Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biomechanic in Clinical Orthodontic Nanda 1st Edi/p 6-7)
Uploaded by
adi raghavOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biomechanic in Clinical Orthodontic Nanda 1st Edi/p 6-7)
Uploaded by
adi raghavCopyright:
Available Formats
12.
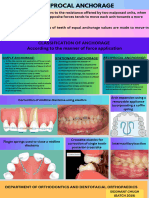
BIOMECHANICS IN ORTHODONTICS
and the tooth which has to be uprighted. The level of L = length of wire
force exerted by the open coil spring is in the range In addition, Y is modulus of elasticity of the material
of 90-100 grams. This coil spring will push the titled used for fabricating the spring.
tooth to more distal position and will upright it also. So, when length of a spring is doubled, the force ex
So, at the end of treatment the tooth will get upright erted by the spring will reduce/decrease by a factor of
and move to a more distal position, thus creating the 8.
space for further orthodontic correction.
23. When a simple tipping force is applied to the crown of
an incisor, the center of rotation is usually located
a) At the apex
b) At the incisor edge
c) 2/3rd the root length from the apex
d) 1/3rd the root length from the apex
Ans d (Ref: Biomechanics in clinical orthodontics-Nanda.
1st edi/p 6-7)
Orthodontic force is required for tooth movement. The
type of tooth movement by a tooth to a greater ex
tent depends on the point of force application and its
relationship with the center of resistance of the tooth.
When a force is applied at the crown level, it will cre
ate a moment arm which is equal to the magnitude
of the force and the perpendicular distance form the
point of force to the center of resistance. The mo
ment which is created will try to rotate and tip the
crown of the tooth with center of resistance located at
Fig 12.6 Open coil spring the l/3rd of the root length from the apex. This is
some sort of uncontrolled tippinq of the tooth, in which
21. The resiliency of the orthodontic wire as regards to root apex will move in one direction and crown of the
its cross section will tooth will move in the opposite direction. This type of
a) Increase with increase in the cross section area tooth movement is usually not needed during orth
b) Decrease with increase in the cross section area odontic treatment except in Class II div 2 malocclu
c) Remains same sion with retroclined upper anteriors, which requires
d) Independent of the cross sectional area root movement of the retroclined upper anteriors in
the palatal direction and crown to move in labial di
Ans b (Ref: Philip's science of dental material rection.
Anusavice.11th edi/p 84, 622-623)
24. A material when subjected to enough force eventu
Resilience is defined as "the amount of energy ab ally fractures or ruptures. This point is
sorbed within a unit of a structure when it is stressed a) Deformation point b) Fracture point
to its proportional limit". Resiliency is also known as c) Ultimate strength d) Yield strength
springiness of the material.
Resilience of two or more materials can be com Ans c (Ref: Q no. 26 for explanation)
pared by plotting and observing the area under the
elastic region of the stress-strain curve. The material 25. During correction of malocclusion various types of
with larger elastic area has the higher resilience. orthodontic tooth movements are performed. Which
Resilience of an orthodontic wire is inversely pro of the following orthodontic tooth movements re
portional to the diameter/cross-sectional area of the quires very careful planning and execution?
wire. So, as the cross-sectional area of the orthodon a) Intrusion b) Translation
tic wire increases, the diameter of the wire will also c) Tipping d) Rotation
increase, which will decrease the resiliency of the wire,
thus makeing it more rigid. Ans a (Ref: Bioengineering analysis in orthodontic
mechanics.Nikoli.1st edi/p 163-169)
22. When length of a spring is doubled, the force ex
erted by the spring Translation is one of the most difficult types of move
a) Decreases by 8 times ments to achieve in orthodontics. This is caused by
b) Increases by 8 times the anatomic characteristics that surround the teeth
c) Decreases by 16 times that make the application of a force through the C
d) Increases by 18 times res very difficult, so pure translation is hard to obtain.
Orthodontic intrusion is a type of body movement in
Ans a (Ref: Textbook of orthodontics-Gown Shankar.1st the vertical dimension. During intrusion tooth is forced
edi/p 347) to move in more apical direction thus causing com
pression of the periodontal ligament fibers and the
Spring formula for a given material is: peri-apical tissues. If during intrusion, forces are not
F a. (D)4/L3 controlled in the proper way might lead to resorption
F = Y X (D)4/L3 of root and loss of vitality of the tooth structure. There
Here, fore, precise control of force (magnitude and direc
F= force exerted by the spring tion) is very important during intrusive movement of
D = diameter of the wire the tooth.
You might also like
- A Couple Cons I S: 4th Edi/p 65)Document1 pageA Couple Cons I S: 4th Edi/p 65)adi raghavNo ratings yet
- BIOMECHANICSDocument1 pageBIOMECHANICSadi raghavNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics in OrthodonticsDocument1 pageBiomechanics in Orthodonticsadi raghavNo ratings yet
- Stresses Induced by CPD-FinalDocument26 pagesStresses Induced by CPD-FinalNikita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Friccion SeminarsDocument5 pagesFriccion SeminarsROSA.MELGAREJO.PNo ratings yet
- Orthodontics AnchorageDocument10 pagesOrthodontics AnchorageSRO oONo ratings yet
- Analysis of resistance and retention of complete veneer crown retainersDocument8 pagesAnalysis of resistance and retention of complete veneer crown retainerssara luciaNo ratings yet
- Concepts On Control of The Anterior Teeth Using The Lingual ApplianceDocument8 pagesConcepts On Control of The Anterior Teeth Using The Lingual AppliancesmritiNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4 - Crown and BridgeDocument6 pagesLecture - 4 - Crown and Bridgeد.فستقهNo ratings yet
- Bridges-Biomechanics: Abutment AssessmentDocument18 pagesBridges-Biomechanics: Abutment AssessmentRik ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Arches ShinuDocument66 pagesIntrusion Arches ShinuYuvashreeNo ratings yet
- implant-protective-occlusion-a-reviewDocument7 pagesimplant-protective-occlusion-a-reviewlayla.adham94No ratings yet
- Lec. 9 Retention and Removable Partial Denture RetainersDocument8 pagesLec. 9 Retention and Removable Partial Denture RetainersTik TakNo ratings yet
- Appliance Design Lec. 1 2017Document6 pagesAppliance Design Lec. 1 2017Rebin AliNo ratings yet
- Ijp 9 4 Ur 10Document5 pagesIjp 9 4 Ur 10Anthony LiNo ratings yet
- Anterior and Canine RetractionDocument10 pagesAnterior and Canine RetractionLisbethNo ratings yet
- Abutmentt SelectionDocument6 pagesAbutmentt Selectionmenonann866No ratings yet
- Aprd 2 (1) 17-20Document4 pagesAprd 2 (1) 17-20Dr FarhatNo ratings yet
- Various Intrusive ArchsDocument10 pagesVarious Intrusive ArchsmutansNo ratings yet
- Anchorage in OrthodonticsDocument49 pagesAnchorage in Orthodonticsheena malikNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pros 1 - All NotesDocument18 pagesAdvanced Pros 1 - All NotesArbnor KicaNo ratings yet
- Anchorage SinaiDocument10 pagesAnchorage SinaiMohamed Yosef MoradNo ratings yet
- AnchorageDocument52 pagesAnchorageharshiniNo ratings yet
- PeriodonticsDocument1 pagePeriodonticsAnuvansh ChughNo ratings yet
- 2 Biomichanics of RPD FayadDocument29 pages2 Biomichanics of RPD FayadMostafa Fayad80% (5)
- Partial Dentures and Operative Dentistry: FixedDocument9 pagesPartial Dentures and Operative Dentistry: FixedPalaniappan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- The Anchorage Bend in The Begg TechniqueDocument7 pagesThe Anchorage Bend in The Begg TechniqueSyed Mohammad Osama AhsanNo ratings yet
- Eview Rticle: Splinting-A Dilemma in Periodontal TherapyDocument7 pagesEview Rticle: Splinting-A Dilemma in Periodontal TherapyDr.Niveditha SNo ratings yet
- Vibration analysis of beams with multiple height-edge cracksDocument8 pagesVibration analysis of beams with multiple height-edge cracksDamarla KiranNo ratings yet
- Monteith 1984Document9 pagesMonteith 1984PradeepNo ratings yet
- T1 - Biomechanics of Torque - Vijay Jayde PDFDocument7 pagesT1 - Biomechanics of Torque - Vijay Jayde PDFAnonymous LNLz3MtVNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Retraccction1Document46 pagesBiomechanics of Retraccction1PARIJAT CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- Clinical Consideration Before Bridge ConstructioDocument19 pagesClinical Consideration Before Bridge ConstructioAseelNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Frictionless Loop MechanicsDocument104 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Frictionless Loop Mechanicsjohn suryavardhanNo ratings yet
- 17 The Effect of Finish Line Curvature On Marginal Fit of All-Ceramic CAD - CAM Crowns and Metal-Ceramic CrownsDocument9 pages17 The Effect of Finish Line Curvature On Marginal Fit of All-Ceramic CAD - CAM Crowns and Metal-Ceramic CrownsJose Enrique AvilaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics in Orthodontics Anchorage Considerations-A ReviewDocument11 pagesBiomechanics in Orthodontics Anchorage Considerations-A ReviewputraNo ratings yet
- 2023 Article 1042Document7 pages2023 Article 1042Rami MagdiNo ratings yet
- Retraction Hooks of Different Lengths For Maxillary Whole Arch Distalization With Miniscrew Anchorage: A Finite Element AnalysisDocument14 pagesRetraction Hooks of Different Lengths For Maxillary Whole Arch Distalization With Miniscrew Anchorage: A Finite Element AnalysisKanchit SuwanswadNo ratings yet
- Bomechancs in OrthodotnicsDocument74 pagesBomechancs in OrthodotnicsheycoolalexNo ratings yet
- Principles of RPD DesignDocument59 pagesPrinciples of RPD DesignanushiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Abutment Tooth:: Prof. Adel Farhan IbraheemDocument12 pagesEvaluation Abutment Tooth:: Prof. Adel Farhan IbraheemMohammad ANo ratings yet
- Stress Reduction in Spur Gears Using Aero-Fin Shaped HolesDocument11 pagesStress Reduction in Spur Gears Using Aero-Fin Shaped HolesJojee MarieNo ratings yet
- Adminatharva, 1. JOFR-12-2020 Torque in OrthodonticsDocument7 pagesAdminatharva, 1. JOFR-12-2020 Torque in OrthodonticsKanchit SuwanswadNo ratings yet
- Bracing and ReciprocationDocument5 pagesBracing and ReciprocationMohsin HabibNo ratings yet
- 7 Davenport ReciprocidadDocument7 pages7 Davenport ReciprocidadandrebarrevzlaNo ratings yet
- Rotational Path Removable Partial Denture DesignDocument7 pagesRotational Path Removable Partial Denture DesignNapatsorn RakpakwanNo ratings yet
- Jacobson 1979Document26 pagesJacobson 1979Paola LoloNo ratings yet
- Southard Et Al. (2007) Friction Does Not Increase Anchorage LoadingDocument3 pagesSouthard Et Al. (2007) Friction Does Not Increase Anchorage LoadingDominikaSkórkaNo ratings yet
- Canine Retraction A Photoelastic StudyDocument13 pagesCanine Retraction A Photoelastic StudyOdilon SouzaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Prosthodontics Treatment for Missing Teeth Special ProblemsDocument12 pagesFixed Prosthodontics Treatment for Missing Teeth Special ProblemsMatheel JabbarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - BiomechanicsDocument73 pagesLecture 3 - BiomechanicsAlex ChangNo ratings yet
- Fixed Prosthodontics and Operative DentistryDocument8 pagesFixed Prosthodontics and Operative Dentistrysara luciaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of RPD DesignDocument43 pagesBiomechanics of RPD Designreem eltyebNo ratings yet
- Total Arch Distalization A ReviewDocument4 pagesTotal Arch Distalization A ReviewsmritiNo ratings yet
- Removable Partial Denture RetainersDocument10 pagesRemovable Partial Denture RetainersHaider Khaled AbedNo ratings yet
- 3D-Finite Element Analysis of Molars Restored WithDocument9 pages3D-Finite Element Analysis of Molars Restored Withabhilashanand3No ratings yet
- Yalisove1966Document17 pagesYalisove1966luis sanchezNo ratings yet
- 0 Aspectos Biomecánicos de Puentes Fijos Soportados Por Dientes Naturales e Implantes EndoóseosDocument18 pages0 Aspectos Biomecánicos de Puentes Fijos Soportados Por Dientes Naturales e Implantes EndoóseosJorge Prentice JiraldoNo ratings yet
- Orthodontically Driven Corticotomy: Tissue Engineering to Enhance Orthodontic and Multidisciplinary TreatmentFrom EverandOrthodontically Driven Corticotomy: Tissue Engineering to Enhance Orthodontic and Multidisciplinary TreatmentFederico BrugnamiNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Orthodontics: H A T o TH R Ti U Ar T H N - TH eDocument1 pageMcqs in Orthodontics: H A T o TH R Ti U Ar T H N - TH eadi raghavNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ComputerDocument54 pagesFundamentals of ComputerpsvinaNo ratings yet
- Tissue ProcessingDocument34 pagesTissue ProcessingMalliga Sundareshan100% (1)
- Normal Oral Flora 9Document95 pagesNormal Oral Flora 9adi raghav50% (2)
- Theory of StainDocument86 pagesTheory of StainalexNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ComputerDocument54 pagesFundamentals of ComputerpsvinaNo ratings yet
- Basic Genetics Part IIDocument32 pagesBasic Genetics Part IIadi raghavNo ratings yet
- Basic Genetics Part IDocument96 pagesBasic Genetics Part Iadi raghavNo ratings yet
- MeraDocument13 pagesMeraadi raghavNo ratings yet
- H 504 Oil Red O in Propylene Glycol MethodDocument2 pagesH 504 Oil Red O in Propylene Glycol Methodadi raghavNo ratings yet
- MeraDocument13 pagesMeraadi raghavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Histological EquipmentsDocument106 pagesIntroduction To Histological Equipmentshenryjack1100% (3)
- Practical PathologyDocument94 pagesPractical Pathologyadi raghavNo ratings yet
- SQL Plus UsersGuide and Quick ReferenceDocument432 pagesSQL Plus UsersGuide and Quick Referenceapi-25930603No ratings yet
- Jongka:the Traditional Korean Family: Exploring Jongka Food in The Context of Korean Food CategoriesDocument14 pagesJongka:the Traditional Korean Family: Exploring Jongka Food in The Context of Korean Food CategoriesSözen BayraktarNo ratings yet
- Design Regulations BKRDocument187 pagesDesign Regulations BKRn_costiqueNo ratings yet
- Saab Seaeye LTD: Benefits of Distributed Control Systems in Electric ROV Development and OperationDocument12 pagesSaab Seaeye LTD: Benefits of Distributed Control Systems in Electric ROV Development and OperationNdomaduNo ratings yet
- Controller Tuning Methods for Process ControlDocument17 pagesController Tuning Methods for Process ControltrshaaaNo ratings yet
- Math11 SP Q3 M8 PDFDocument12 pagesMath11 SP Q3 M8 PDFJessa Banawan EdulanNo ratings yet
- Implantable Technology: History, Controversies, and Social ImplicationsDocument11 pagesImplantable Technology: History, Controversies, and Social ImplicationssolomongNo ratings yet
- Quick Start GuideDocument3 pagesQuick Start Guideswornavidhya.mahadevanNo ratings yet
- Exit StrategyDocument2 pagesExit StrategyMuhammad KashifNo ratings yet
- C#Brain TeasersDocument5 pagesC#Brain TeasersNishant.kumaridNo ratings yet
- Iec 61724-1 2017 Version-Selection of Pyranometers v2008Document4 pagesIec 61724-1 2017 Version-Selection of Pyranometers v2008wwahib2100% (1)
- Macbeth PerformanceDocument4 pagesMacbeth Performanceapi-541677543No ratings yet
- The Roots and Method of Phenomenological RealismDocument133 pagesThe Roots and Method of Phenomenological RealismYuri OberlaenderNo ratings yet
- ProrepDocument24 pagesProrepKrishna RaoNo ratings yet
- 928g Bomba de Frenos Con SolenoideDocument6 pages928g Bomba de Frenos Con SolenoideMiguel Angel Garrido CardenasNo ratings yet
- Presentation Kaizen BaDocument87 pagesPresentation Kaizen BaAbela DrrsNo ratings yet
- GLA University - Student's No Dues DetailsDocument2 pagesGLA University - Student's No Dues DetailsRishi JakarNo ratings yet
- Bulk Storage Optimization for Large QuantitiesDocument3 pagesBulk Storage Optimization for Large Quantitiesbirojivenkat100% (1)
- Barclays Bank UPDATEDocument32 pagesBarclays Bank UPDATEAbdul wahidNo ratings yet
- Everything an Employee Experiences at WorkDocument1 pageEverything an Employee Experiences at WorkAnushka Seth BBA2021MCNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Master Thesis SampleDocument7 pagesAcknowledgement Master Thesis Samplebk3q07k5100% (2)
- DISC-Test Test PDFDocument22 pagesDISC-Test Test PDFKazekamiXNo ratings yet
- CSS Interview Questions 2022Document21 pagesCSS Interview Questions 2022christianlamb999No ratings yet
- Management Science Chapter 11Document42 pagesManagement Science Chapter 11Myuran SivarajahNo ratings yet
- Qualcomm Snapdragon 732g Mobile Platform Product BriefDocument2 pagesQualcomm Snapdragon 732g Mobile Platform Product BriefGilqlobroNo ratings yet
- 4.1 The Plausibility of µ as a Value for a Normal Population Mean μDocument23 pages4.1 The Plausibility of µ as a Value for a Normal Population Mean μTolesa F BegnaNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument14 pagesUntitled PresentationThe BeatableNo ratings yet
- Abstract Asef 2017Document3 pagesAbstract Asef 2017DeiviBarciNo ratings yet
- "Enhancement of A Heat Exchanger by Conical Inserts": A Project Report OnDocument32 pages"Enhancement of A Heat Exchanger by Conical Inserts": A Project Report OnDevashish RaturiNo ratings yet
- Learner's Activity Sheet: Mathematics (Quarter III - Week 6-7)Document13 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet: Mathematics (Quarter III - Week 6-7)Bai Shalimar PantaranNo ratings yet