Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment PDF
Assignment PDF
Uploaded by
Ibrahim Isleem0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views3 pagesOriginal Title
253512708-assignment.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views3 pagesAssignment PDF
Assignment PDF
Uploaded by
Ibrahim IsleemCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
TORINO, IANNE MARY C.
EE1
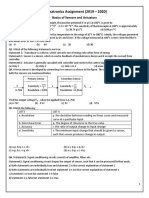
1.1What is the difference between controlled and manipulated variables?
Controlled variables are the variables measured to indicate the
condition of the process output while manipulated variables are
variables controlled by an actuator to correct for changes in the
measured variable.
1.2What is the difference between set point, error signal, and correction signal?
Set point is the reference value for a controlled variable in a process
control loop; Error signal is the difference in value between a
measured signal and a set point; Correction signal is the signal to
the manipulated variable.
1.3How many pounds are equivalent to 63 kg?
63kg (1kg/2.205lbs) = 138.925 lbs
1.4How many micrometers are equivalent to 0.73 milli-in?
0.73 x 10-3 in (25400 μm/1in) = 18.542 μm
1.5 How many pounds per square inch are equivalent to 38.2 kPa?
38.2 kPa (14.7 psi/101.325 kPa) = 5.54 psi
1.6 How many foot-pounds of energy are equivalent to 195 J?
195 J ( 0.7376 foot-pound/1 J) = 143.82 foot pounds
1.7 What force in pounds is equivalent to 385 N?
385 N (.225 lbs/ 1 N) = 86.625 lbs
1.8 How many amperes are required from a 110-V supply to generate 1.2 hp?
Assume 93- percent efficiency.
1.2 hp ( 746 W/ 1 hp) = 895.2 W
Input power = 895.2 W /.93 = 962.5806 W
Current = 962.5806 W / 110 V = 8.7507 A
1.9 How many joules are equivalent to 27 ft⋅lb of energy?
27 ft⋅lb ( 1 J/ 0.7376 ft⋅lb) = 36.61 J
1.10 What is the sensitivity of an instrument whose output is 17.5 mV for an input
change of 7°C?
Sensitivity = 17.5 mV/ 7°C = 2.5 mV/7°C
1.11 A temperature sensor has a range of 0 to 120°C and an absolute accuracy of
±3°C. What is its FSD percent accuracy?
% FSD accuracy = ± (3 × 100/120) % = ± 2.5 %
1.12 A flow sensor has a range of 0 to 25 m/s and a FSD accuracy of ±4.5 percent.
What is the absolute accuracy?
Absolute accuracy = ± ( 25 × 4.5/100) % = ± 1.125 %
1.13 Introduction and Review 131.13 A pressure sensor has a range of 30 to 125 kPa
and the absolute accuracy is ±2 kPa. What is its percent full-scale and span
accuracy?
% FSD accuracy = ± (2 × 100/125) % = ± 1.6 %
% Span accuracy =± (2 × 100/95) % = ± 2.1 %
1.14 A temperature instrument has a range −20°F to 500°F. What is the error at
220°F? Assume the accuracy is (a) ±7 percent of FSD and (b) ±7 percent of span.
(a)
(b)
1.15 A spring balance has a span of 10 to 120 kg and the absolute accuracy is ±3
kg. What is its %FSD accuracy and span accuracy?
% FSD accuracy = ± (3 × 100/120) kg = ± 2.5 kg %
% Span accuracy = ± (3 × 100/110) kg = ± 2.7 kg %
1.16 A digital thermometer with a temperate range of 129.9°C has an accuracy
specification of ±1/2 of the least significant bit. What is its absolute accuracy, %FSD
accuracy, and its resolution?
Absolute accuracy = ±
% FSD accuracy = ±
% Span accuracy = ±
1.17 A flow instrument has an accuracy of (a) ±0.5 percent of reading and (b)
0.5%FSD. If the range of the instrument is 10 to 100 fps, what is the absolute
accuracy at 45 fps?
(a) Absolute accuracy = ± (45 × 0.5/100) fps = ± 2.25 fps
(b) Absolute accuracy = ± (100 × 0.5/100) fps = ± 0.5 fps
1.18 A pressure gauge has a span of 50 to 150 psi and its absolute accuracy is ±5
psi. What is its %FSD and span accuracy?
% FSD accuracy = ± (5 × 100/150) psi = ± 3.33 kg %
% Span accuracy = ± (3 × 100/100) psi = ± 3 kg %
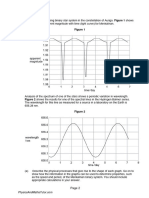
1.19 Plot a graph of the following readings for a pressure sensor to determine if
there is hysteresis, and if so, what is the hysteresis as a percentage of FSD?
True pressure (kPa) 0 20 40 60 80 100 80 60 40 20 0
Gauge pressure (kPa) 0 15 32 49.5 69 92 87 62 44 24 3
Hysteresis = ± 7 % FSD (see Fig. A1.1)
1.20 Plot a graph of the following readings for a temperature sensor to determine
the linearity of the sensor. What is the nonlinearity as a percentage of FSD?
True pressure (kPa) 0 20 40 60 80 100
Gauge reading (kPa) 0 16 34 56 82 110
You might also like
- Astm E617-18 - 2018Document17 pagesAstm E617-18 - 2018japofff100% (10)
- Cargo CalcDocument32 pagesCargo CalcAhmad Imran94% (17)
- Chapter S1 (Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation)Document28 pagesChapter S1 (Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation)Марко Д. Станковић0% (1)
- 400 MM Digital Clamp Meter Make-Kyoritsu Model-KEW SNAP 2009R, SL No-W8039512Document20 pages400 MM Digital Clamp Meter Make-Kyoritsu Model-KEW SNAP 2009R, SL No-W8039512Ashutosh MondalNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Training Tutorial Part4Document11 pagesInstrumentation Training Tutorial Part4Gary8100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 - Suggested AnswerDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - Suggested AnswerBárbara VictóriaNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Leak Rate Accuracy Sentinel I24 and M24 Pressure Decay InstrumentsDocument3 pagesPressure and Leak Rate Accuracy Sentinel I24 and M24 Pressure Decay Instrumentsviernes06No ratings yet
- Difference Between Calibration, Testing and Validation: Accuracy, Precision, Resolution & SensitivityDocument27 pagesDifference Between Calibration, Testing and Validation: Accuracy, Precision, Resolution & SensitivityAmit NainNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document1 pageHomework 2Osama AlgueferNo ratings yet
- Mecha Sensor 2Document21 pagesMecha Sensor 2Mohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Fluke 83V and 87V Digital Multimeters: Detailed SpecificationsDocument4 pagesFluke 83V and 87V Digital Multimeters: Detailed SpecificationsAmer KerešNo ratings yet
- EE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 2: R R R E GR e G D e R E R GDocument2 pagesEE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 2: R R R E GR e G D e R E R GAbhishekNo ratings yet
- ANSI - Ahri Standard 550-590 (I-P) With Addendum 3Document109 pagesANSI - Ahri Standard 550-590 (I-P) With Addendum 3Afzal KhanNo ratings yet
- Oic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and ProblemDocument41 pagesOic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and ProblemPoovarasan SNo ratings yet
- OCW SKN3022 Instrumentation CH 3Document31 pagesOCW SKN3022 Instrumentation CH 3ramajaxNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1danielruthers2No ratings yet
- Fluke 345Document8 pagesFluke 345juancarlosmoreno1964No ratings yet
- User Manual For Electromagnetic Flowmeter Transmitter PCB BoardDocument28 pagesUser Manual For Electromagnetic Flowmeter Transmitter PCB BoardBelos SahajiNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Pressure MeasurementDocument30 pagesSession 4 Pressure Measurementmuh amarNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document34 pagesWeek 7Nigel MagayaNo ratings yet
- Pla2.5k 60 1000Document2 pagesPla2.5k 60 1000Suman RachaNo ratings yet
- 02-Instrument Types and Performance Characteristics PDFDocument28 pages02-Instrument Types and Performance Characteristics PDFPao Castillon100% (2)
- IndustrialDocument1 pageIndustrialTaanzNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of TransducerDocument40 pagesCharacteristic of Transducergkarthikeyan50% (2)
- Agilent 4155CDocument14 pagesAgilent 4155CBennyavNo ratings yet
- The Digital Oscilloscope and The Function Generator: Part I: Amplitude and Frequency MeasurementsDocument6 pagesThe Digital Oscilloscope and The Function Generator: Part I: Amplitude and Frequency MeasurementsNour ShamiNo ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio Ventilador Bear Cub 750psvDocument64 pagesManual de Servicio Ventilador Bear Cub 750psvVladimir BorjaNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics AssignmentDocument20 pagesMechatronics AssignmentPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Agilent 34405A Multimeter 5.5 Digit Dual Display, Benchtop DMM More Capabilities at A Value PriceDocument9 pagesAgilent 34405A Multimeter 5.5 Digit Dual Display, Benchtop DMM More Capabilities at A Value PriceSergiu BadalutaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Training Tutorial4 PDFDocument11 pagesInstrumentation Training Tutorial4 PDFchdiNo ratings yet
- PI2 MeasurementDocument37 pagesPI2 MeasurementRamkumar ANo ratings yet
- Performance Characteristics For Measurement and Instrumentation SystemDocument27 pagesPerformance Characteristics For Measurement and Instrumentation SystemFemi PrinceNo ratings yet
- Self Test CH - 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesSelf Test CH - 2 SolutionsolomonNo ratings yet
- FC001 TMF Transmitter Operating ManualDocument23 pagesFC001 TMF Transmitter Operating ManualMinh KỳNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: DC and Ac Bridge Circuits 10/2/13Document6 pagesExperiment 5: DC and Ac Bridge Circuits 10/2/13ampangetkokasihahahahaNo ratings yet
- Class 6Document51 pagesClass 6lelisadiriba849No ratings yet
- Measuremnts - Sheet 2Document2 pagesMeasuremnts - Sheet 2engshimaaNo ratings yet
- (Answer 1470 To 1530 Rev/min) : Self Assessment Exercise No.4Document1 page(Answer 1470 To 1530 Rev/min) : Self Assessment Exercise No.4renvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 EMIDocument59 pagesChapter 1 EMIGarima PantNo ratings yet
- Calibration Techniques and Process: Abdul Latif, Pe H (NI)Document69 pagesCalibration Techniques and Process: Abdul Latif, Pe H (NI)Engr Umair AzizNo ratings yet
- Agilent 34401A Multimeter 33K8!4!1029-1Document14 pagesAgilent 34401A Multimeter 33K8!4!1029-1Serrot OnaivlisNo ratings yet
- Instrument System - Week 2Document12 pagesInstrument System - Week 2Muhammad Ismunandar Al Fajr100% (1)
- Experiment # 1 - Subject: Calibration of Displacement Transducer Section #1 - Group 14Document16 pagesExperiment # 1 - Subject: Calibration of Displacement Transducer Section #1 - Group 14Batuhan AydoğanNo ratings yet
- Fluke 123 Industrial Scopemeter: SpecificationsDocument4 pagesFluke 123 Industrial Scopemeter: SpecificationsTro Nhu Khi HiemNo ratings yet
- Fluke 345: Power Quality Clamp MeterDocument11 pagesFluke 345: Power Quality Clamp MeterAmer KerešNo ratings yet
- LM-8102 en Manual PDFDocument16 pagesLM-8102 en Manual PDFBiran AbadiNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: EJA115E Low Flow TransmitterDocument13 pagesGeneral Specifications: EJA115E Low Flow TransmitterzaffarNo ratings yet
- 9 IndexDocument25 pages9 IndexbuturcasNo ratings yet
- 34405A Data SheetDocument9 pages34405A Data SheetcciproductsNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation AssignmentDocument1 pageInstrumentation Assignmentamosainamani6No ratings yet
- Industrial InstrumentationDocument34 pagesIndustrial InstrumentationNhân Phạm ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Electronics Instrumentation - Module-01Document24 pagesElectronics Instrumentation - Module-01GURURAJ GOURNo ratings yet
- 02 Measurement CharacteristicsDocument36 pages02 Measurement CharacteristicsLuckily LuckyNo ratings yet
- Bear Cub 750PSV Service Manual: L2343 Draft Date L Revision A DateDocument64 pagesBear Cub 750PSV Service Manual: L2343 Draft Date L Revision A DateDavid AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 6655 Control HandoutDocument133 pages6655 Control Handouthann_dleNo ratings yet
- Digital Voltmeters Can Be Classified in To The Following Broad CategoriesDocument22 pagesDigital Voltmeters Can Be Classified in To The Following Broad CategoriesSysu KumarNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Filter: Enhancing Computer Vision Through Adaptive FilteringFrom EverandAdaptive Filter: Enhancing Computer Vision Through Adaptive FilteringNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- Good Morning,: Grade 7-Maaasahan!Document58 pagesGood Morning,: Grade 7-Maaasahan!THERESE MARIE DE VERANo ratings yet
- CHAPTER (2) Statistical Treatment of Experimental DataDocument30 pagesCHAPTER (2) Statistical Treatment of Experimental DataAhamed Saleel C100% (1)
- Welding Dept. (En15085-2) Calibration Status: Least CountDocument1 pageWelding Dept. (En15085-2) Calibration Status: Least CountAMIT SHAHNo ratings yet
- Pfi Es 3Document2 pagesPfi Es 3EstefaníaNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics (4) : Uncertainty Analysis Error PropagationDocument18 pagesApplied Statistics (4) : Uncertainty Analysis Error PropagationSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Workshop Basic WorkshopDocument44 pagesBasic Workshop Basic Workshoppceautohod100% (1)
- Topographic Map of Rio FrioDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Rio FrioHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- 16.346 Astrodynamics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument2 pages16.346 Astrodynamics: Mit OpencoursewareJoséManuelEspinozaRochaNo ratings yet
- Vidur NitiDocument30 pagesVidur NitiKaushaljm PatelNo ratings yet
- Drug CalculationsDocument32 pagesDrug CalculationsNisha Vats100% (1)
- Instrumental Methods of Analysis Question Bank For B Tech BiotechDocument3 pagesInstrumental Methods of Analysis Question Bank For B Tech BiotechJency BavithraNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Instrumentation: Dr. Mohamed Lotfy Taha Lecturer, Mechanical Engineering BUE AY2016-17 S1Document24 pagesMeasurement and Instrumentation: Dr. Mohamed Lotfy Taha Lecturer, Mechanical Engineering BUE AY2016-17 S1Ali ZaghloulNo ratings yet
- Valve KV Sizing CalculatorDocument7 pagesValve KV Sizing CalculatorKemasAlsyaAfrilianNo ratings yet
- Catalog TranzistoriDocument50 pagesCatalog TranzistoriAlex AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Linear Dimensions Using ComparatorDocument1 pageMeasurement of Linear Dimensions Using ComparatorRICKY MARTIN J 4096No ratings yet
- Cadastral Surveying IIDocument16 pagesCadastral Surveying IISafwan Izzaty67% (12)
- Absolute Magnitude QPDocument4 pagesAbsolute Magnitude QPJohnNo ratings yet
- Ch02 Radiat PDFDocument26 pagesCh02 Radiat PDFPa Loma B. SantosNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Analisa Karakteristik Getaran Truk MolenDocument20 pagesJurnal Analisa Karakteristik Getaran Truk MolenM Willy TarmidziNo ratings yet
- Positioning Techniques - Horizontal Vertical PDFDocument34 pagesPositioning Techniques - Horizontal Vertical PDFMuhd Zuhairi100% (1)
- Units Measurements MCQ PDFDocument9 pagesUnits Measurements MCQ PDFkathyayaniNo ratings yet
- G. T. McCaw - Resection in SurveyDocument22 pagesG. T. McCaw - Resection in Surveydelenda3No ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy HandwrittenDocument38 pagesMass Spectroscopy HandwrittenMohamed Dahmane100% (5)
- Whitepaper NIR Spectrometer Technology Comparison PDFDocument14 pagesWhitepaper NIR Spectrometer Technology Comparison PDFMostafa Medhat Mostafa HassanNo ratings yet
- Azimuth TheoryDocument5 pagesAzimuth TheoryShip Wonders100% (3)
- Sison, Marcus Ceazar - Module 3 - SurveyingDocument3 pagesSison, Marcus Ceazar - Module 3 - SurveyingMarcus Ceazar SisonNo ratings yet