Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Note On Electrical Energy 2021
Uploaded by
Samuel AjanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Note On Electrical Energy 2021
Uploaded by
Samuel AjanaCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRICAL ENERGY
CONCEPT OF ELECTRON FLOW
The structure of an atom shows that an atom is made up of a central nucleus and electrons revolving
round the nucleus through orbits or shells.
Electrons are held to the nucleus by a strong force. If the electrons are tightly held to the nucleus such that
they will not be made free by energy; materials with such atoms are called insulator. E.g.
non-metals. But if the energy emitted makes the electrons free, such materials are called conductors e.g.
metals and carbon (graphite).
The motion of free electrons in a conductor is called electron flow or electric current which constitutes
electricity in an electric circuit.
The flow of electrons in one direction in a circuit is called direct current (DC). If the direction of
electron flow changes regularly, the current is called alternating current (AC).
DIRECTION OF ELECTRON FLOW
Electric current is the flow of negative electrons from the negative terminal of battery to the positive
terminal of the battery. But conventional electric current flows from the positive terminal to the negative
terminal.
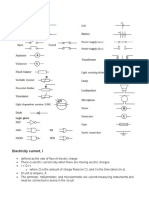
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
A circuit is a diagram representing the pathway of electric current when some electric materials are
connected together. The symbols or signs used for electrical materials are shown below;
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
This is a loop of wire connected at each end to an energy source e.g. battery. For a circuit to work, it must
be a complete circuit of conducting materials. If it breaks, the electrons cannot complete the whole circuit
and flow stops. When electricity flows through a complete circuit, it produces an electric current.
Convectional Current and the Flow of Electrons
Series and Parallel Circuits
Series Circuits: The parts n series circuits are connected to form one continuous loop. In this case, the
current can flow through all the different components through one path.
Disadvantages of Series Circuit
(i) The current has only one path. If a lamp or component is disconnected or faulty, all the
components will stop working because of a gap in the circuit.
(ii) When there are more lamps in the series circuit, the lamps will be dimmed as the current flows
through each component in turn.
Parallel Circuits
In parallel circuit, each component is connected separately in its own loop from one end of the battery to
the other. This means that, the current can flow in a different path around the circuit. If a component is
faulty, the current can flow through another branch in the circuit.
Advantages of Parallel Circuit
(i) Each component of the circuit works equally well even when more bulbs are connected.
(ii) The total circuit current is the sum of the separate currents in the branches.
(iii) The amount of current in each branch depends on the components of the branches as each
component has a separate resistance to the flow of the current.
A simple Parallel Circuit
Measuring the Electric Current
1 Ammeters
Current is measured in amperes or amps (A). We measure current using an ammeter. An ammeter must
always be connected in series in the circuit. The variable resistance also called rheostat is used to vary
the amount of current in the circuit. When the resistance in the rheostat increased, the ammeter reading is
lower.
In a parallel circuit, several ammeters are needed, one ammeter for every branch. An ammeter must
always be connected in series in the branch to measure the current.
When several ammeters are placed in a parallel circuit, the total current can be measured by adding the
values of each ammeter. For example:
0.9A
0.3A
0.3A 1
0.3A
2
Ammeter in Parallel circuit Ammeter in series circuit
A1= A2 + A3 +A4 A1 = A2 = A3
2. Voltmeters
The energy that the battery gives to the circuit is measured in Volts (V). Voltmeter is used to measure the
voltage. Voltage is a measure of the differences in electrical energy between two parts of a circuit also
known as potential difference (p.d). The higher the voltage, the greater the amount of energy that the
battery transfers.
A voltmeter must be connected in parallel.
HOUSEHOLD WIRING
Household wiring is done in parallel circuits so that if there is a faulty appliance or component then the
rest of the house can still be supplied with electric current.
The electric current that is supplied to our homes can be dangerous as it can shock or even kill if touched.
LIVE, NEUTRAL AND EARTH WIRES
Live wire carries a high voltage into the appliances and is very dangerous.
The Neutral wire carries current back from the appliances to the power station. The voltage in the
neutral wire is lower than the voltage in the live wire.
An Earth wire is connected directly to the metal parts of the casing of an appliance.
If a fault develops and the live wire touches the metal case, then a large current flows to the earth wire.
The surge current will cause the fuse to melt. But if the appliance is not earthed, the current can flow
through a person touching the case causing injury (shock) or even death.
Nowadays, most appliances have plastic case which is an insulator and this do not need earth wire.
Wiring of a Fused Plug
Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Fuse: This is a safety device in an appliance made of a thin piece of wire that is inclined in a circuit. It is
made up of tin lead alloy which has a low melting point.
Fuses have ratings e.g. 3A – Fuse, 5A – Fuse and 30A – Fuse. The wire melts (becomes hot and melts)
when an electric current that is too high tries to flow through the fuse. This can happen when there is a
fault in the appliance. This will break the circuit by cutting off current flow.
The Circuit Breaker contains an electromagnet which makes the contact points separate when current
exceeds the rated value of the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker acts as a safety device just like a fuse. It
protects an electric circuit from damage caused by overload. One other advantage is that it can be reset be
pressing a button but fuse cannot be reset that way, the fuse – wire must be replaced.
Reading an Electric Meter
The electric meters in our homes measure the amount of electricity the households use. This is used to
produce the bills. The use of electric energy is shown on the meter as kilowatts – hour (Kwh). That is one
kilowatt – hour is the electric energy used by 1 Kw appliance in one hour.
Total amount of energy is:
*Energy = Power x Time
(Joules) (J) = (watt) (w) (second) (s)
Worked examples on calculating the cost of electricity
1. A 2000W electric heater is used for 10 hours. What is the cost at ₦6.00 per kWh?
Solution:
Energy used (kWh) = power (kW) x time (hours)
= 2 kW x 10 hours
= 20 kWh
Cost at ₦6.00 per kWh x 6.00 = ₦120.00
2. In 1 minute how much energy does a 100 W electric bulb transfers?
Energy = Power x time
POWER = 100WATT
TIME= 1 MINUTES = 60 SECONDS
WORK DONE = POWER X TIME
100 X 60 =6000 J
3. Gravriel watches Television 4 hours every day for 30 days. If the power rating of the TV is 75
watt, what is the cost of watching that T V at the end of the month if the unit cost of electricity
is 100 naira per kilowatt.
Power rating of TV= 75 watt
If 1000w= 1kw
75 watt= 0.075kw
For watching TV for 4hour every day 0.075 x 4= 0.3kwh units of energy is used
Daily.
For watching the TV for 4hours daily for 30 days, 0.3 x30= 9kwh units of energy is used.
If 1kwh -100 naira, the total cost of watching that TV 4 hours daily for 30 days will be:
N100 x9kwh = N900
Assignment
1. Two or more cells when connected in series make a______
A. battery B. circuit C. terminal D. resistor
2. Inside cell positive terminal is made of_______
A. zinc case B. graphite rod C. carbon D. manganese
3. A positive terminal and a negative terminal are present in a______
A. cell B. battery C. circuit D. bulb
4. The chemical reactions which take place inside a cell provides_______
A. heat B. energy C. product D. resistor
5. The instrument which is used to measure electric current is called_____
6. In a lighted bulb there is a flow of electrons in_______
A. filament B. socket C. glass D. holder
7. The path along which electric current flows is called_______
8. Ammeter should be connected in_______ to measure current flow in circuit
9. The current which flows through each component of a series circuit is______
A. same B. different C. greater D. lesser
10. There are approximately 90 million households that use TVs in the United States. Each TV uses
an average of 5watt of power and is turned on for 6.0 hours a day.
If electrical energy costs ₦0.11 per KWh, how much money is spent every day in keeping 90
million TVs turned on?
You might also like
- Corolla L 2014 2zr FaeDocument526 pagesCorolla L 2014 2zr Faeelizardo macias condoriNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitsDocument50 pagesElectrical Circuitsapi-222503660No ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN On Drug AbuseDocument2 pagesLESSON PLAN On Drug AbuseSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- MODULE Class VIII C08Document37 pagesMODULE Class VIII C08gpfphysicsNo ratings yet
- MODULE Class VIII C08Document30 pagesMODULE Class VIII C08gpfphysicsNo ratings yet
- MODULE Class VIII C08Document35 pagesMODULE Class VIII C08gpfphysicsNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits & QuantitiesDocument29 pagesElectrical Circuits & QuantitiesDejaunae Lawson50% (2)
- M2-EUtilities 1Document62 pagesM2-EUtilities 1Aguinaldo OweneNo ratings yet
- Electricity 2023Document48 pagesElectricity 2023fudright14No ratings yet
- Local Media861834077404597152-1Document62 pagesLocal Media861834077404597152-1Patrick GorospeNo ratings yet
- Nee2102 Experiment Report 2Document15 pagesNee2102 Experiment Report 2Lynndon VillamorNo ratings yet
- AQA P2 Physics Electricity BookletDocument19 pagesAQA P2 Physics Electricity BookletSteve BishopNo ratings yet
- Current and Voltage in CircuitsDocument31 pagesCurrent and Voltage in CircuitsChalitha RanasingheNo ratings yet
- Electricity and LightingDocument15 pagesElectricity and LightingdarielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsDocument32 pagesIGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsSam JordanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics Theory: English For EEITDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Electronics Theory: English For EEITYou Can Shine AtomNo ratings yet
- Direct Current: Cells and Batteries Supply Electric Current Which Always Flows This Is CalledDocument42 pagesDirect Current: Cells and Batteries Supply Electric Current Which Always Flows This Is CalledMokYikLamNo ratings yet
- DC Network - 6 - 26 - 18Document61 pagesDC Network - 6 - 26 - 18Neli Aguilar SenupeNo ratings yet
- F5 Chapter 2 - ElectricityDocument50 pagesF5 Chapter 2 - ElectricitySudhan NairNo ratings yet
- Bmat Physics KnowledgeDocument25 pagesBmat Physics KnowledgeSummer GUO [07C15M]No ratings yet
- 13 Electric Circuits Batteries and ResistorsDocument10 pages13 Electric Circuits Batteries and ResistorsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Circuits: What Is Electric Circuit?Document48 pagesCircuits: What Is Electric Circuit?Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - ElectricityDocument29 pagesUnit 2 - ElectricityT. Christabel VijithaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document13 pagesLab 2devchithNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument17 pagesElectricitymisterbrownerNo ratings yet
- Familiarization of The Electrical Machine Laboratory ApparatusDocument5 pagesFamiliarization of The Electrical Machine Laboratory ApparatusRosalinda CondeNo ratings yet
- c19 Practical Electricity CompressedDocument11 pagesc19 Practical Electricity CompressedSherazNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit SymbolsDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Symbolsanwar9602020No ratings yet
- MODULE 5 TABAOelectricity and CircuitsDocument13 pagesMODULE 5 TABAOelectricity and Circuitsannetabao01No ratings yet
- Physics PresentationDocument24 pagesPhysics PresentationGrace jereNo ratings yet
- Ans Electricity Additional Questions 1Document5 pagesAns Electricity Additional Questions 1Rohit JindalNo ratings yet
- Directional Feature: It Is One of The Key Features Which DiffersDocument5 pagesDirectional Feature: It Is One of The Key Features Which DiffersDaniele Jenna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Works - Write UpDocument63 pagesElectrical Works - Write UpKenzo Braye GeraleNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument10 pagesCurrent ElectricityClemence TafitiNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument27 pagesBasic ElectronicsKarem Gómez-CadenasNo ratings yet
- Ee 003 Lecture11Document39 pagesEe 003 Lecture11JC LoplopNo ratings yet
- 2 Ohm's Law: ExperimentDocument25 pages2 Ohm's Law: ExperimentSabling DritzcNo ratings yet
- 9.1-Electrostatic Phenomena: Like Charges Repel, Unlike Charges AttractDocument17 pages9.1-Electrostatic Phenomena: Like Charges Repel, Unlike Charges AttractArkar Myint ShweNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10 NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity Class 10 NotesKota SrinadhNo ratings yet
- 01D Basic ConceptsDocument64 pages01D Basic ConceptsRA MemijeNo ratings yet
- Igcse 23 Current&VoltageincircuitsDocument32 pagesIgcse 23 Current&VoltageincircuitsHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- ECS203 - Handout 1ADocument29 pagesECS203 - Handout 1ArsrodcNo ratings yet
- Practical Electricity: Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book DraftDocument21 pagesPractical Electricity: Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book DraftJason CandelariaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Notes 3Document9 pagesElectricity Notes 3Jimena YoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in ScienceDocument13 pagesPortfolio in ScienceMarkLesterEstrellaMabagosNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter-12-: Electricity CBSE Study NotesDocument11 pages10 Chapter-12-: Electricity CBSE Study Notesrucha BNo ratings yet
- 10th Electricity Study Notes For Chapter - 12 Ncert PDFDocument11 pages10th Electricity Study Notes For Chapter - 12 Ncert PDFNaseeb YadavNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 8 - Generation of Electricity PDFDocument7 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 8 - Generation of Electricity PDFFarah Sofea Razali50% (8)
- P503 - CircuitsDocument53 pagesP503 - Circuitstai057482No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Physics Electricity - Get RevisingDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Physics Electricity - Get RevisingaNo ratings yet
- Direct Current: Ohm'S Law, Series, Parallel Connections, Batteries and PowerDocument50 pagesDirect Current: Ohm'S Law, Series, Parallel Connections, Batteries and PowerTamaki DellosaNo ratings yet
- I DQ DT: Topic 1: Basic Concepts 1.0 CurrentDocument11 pagesI DQ DT: Topic 1: Basic Concepts 1.0 Currentkumares_nfbmNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Electricity NotesDocument12 pagesYear 9 Electricity Notesapi-408461912100% (1)
- Electricity 1Document9 pagesElectricity 1okguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- G9, 2.7 Current and Voltage in CircuitsDocument4 pagesG9, 2.7 Current and Voltage in CircuitsKinmokusei MyoeNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Grade 12Document53 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Grade 12Del Mundo, Jelo ArsuaNo ratings yet
- Cicuits REVISIONDocument3 pagesCicuits REVISIONSally SargentNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 2023 Checkpoint Experiment - Chlorophyll and PhotosynthesisDocument7 pages2023 Checkpoint Experiment - Chlorophyll and PhotosynthesisSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- How Do Colour Filters WorkDocument5 pagesHow Do Colour Filters WorkSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Note REACTIVITY SERIES OF METALSDocument3 pagesNote REACTIVITY SERIES OF METALSSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- DRUG and SUBSTANCE ABUSEDocument8 pagesDRUG and SUBSTANCE ABUSESamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint POWER POINT ON CHEMICAL FORMULAEDocument55 pagesCheckpoint POWER POINT ON CHEMICAL FORMULAESamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Carbon Dioxide and PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesExperiment - Carbon Dioxide and PhotosynthesisSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Crude Oil and PetrochemicalsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan On Crude Oil and PetrochemicalsSamuel Ajana100% (1)
- Lesson Plan On Resources From Living and Non Living ThingsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan On Resources From Living and Non Living ThingsSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Note On Resources From Living and Non-Living ThingsDocument2 pagesNote On Resources From Living and Non-Living ThingsSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Resources From Living and Non Living ThingsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan On Resources From Living and Non Living ThingsSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument17 pagesSeparation TechniquesSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- WK 2 Lesson Plan On ChemicalsDocument3 pagesWK 2 Lesson Plan On ChemicalsSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Note On UNIQUENESS OF MAN.Document2 pagesNote On UNIQUENESS OF MAN.Samuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- NOTES ON Changes in Non-Living Things 2022Document2 pagesNOTES ON Changes in Non-Living Things 2022Samuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Count Your Blessings - 3vsDocument6 pagesCount Your Blessings - 3vsSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Basic 7 Note On Drug AbuseDocument4 pagesBasic 7 Note On Drug AbuseSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- To God Be The GloryDocument4 pagesTo God Be The GlorySamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Great Is Thy Faithfulness - WidescreenDocument6 pagesGreat Is Thy Faithfulness - WidescreenSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Note On Changes in Living Things 2023Document2 pagesNote On Changes in Living Things 2023Samuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument17 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Coal Mill & Fan PerformanceDocument52 pagesCoal Mill & Fan PerformanceManohar TatwawadiNo ratings yet
- PSP Lab 4 Group 7 Section (A)Document4 pagesPSP Lab 4 Group 7 Section (A)Kazi ShahadatNo ratings yet
- Jess 101Document19 pagesJess 101SampathiNo ratings yet
- Lect11 SteamTurbine 01Document9 pagesLect11 SteamTurbine 01SpidyNo ratings yet
- Swellex Pumps: Intelligence Built-In "Be Smart"Document4 pagesSwellex Pumps: Intelligence Built-In "Be Smart"Sebastian Nuñez RiquelmeNo ratings yet
- H2 NOx AftertreatmentsDocument13 pagesH2 NOx AftertreatmentsFacu Spivak100% (1)
- GravitationDocument26 pagesGravitationNashwa ObaidNo ratings yet
- Workshop 29: Accessing, Reading & Erasing Engine Trouble Codes 2.7tdiDocument3 pagesWorkshop 29: Accessing, Reading & Erasing Engine Trouble Codes 2.7tdimorusNo ratings yet
- Research On Applications of Low Wind Speed Power in ASEANDocument127 pagesResearch On Applications of Low Wind Speed Power in ASEANGiang VuNo ratings yet
- CR4000 Series Service Regulators: Technical BulletinDocument5 pagesCR4000 Series Service Regulators: Technical BulletinFRANKLIN RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Cyme Modules2Document3 pagesCyme Modules2ArcGis TranscoNo ratings yet
- PC220-8M0-Serial No.Y221001 and UpDocument640 pagesPC220-8M0-Serial No.Y221001 and UpRashid MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Mains Dimmable Liner LED Driver Description Features: Is A High Current PrecisionDocument7 pagesMains Dimmable Liner LED Driver Description Features: Is A High Current PrecisionMechín Rodriguez Ejvr100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0360319912017181 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0360319912017181 MainNafees VakilNo ratings yet
- Vt230se English ManualDocument253 pagesVt230se English ManualQuang Bách100% (4)
- Waaree Gurantee CertificateDocument9 pagesWaaree Gurantee Certificatemurugan199118No ratings yet
- Previous 6th Verification ReportDocument27 pagesPrevious 6th Verification ReportAtul TakarkhedeNo ratings yet
- 3.A - The First Law of Thermodynamics (Answer) - Physics LibreTextsDocument5 pages3.A - The First Law of Thermodynamics (Answer) - Physics LibreTextsFASIKAW GASHAWNo ratings yet
- SUPER 1803-3 EN 2509980 MPW 1117Document22 pagesSUPER 1803-3 EN 2509980 MPW 1117chintia nugraheniNo ratings yet
- Kick Control: BY: Naga Ramesh D. Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering Dept. KlefDocument13 pagesKick Control: BY: Naga Ramesh D. Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering Dept. Klefavula43No ratings yet
- Hard Reference Sensor Section 8 Electrical Torque 5665001 01Document13 pagesHard Reference Sensor Section 8 Electrical Torque 5665001 01Daniel Rolando Gutierrez FuentesNo ratings yet
- We Wlsk3012a Wlsk6012a Wlsk8012a SolderDocument2 pagesWe Wlsk3012a Wlsk6012a Wlsk8012a Solderzeroescobar9No ratings yet
- Bueno Eaton-Secondary-Unit-Substation-Design-GuideDocument48 pagesBueno Eaton-Secondary-Unit-Substation-Design-GuideGEISON JUNIOR CAJA GUERRANo ratings yet
- Manual Do ProprietárioDocument51 pagesManual Do ProprietárioRonaldo FariaNo ratings yet
- Bsme Program of StudyDocument3 pagesBsme Program of StudyIan Joseph DalanginNo ratings yet
- Inf # 2Document18 pagesInf # 2Ahmed Shaaban Soliman HamedNo ratings yet
- SSED - Solved Problems For Chapter 3Document7 pagesSSED - Solved Problems For Chapter 3MINH NGUYỄN THẾNo ratings yet
- Employee Satisfation at IOCL Project Final ReportDocument67 pagesEmployee Satisfation at IOCL Project Final ReportShivani AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 7 Set-Up Welding Equipment SMAWDocument45 pages7 Set-Up Welding Equipment SMAWRobinson ConcordiaNo ratings yet