflection of the
drilling tools
• Good estimate of the
speed at which the
borehole can be
deflected
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 3
Segments of a deviated well
• Rig Floor • Hold Section
– Datum for all MD’s – No inclination variation
• Well Reference Pt • DoP / 2nd KoP
– Normally vertically below – S wells
rig • EoD / Eo2ndB
• KoP – Amount of curved section
– Amount drilled from WRP • Target
to get competent formation
– Geological formation
• EoB
• Total Depth
– Curved section to get
– Reservoir exposure to get
• Tangent angle production
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 4
Well Types
• Vertical
0
0 Tie-In 0
Seabed
– Design
1000 1000
2000 2000
• 0º inclination, azimuth
does not matter
3000 3000
– Regular drilled
4000 4000
5000 5000
• > 0º inclination, azimuth
TVD Scale = 1(in):1426.84(ft)
does matter
6000 6000
-400 -200 0 200
– Control drilled
7000 7000
400 400
<<< S Scale = 1(in):300(ft) N >>>
8000 8000
• Depends on the control 200
Tie-In
200
9000 9000
• Can still end up with
RGU_C01
KOP RGU_C01
v1.00
0 0
inclination variation
Seabed
10000 10000
• Could be truly vertical
11000 RGU_C01 RGU_C01 11000 -200 -200
KOP v1.00
12000 12000
-400 -200 0 200
0
Vertical Section (ft) Azim = 0°, Scale = 1(in):1426.84(ft) Origin = 0 N/-S, 0 E/-W <<< W Scale = 1(in):300(ft) E >>>
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 5
Well Types
• J-shaped
-14000 -12000 -10000 -8000 -6000 -4000 -2000 0
Tie-In
0 seabed
0
KOP
– Design
• Build angle2000from a point of 2000
0º inclination along a
curve of a designed radius
4000 4000
on a fixed heading until an EOC (Curve-Hold)
angle is obtained, which,
when maintained
6000 will 6000
intercept a ‘target’ point 0
-10000 -8000 -6000 -4000 -2000 0
0
Keabed
Tie-In
sOP
– Regular drilled variations
8000
-2000
EOC(Curve-Hold)
8000
-2000
• Rate of change of angle -4000 -4000
• Inclinations10000 RGU_SW3
td
-6000
10000
-6000
RGU_SW3
• Azimuths v1.00
-8000 -8000
-14000 -12000 -10000 -8000 -6000 -4000 -2000 0
– Control drilled -10000 -10000
• Better control of variations
RGU_SW3
v1.00 RGU_SW3
td
-10000 -8000 -6000 -4000 -2000 0
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 6
Well Types -7000 -6000 -5000 -4000 -3000 -2000 -1000 0
• S-shaped 0 Tie-In
seabed
KOP
0
– Design 1000 1000
• Build angle from a point of 0º 2000 2000
inclination along a curve of a
designed radius on a fixed 3000
EOC #1 (3D-S)
3000
heading until an angle is
obtained, which, when 4000 4000
maintained will intercept a 5000 5000
secondary curve towards a
‘target’ point and thereafter 6000 6000
intercept the target at a -5000 -4000 -3000 -2000 -1000 0
known inclination and azimuth 7000
RGU_
v1.00 NW5
RGU_NW5 7000
– Regular drilled variations
5000 td 5000
8000 KOP #2 8000
• Rate of change of angle 4000 4000
9000 9000
• Inclinations KOP #2 3000 3000
• Azimuths 10000
2000
10000
2000
– Control drilled 11000
RGU_NW5 1000
11000
1000
• Better control of variations td
RGU_NW5
v1.00
EOC #1 (3D-S)
12000 0 12000 0
sea
Tie
Kbed
OP
-In
-7000 -6000 -5000 -4000 -3000 -2000 -1000 0
-5000 -4000 -3000 -2000 -1000 0
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 7
What’s best..?
• ∞ number of
possibilities
0
200
• Has to be engineered
400 correctly
600
– Mechanical stresses
800
1000
– Hydraulic limitations
1200 • Minimising time
• Maximising
1400
1600
1800
performance
2d-10deg 2d-30deg 2d-45deg 2d-60deg 2d-75deg 2d-90deg
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 8
Circular Functions
• An arc of a circle is a
segment of the circumference
of the circle.
• Arc length of a circle in
radians = θr
• Arc length of a circle in
degrees = θ π r / 180
© The Robert Gordon University 2006
Circular Functions
Arc AB = 2πR x a/360°
= πR x a/180°
If R = 15m and
a = 60°
C = 2πR
= 2π(15) = 94.2m
Arc AB = π R x a/180
= π(15)(60)/180
= 15.7m
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 10
Build up Rate formula
Ra = Radius in Feet or Meters
BUR is usually in: °/100ft or °/ 30m
a) English units:
BUR = 57.29580 x 100/ Radius (ft)
BUR = 5729.580/ Radius (ft)
Radius (ft) = 5729.580/BUR
b) Metric unit:
BUR = 57.29580 x 30/ Radius (m)
BUR = 1718.870/ R(m)
Radius (m) = 1718.870/BUR
BUR = 5729.58/ ΔTVD
or
BUR = 5729.58/ ΔHD
© The Robert Gordon University 2006
Radius of Curvature
C = 2πRc
= 360 x 100 / BUR
BUR = 360 x 100 / 2πRc in °/100 ft
Rc = 18000 / πBUR in feet
TVD1 = Rc × sinI1
TVD2 = Rc × sinI2
ΔTVD = TVD2 - TVD1
= Rc ( sinl2 - sinI1)
ΔTVD = 5729.58( sinl2 - sinI1)/BUR
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 12
Radius of Curvature
HD1 = Rc - Rc × cosI1
= Rc (1 - cosI1)
HD2 = Rc - Rc × cosI2
= Rc (1 - cosI2)
ΔHD = HD2 - HD1
= Rc (cos I1 - cosI2)
ΔHD = 5729.58(cos I1 - cosI2)/BUR
ΔMD = πRc × (I2 – I1)/360 = length of the arc (ft)
ΔMD = (I2 – I1) x 100/BUR
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 13
Fundamentals
400
500
ΔTVD 400 500
ΔHD
400 500
900 500
200
ΔTVD
90 0
ΔHD
200
© The Robert Gordon University 2006
Determine End of Build
KOP TVD Build Radius
∅
∅ = 500
ΔTVD
EOB TVD = KOP (TVD) +
EOB 900
ΔHD ΔTVD
© The Robert Gordon University 2006
Slant (departure > R)
• Given:
– Wellhead coordinates
– Target coordinates
– Target TVD, V3
• To determine:
– KOP vertical depth, V1
– Build up rate, BUR
– KOP Kick-off point.
– V1 TVD of straight section/surface to
KOP.
– V2 TVD of end of build up.
– V2 - V1 TVD of Build up section with
BUR corresponding to radius of
curvature R.
– V3 - V2 TVD of Tangent section to
total depth.
– D1 Displacement at end of build up.
– D2 Total horizontal displacement of
target.
– Ǿ Maximum inclination of well.
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 16
Slant (R > departure)
• Given:
– Wellhead coordinates
– Target coordinates
– Target TVD, V3
• To determine:
– KOP vertical depth, V1
– Build up rate, BUR
– KOP Kick-off point.
– V1 TVD of straight section/surface to
KOP.
– V2 TVD of end of build up.
– V2 -V1 TVD of Build up section with BUR
corresponding to radius of
– curvature R.
– V3 - V2 TVD of Tangent section to total
depth.
– D1 Displacement at end of build up.
– D2 Total horizontal displacement of target.
– Ǿ Maximum inclination of well.
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 17
S-shaped (R1 + R2) < total target displacement
• Given:
– Wellhead coordinates
– Target coordinates
– Target TVD, V5
• To determine:
– KOP vertical depth, V1
– Build up rate, BUR
– Drop off rate, DOR
– Vertical depth at end of drop, V4
– KOP Kick-off point.
– V1 TVD of straight section/surface to KOP.
– V2 TVD of end of build up.
– V3 TVD of start of drop.
– V4 TVD of end of drop.
– V2 - V1 TVD of Build up section with BUR
corresponding to radius of curvature R1.
– V3 - V2 TVD of Tangent section.
– V4 - V3 TVD of drop section
– D1 Displacement at end of build up.
– D2 Displacement at end of tangent
– D3 Total horizontal displacement of target.
– Ǿ Maximum inclination of well.
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 18
S-shaped (R1 + R2) > total target displacement
• Given:
– Wellhead coordinates
– Target coordinates
– Target TVD, V5
• To determine:
– KOP vertical depth, V1
– Build up rate, BUR
– Drop off rate, DOR
– Vertical depth at end of drop, V4
– KOP Kick-off point.
– V1 VD of straight section/surface to KOP.
– V2 VD of end of build up.
– V3 VD of start of drop.
– V4 VD of end of drop.
– V2 - V1 TVD of Build up section with BUR
corresponding to radius of curvature R1.
– V3 -V2 TVD of Tangent section.
– V4 -V3 TVD of drop section.
– D1 Displacement at end of build up.
– D2 Displacement at end of tangent.
– D3 Total horizontal displacement of target.
– Ǿ Maximum inclination of well.
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 19
Manual Profile Design
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 20
Manual Profile Design
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 21
End of Module
© The Robert Gordon University 2006 22
You might also like
- Lilavat AR GH SC: Ibaipod HI Hool ISCDocument4 pagesLilavat AR GH SC: Ibaipod HI Hool ISCPrakash KapadiaNo ratings yet
- LAW ConsiderationandIntentionDocument1 pageLAW ConsiderationandIntentionYing FerngNo ratings yet
- Process Map 1-24-05Document1 pageProcess Map 1-24-05Giang LuuNo ratings yet
- Requirements estimating process flowDocument1 pageRequirements estimating process flowЕлена КоваленкоNo ratings yet
- Q Q M Indz: BossesliseDocument13 pagesQ Q M Indz: BosseslisePranav MishraNo ratings yet
- RC Construction and Structural SteelworkDocument7 pagesRC Construction and Structural SteelworkBharath AkurathiNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument8 pagesIlovepdf Mergedbrajeshpandey25No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: General Chemistry E 1 F 1 2 N All Work Must Be Sho V IDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: General Chemistry E 1 F 1 2 N All Work Must Be Sho V ISmartunblurrNo ratings yet
- Tploı L: Tablea 10 Oh T LL FR D WDocument9 pagesTploı L: Tablea 10 Oh T LL FR D WNuyul FaizahNo ratings yet
- ThomasDeloney 10230560Document250 pagesThomasDeloney 10230560Nicizak masudaNo ratings yet
- Art 35a J&KDocument2 pagesArt 35a J&KNareshNo ratings yet
- TheDoctrineandLiteratureoftheKabalah 10007220Document534 pagesTheDoctrineandLiteratureoftheKabalah 10007220jurebieNo ratings yet
- Allen Test Papers MainsDocument72 pagesAllen Test Papers MainsSridhar CheeraNo ratings yet
- LAW VfactorsDocument1 pageLAW VfactorsYing FerngNo ratings yet
- LAW VfactorsDocument1 pageLAW VfactorsYing FerngNo ratings yet
- LAW VfactorsDocument1 pageLAW VfactorsYing FerngNo ratings yet
- General Shareholder's Assembly Org ChartDocument1 pageGeneral Shareholder's Assembly Org ChartMihaela PaduraruNo ratings yet
- GlucosamineDocument3 pagesGlucosaminedhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Inventory and Production Cycle: Learning ObjectivesDocument16 pagesChapter 12 Inventory and Production Cycle: Learning ObjectivesKelvin LeongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Inventory and Production Cycle: Learning ObjectivesDocument16 pagesChapter 12 Inventory and Production Cycle: Learning ObjectivesCastleclash CastleclashNo ratings yet
- TarunDocument1 pageTarunDivyanshu LalNo ratings yet
- CPT 205 - Tutorial 5Document3 pagesCPT 205 - Tutorial 5Nishfaan NaseerNo ratings yet
- Applet Life CycleDocument3 pagesApplet Life CycleshyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Cash and Funding Strategies: Learning ObjectivesDocument38 pagesChapter 10 Cash and Funding Strategies: Learning ObjectivesZahid UsmanNo ratings yet
- 2013Document5 pages2013abC AdobeNo ratings yet
- Question PDFDocument38 pagesQuestion PDFRoshan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- BlowholesPorosityandUnsoundnessinAluminumAlloyCastings 10581553Document43 pagesBlowholesPorosityandUnsoundnessinAluminumAlloyCastings 10581553shivkeshNo ratings yet
- Modern English GrammarDocument371 pagesModern English GrammarvijayNo ratings yet
- ATreatiseontheMathematicalTheoryoftheMotionofFluids 10030931Document269 pagesATreatiseontheMathematicalTheoryoftheMotionofFluids 10030931jurebieNo ratings yet
- CAPE Caribbean Studies Solutions 2005Document15 pagesCAPE Caribbean Studies Solutions 2005timahNo ratings yet
- Clinical features of dermatophytosisDocument7 pagesClinical features of dermatophytosisrhlzuraNo ratings yet
- Export Clearance Flow ChartDocument2 pagesExport Clearance Flow ChartMuthu KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Building Software Test CompetencyDocument4 pagesBuilding Software Test Competencykishore75No ratings yet
- Doc4 Website GameDocument1 pageDoc4 Website GameLo Long YinNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Prismatic BarsDocument56 pagesTorsion of Prismatic BarsHasiniNo ratings yet
- General-Music Realpiano Rp1Document8 pagesGeneral-Music Realpiano Rp1Sébastien SAMIEZNo ratings yet
- PracticalSheetandPlateMetalWork_10278879Document553 pagesPracticalSheetandPlateMetalWork_10278879Phillip JuanNo ratings yet
- Msts FeedbacksDocument4 pagesMsts Feedbacksapi-339115602No ratings yet
- 5S workplace organization systemDocument1 page5S workplace organization systemallanjulesNo ratings yet
- ATranscriptoftheRegistersoftheWorshipfulCompanyofStationers 10249393Document497 pagesATranscriptoftheRegistersoftheWorshipfulCompanyofStationers 10249393Carlos Pérez SeguraNo ratings yet
- T Ojjjg B&Chddorcjqd甲 /: G A Knowl Dge Paper IiiDocument23 pagesT Ojjjg B&Chddorcjqd甲 /: G A Knowl Dge Paper IiiVishal BantiNo ratings yet
- RE Tutorial 4Document2 pagesRE Tutorial 4Gin ManNo ratings yet
- Introduction Mathematical Portfolio TheoDocument159 pagesIntroduction Mathematical Portfolio Theojmgnsa5405No ratings yet
- The Business of the TheatreDocument110 pagesThe Business of the TheatreFlavia BorbasNo ratings yet
- GMP of NutraceuticalsDocument6 pagesGMP of Nutraceuticalsliakot prantoNo ratings yet
- Our Place in The SunDocument16 pagesOur Place in The SunAlexa Bulayungan FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Impact 3 Student S BookDocument163 pagesImpact 3 Student S BookTanyaNo ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument1 pageMapa ConceptualRAFAELNo ratings yet
- General Music Service Manual IndexDocument8 pagesGeneral Music Service Manual IndexMeesterNo ratings yet
- Object-oriented programming paradigm questionsDocument18 pagesObject-oriented programming paradigm questionsJatin ThakurNo ratings yet
- PFA Ratrappage 2015Document6 pagesPFA Ratrappage 2015Ez BalehNo ratings yet
- ConstructionAccountingandFinancialManagement - 10015068 344Document1 pageConstructionAccountingandFinancialManagement - 10015068 344VidNo ratings yet
- BCMSN30SG Vol.1Document306 pagesBCMSN30SG Vol.1Gervasio MellinasNo ratings yet
- DifferentialCalculusforBeginners 10004634Document275 pagesDifferentialCalculusforBeginners 10004634Franknire IgNo ratings yet
- Osca AnesthDocument2 pagesOsca AnesthFazil KfNo ratings yet
- EarlyChristianityandPaganism 10150123Document653 pagesEarlyChristianityandPaganism 10150123Túlio Coelho SampaioNo ratings yet
- Fault Tree Analysis-Air BubblesDocument7 pagesFault Tree Analysis-Air BubblesHeart Touching VideosNo ratings yet
- Fault Tree Analysis-Air BubblesDocument7 pagesFault Tree Analysis-Air BubblesHeart Touching VideosNo ratings yet
- Hivern ArroyoDocument1 pageHivern ArroyoCarmen FarromequeNo ratings yet
- All Depths Are Driller's Depth: Job Events SummaryDocument7 pagesAll Depths Are Driller's Depth: Job Events SummarySlim.BNo ratings yet
- Wellbore Seismic ImagingDocument5 pagesWellbore Seismic ImagingselasenuapahNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument7 pagesChapter1 PDFAnditya Sapta RahesthiNo ratings yet
- 13 Mechanical Properties of RocksDocument18 pages13 Mechanical Properties of RocksSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Lithology and Porosity Determination: Mark of SchlumbergerDocument13 pagesLithology and Porosity Determination: Mark of SchlumbergerSlim.B100% (1)
- 3 SP - GR Logs PDFDocument11 pages3 SP - GR Logs PDFSlim.BNo ratings yet
- 5 Porosite Logs PDFDocument24 pages5 Porosite Logs PDFSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Basic Well Log Analysis - Introduction - Oct2013Document35 pagesBasic Well Log Analysis - Introduction - Oct2013Jorge PirelaNo ratings yet
- P15 Wilden PumpsDocument35 pagesP15 Wilden PumpsWalter LrNo ratings yet
- Parts Book Franks 300Document341 pagesParts Book Franks 300Slim.B100% (4)
- Battery SpecsDocument8 pagesBattery SpecsIng Sergio J Poot HuitzNo ratings yet
- Configurations & Parts Identification: Trailer Suspension SeriesDocument19 pagesConfigurations & Parts Identification: Trailer Suspension SeriesSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Fundamentos de Interpretacion de RegistrosDocument9 pagesFundamentos de Interpretacion de RegistrosJoseline TorresNo ratings yet
- Basic Well Log InterpretationDocument12 pagesBasic Well Log InterpretationShahnawaz Mustafa100% (2)
- Chapter 04 - Pore PressureDocument70 pagesChapter 04 - Pore PressureSlim.BNo ratings yet
- T210 PS145 7 - 49 PDFDocument34 pagesT210 PS145 7 - 49 PDFSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Operating and Maintenance GuideDocument100 pagesOperating and Maintenance GuideSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Parts Book & Maintenance Manual: UTB-75-D Unitized Hook BlockDocument16 pagesParts Book & Maintenance Manual: UTB-75-D Unitized Hook BlockSlim.BNo ratings yet
- When Your Gas Reservoir Is Unconventional So Is Our SolutionDocument11 pagesWhen Your Gas Reservoir Is Unconventional So Is Our SolutionIngeniería de Petróleos UnitropicoNo ratings yet
- CAVINSDocument20 pagesCAVINSSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Subsurface Environments: Instructor: Nawarat Intarapanich Course: Basic Petroleum GeologyDocument22 pagesSubsurface Environments: Instructor: Nawarat Intarapanich Course: Basic Petroleum GeologySlim.BNo ratings yet
- SC RE Chap6 LiquidsDocument54 pagesSC RE Chap6 LiquidsweldsvNo ratings yet
- SC RE Chap18 - Immiscible DisplDocument130 pagesSC RE Chap18 - Immiscible DisplSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Chap15 - MBalDocument38 pagesChap15 - MBalSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Chap 17 - Water InfluxDocument57 pagesChap 17 - Water InfluxSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Chap 14 PVTDocument109 pagesChap 14 PVTYujeisly Reina100% (2)
- Formation PressureDocument79 pagesFormation PressureRian MonterryNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow in Porous MediaDocument206 pagesFluid Flow in Porous MediaSlim.B100% (1)
- Heriot - Watt University - Production Technology IDocument476 pagesHeriot - Watt University - Production Technology IBrahim Letaief75% (12)
- Brent Dev HistoryDocument26 pagesBrent Dev HistorySlim.BNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Penyakit Infeksi: in Infectious Diseases Dewi Rahmawati, M.Farm-Klin.,AptDocument87 pagesFarmakoterapi Penyakit Infeksi: in Infectious Diseases Dewi Rahmawati, M.Farm-Klin.,AptYemima MNo ratings yet
- Wilkinson 2001Document44 pagesWilkinson 2001Toño Gaspar MuñozNo ratings yet
- Digital Fuel Calculation v.1Document4 pagesDigital Fuel Calculation v.1Julian ChanNo ratings yet
- Hospital Food Service: October 2019Document28 pagesHospital Food Service: October 2019Shaikh Sobiya 57No ratings yet
- Monitoring Rock and Soil Mass Performance: To The ConferenceDocument1 pageMonitoring Rock and Soil Mass Performance: To The ConferenceÉrica GuedesNo ratings yet
- Switchword PairsDocument6 pagesSwitchword PairsLaleKulahli100% (7)
- Югоизточна Европа под османско владичество 1354-1804Document531 pagesЮгоизточна Европа под османско владичество 1354-1804auroradentataNo ratings yet
- Attendance: Umut KurtoğluDocument2 pagesAttendance: Umut KurtoğluHavvaNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Se2370.501 05s Taught by Weichen Wong (Wew021000)Document1 pageUT Dallas Syllabus For Se2370.501 05s Taught by Weichen Wong (Wew021000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- NEM Report - IntroDocument11 pagesNEM Report - IntroRoshni PatelNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Nursing Students on Dengue FeverDocument9 pagesKnowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Nursing Students on Dengue FeverElinNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p8Document1 pageCCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p8MeMe AmroNo ratings yet
- Crisil DataDocument6 pagesCrisil DataVihang NaikNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Factor AnalysisDocument170 pagesExploratory Factor AnalysisSatyabrata Behera100% (7)
- Nescafe Cold CoffeeDocument24 pagesNescafe Cold CoffeeMuhammad Omer SaeedNo ratings yet
- UX DesignDocument96 pagesUX DesignParisa Zarifi100% (3)
- 4147ictte384 PDFDocument6 pages4147ictte384 PDFKandasamy AsohanNo ratings yet
- (Oxford Studies in Digital Politics) Jack Parkin - Money Code Space - Hidden Power in Bitcoin, Blockchain, and Decentralisation-Oxford University Press (2020)Document297 pages(Oxford Studies in Digital Politics) Jack Parkin - Money Code Space - Hidden Power in Bitcoin, Blockchain, and Decentralisation-Oxford University Press (2020)berpub0% (1)
- Logistic Growth Rate Functions Blumberg1968Document3 pagesLogistic Growth Rate Functions Blumberg1968Jonnathan RamirezNo ratings yet
- The 8 Body ConstitutionsDocument29 pagesThe 8 Body ConstitutionsNiNo ratings yet
- Cookery 9 - Food - PackagingDocument47 pagesCookery 9 - Food - PackagingJP AballeNo ratings yet
- RRB NTPC Cut Off 2022 - CBT 2 Region Wise Cut Off Marks & Answer KeyDocument8 pagesRRB NTPC Cut Off 2022 - CBT 2 Region Wise Cut Off Marks & Answer KeyAkash guptaNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds ExplainedDocument37 pagesOrganic Compounds ExplainedAlejandro VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Hotel Training ReportDocument14 pagesHotel Training ReportButchick Concepcion Malasa100% (1)
- Ergonomía y Normatividad en 3Document5 pagesErgonomía y Normatividad en 3Rogers DiazNo ratings yet
- A Survey of English and American Literature Module 1 3Document80 pagesA Survey of English and American Literature Module 1 3Jathalia VillaNo ratings yet
- Y10 ICT End of TermDocument7 pagesY10 ICT End of TermIvy Atuhairwe BisoborwaNo ratings yet
- BS 0812-114 - 1989Document12 pagesBS 0812-114 - 1989عمر عمرNo ratings yet
- LOGIK Fridge Freezer With Water Dispenser LSD55W18 ManualDocument20 pagesLOGIK Fridge Freezer With Water Dispenser LSD55W18 Manualfbunt2777No ratings yet
- TZMmanual PDFDocument8 pagesTZMmanual PDFccardenas3907No ratings yet