Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Directional Feature: It Is One of The Key Features Which Differs
Uploaded by
Daniele Jenna EsguerraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Directional Feature: It Is One of The Key Features Which Differs
Uploaded by
Daniele Jenna EsguerraCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Demonstrate the difference between AC and DC Circuit
Direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) are the are two types
of electric current. The electrons in direct current flow in one
direction. The current produced by a battery is direct current. The
electrons in alternating current flow in one direction, then in the
opposite direction—over and over again. The current supplied to your
home by the local utility is alternating current. The current flow
alternates 120 times per second in the United States. In Europe it
alternates 100 times per second.
In which the direction of the current's flow is reversed, or alternated,
on a regular basis, AC current is a specific type of electric current.
Direct current is no different electrically from alternating current
except for the fact that it flows in the same direction at all times.
Alternating current was chosen early in the 20th century as the North
American standard because it presented fewer risks and promised higher
reliability than competing DC systems of the day. DC is the European
standard.Many of DC's deficiencies were later corrected, but not until a
substantial North American infrastructure had already been developed.
The difference between AC and DC is that AC is an alternating
current (the amount of electrons) that flows in both directions and
DC is direct current that flows in only one direction; the product
that is flowing being electrons. AC power is what fuels our homes.
The wires outside of our house are connected at two ends to AC
generators. DC is found in batteries and solar cells. Both AC and DC
employ magnets to repel electrons. Electrons are negatively charged
particles that are one of 3 components that make up an atom.
Negative charges will repel negative charges and positive charges
will repel positive charges, so one only needs to introduce a
negatively charged item next to electrons to force them to move in
the opposite direction.
Key Differences Between AC and DC
1. Directional Feature: It is one of the key features which differs
AC and DC. DC is a unidirectional type of electric current while AC
is bidirectional electric current.
2. Generation: AC and DC possess different generation procedures and
devices. DC is generated by static magnetic field while AC is
generated with the aid of dynamic magnetic field. Besides, AC is
generated by generators while DC is generated by cell, batteries by
converting the chemical energy of cell or battery into electrical
energy.
3. Frequency of Signal: The frequency of AC signal varies from 50
Hz to 60 Hz. It is different in different countries. DC signal has
zero frequency. Frequency is the number of cycles per second. As DC
signal do not cycle varying with time, thus it has zero frequency.
4. Type of Load: Load connected in AC can be capacitive, resistive,
or inductive. On the contrary, the load connected in DC circuit is
always resistive.
5. Power Factor: The power factor of alternating current lies
between 0 to 1 while power factor of DC is 1.
6. Ease of transmission: The AC power can be transferred easily and
efficiently as compared to DC power.
7. Voltage level: The DC voltage is low-level voltage while the AC
voltage is high in magnitude.
8. Storage: AC cannot be stored while DC can be stored in cell or
batteries. We can convert AC into DC using rectifier in our chargers
while we can convert DC into AC using inverters. But the storage of
AC is not possible.
2. Demonstrate the difference between Three phase and Single Phase
Circuit
Key Differences Between Single Phase and Three Phase
1. In single phase supply, the power flows through one conductor
whereas the three phase supply consists three conductors for power
supply.
2. The single phase supply requires two wires (one phase and one
neutral) for completing the circuit. The three phase requires three
phase wires and one neutral wire for completing the circuit.
3. The single phase supplies the voltage up to 230V whereas the
three phase supply carries the voltage up to 415V.
4. The maximum power is transferred through three phases as compared
to single phase supply.
5. The single phase has two wire which makes the network simple
whereas the three phase network is complicated as it consists four
wires.
6. The single phase system has only one phase wire, and if the fault
occurs on the network, then the power supply completely fails. But
in three phase system the network has three phases, and if the fault
occurs on any one of the phases, the other two will continuously
supply the power.
7. The efficiency of the single phase supply is less as compared to
three phase supply. Because the three phase supply requires less
conductor as compared to single phase supply for the equivalent
circuit.
8. The single phase supply requires more maintenance and become
costly as compared to three phase supply.
9. The single phase supply is mostly used in the house and for
running the small loads. The three phase supply is used in large
industries and for running the heavy loads.
3. How is electricity produced through magnetism?
Induction is the "sweeping" of a magnetic field across a
conductor and the generation of electromotive force (EMF) or voltage
in this action. By taking a rotor with many turns of wire on it and
rotating it inside a stator, which has a permanent magnetic field
(either from permanent magnets or, more likely, an electromagnet),
we generate electricity. It's done all the time.
Moving a coil across a magnetic field will produce a current . This is
called electromagnetic induction. The direction of the current depends
on how the coil is moved. The current produced in called the induced
current. Electromagnetic current is key to how a transformers, generator
electric motors and solenoids works.
4.Which is more dangerous, 3phase or single phase? Why?
“Is a 3-phase electric more dangerous than a single phase?
Yes, because three phase devices have more power per size. A device
powered by a three phase motor could drag you into moving parts,
pulling off body parts. Of course a single phase motor could do the
same, but people inexperienced with three phase motors sometimes do
not appreciate the amount of torque a three phase motor develops.
But inherently, three phase power is not more dangerous than single
phase power.
I’ve never heard of anyone being shocked by all three phases. You
would have to step on one phase with your bare foot, then grab the
other two phases with each hand. This would result in having current
flow first between your foot and your left hand, then your foot and
your right hand, and finally between your left and right hand,
repeating 120 times each second.
Which is more efficient, 3 phase or single phase? Why?
Single phase is mostly used for small consumers, like individual
houses - sockets in rooms, heating, etc. 3-phase is used on large-
scale objects like skyscrapers, factories, etc., especially when
electric engines are used (3-phase are ubiquitous and more
economical than 1/2-phase). The bigger your electricity/power needs,
the more economical sense does 3-phase make.
3-phase is only more efficient if you have a balanced 3-phase load.
It does then require less conductor area than the same power
delivered over single phase. But every piece of equipment would need
to be 3 phase to achieve this. For large industrial equipment it is
worth investing in this, but it is not economic to do for lots of
small pieces that can work equally well on single phase. You would
save on the electrical distribution cost, but at the small scale the
increased costs of connections, switches and controls would outweigh
the saving in copper.
Large office buildings tend to have three phase up to the
distribution boards, but then use single phase to the sockets and
appliances.
There would also be higher voltage at the sockets, which would be a
safety issue. The three phase is at 400v in UK, while single phase
is 220, from the same supply, so more power is delivered for the
same current in the 3 phase section, but at a lower, safer voltage
in the single phase section.
5. Which type of connection delivers more power, series or parallel?
Why?
In general, if the power consumed would depend on the circuit
structure. But for a simple case, such as two resistors connected in
series versus the same resistors connected in parallel (with
identical voltage sources in both), the power dissipated in the
parallel combination will be greater.
You might also like
- Circuits: What Is Electric Circuit?Document48 pagesCircuits: What Is Electric Circuit?Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsEngr Muhammad Faisal YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Magnetic EffectsDocument11 pagesMagnetic Effectsreenu rawat52No ratings yet
- Physics Ac DC ProDocument6 pagesPhysics Ac DC Prohi_scribdNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity Concepts: Electron Flow, Resistance, ConductorsDocument10 pagesBasic Electricity Concepts: Electron Flow, Resistance, ConductorsdanshokNo ratings yet
- Alternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)Document4 pagesAlternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)MonirNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart: Alternating Current Direct CurrentDocument6 pagesComparison Chart: Alternating Current Direct CurrentTafsir Hossain 1921890043No ratings yet
- Topics To Be Covered: Unit-2: Basic Circuit ElementsDocument11 pagesTopics To Be Covered: Unit-2: Basic Circuit ElementsParthaNo ratings yet
- Service 3Document22 pagesService 3Hriday PaulNo ratings yet
- Electron Current Voltage Semiconductor Frequency Hertz RFDocument1 pageElectron Current Voltage Semiconductor Frequency Hertz RFDean ParconNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- AC Vs DCDocument3 pagesAC Vs DCKhushi YadavNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument27 pagesBasic ElectronicsKarem Gómez-CadenasNo ratings yet
- Electrical QuestionsDocument32 pagesElectrical Questionselec310No ratings yet
- Electrodynamics slides-sO+sH.1Document19 pagesElectrodynamics slides-sO+sH.1Sarmad AliNo ratings yet
- Group 1 AC GeneratorDocument26 pagesGroup 1 AC GeneratorKhen Joshua VillegasNo ratings yet
- Familiarization of The Electrical Machine Laboratory ApparatusDocument5 pagesFamiliarization of The Electrical Machine Laboratory ApparatusRosalinda CondeNo ratings yet
- Electricity DefinitionDocument18 pagesElectricity DefinitionSumolmal Srisukri100% (1)
- MotorDocument19 pagesMotoreshet chafNo ratings yet
- Getting Started with Basic ElectronicsDocument19 pagesGetting Started with Basic ElectronicsRavitchandiran RNo ratings yet
- Basic Principal of Electrical CircuitryDocument19 pagesBasic Principal of Electrical CircuitryAreeba ParvezNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 - Basic ElectricityDocument48 pagesMODULE 7 - Basic ElectricityAna Cristina Castro-CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Solution - EnglishDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Solution - EnglishsegsNo ratings yet
- Electric Power SystemDocument10 pagesElectric Power SystemMiguel CbNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals OF ElectricityDocument37 pagesFundamentals OF ElectricityMarvin Sarmiento TalimonganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1kumalnimesh2No ratings yet
- Introductory Slides-1Document22 pagesIntroductory Slides-1Tawsif ahmedNo ratings yet
- Circuits 1Document29 pagesCircuits 1Gul Hassan MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Physics Electricity - Get RevisingDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Physics Electricity - Get RevisingaNo ratings yet
- CE115 Electrical Part ADocument45 pagesCE115 Electrical Part AMrSamspartNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview QuestionsDocument43 pagesElectrical Interview QuestionsAbbas JaveedNo ratings yet
- Amta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical SafetyDocument67 pagesAmta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical Safetydunlut pelemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity 1.1Document23 pagesIntroduction To Electricity 1.1August DuqueNo ratings yet
- Electric Power SystemDocument9 pagesElectric Power SystemSuterm SeccionNo ratings yet
- Electrical Notes For VIVA VOCEDocument5 pagesElectrical Notes For VIVA VOCE8ke0472xre4lzzw72r8No ratings yet
- Electricity Class X NotesDocument15 pagesElectricity Class X NotesGrgg Hkhkk100% (5)
- Activity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicoleDocument8 pagesActivity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicolenicsNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview QuestionsDocument43 pagesElectrical Interview QuestionsIsabella SwanNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL Engineering Interview / Viva Questions With AnswersDocument16 pagesELECTRICAL Engineering Interview / Viva Questions With AnswersnashinNo ratings yet
- Brany Alejandro Gomezzz Physics..!!!Document8 pagesBrany Alejandro Gomezzz Physics..!!!Brany Alejandro Gomez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview QuestionsDocument19 pagesElectrical Interview QuestionsAbhishek Chandrakanth Mugali100% (1)
- Basic Electricity: Volts, Amps, Resistance and PowerDocument37 pagesBasic Electricity: Volts, Amps, Resistance and PowerCris Yirah DaclanNo ratings yet
- Bigger Perspective Why Are Circuits Important?Document5 pagesBigger Perspective Why Are Circuits Important?Shaezer AlpayNo ratings yet
- Unit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsDocument21 pagesUnit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsMonte CarloNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL ENERGY CIRCUITSDocument4 pagesELECTRICAL ENERGY CIRCUITSSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 PDFDocument25 pagesCH 1 PDFVikas UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- BaliwDocument3 pagesBaliwZeref SprigganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesKib-anne Miguel PasikanNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Beee Ac-I NewDocument19 pagesUnit-II Beee Ac-I NewParikshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Transformer Parallel Operation ConditionsDocument42 pagesTransformer Parallel Operation ConditionsArunraj Venugopal100% (1)
- IAM PPT GRPDocument19 pagesIAM PPT GRPAshwin SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Electrical InterviewDocument49 pagesElectrical InterviewRaed Mohsen100% (3)
- Electricity 1Document9 pagesElectricity 1okguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument13 pagesCircuitsMinimus MaximusNo ratings yet
- Research Work No. 1Document47 pagesResearch Work No. 1penguinNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Symbols GuideDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Symbols Guideanwar9602020No ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission System EE 4029 Question Bank Short Questions: Module - 1Document17 pagesHVDC Transmission System EE 4029 Question Bank Short Questions: Module - 1Sreebash KhanNo ratings yet
- Ans Electricity Additional Questions 1Document5 pagesAns Electricity Additional Questions 1Rohit JindalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Theory PDFDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Theory PDFVilcu IonNo ratings yet
- If You Don'T Pass This Word Document To 20 People You Won'T Pass The Finals!!!!!Document1 pageIf You Don'T Pass This Word Document To 20 People You Won'T Pass The Finals!!!!!Daniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Light (Density 2.7 g/cm3), Thick (40Document11 pagesLight (Density 2.7 g/cm3), Thick (40Daniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- BUFFIN Andrew Petrophysics Across The Petroleum IndustryDocument12 pagesBUFFIN Andrew Petrophysics Across The Petroleum IndustrydquispefNo ratings yet
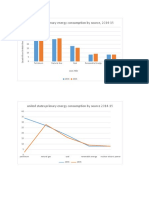
- United States Primary Energy Consumption by Source, 2014-15: Axis TitleDocument2 pagesUnited States Primary Energy Consumption by Source, 2014-15: Axis TitleDaniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- 0QFKnrDS Application-Form PDFDocument2 pages0QFKnrDS Application-Form PDFDaniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- 0QFKnrDS Application-Form PDFDocument2 pages0QFKnrDS Application-Form PDFDaniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Matrix AlgorithmDocument1 pageMatrix AlgorithmSethu RamanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Final RequirementDocument2 pagesGuidelines For Final RequirementDaniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- How To Be A VOLUNTEERDocument3 pagesHow To Be A VOLUNTEERDaniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- How To Be A VOLUNTEERDocument3 pagesHow To Be A VOLUNTEERDaniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Complete 11 KV Assemblies Final 01-2016Document70 pagesComplete 11 KV Assemblies Final 01-2016zararNo ratings yet
- Chem B Unit 3 Heat of Combustion Lab ReplacementDocument3 pagesChem B Unit 3 Heat of Combustion Lab ReplacementjocelynNo ratings yet
- PS Basic ConceptDocument22 pagesPS Basic ConceptORBIZ ORBIZNo ratings yet
- MEL301 2014 Tutorial4 Draft Version 01 PDFDocument2 pagesMEL301 2014 Tutorial4 Draft Version 01 PDFAkhil NekkantiNo ratings yet
- Electric QuantitiesDocument34 pagesElectric Quantitiestear6025No ratings yet
- Capacitance - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesCapacitance - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- Orifice Plate Flow Calculator Pressure DropDocument6 pagesOrifice Plate Flow Calculator Pressure Droplutfi awnNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure)Sahil Kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering I: Barham S. Mahmood E-Mail: Petroleum Engineering DepartmentDocument16 pagesReservoir Engineering I: Barham S. Mahmood E-Mail: Petroleum Engineering DepartmentAbdulla MohammadNo ratings yet
- Structures 7th Edition Schodek Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesStructures 7th Edition Schodek Solutions Manuala739355516100% (1)
- Using CFD to Design Thermal RollersDocument9 pagesUsing CFD to Design Thermal RollersRocky DarkNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of Moist Air (Total Heat) Dry Bulb TemperatureDocument6 pagesEnthalpy of Moist Air (Total Heat) Dry Bulb Temperatureammar100% (1)
- CV For JobDocument2 pagesCV For JobSuleman AwanNo ratings yet
- WW3 - Long QuizDocument3 pagesWW3 - Long QuizOLIVEROS DESIREE L.No ratings yet
- Group Theory-Part 10 Normal Modes of VibrationDocument10 pagesGroup Theory-Part 10 Normal Modes of VibrationRD's AcademyNo ratings yet
- Three Phase CircuitsDocument17 pagesThree Phase CircuitsKrishna Reddy Y.VNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialDocument80 pagesStrength of Materialpriyankar007No ratings yet
- DR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer HW NO-6Document1 pageDR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer HW NO-6Safaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Certification and personnel qualification for ultrasonic testing of steel plateDocument8 pagesCertification and personnel qualification for ultrasonic testing of steel plateNooruddin SheikNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Architectural AcousticsDocument4 pagesEssential Elements of Architectural AcousticsJoanna TamanoNo ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics in the Canonical EnsembleDocument42 pagesStatistical Mechanics in the Canonical Ensemblepesta0% (1)
- BOLTGRP13Document31 pagesBOLTGRP13taddeoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0029801815005089 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0029801815005089 MainAhmad RidhoNo ratings yet
- In Term Ol Forces Form Quiz KeyDocument2 pagesIn Term Ol Forces Form Quiz KeyRasheleen Jane WongNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 PDFDocument1 pageHomework 4 PDFVamsikrishna YadavNo ratings yet
- List of FormulasDocument1 pageList of FormulasKevin ElevenNo ratings yet
- Main Engineering MechanicsDocument42 pagesMain Engineering Mechanicsarnoldewood1No ratings yet
- Atpl Pof 1-16Document16 pagesAtpl Pof 1-16blessedbuddhaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Atoms and Nuclei PDFDocument25 pages8 - Atoms and Nuclei PDFthinkiit67% (3)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesFrom EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsFrom EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- OFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyFrom EverandOFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyNo ratings yet
- The Boy Who Harnessed the Wind: Creating Currents of Electricity and HopeFrom EverandThe Boy Who Harnessed the Wind: Creating Currents of Electricity and HopeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (130)
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemFrom EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentFrom EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesFrom EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Implementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachFrom EverandImplementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successFrom EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresFrom EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNo ratings yet
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsFrom EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureFrom EverandThe Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (48)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualFrom EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridFrom EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Biogas Production: Pretreatment Methods in Anaerobic DigestionFrom EverandBiogas Production: Pretreatment Methods in Anaerobic DigestionNo ratings yet
- DIY Free Home Energy Solutions: How to Design and Build Your own Domestic Free Energy SolutionFrom EverandDIY Free Home Energy Solutions: How to Design and Build Your own Domestic Free Energy SolutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Machine Learning and Data Science in the Oil and Gas Industry: Best Practices, Tools, and Case StudiesFrom EverandMachine Learning and Data Science in the Oil and Gas Industry: Best Practices, Tools, and Case StudiesPatrick BangertRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Energy, Light and Electricity - Introduction to Physics - Physics Book for 12 Year Old | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandEnergy, Light and Electricity - Introduction to Physics - Physics Book for 12 Year Old | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Solar Electricity Basics: Powering Your Home or Office with Solar EnergyFrom EverandSolar Electricity Basics: Powering Your Home or Office with Solar EnergyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Air-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AFrom EverandAir-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&ARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)