Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endemic Diseases Reading Skills
Uploaded by
ahissiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endemic Diseases Reading Skills
Uploaded by
ahissiCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 7: HYGIENE AND HEALTH
(READING SKILLS)
ENDEMIC DISEASES
(les maladies endémiques)
i. Introduction
Endemic diseases are sudden outbreak diseases. There are very
dangerous. We can note that in Africa, there are several endemic
diseases. However there is a different between a pandemic, an epidemic
and an endemic disease. Most of them can be avoided.
ii. Characteristics
1. An endemic disease is constantly present in a group or geographic
area. It is not always present at high levels. It can be relatively rare. It is
caused by germs like bacteria or viruses. E.g MALARIA
2. A pandemic disease is a sudden outbreak. It spreads around the world.
It is contagious. E.g: THE CORONA VIRUS
3. An epidemic disease is a sudden outbreak in a limited specific
geographic region. It is contagious and its spreads to many people. E.g
EBOLA FEVER
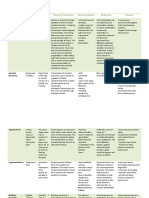
iii. Examples of some endemic diseases
DISEASES SYMPTOMS MODE OF PREVENTION
TRANSMISSION
Malaria High fever -Anopheles -remove stagnant water
Body aches mosquito bites -use insect spray or
Chills headaches insect repellent or sleep
Lack of appetite under a mosquito net
_
Ebola High fever -contact with the -wash your hands with
Body aches skin or bodily soap and water or a
Diarrhoea fluids of an hand sanitizer
Bleeding infected animal -avoid contact with blood
headaches -from person to and body fluids.
person -do not handle items
from an infected
person’s fluids
AIDS/HIV fever, headache -sexual -sexual abstinence
chronic diarrhoea intercourses -use of condom during
_blood transfusion sexual intercourses
fatigue -mother to her -prenatal cure
loss of weight unborn baby -avoid sharing any
skin rash shape object
Poliomyelitis progressive -Direct contact -vaccination
muscle or joint with someone
weakness and infected with the
pain virus.
fatigue
muscle atrophy
Cholera dehydration -from person to -drink safe
diarrhoea in very person water(hydration)
large quantities -by drinking -use toilets to defecate
vomiting contaminated -wash your hands with
leg cramps water soap and water
weakness frequently
-take antibiotics
Diarrhoea stomach cramps -from person to -wash your hands with
frequent and person soap or hand sanitiser
watery poos -by drinking after using the toilets.
fever contaminated -Avoid
stomach water sharing towels
pain/ache
Hepatitis A nausea and -by eating -wash properly fruits
vomiting contaminated and vegetables
loss of appetite food -wash your hands
dark urine before eating and after
using the toilets
Conclusion
“PREVENTION IS BETTER THAN CURE” ONLY A STRICT RESPECT OF SOME
HYGIENIC RULES CAN HELP US TO AVOID THESE DEADFUL DISEASES AND
BREAK THEIR CHAIN OF TRANSMISSION.
You might also like
- FF0217 01 Free Technology Powerpoint TemplateDocument10 pagesFF0217 01 Free Technology Powerpoint TemplateAtif MajeedNo ratings yet
- Crisis of Hypertension Revised 1Document57 pagesCrisis of Hypertension Revised 1keenmunir100% (4)
- Health 8 Q3 Week 7-8 Module 1-6Document22 pagesHealth 8 Q3 Week 7-8 Module 1-6Richard CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Natural Antibiotics and Antivirals: Homemade Herbal Remedies that Kill Pathogens and Cure Bacterial Infections and Allergies. Prevent Illness, Cold and FluFrom EverandNatural Antibiotics and Antivirals: Homemade Herbal Remedies that Kill Pathogens and Cure Bacterial Infections and Allergies. Prevent Illness, Cold and FluNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Exam GuideDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Exam GuidearchanaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Problem Key Biol 121Document13 pagesGenetics Problem Key Biol 121S0% (1)
- Herbal Med1 Samuel Thomson 2015 16Document35 pagesHerbal Med1 Samuel Thomson 2015 16connieonline6149100% (1)
- A Student Manual of Clinical Skills 13 7 8Document194 pagesA Student Manual of Clinical Skills 13 7 8mofath100% (5)
- Construction Manpower SafetyDocument25 pagesConstruction Manpower SafetyFritz BalasabasNo ratings yet
- Recommendations Document On National Roaming Access Terms and Conditions, As Well As MVNO Access Terms and ConditionsDocument50 pagesRecommendations Document On National Roaming Access Terms and Conditions, As Well As MVNO Access Terms and ConditionsahissiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Disease and Infection Worksheet 1Document1 pageLesson 1 - Disease and Infection Worksheet 1kiannatherese andradaNo ratings yet
- 10.10 Health and Diseases - Centre of Excellence Trust AcademyDocument11 pages10.10 Health and Diseases - Centre of Excellence Trust AcademyeducationkasondeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Disease Prevention and Control (Communicable) : Health 8Document4 pagesLesson 1 - Disease Prevention and Control (Communicable) : Health 8Ashleigh ReignNo ratings yet
- Common Childhood Diseases and Healthy HabitsDocument6 pagesCommon Childhood Diseases and Healthy HabitsHF ManigbasNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument41 pagesCommunicable DiseasesThirdy EstolanoNo ratings yet
- Winterbourne Diseases Causative Agent Incubation Period of Transmission Signs of Symptoms Medications MeasuresDocument7 pagesWinterbourne Diseases Causative Agent Incubation Period of Transmission Signs of Symptoms Medications MeasuresJeanie Rose AlduesoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Prevention TipsDocument5 pagesCommunicable Disease Prevention TipsMaristelaMolinaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument26 pagesCommunicable DiseasesFRANCES TREESA LOUISE JUMAWANNo ratings yet
- Ang DépliantsDocument2 pagesAng DépliantsChristelle NyadjouNo ratings yet
- Protect yourself from COVID-19Document1 pageProtect yourself from COVID-19rsi yatofaNo ratings yet
- Biology Organelle DNA Function WBC Disease PreventionDocument7 pagesBiology Organelle DNA Function WBC Disease PreventionMISS RASHMINo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 8 Our Health, Diseases and Prevention – RBSE GuideDocument5 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 8 Our Health, Diseases and Prevention – RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Influenza Tri Fold BrochureDocument2 pagesInfluenza Tri Fold BrochureTina Tripp100% (1)
- Stop The Spread: Source: World Health OrganizationDocument1 pageStop The Spread: Source: World Health OrganizationAlbert CostaNo ratings yet
- National Service Training Program 1Document2 pagesNational Service Training Program 1Ivan MoralesNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument8 pagesCommunicable Diseaseabhishek.abhiy24No ratings yet
- 10.-Communicable-Diseases-2Document7 pages10.-Communicable-Diseases-2jeromejamora7No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseaseKim FresnilloNo ratings yet
- Hindari Penyebaran: Source: World Health OrganizationDocument1 pageHindari Penyebaran: Source: World Health OrganizationMaureen Yanita DjohariNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease ResearchDocument4 pagesInfectious Disease ResearchEpic EssayNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument6 pagesHuman Health and DiseaseRisshu Farms100% (2)
- Chapter 1. Health and Hygiene - SADocument8 pagesChapter 1. Health and Hygiene - SAPalakNo ratings yet
- Corona Ebook PDFDocument18 pagesCorona Ebook PDFManish Mishra100% (1)
- Science & Tech WritingDocument4 pagesScience & Tech WritingApril BuenoNo ratings yet
- Health Q3 M2Document15 pagesHealth Q3 M2olameonfrixandrei486No ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument64 pagesCommunicable DiseaseMorris AngelaNo ratings yet
- Home Monitoring PackageDocument7 pagesHome Monitoring PackagenkhhhNo ratings yet
- Nurs 3710 Ysu Poster TemplateDocument1 pageNurs 3710 Ysu Poster Templateapi-607717122No ratings yet
- Diarrhea and Vomiting Illness 2015Document1 pageDiarrhea and Vomiting Illness 2015Anonymous UpWci5No ratings yet
- Common Food Borne Diseases-IDocument16 pagesCommon Food Borne Diseases-IPriyanka SinghNo ratings yet
- Ebola Virus RESPIDocument11 pagesEbola Virus RESPIAlih KathlyannNo ratings yet
- Name of Disease Common Name (If Any) How Is It Contracted? Symptoms Prevention or Treatment Sketch or ImageDocument4 pagesName of Disease Common Name (If Any) How Is It Contracted? Symptoms Prevention or Treatment Sketch or ImageNichole AlbaracinNo ratings yet
- Understanding HIV/AIDSDocument2 pagesUnderstanding HIV/AIDSMbiatat BrandonNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Human Health and Disease Final PYQs and Exemplar 1Document186 pagesMind Map Human Health and Disease Final PYQs and Exemplar 1Mohit Devraj ParasharNo ratings yet
- Leprosy: by Isabel ThompsonDocument16 pagesLeprosy: by Isabel ThompsonIsabel ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Basics On DiseasesDocument15 pagesBasics On Diseasesraghu ramNo ratings yet
- ScienceWhatareInfectiousDiseases-1 (Autosaved)Document9 pagesScienceWhatareInfectiousDiseases-1 (Autosaved)Shumaila Sultan - 70749/TCHR/BPC K & PNo ratings yet
- Covid-: The New Mutation Affects HumansDocument1 pageCovid-: The New Mutation Affects HumansJaneth Calderón MoralesNo ratings yet
- Pink Ballet Dance PosterDocument1 pagePink Ballet Dance PosterEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Uts ReportDocument45 pagesUts ReportAlex ArenasNo ratings yet
- Purple Yellow Blue and Pink Disease Prevention Coronavirus Awareness PosterDocument1 pagePurple Yellow Blue and Pink Disease Prevention Coronavirus Awareness PosterKelly A Guzman RNo ratings yet
- Diseases Caused by ProtozoaDocument2 pagesDiseases Caused by Protozoaorigami ninjaNo ratings yet
- Norovirus: Facts For Food Workers: Foods Contaminated With Norovirus Can Make People SickDocument2 pagesNorovirus: Facts For Food Workers: Foods Contaminated With Norovirus Can Make People Sickwow proNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Health Education Quarter 3 Disease Prevention and ControlDocument25 pagesGrade 8 Health Education Quarter 3 Disease Prevention and ControlRandom GuyNo ratings yet
- Lum Bang Activity 1Document4 pagesLum Bang Activity 1Hoshi KwonNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Activity Partial 1Document3 pagesIntermediate Activity Partial 1JOSE ALFONSO RODRIGUEZ GARCIANo ratings yet
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Viruses) : AIDS Is A ConditionDocument7 pagesHIV (Human Immunodeficiency Viruses) : AIDS Is A ConditionSofia Reinne Ong LafortezaNo ratings yet
- USC AH1N1 PosterDocument1 pageUSC AH1N1 PosterBrian K. Ong100% (1)
- Corona Virus Debunking Myths & Creating AwarenessDocument7 pagesCorona Virus Debunking Myths & Creating AwarenessSAMEER JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Prevent Communicable DiseasesDocument42 pagesPrevent Communicable DiseasesKristela Mae ColomaNo ratings yet
- Disease Preventions and ControlDocument9 pagesDisease Preventions and ControlPhoebe Grace BeduaNo ratings yet
- Waterborne and Food-borne Diseases GuideDocument10 pagesWaterborne and Food-borne Diseases GuideClaire MedianaNo ratings yet
- Role of Personal Hygiene in Communicable and Non Communicable DiseasesDocument29 pagesRole of Personal Hygiene in Communicable and Non Communicable DiseasesD E A DNo ratings yet
- Health and disease organismsDocument59 pagesHealth and disease organismsAlian WilliansNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument52 pagesBiology ProjectBhagat Bhandari67% (3)
- Report EbolaDocument21 pagesReport EbolaCerilo RegineNo ratings yet
- Procedures for Self-Quarantine Under Covid-19Document4 pagesProcedures for Self-Quarantine Under Covid-19BEVERLY TABLIZONo ratings yet
- Emerging and Reemerging InfectionDocument1 pageEmerging and Reemerging InfectionKurt Bryan CortezNo ratings yet
- Aetna Pioneer Plan Application: Full Medical Underwriting (FMU)Document13 pagesAetna Pioneer Plan Application: Full Medical Underwriting (FMU)ahissiNo ratings yet
- LTEDocument24 pagesLTEsotodolNo ratings yet
- Metro Cell Concealment Solutions - EuropeDocument1 pageMetro Cell Concealment Solutions - EuropeahissiNo ratings yet
- Summit 2012: Equipment Identity RegisterDocument14 pagesSummit 2012: Equipment Identity RegisterahissiNo ratings yet
- PCC (Policy and Charging Control) in Mobile Data: PCC: Access Independent ArchitectureDocument8 pagesPCC (Policy and Charging Control) in Mobile Data: PCC: Access Independent ArchitectureahissiNo ratings yet
- GSMA DRC-report ENGLISH 72pp WEBDocument72 pagesGSMA DRC-report ENGLISH 72pp WEBahissiNo ratings yet
- TR 104 PDFDocument66 pagesTR 104 PDFGrandstream LATAMNo ratings yet
- Dirbs Cons Paper 220616Document29 pagesDirbs Cons Paper 220616Sana KhanNo ratings yet
- Place Your Headline with 15% Discount CouponDocument4 pagesPlace Your Headline with 15% Discount CouponahissiNo ratings yet
- Light Type Approval Scheme For Communication EquipmentDocument2 pagesLight Type Approval Scheme For Communication EquipmentahissiNo ratings yet
- Light Type Approval Scheme For Communication EquipmentDocument2 pagesLight Type Approval Scheme For Communication EquipmentahissiNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Hemostasis: Sub Bag. Hemato-Onkologi Anak FK UsuDocument11 pagesMekanisme Hemostasis: Sub Bag. Hemato-Onkologi Anak FK UsuSukhrian MuhdaNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Funda Death & DyingDocument1 pageSample Test Funda Death & DyingDanna Kim AuxteroNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Retinopathy Disease Classification Using Deep Neural Network and Retina ImagesDocument13 pagesDiabetic Retinopathy Disease Classification Using Deep Neural Network and Retina ImagesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Macadamia Felted Coccid: Eriococcus IronsideiDocument2 pagesMacadamia Felted Coccid: Eriococcus IronsideiAUDIR audirNo ratings yet
- INP CU 10 GlomeruloDocument5 pagesINP CU 10 GlomeruloMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument6 pagesReferencesAndrew MakariosNo ratings yet
- COVID Toes, Rashes: How The Coronavirus Can Affect Your SkinDocument6 pagesCOVID Toes, Rashes: How The Coronavirus Can Affect Your SkinlittlemisseeeNo ratings yet
- Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument7 pagesNon-Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemadarmariantoNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve Perthes DiseaseDocument7 pagesLegg Calve Perthes DiseaseMatthew Rich Laguitao CortesNo ratings yet
- Problems faced by construction workers in Tamil NaduDocument3 pagesProblems faced by construction workers in Tamil NaduYamini HarshaNo ratings yet
- Six Tiered HMDocument21 pagesSix Tiered HMDoctors NewsNo ratings yet
- Shea Dorsey CV 07-Apr-2023Document3 pagesShea Dorsey CV 07-Apr-2023api-668697374No ratings yet
- Malignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureDocument6 pagesMalignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureRachel AutranNo ratings yet
- Asssessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAsssessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Interventions Rationale EvaluationRoldan VidadNo ratings yet
- Acute Paracetamol Poisoning Case Studies ReviewDocument5 pagesAcute Paracetamol Poisoning Case Studies Reviewbiya ao0No ratings yet
- Endoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyDocument7 pagesEndoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyMat JawiNo ratings yet
- Kingdom MycotaDocument33 pagesKingdom MycotaSariska MehraNo ratings yet
- Why SufferingDocument7 pagesWhy SufferingRandall Dean WestNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual Electronic Column Scale M20610Document8 pagesOperating Manual Electronic Column Scale M20610Bryan GarciaNo ratings yet
- An Occupational Health & Safety Presentation For Young Workers: Storyboard and ScriptDocument21 pagesAn Occupational Health & Safety Presentation For Young Workers: Storyboard and ScriptALEN GEONo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument14 pagesPyloric Stenosisgangguan hepatobilierNo ratings yet
- Production Recombinant Therapeutics in E. ColiDocument11 pagesProduction Recombinant Therapeutics in E. ColiStephany Arenas100% (1)
- Cardiogenic Shock and Septic Shock: Perioperative ManagementDocument21 pagesCardiogenic Shock and Septic Shock: Perioperative ManagementachyutsharmaNo ratings yet