Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Grammar: Following Mandatory Rules Are Using For Correction of English
Uploaded by
MirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Grammar: Following Mandatory Rules Are Using For Correction of English
Uploaded by
MirCopyright:
Available Formats
English Grammar
31th January, 2020
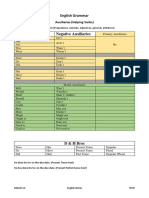
Following mandatory rules are using for correction of English.
If we use these helping verb (may, might, will, would, shall,
should, can, could) in sentences then we must use first form of
the main verb.
Example:
I can lift this table. (Correct)
I may go to Lahore tomorrow. (Correct)
He might go to Lahore tomorrow. (Correct)
I should do my duty honesty. (Correct)
If we use let or to in sentence then must use first form of the
main verb on sentence.
Example:
Let him go there. (Correct)
I intend to pass B.E this year. (Correct)
If we use sentence which is combination of two sentence
(conjunction sentence), if its first sentence in past tense also
their second sentence have any shape of past tense. But if
second sentence is on reality of GOD so its second sentence
should be in present tense otherwise past tense.
Example:
He said (past) that he was ill (past). (Correct)
The teacher told (Past) the boy that he might (Past) go to
Lahore. (Correct)
He said (past) that earth is (past) round (God Base so 2nd
sentence in present tense.) (Correct)
Kisi b single sentence men had k sath verb ka 3rd form use kark
past perfect na banaen, but agar kisi sentence me koi adverb ya
conjuction laga hua ho to hm had k sath 3rd form laga sakte hein.
Adverb: (Never, Already, Till, Seldom= kabi, Ever before)
Example:
He had gone to Lahore (Incorrect)
He went to Lahore (Correct)
He had already (Adverb) gone to Lahore (Correct)
We never use both clauses of sentence on future tense, but if
first one clause is in present simple tense then 2nd should be
future tense.
Example:
If you work hard, you will pass. (Correct)
Present Future
You can’t use “not” after “unless and untill” in English.
Example:
Unless he works hard, he will not pass to examination.
Use were or any shape of past tense after “as though” or “As if”,
but never use (am, is, are)
Example:
It looks as if he were made.
If following words use as verb never use any proposition, please.
Incorrect Correct
Reach at home Reach home
Love with her Love her
Inform to you Inform you
Marry with her Marry her
Order to you Order you
Resemble with him Resemble him
Control on it Control it.
Example:
He resembles his brothers. (Correct)
He married a beautiful girl. (Correct)
We don’t use “that” with interrogative words beginning with
(why, who, how, what, whether, if) etc.
Example:
He asked me that where I lived. (Incorrect)
He asked me where I lived. (Correct)
He asked me that if I was going to Lahore. (Incorrect)
He asked me if I was going to Lahore. (Correct)
5th February, 2020
COUNTABLE AN D UNCOUNTABLE NOUNS
Countable Nouns
We can use numbers and the, A & An articles with countable
nouns. They have plurals.
Example:
A boy, A book, three boys, three books.
Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns have not plurals, we can’t use a, an or one
before an uncountable noun, but we use some, much, little, a
large amount of, a lot of, lots of, plenty of, good deal of, all, any,
enough.
Example:
She needs some information
Where we can put all the furniture.
Note: To refer to a specific amount, use piece of, bit of, slice of
cup of etc.
Names of illnesses are usually uncountable in English including
those end in “S”
Advice, information and news are uncountable nouns, we can’t
use them with a, an or in the plural.
14th February, 2020
Furniture a Furniture (X) Some Furniture
Much Furniture
A lot of Furniture
Information An information (X) Some information
A lot of information
Money A Money (X) Some Money
Much Money
A lot of Money
Advice A/ An Advice (X) Some Advice
A lot of/ lots of
advice
Plenty of advice
Note: Do not use the following words before uncountable nouns.
Another, both, each, either, every, few, many, several, these, those, two, or
three.
Note: following words can be used before countable nouns.
A, an, the, this, that, all, a lot of plenty of, any, enough, no, my, our, her
23th February, 2020
Participles
Present Participle Past Participle
V1+ing V3
go+ ing went
Example:
I will buying a jumping doll.
The news left us shocked.
She went away carying.
Complex Sentence
A sentence which consists of main clause (Principle Clause)
You might also like
- How to Use the Word “Have” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Have”From EverandHow to Use the Word “Have” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Have”No ratings yet
- DativDocument3 pagesDativKeti RukhadzeNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - PA 3 - ExplanationDocument9 pagesClass 9 - PA 3 - ExplanationaanaNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument12 pagesPresent ContinuousCristian Ramirez RodasNo ratings yet
- Proyek InggrisDocument22 pagesProyek InggrisFitri AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- Libro Basico para Teacher1Document23 pagesLibro Basico para Teacher1Pam UrtechoNo ratings yet
- TSPH 1Document5 pagesTSPH 1aeadNo ratings yet
- Identify Part SpeechDocument4 pagesIdentify Part SpeechpatrililianNo ratings yet
- LPAT GrammarDocument16 pagesLPAT GrammarAmelie SummerNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs: Here Starts The Lesson!Document23 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs: Here Starts The Lesson!Katherine Caballero RiveroNo ratings yet
- Pronoun Replacement GuideDocument2 pagesPronoun Replacement GuidecokihihihiNo ratings yet
- Apuntes JobsDocument12 pagesApuntes JobsMAIKE BELEN LUCAS BOHORQUEZNo ratings yet
- Common Errors With AdverbsDocument12 pagesCommon Errors With AdverbsSmarty Town100% (1)
- 1.proyecto Tema 1 Del 1-9 INGLESDocument30 pages1.proyecto Tema 1 Del 1-9 INGLESKaryme GomezNo ratings yet
- Sample CollocationsDocument8 pagesSample CollocationsVictor Jurado MartínezNo ratings yet
- Common+Errors+in+Parts+of+Speech+ +1Document56 pagesCommon+Errors+in+Parts+of+Speech+ +1facc6982No ratings yet
- Spoken EnglishDocument23 pagesSpoken Englishmaddy92% (13)
- Prepositons and Prepositional Phrases (Grammar 6) : JCS, LLBDocument24 pagesPrepositons and Prepositional Phrases (Grammar 6) : JCS, LLBAnya RiveraNo ratings yet
- PEL125 - Lecture5 - Parts of SpeechDocument42 pagesPEL125 - Lecture5 - Parts of SpeechRam BaghelNo ratings yet
- Grammar 5Document46 pagesGrammar 5drakness722No ratings yet
- Wo-/ Da-Wörter Theorie: German EnglishDocument4 pagesWo-/ Da-Wörter Theorie: German EnglishXtin ClaraNo ratings yet
- Future Simple Tense: Basic FormDocument20 pagesFuture Simple Tense: Basic FormElena PorceanuNo ratings yet
- Structure-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesStructure-WPS OfficeAndika PratamaNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument28 pagesNounsReddaveni Nagaraju100% (1)
- Week 3.pdf Version 1Document8 pagesWeek 3.pdf Version 1HasnatNo ratings yet
- Grammar Week 8 Future TenseDocument11 pagesGrammar Week 8 Future TenseSebastian PachecoNo ratings yet
- A. Grammar ReviewDocument19 pagesA. Grammar ReviewOchie Bieber ElfNo ratings yet
- Fiuture and Future in The PastDocument11 pagesFiuture and Future in The PastElena PorceanuNo ratings yet
- Word Order and Verb PatternsDocument5 pagesWord Order and Verb Patternsmarcela noemi0% (1)
- What Is PrepositionDocument7 pagesWhat Is PrepositionSam YanNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument17 pagesRelative Clausesraiganat134No ratings yet
- English Grammar Exercises For High-School StudentsDocument20 pagesEnglish Grammar Exercises For High-School Studentspck1004No ratings yet
- 6 Simple Future Tense - PBKLDocument5 pages6 Simple Future Tense - PBKLMega TobingNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Parts of SpeechDocument53 pages1.1 Parts of Speechrani priyanka GsitsNo ratings yet
- Grammatica Inglese 2Document9 pagesGrammatica Inglese 2Cristina BonansingaNo ratings yet
- Meeting 8Document13 pagesMeeting 8Fitri DelitaNo ratings yet
- Concessive Clause - Although, Even Though..Document8 pagesConcessive Clause - Although, Even Though..Ana-Maria PopNo ratings yet
- 100 Subject Verb Agreement RulesDocument2 pages100 Subject Verb Agreement Rulesjosephchidubem23No ratings yet
- Angliski VezbiDocument68 pagesAngliski VezbiSnezhana StamenovskaNo ratings yet
- Verb & Its Types - Right Form of Verbs, Sub-Verb Agreement - Subjunctive - Modal Auxillaries - Conditionals - Inversion - Vocab - D To G - Appropriate Preposition - C, D, EDocument61 pagesVerb & Its Types - Right Form of Verbs, Sub-Verb Agreement - Subjunctive - Modal Auxillaries - Conditionals - Inversion - Vocab - D To G - Appropriate Preposition - C, D, EUshrat Refat JajiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Ingles2Document18 pagesPresentation Ingles2Pinel GustavoNo ratings yet
- Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument4 pagesSimple Past and Present PerfectBeri DarioNo ratings yet
- Both - Ambos Either - Cualquiera de Los Dos Neither - Ninguno (De Dos)Document15 pagesBoth - Ambos Either - Cualquiera de Los Dos Neither - Ninguno (De Dos)PepeArandaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument7 pagesSimple Present TenseDaniel Giraldo CastroNo ratings yet
- Use of EnglishDocument10 pagesUse of EnglishijhernandezarenasNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Adverbs of DegreeDocument19 pagesENGLISH Adverbs of DegreealucardoxxNo ratings yet
- Bhs InggrisDocument16 pagesBhs InggrisMuhammad WardiNo ratings yet
- 4 Past Tenses in English With ExamplesDocument12 pages4 Past Tenses in English With ExamplesJojo LeaonNo ratings yet
- Some Important Aspect of English-1688878779554-293966464Document10 pagesSome Important Aspect of English-1688878779554-293966464taofeekdewoleNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document17 pagesGroup 2MiaNo ratings yet
- Quantifiers With Countable and Uncountable NounsDocument21 pagesQuantifiers With Countable and Uncountable NounsGuillermo René Cuellar GómezNo ratings yet
- Esl 3301 Midterm Exam - With AnswersDocument5 pagesEsl 3301 Midterm Exam - With AnswersTonya PettigrewNo ratings yet
- Unidad 1Document23 pagesUnidad 1Deyvid Reto HNo ratings yet
- E-Book Inglés IDocument18 pagesE-Book Inglés IJake JumNo ratings yet
- Nuevo English BookDocument80 pagesNuevo English BookEduardo Casanova100% (1)
- Bookthree-2week Optimized.2Document38 pagesBookthree-2week Optimized.2avaragort04No ratings yet
- Resumo de InglêsDocument8 pagesResumo de InglêsLuana AndradeNo ratings yet
- Prepositions RulesDocument6 pagesPrepositions RulesBaSash ChiwaraNo ratings yet
- Group 10 - Correct UsageDocument39 pagesGroup 10 - Correct UsageIntan HazawaNo ratings yet
- Study Zone - IntermediateDocument88 pagesStudy Zone - IntermediateAisy AstarinaNo ratings yet
- Islamic Study: B. Quraishi C. Makki D. MadniDocument23 pagesIslamic Study: B. Quraishi C. Makki D. MadniMirNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Studies: 31th January, 2020Document27 pagesPakistan Studies: 31th January, 2020MirNo ratings yet
- World Current Affairs: A. Gran Telescopio Canarias B. Hobby-Eberly Telescope C. GREGOR, Teide ObservatoryDocument5 pagesWorld Current Affairs: A. Gran Telescopio Canarias B. Hobby-Eberly Telescope C. GREGOR, Teide ObservatoryMirNo ratings yet
- Important Days of PakistanDocument2 pagesImportant Days of PakistanMir100% (1)
- General Knowledge: A. Isaac Walton C. Samuel Butler D. Sir Thomas BrowneDocument23 pagesGeneral Knowledge: A. Isaac Walton C. Samuel Butler D. Sir Thomas BrowneMirNo ratings yet
- Short WordDocument2 pagesShort WordArbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- CSS - Everyday Science Notes by (NOA) PDFDocument138 pagesCSS - Everyday Science Notes by (NOA) PDFMirNo ratings yet
- Accident Prevention in Industry PDFDocument75 pagesAccident Prevention in Industry PDFpowerandcontrolguyNo ratings yet
- Every Day ScienceDocument31 pagesEvery Day ScienceMirNo ratings yet
- GSK Interview Preparation (Repaired)Document8 pagesGSK Interview Preparation (Repaired)MirNo ratings yet
- Accident Prevention in Industry PDFDocument75 pagesAccident Prevention in Industry PDFpowerandcontrolguyNo ratings yet
- Basic EHSDocument3 pagesBasic EHSMirNo ratings yet
- EIA MethodologiesDocument26 pagesEIA MethodologiesRevo D CreaterNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Blade AerodynamicsDocument10 pagesWind Turbine Blade AerodynamicsMahesh MunjalNo ratings yet
- HSE-CR Risk Assessment For Bhit Black Top Road From CP5 To D9 Repair WorksDocument15 pagesHSE-CR Risk Assessment For Bhit Black Top Road From CP5 To D9 Repair WorksMirNo ratings yet
- My Spanish - Melissa Lozada-OlivaDocument3 pagesMy Spanish - Melissa Lozada-OlivaAna Julia MarkoNo ratings yet
- Rule 1. Two Singular Subjects Connected by or or NorDocument3 pagesRule 1. Two Singular Subjects Connected by or or NorAdil AnwarNo ratings yet
- G2 - Worksheet No.7Document4 pagesG2 - Worksheet No.7marianne katrin gelinaNo ratings yet
- Wsheet InfinitivesKEYDocument2 pagesWsheet InfinitivesKEYIC10No ratings yet
- The Learning Objective 1Document7 pagesThe Learning Objective 1Ankur K ZaverriNo ratings yet
- PAST SIMPLE Reading ExerciseDocument1 pagePAST SIMPLE Reading ExerciseRené Ramos82% (91)
- Planificare Anuală La Limba Engleză (L2) Filiera Tehnologică AN ȘCOLAR 2018/2019Document6 pagesPlanificare Anuală La Limba Engleză (L2) Filiera Tehnologică AN ȘCOLAR 2018/2019Calinescu CristinaNo ratings yet
- Noun + LY AdjectiveDocument2 pagesNoun + LY AdjectiveEliJonesNo ratings yet
- Empty VerbsDocument2 pagesEmpty VerbsAriel Logacho100% (1)
- Activities On VerbalsDocument6 pagesActivities On VerbalsEdgar Custodio FerrerNo ratings yet
- Atividade Avaliativa Mensal 6°ano 2º BimestreDocument2 pagesAtividade Avaliativa Mensal 6°ano 2º BimestreJuliane GuedesNo ratings yet
- Infinitive: 1.1 After Certain Verbs: A. Verbs Followed by TO+ InfinitiveDocument6 pagesInfinitive: 1.1 After Certain Verbs: A. Verbs Followed by TO+ InfinitiveAntonia FerriolNo ratings yet
- Handout - Kasus - Nominativ Und AkkusativDocument3 pagesHandout - Kasus - Nominativ Und AkkusativpsjcostaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Type 1Document1 pageConditional Type 1sneyder.mahechaNo ratings yet
- Bricks Reading 200 - L3 - Grammar SheetDocument20 pagesBricks Reading 200 - L3 - Grammar SheetJIYOON IRIS HUNo ratings yet
- Beehive - Tests - Level 2 - Unit Test 8Document4 pagesBeehive - Tests - Level 2 - Unit Test 8Adrian Andres Gallo LopezNo ratings yet
- ''Adhibeo'' in LatinDocument5 pages''Adhibeo'' in LatinThriw100% (1)
- Reported Speech Homework Upload1Document1 pageReported Speech Homework Upload1Josue CrespoNo ratings yet
- Watching TV Listening To Music Reading BooksDocument20 pagesWatching TV Listening To Music Reading BooksScentCandleNo ratings yet
- Adjectives q2 Module 2 Lesson2Document33 pagesAdjectives q2 Module 2 Lesson2Noemie LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- PPP PlanningDocument5 pagesPPP Planningapi-257825409No ratings yet
- Augmented Transition Networks: An Augmented Transition Network (ATN) Is A Type of GraphDocument8 pagesAugmented Transition Networks: An Augmented Transition Network (ATN) Is A Type of GraphshwetaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus de Inglés Nivel Primaria-2019: Greetings and Farewells Greetings and Farewells Greetings and FarewellsDocument2 pagesSyllabus de Inglés Nivel Primaria-2019: Greetings and Farewells Greetings and Farewells Greetings and FarewellsDavid Fernando Alpaca ChavezNo ratings yet
- Past ModalsDocument2 pagesPast ModalsTijana DoberšekNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Reflexive Pronoun Grade 10Document89 pagesLesson Plan in Reflexive Pronoun Grade 10Elmer Pineda Guevarra0% (1)
- Simple PresentDocument13 pagesSimple PresentAhmad SyaifullahNo ratings yet
- Abeera Sadi Arabic Grammar Advanced Year 1: Total 90.5/100Document5 pagesAbeera Sadi Arabic Grammar Advanced Year 1: Total 90.5/100uzmasultanaNo ratings yet
- To Lecture 3 Home Task Parts of Speech in English OutlineDocument5 pagesTo Lecture 3 Home Task Parts of Speech in English OutlineДенис МитрохінNo ratings yet
- Preposition Gerund NewDocument3 pagesPreposition Gerund NewNicolas Velez ViafaraNo ratings yet
- Non Finite Verbs - Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesNon Finite Verbs - Revision WorksheetViswanathan SundaresanNo ratings yet