Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology 9B Plant Growth: Hedingham School
Uploaded by
Anonymous RuslwNZZlOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology 9B Plant Growth: Hedingham School
Uploaded by
Anonymous RuslwNZZlCopyright:
Available Formats
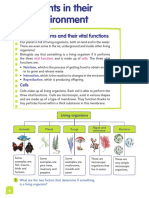
HEDINGHAM SCHOOL Biology 9B Plant Growth KNOWLEDGE MAP
9Ba Reactions in Plants 9Bb Plant Adaptations 9Bd Growing Crops
Photosynthesis: Roots are branched and spread out. Fertilisers contain mineral salts e.g. potassium,
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen phosphate, nitrates.
Root hair cells have a large surface area.
reactants products
Pesticides kill pests. Insecticides kill insect pests.
Xylem vessels are hollow tubes for carrying water and
Chlorophyll inside chloroplasts in plant cells Fungicides kill fungi that cause plant diseases.
dissolved mineral ions.
trap light energy for photosynthesis. Herbicides kill weeds.
Water is needed for photosynthesis, keeping leaves cool and
Limiting factors are variables that slow down
stopping the plant from wilting. Selective herbicides kill weeds but not crop plants.
the rate of a reaction.
Stomata are opened and closed by guard cells. A variety is a group of plants that have been bred to
Limiting factors of photosynthesis are light,
carbon dioxide and temperature. Stomata allow gaseous exchange. They open when it is light have certain characteristics.
so that carbon dioxide can enter the leaf by diffusion. Cross-breeding is breeding different varieties to
Aerobic respiration:
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water Leaves are thin so there is a shorter distance for diffusion. produce offspring with characteristics of both
reactants products breeds.
Leaves are broad and have a large surface area.
Phloem vessels carry the glucose made by Selective breeding is when only plants with certain
photosynthesis as a sugar solution to all parts The waxy cuticle reduces water loss from the leaf. characteristics are used to breed.
of the plant. Palisade cells contain many chloroplasts. 9Be Farming Problems
Waterlogged soil lacks oxygen and can cause
9Bc Plant Products Fertilisers can wash into rivers and lakes causing
roots to die.
Lipids (fats and oils) are found in the leaf cuticle, cell algae to grow quickly.
membranes and as an energy store in seeds and some fruits. Decomposers break down the dead algae and
plants, using up oxygen.
Glucose is stored as starch or made into other carbohydrates
such as cellulose. Insecticides can kill useful insects.
Iodine solution turns blue-black in the presence of starch. Some insecticides are persistent and build up in
food chains.
Proteins are made of amino acids. Plants need nitrates to
make amino acids. Selective weedkillers can kill broad leaved plants in
hedges.
Enzymes are proteins.
Deforestation and burning fossil fuels increases the
Seeds store proteins. amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere,
causing increased global warming.
For a seed to germinate, water and oxygen must enter.
Planting a single crop variety reduces biodiversity.
HEDINGHAM SCHOOL Chemistry 9F Reactivity KNOWLEDGE MAP
9Fa Types of Explosion 9Fb Reactivity 9Fd Displacement
Explosions can be caused by physical changes In a displacement reaction, the more reactive
or chemical reactions. metal takes the place of the less reactive
metal.
In explosions there is a sudden increase in
volume and a huge transfer of energy. The thermite reaction is an example of a
displacement reaction:
In physical changes there are no new aluminium + iron oxide → aluminum oxide +
substances made. iron
In chemical reactions there are new substances
formed. 9Fe Extracting Metals
Atoms of the reactants are rearranged to form Very unreactive metals such as gold are found
new products. in their native state in the Earth’s crust.
Pressure in gases is caused by the particles More reactive metals are found as
hitting the walls of the container. compounds.
Gas pressure can be increased by increasing the An ore is a rock which contains enough of a
number of gas particles, decreasing the size of metal or metal compound to be worth mining.
the container, increasing the temperature.
Reactive metals need to be chemically
extracted from their ores.
9Fc Energy and Reactions
Iron is extracted from iron oxide by heating it
Oxidising agents release oxygen for chemical metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen with carbon. The carbon acts as a reducing
reactions. agent.
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
Increasing the surface area increases the iron oxide + carbon → iron + carbon dioxide
reaction speed. Hydrochloric acid forms chloride salt.
Sulfuric acid forms sulfate salts.
Exothermic reactions transfer energy from the Nitric acid forms nitrate salts. Oxidation is the addition of oxygen. Reduction
reactants to the surroundings. is the removal of oxygen.
metal + oxygen → metal oxide.
Endothermic reactions transfer energy from the This is an oxidation reaction. Aluminium is extracted from aluminium oxide
surroundings to the reactants. by electrolysis.
Iron and steel rust when they are in contact with water and air.
Many exothermic reactions need an initial input Salt speeds up rusting. Electrolysis is a more expensive process as it
of energy to break some of the bonds of the requires a lot of electricity. It is only used for
reactants. Rusting can be prevented by a physical barrier such as paint or extraction of metals the are more reactive
oil, or sacrificial protection using a more reactive metal. than carbon.
HEDINGHAM SCHOOL Physics 9I Forces and Motion KNOWLEDGE MAP
9Ia Forces and Movement 9Ib Energy for Movement 9Id Turning Forces
Friction is the force between two objects that Kinetic energy is energy stored in moving objects. A lever is a long bar that turns around a pivot or
are touching. fulcrum.
Gravitational potential energy is energy stored in raised
Air resistance and water resistance are drag objects.
forces.
Elastic potential energy (or strain energy) is energy stored in
Drag forces slow down objects moving elastic materials when they are deformed (change shape).
through fluids.
Internal (or thermal) energy is the energy stored in the
The size of the drag force increases as the movement of particles.
A lever acts as a force multiplier if the effort
speed of the object increases.
Wind, moving water or solar energy are renewable resources. distance is greater than the load distance.
If the forces acting on a moving object are
Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources. A lever acts as a distance multiplier when a large
balanced, the object will move at a constant
effort force moves a small distance and the load
speed. The law of conservation of energy states that energy is never moves a greater distance.
If the forces acting on an object are created or destroyed, only transferred.
unbalanced, the difference between the two Efficiency of energy transfer compares the useful energy The turning effect of a force is called a moment.
forces is the resultant force. transferred to the total energy transferred.
Moment of the force = force x distance from pivot
The top speed of a moving object depends on Wasted energy such as sound or heating is dissipated (spread Nm N m
the maximum force that can move it forwards out)
and the friction or drag acting to slow it down. If the clockwise moment balanced the anticlockwise
9Ic Speed moment, the lever is in equilibrium.
𝒅𝒊𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒄𝒆
𝑺𝒑𝒆𝒆𝒅 = 9Ie More Machines
𝒕𝒊𝒎𝒆
Units of speed depend on the measurements you take. Levers are simple machines that help us use a
mph (miles per hour) smaller force to move an object.
km/h (kiliometres per hour) Ramps are simple machines that help us to push an
m/s (metres per second) object up a slope.
𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝒅𝒊𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒄𝒆 𝒕𝒓𝒂𝒗𝒆𝒍𝒍𝒆𝒅
𝑴𝒆𝒂𝒏 𝒂𝒗𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒈𝒆 𝒔𝒑𝒆𝒆𝒅 = Pulleys ae simple machines to help us move things.
𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝒕𝒊𝒎𝒆 𝒕𝒂𝒌𝒆𝒏
𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑘 𝑑𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝐽
Displacement is the distance, in a straight line, between and
= 𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑐𝑒 𝑁 × 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑚𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑑 (𝑚)
object and its starting point.
Relative speed is the speed of one object compared to
another.
You might also like
- 9B Summary SheetsDocument2 pages9B Summary Sheetsameema75% (4)
- REEPS CH 4 Solns DG PDFDocument7 pagesREEPS CH 4 Solns DG PDFKotulai HujakNo ratings yet
- h2 Chem ChecklistDocument3 pagesh2 Chem ChecklistJohn TanNo ratings yet
- Biology NMATDocument7 pagesBiology NMATMa. Ellah Patricia M. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Excerpt PDFDocument10 pagesExcerpt PDFerikNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesBIOLOGYNadine PascuaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument68 pagesPhotosynthesisTaru The MasterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document27 pagesLecture 16deepak_rc731757No ratings yet
- My Photosynthesis Summary Poster March 2016Document1 pageMy Photosynthesis Summary Poster March 2016amr ahmedNo ratings yet
- 9b PlantsDocument2 pages9b PlantsOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Biology SQ3RDocument68 pagesBiology SQ3RJay JustNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Animation.12.1: Nutrition Source & Credit: WordpressDocument36 pagesNutrition: Animation.12.1: Nutrition Source & Credit: WordpressChemist ChemistNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument19 pagesPlant NutritionOjok JodNo ratings yet
- T1.10 Mineral NutritionDocument10 pagesT1.10 Mineral NutritionKudaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nutrition in Plants .PMDDocument16 pages1 Nutrition in Plants .PMDvivek tripathiNo ratings yet
- PhytoremediationDocument26 pagesPhytoremediationlkokodkodNo ratings yet
- Biology Section 2 Lesson 2Document56 pagesBiology Section 2 Lesson 2Qiao EnNo ratings yet
- Answerkey 2Document34 pagesAnswerkey 2Yash BarureNo ratings yet
- AaronDocument2 pagesAaronaaronponderjoshua9No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesisSultana KhanNo ratings yet
- 1B EcologyDocument33 pages1B EcologyDeepak ThakurNo ratings yet
- Plants Evolved From Green Algae: Plant Evolution and DiversityDocument9 pagesPlants Evolved From Green Algae: Plant Evolution and DiversityUbaid GurmaniNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 Biotic Relationships: Positive Interaction ObjectivesDocument8 pagesActivity 8 Biotic Relationships: Positive Interaction ObjectivesJoshua BaltazarNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology GCSE Combined B8 Summary AnswersDocument5 pagesAQA Biology GCSE Combined B8 Summary AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Lesson 2: Plant Defense Responses: BiologyDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Lesson 2: Plant Defense Responses: BiologyIvimina Jack DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Ciences 4º PrimariaDocument8 pagesCiences 4º PrimariaM Ángeles Casla MartínNo ratings yet
- Class-Vii Subject-Science: Nutrition in PlantsDocument25 pagesClass-Vii Subject-Science: Nutrition in PlantsNisha ShahNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument10 pagesBooksbilingual B.No ratings yet
- BooksDocument10 pagesBooksbilingual B.No ratings yet
- Na Mlbio Ch22Document40 pagesNa Mlbio Ch22vxlrNo ratings yet
- Bio Term 1 2Document19 pagesBio Term 1 2Abirami SathishNo ratings yet
- SOIL 2A - NUTRIENT Available Form and FunctionsDocument7 pagesSOIL 2A - NUTRIENT Available Form and FunctionsMARY ANN HUBILLANo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology PDFDocument2 pagesPlant Physiology PDFGeorge KaridisNo ratings yet
- Plant PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPlant PhysiologyGeorge Karidis0% (1)
- Nutrition in Plants NotesDocument7 pagesNutrition in Plants NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument33 pagesNutrition in PlantsTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- 9B Summary SheetsDocument5 pages9B Summary SheetsNafiul Munsur Year 7No ratings yet
- Plant Evolution II 2021Document35 pagesPlant Evolution II 2021Yashika YashikaNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification (L9) - 27 TH MayDocument52 pagesBiological Classification (L9) - 27 TH MayUpal PramanickNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizers and VAM FungiDocument7 pagesBiofertilizers and VAM FungiManikandanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Waste OrganismDocument7 pagesMetabolic Waste OrganismAlrich VentusNo ratings yet
- Soil MicrobiologyDocument104 pagesSoil MicrobiologyEric Coluban AlipanNo ratings yet
- MICROORGANISMSDocument4 pagesMICROORGANISMSRidham JainNo ratings yet
- Lazan Weinberg q4 Module 2 AnswersDocument7 pagesLazan Weinberg q4 Module 2 AnswerszabNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-10-24 at 7.02.59 PMDocument9 pagesScreenshot 2022-10-24 at 7.02.59 PMKyanaNo ratings yet
- B 10 VRV 6221Document25 pagesB 10 VRV 6221Wildboy 2008No ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument28 pagesPDF Documentkaleb.kgzlNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesischikinenang eksdiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Uses of GlucoseDocument12 pagesLesson 2 Uses of Glucosekaniewska262No ratings yet
- Seeds and Seed GerminationDocument57 pagesSeeds and Seed GerminationAnonymous 77mrXm5No ratings yet
- 3 - Plant Processes - Respiration in PlantsDocument20 pages3 - Plant Processes - Respiration in Plantsalicia.ayubi01No ratings yet
- Bio Ch9 BookDocument28 pagesBio Ch9 Book4B21 Renee Sin Yat HeiNo ratings yet
- Landscape M StudyDocument52 pagesLandscape M StudypalaniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in Bio 102: Microbiology and Parasitology - Week No. 3Document4 pagesWorksheet in Bio 102: Microbiology and Parasitology - Week No. 3DELOS SANTOS JESSIECAHNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Plant Responses#3Document29 pagesPhotosynthesis and Plant Responses#3BALQIS NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument24 pagesSciencePradip KumarNo ratings yet
- Energy From PlantsDocument14 pagesEnergy From PlantsJohnC75No ratings yet
- Transportation of PlantsDocument3 pagesTransportation of Plantstaren17470No ratings yet
- How To Make Your Own EM-1 Inoculant and Bokashi: Rhodobacter SphaeroidesDocument10 pagesHow To Make Your Own EM-1 Inoculant and Bokashi: Rhodobacter SphaeroidesfrossopapaNo ratings yet
- Gesc101 PDFDocument10 pagesGesc101 PDFlakhuindiaNo ratings yet
- Class - 12 Chemistry - AminesDocument34 pagesClass - 12 Chemistry - AminesAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
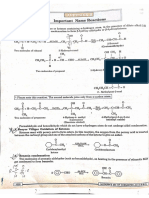
- Important Name Reactions XII ChemistryDocument13 pagesImportant Name Reactions XII ChemistryAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Chemical KineticsDocument73 pagesXII Chemistry Chemical KineticsAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- 7C Habitats HjMzC6Document8 pages7C Habitats HjMzC6Anonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- G8 Food Chain PuzzleDocument3 pagesG8 Food Chain PuzzleAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- Seed Dispersal: How Do Plants Reproduce?Document8 pagesSeed Dispersal: How Do Plants Reproduce?Anonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- 9 BCDocument21 pages9 BCAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- PagingDocument76 pagesPagingAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- Two-Step Production of 13-Butadiene From EthanolDocument197 pagesTwo-Step Production of 13-Butadiene From EthanolSanchez JorgeNo ratings yet
- Pak McqsDocument540 pagesPak McqsReki BalochNo ratings yet
- SPM Trial 2009 Che (MRSM)Document68 pagesSPM Trial 2009 Che (MRSM)SimPorNo ratings yet
- Recovery and Separation of Palladium From Spent CatalystDocument5 pagesRecovery and Separation of Palladium From Spent Catalystm_angel_monroyNo ratings yet
- Science q1m2Document30 pagesScience q1m2Juana Isabel B. LunaNo ratings yet
- Methanol Production Data Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesMethanol Production Data Sheet PDFAditiya Muhammad FattahNo ratings yet
- The Sacred Depths of Nature Ursula Goodenough Full ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Sacred Depths of Nature Ursula Goodenough Full Chaptermarta.scordato502100% (4)
- (CSEC Chemistry) Section B Notes and ESQsDocument45 pages(CSEC Chemistry) Section B Notes and ESQsNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Bio 110 - Ch2Document30 pagesBio 110 - Ch2محسن الشاطريNo ratings yet
- PVC's Physical Properties - PVCDocument8 pagesPVC's Physical Properties - PVCalguzduxtanNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.3 - Covalent Structures Short Answer QuestionsDocument31 pagesTopic 4.3 - Covalent Structures Short Answer QuestionsDonal GrayNo ratings yet
- Elements Cards 8.5x11 2sided PDFDocument32 pagesElements Cards 8.5x11 2sided PDFJuan A. ConesaNo ratings yet
- Paper SjaifullahDocument5 pagesPaper SjaifullahziNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Monitoring - Hydrogen BakeoutsDocument2 pagesCorrosion Monitoring - Hydrogen BakeoutsBharat KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Modeling of The Catalytic Oxidation of Xylene Over An Industrial V205-Ti02 (Anatase) CatalystDocument27 pagesKinetic Modeling of The Catalytic Oxidation of Xylene Over An Industrial V205-Ti02 (Anatase) CatalystQasim SarwarNo ratings yet
- Styrene ADocument4 pagesStyrene AIng QuimNo ratings yet
- Sdewes 2019Document737 pagesSdewes 2019renata portelaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltDocument37 pagesCHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltRaghav ParasharNo ratings yet
- Neet Ug Achiever Online Test Series Classic Target EngDocument4 pagesNeet Ug Achiever Online Test Series Classic Target Engcharsi anjumNo ratings yet
- 40 Chemistry Question For RevisionDocument5 pages40 Chemistry Question For RevisionSathish Sarma SathianarayananNo ratings yet
- Advanced Energy Materials - 2024 - Abdelhafiz - Tri Metallic Catalyst For Oxygen Evolution Reaction Enables ContinuousDocument11 pagesAdvanced Energy Materials - 2024 - Abdelhafiz - Tri Metallic Catalyst For Oxygen Evolution Reaction Enables ContinuousShizhao SuNo ratings yet
- 2022 Chem Bond Tut Qns and SolnsDocument16 pages2022 Chem Bond Tut Qns and SolnsBooNo ratings yet
- CheIng - June 2010 PDFDocument68 pagesCheIng - June 2010 PDFErvin WatzlawekNo ratings yet
- Nakshatras - PURVA ASHADA (Early Victory or The Undefeated) THE INVINCIBLE STARDocument3 pagesNakshatras - PURVA ASHADA (Early Victory or The Undefeated) THE INVINCIBLE STARANTHONY WRITER50% (2)
- Hydrogen BondingDocument16 pagesHydrogen BondingBalen I. MohammedNo ratings yet
- Daniel Fry ATOMS GALAXIES AND UNDERSTANDINGDocument44 pagesDaniel Fry ATOMS GALAXIES AND UNDERSTANDINGNyTamasNo ratings yet
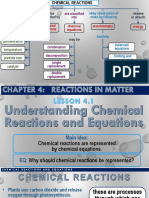
- Chemical Reaction Chapter 4Document37 pagesChemical Reaction Chapter 4Portia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Matter Properties and ChangeDocument103 pagesCH 3 Matter Properties and ChangeBryant BachelorNo ratings yet