Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sy 19
Sy 19
Uploaded by
api-506389013Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sy 19
Sy 19
Uploaded by
api-506389013Copyright:
Available Formats
SY19.
20 Teacher Practice Rubric- Summer Teaching Practices
The mission of Urban Teachers is to improve the educational and life outcomes of children in urban schools by preparing culturally competent, effective career teachers who accelerate
student achievement and disrupt systems of racial and socioeconomic inequity. Our high-quality coaching program is one of the more unique aspects of our teacher training and
development model. Summer teaching experiences at the beginning and end of the Urban Teachers residency year are a crucial component of our coaching program. We strongly
believe that excellent teachers develop over time and as a result of their engagement in quality coaching.
Urban Teachers participants are expected to demonstrate evidence of their ability to enact specific teaching practices for, and with, students during the summer school program. Our
coaches visit summer sites to observe instruction and provide real-time coaching aligned to these teaching practices:
• Establishing a Nurturing Environment
• Managing Expectations for Behavior
• Gathering Standards-Aligned Data
• Ensuring Standards-Based Objectives & Practice
• Promoting Talk
NOTE: Summer B participants will focus on all 10 of the summer teaching practices. Summer A participants will only focus on the highlighted summer teaching practices.
Updated: May 7, 2019
BEGINNING EMERGING PROFICIENT MASTERING
Limited or no skills in the practice Some skill in the practice Proficient skills in the practice Highly skilled in the practice
OUR TEACHERS...
1 2 3 4
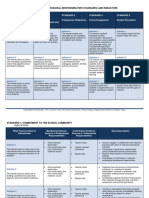
STRAND A: BUILD PRODUCTIVE AND NURTURING CLASSROOM ENVIRONMENTS
A.1 Few, if any, instances of the Some instances of the teacher Instances of the teacher building a Strong evidence of the teacher building
Nurturing Environment
Environment: teacher building a welcoming, building a welcoming, inclusive welcoming, inclusive community. a welcoming, inclusive community. The
Foster the inclusive community. Physical community. Physical environment, Physical environment, words, and physical environment, words, and
physical and A.1.6. Demonstrate environment, words, and actions do words, and actions somewhat place actions mostly place value on the actions consistently place value on the
cultural through words and not place value on the personal or value on the personal or cultural personal or cultural background of personal or cultural background of the
environment actions that everyone is cultural background of the students. background of the students. Some the students. Frequent attempts to students. Consistent attempts to build
to support the a valued member of the Few, if any, attempts to build attempts to build personally build personally relevant relationships personally relevant relationships with
development learning community. personally relevant relationships relevant relationships with students with students in an asset-based, bias students in an asset-based, bias free,
of the whole with students in an asset-based, in an asset-based, bias-free, free, manner. manner.
child bias-free, manner. manner.
A.2 Classroom Teacher presence is weak and Teacher presence is somewhat Teacher presence is strong and Teacher presence is strong and
Management: non-authoritative. Few, if any, strong and authoritative. Able to authoritative. Able to engage students authoritative. Able to engage students
Actively A.2.1. Use a strong instances, of students responding engage students, but after 3 or more after 2nd attempt. Sometimes talks immediately. Does not talk over
manage on- teacher presence to to teacher’s verbal directions (e.g. attempts. Frequently talks over over students and/or still relies students. Consistently uses a variety of
task behaviors engage students. strong, low, and lone voice; speak student voices. heavily on verbal (e.g. strong, low, verbal (e.g. strong, low, and lone voice;
and ensure in bullets; no pleading; does not and lone voice; speak in bullets; no speak in bullets; no pleading; does not
use negative controlling tone; and pleading; does not use negative use negative controlling tone; and use
that
use of attention getting signals) controlling tone; and use of attention of attention getting signals) and non-
instructional and non-verbal (e.g. proximity, getting signals) cues. verbal (e.g. proximity, square up, non-
Expectations for Behavior
time is used square up, non-threatening, and threatening, and teacher stare) cues.
effectively and teacher stare) cues. Consistently
efficiently talks over student voices.
Verbal directions do not provide Verbal directions are sometimes Verbal directions are explicit Verbal directions are consistently explicit
A.2.2. Provide explicit students with explicit cues explicit (movement, voice, (movement, voice, participation, and (movement, voice, participation, and
directions for students (movement, voice, participation, participation, and time) and time) and frequently provide students time) and provide students with clear
about expectations for on- and time) about expectations for sometimes provide students with with cues about expectations for on- cues about expectations for on-task
task behavior. on-task behavior, and MVPT cues about expectations for on-task task behavior, or MVPT directions are behavior, or MVPT directions are not
directions are consistently behavior, and MVPT directions are sometimes necessary. necessary.
necessary. frequently necessary.
Few, if any, instances of teacher Some instances of teacher providing Teacher frequently provides effective Teacher consistently provides effective
providing effective positive effective positive narration that is positive narration that is aligned to positive narration throughout lesson
A.2.3. Use positive
narration that is aligned to aligned to directions. Some off-task directions. Most off-task behaviors that is aligned to directions. All off-task
narration
directions. Off-task behaviors are behaviors are acknowledged and are acknowledged and corrected. behaviors are acknowledged and
to hold students
not acknowledged and corrected. corrected. Teacher sometimes Teacher frequently provides corrected. Teacher consistently
accountable to expectations
Teacher provides no provides consequences for off-task consequences for off-task behavior. provides consequences for off-task
for on-task behavior.
consequences for off-task behavior. behavior.
behavior.
Updated: May 7, 2019 Teacher Practice Rubric (TPR) 2019-2020 1
BEGINNING EMERGING PROFICIENT MASTERING
Limited or no skills in the practice Some skill in the practice Proficient skills in the practice Highly skilled in the practice
OUR TEACHERS...
1 2 3 4
STRAND A: BUILD PRODUCTIVE AND NURTURING CLASSROOM ENVIRONMENTS
A.2 Classroom All instructional time is lost Most of the instructional time is lost Some instructional time is lost due to Instructional time is fully maximized
Management: throughout the lesson’s entirety due due to inefficient transitions and/or inefficient transitions and/or the throughout the lesson’s entirety due to
Pacing & Transitions
Actively to inefficient transitions and/or the the presence of non-productive presence of non-productive behavior. the prompt, smooth enactment of
manage on- A.2.5. Facilitate prompt and presence of non-productive behavior. transitions and/or few, if any, non-
task smooth transitions behavior. productive behaviors.
behaviors and between activities or
ensure that across spaces in the
instructional classroom.
time is used
effectively
and efficiently
Updated: May 7, 2019 Teacher Practice Rubric (TPR) 2019-2020 2
BEGINNING EMERGING PROFICIENT MASTERING
Limited or no skills in the practice Some skill in the practice Proficient skills in the practice Highly skilled in the practice
OUR TEACHERS...
1 2 3 4
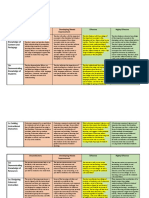
STRAND B: ARE DIAGNOSTICIANS
B.1. Collect data: There is no movement about the Teacher is moving about the Teacher is moving purposefully Teacher is moving purposefully about
Routinely gather B.1.1. Constantly monitor classroom, or there is movement classroom and there is some about the classroom and there is the classroom and there is consistent
formative by moving about the room— which is not purposeful. evidence that he/she is listening frequent evidence that he/she is evidence that he/she is listening in or
routinely and consistently— in or examining student work. listening in or examining student examining student work.
assessment data
to listen in and look at work.
that is aligned to student work.
Gather Standards-Aligned Data
the expectations
of the standards
There is no system for student- There is a system for student- Teacher is moving purposefully Teacher is moving purposefully about
B.1.2. Implement a specific watching being implemented that watching being implemented that about the classroom and there is the classroom and there is consistent
student-watching system to allows the teacher to gather data. allows the teacher to gather frequent evidence that he/she is evidence that he/she is listening in or
strategically gather data for concrete student performance listening in or examining student examining student work and gathering
learning. data on some students. The data work and gathering concrete concrete student performance data on
is related to the lesson, but not student performance data on most all students.
fully aligned to the expectations students.
of the standards AND is not
being used strategically for
learning.
Updated: May 7, 2019 Teacher Practice Rubric (TPR) 2019-2020 3
BEGINNING EMERGING PROFICIENT MASTERING
Limited or no skills in the practice Some skills in the practice Proficient skills in the practice Highly skilled in the practice
OUR TEACHERS...
1 2 3 4
STRAND C. SET PRECISE GOALS AND ENACT THEM
C.1. Lesson Content Coherence Academic content is consistently Academic content is frequently Academic content is frequently Academic content is consistently
Structure and and Accuracy C.1.6. Deliver academic inaccurate and imprecise and inaccurate, unclear, or accurate, with some instances of accurate, clear, and precise.
Alignment: Provide content that is unclear. imprecise. being unclear or imprecise.
high-quality, accurate, precise, and
standards-based, clear.
learning experiences
for students
BEGINNING EMERGING PROFICIENT MASTERING
Limited or no skills in the practice Some skills in the practice Proficient skills in the practice Highly skilled in the practice
OUR TEACHERS...
1 2 3 4
STRAND D: FOSTER ACADEMIC TALK
D.1. Promote Talk: Throughout the lesson, there is no Throughout the lesson, there is Throughout the lesson, there is Throughout the lesson, there is
Hold all students D.1.4. Implement a evidence of effective strategies for some evidence of a range of frequent evidence of a range of consistent evidence of a range of
Strategies for Talk
accountable for range of strategies to facilitating student talk. effective strategies for facilitating effective strategies for facilitating effective strategies for facilitating
participating in foster student talk. student talk. student talk. student talk.
respectful academic
conversations
Updated: May 7, 2019 Teacher Practice Rubric (TPR) 2019-2020 4
BEGINNING EMERGING PROFICIENT MASTERING
Limited or no skills in the practice Some skills in the practice Proficient skills in the practice Highly skilled in the practice
OUR TEACHERS…
1 2 3 4
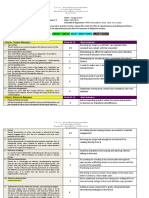
STRAND E: HAVE A GROWTH MINDSET AND EXHIBIT PROFESSIONALISM
E.2 Openness to Feedback: Rarely responds to feedback in a Sometimes responds to feedback Responds to feedback in a Always responds to feedback in a
Is open and responsive to feedback professional manner; defensive, in a professional manner, but still professional manner (e.g., takes professional, proactive manner.
finds ways to devalue feedback, exhibits some defensiveness or notes, asks questions to probe for Consistently exhibits growth mindset.
consistently exhibits fixed mindset. fixed mindset. May be unwilling to further understanding). Typically Implements all feedback in a thoughtful
Does not implement feedback. act on feedback. Reluctant to have exhibits growth mindset. Implements and lasting manner. Frequently asks for
Closed to external observation of external observation of work and feedback. Open to external feedback and/or invites others to view
work and teaching practice (i.e. not teaching practice. observation of work and teaching practice (i.e. seeks opportunities to
following processes that enable practice. Occasionally asks for rehearse).
coaching to take place). feedback and/or invites others to view
practice.
Updated: May 7, 2019 Teacher Practice Rubric (TPR) 2019-2020 5
You might also like
- Responsive Classroom Discipline For Middle SchoolDocument15 pagesResponsive Classroom Discipline For Middle SchoolSusan CollinsNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten Appraisal - 2020-2021Document14 pagesKindergarten Appraisal - 2020-2021api-264963856No ratings yet
- Philippines Professional Standards For Teachers Domain 2Document15 pagesPhilippines Professional Standards For Teachers Domain 2Tintin Yanson Francisco100% (3)
- Classroom Environment ChecklistDocument3 pagesClassroom Environment Checklistapi-506389013No ratings yet
- Cm-Session 3Document34 pagesCm-Session 3api-506389013No ratings yet
- Servitors and EgregoresDocument13 pagesServitors and EgregoresCharles Bentum Vroom100% (4)
- Self AssessmentDocument1 pageSelf Assessmentapi-420688546No ratings yet
- Mid-Term Formative Michael Lauletta 1Document9 pagesMid-Term Formative Michael Lauletta 1api-356010663No ratings yet
- LJ CtevaluationDocument12 pagesLJ Ctevaluationapi-356227663No ratings yet
- Self Reflection Rubric TeacherDocument7 pagesSelf Reflection Rubric TeacherRo MyNo ratings yet
- PPST Domain 2Document15 pagesPPST Domain 2Tintin FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Continuum of Instructional Practice: Level 1: EmergingDocument7 pagesContinuum of Instructional Practice: Level 1: EmergingKhrisAngelPeñamanteNo ratings yet
- Speaking Sub Skills BookletDocument28 pagesSpeaking Sub Skills BookletEmily JamesNo ratings yet
- PPST Domain 2 ReportDocument15 pagesPPST Domain 2 ReportTintin FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Mary Osborn Mentor NC Teacher Candidate Evaluation Spring 2017Document16 pagesMary Osborn Mentor NC Teacher Candidate Evaluation Spring 2017api-353794467No ratings yet
- SG8001 Teaching Students: First Steps - Assessment Rubrics: Criteria Fail Adequate Good Excellent ScoreDocument2 pagesSG8001 Teaching Students: First Steps - Assessment Rubrics: Criteria Fail Adequate Good Excellent Score盧森丘No ratings yet
- 237 EvaluationDocument4 pages237 Evaluationapi-328372259No ratings yet
- Module 1 EBUS5263 Professional Development Framework ACEDocument2 pagesModule 1 EBUS5263 Professional Development Framework ACEThomas FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Metacognition Rubric MYPDocument4 pagesMetacognition Rubric MYPgabrielaNo ratings yet
- Dir. Inst. Practice Profile July 2015Document4 pagesDir. Inst. Practice Profile July 2015NJ NomusNo ratings yet
- Tabing RpmsDocument1 pageTabing RpmsEric John Vegafria100% (3)
- Stringer Formative Observation 2 SignedDocument7 pagesStringer Formative Observation 2 Signedapi-511629507No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CBA2023a Micro Teaching Observation RubricDocument3 pagesMicrosoft Word - CBA2023a Micro Teaching Observation RubricGEMA DANIELA DE LA PARRA SANTANANo ratings yet
- Teacher Preparation Collaborative (TPC) Evaluation FormDocument9 pagesTeacher Preparation Collaborative (TPC) Evaluation Formapi-396872239No ratings yet
- Model Teacher Observation Rubric For ClassDocument5 pagesModel Teacher Observation Rubric For Classapi-542317303No ratings yet
- Blue Yellow Playful Illustration Self Care Infographic PosterDocument7 pagesBlue Yellow Playful Illustration Self Care Infographic PosterAin NurasyikinNo ratings yet
- Wichita Evaluation HandbookDocument56 pagesWichita Evaluation Handbookkshin2518No ratings yet
- DLL Week 1 Psychological SupportDocument8 pagesDLL Week 1 Psychological SupportJudith Asis Betinol LptNo ratings yet
- Dance RubricDocument1 pageDance Rubricapi-532616620No ratings yet
- Approaches and Methods For Teaching English Comparative ChartDocument1 pageApproaches and Methods For Teaching English Comparative ChartMaría B.No ratings yet
- Lesson Observation DocumentDocument3 pagesLesson Observation DocumentCarmen GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 1Document3 pagesLearning Task 1anthonydongonNo ratings yet
- Teacher-Professional Responsibilities RubricDocument13 pagesTeacher-Professional Responsibilities RubriczgyleopardNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For TeacherDocument1 pageRubrics For TeacherLight HouseNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Q2 W8Document3 pagesOral Communication Q2 W8Fhats DuncabNo ratings yet
- Nas Ellen ObservationDocument3 pagesNas Ellen Observationapi-316070797No ratings yet
- August 29 To September 4 2023Document3 pagesAugust 29 To September 4 2023alvinjohnsanchez4No ratings yet
- Reporting CriteriaDocument1 pageReporting CriteriaRAHMA MOLIDNo ratings yet
- Episode 7Document9 pagesEpisode 7guirillita acutNo ratings yet
- Lex Spears October 14th Observation Record InternshipiDocument2 pagesLex Spears October 14th Observation Record Internshipiapi-581487279No ratings yet
- Evaluation September 2020Document14 pagesEvaluation September 2020api-481566520No ratings yet
- Artifact Binder RubricDocument8 pagesArtifact Binder Rubricapi-355955038No ratings yet
- Outcomes Assessment Forum - 9 Apr 2010Document13 pagesOutcomes Assessment Forum - 9 Apr 2010PersonNo ratings yet
- Eng116 - Langueage Learning Materials DevelopmentDocument6 pagesEng116 - Langueage Learning Materials DevelopmentKit Oseias H. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 13 Cantos FlorenceDocument4 pagesLearning Task 13 Cantos FlorenceCantos FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Profession: Role of A Teacher Role of A TeacherDocument5 pagesProfession: Role of A Teacher Role of A TeacherAHMAD NAWAZNo ratings yet
- Octobet 16 - 20, 2023Document3 pagesOctobet 16 - 20, 2023alvinjohnsanchez4No ratings yet
- Classroom Management Khilola AlihonDocument4 pagesClassroom Management Khilola AlihonHilola AlihonNo ratings yet
- DepEd Teacher 1 Demonstration TeachingDocument13 pagesDepEd Teacher 1 Demonstration TeachingroyNo ratings yet
- DepEd Teacher 1 Demonstration TeachingDocument13 pagesDepEd Teacher 1 Demonstration TeachingRoy C. EstenzoNo ratings yet
- Pip AnalysisDocument4 pagesPip Analysisapi-545998611No ratings yet
- Midterm Cast AssessmentDocument8 pagesMidterm Cast Assessmentapi-660083506No ratings yet
- SB Feb12 7edanielsonDocument21 pagesSB Feb12 7edanielsonapi-369936679No ratings yet
- George Washington Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesGeorge Washington Lesson Planapi-306790814No ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1 - RubricDocument2 pagesAssessment Task 1 - RubricjayNo ratings yet
- BehaviourismDocument3 pagesBehaviourismapi-533984280No ratings yet
- FS 2 ModuleDocument201 pagesFS 2 ModuleJosh GandelaNo ratings yet
- Audio Lingual TPR TBDocument2 pagesAudio Lingual TPR TBVaal de TamrielNo ratings yet
- I. Step 4 TEACHINGDocument18 pagesI. Step 4 TEACHINGBrandon CuarezNo ratings yet
- Brown Observation 1Document13 pagesBrown Observation 1api-285426028No ratings yet
- Fa21 Mued376 Carter 18eDocument5 pagesFa21 Mued376 Carter 18eapi-425381470No ratings yet
- Ofsted Key IndicatorsDocument2 pagesOfsted Key IndicatorsrajeshbarasaraNo ratings yet
- The Keys to Effective Teaching: Culturally Revelant Teaching StrategiesFrom EverandThe Keys to Effective Teaching: Culturally Revelant Teaching StrategiesNo ratings yet
- CM - Session 4Document33 pagesCM - Session 4api-506389013No ratings yet
- Udl GuidelinesDocument1 pageUdl Guidelinesapi-506389013No ratings yet
- Nbss Learning Behaviour Checklist LecDocument10 pagesNbss Learning Behaviour Checklist Lecapi-506389013No ratings yet
- Resource 9 Classroom Learning Environment ChecklistDocument4 pagesResource 9 Classroom Learning Environment Checklistapi-506389013No ratings yet
- SharingazoomrecordingDocument3 pagesSharingazoomrecordingapi-506389013No ratings yet
- Skinfolk Ain T Always Kinfolk The Dangers of Assuming and Assigning Inherent Cultural Responsiveness To Teachers of ColorDocument12 pagesSkinfolk Ain T Always Kinfolk The Dangers of Assuming and Assigning Inherent Cultural Responsiveness To Teachers of Colorapi-506389013No ratings yet
- SW285@jh - Edu/: Classroom Management IDocument16 pagesSW285@jh - Edu/: Classroom Management Iapi-506389013No ratings yet
- ct3 Full NNN ProgramDocument112 pagesct3 Full NNN Programapi-506389013No ratings yet
- Rce Syllabussummer2020Document22 pagesRce Syllabussummer2020api-506389013No ratings yet
- Willing To Be DisturbedDocument4 pagesWilling To Be Disturbedapi-506389013No ratings yet
- Sw-Cmisummer2020elasyllabus 1Document16 pagesSw-Cmisummer2020elasyllabus 1api-506389013No ratings yet
- Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Language Acquisition Session 14Document14 pagesCopy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Language Acquisition Session 14api-506389013No ratings yet
- Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Language Acquisition Session 13Document17 pagesCopy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Copy of Language Acquisition Session 13api-506389013No ratings yet
- Language Acquistion Session 15Document13 pagesLanguage Acquistion Session 15api-506389013No ratings yet
- PDF 1Document302 pagesPDF 1LuckyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering Management: April 2020Document51 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Management: April 2020JoshuaNo ratings yet
- LT-4208 Brochure For Caravan LumatechDocument2 pagesLT-4208 Brochure For Caravan LumatechMarcus DragoNo ratings yet
- Advances in Innovative Geotechnical Engineering: Yong Liu Sabatino Cuomo Junsheng Yang EditorsDocument153 pagesAdvances in Innovative Geotechnical Engineering: Yong Liu Sabatino Cuomo Junsheng Yang EditorsHenryNo ratings yet
- Band 9 EssaysDocument24 pagesBand 9 Essaysa1english academyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2020: Introduction To Research Methodology For Law and Criminal JusticeDocument19 pagesTutorial Letter 101/3/2020: Introduction To Research Methodology For Law and Criminal JusticeMichelle UngererNo ratings yet
- LDA Jaywant ArakeriDocument38 pagesLDA Jaywant ArakerirajuvadlakondaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesMaria Angeline Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Echocardiographic Versus Invasive Aortic Valve Gradients in Different Clinical Scenarios - Journal of The American Society of EchocardiographyDocument14 pagesEchocardiographic Versus Invasive Aortic Valve Gradients in Different Clinical Scenarios - Journal of The American Society of EchocardiographyNeison DuarteNo ratings yet
- Cities and Their Brands Lessons From Corporate BraDocument13 pagesCities and Their Brands Lessons From Corporate BraAleksandar MihajlovićNo ratings yet
- Math MYP I Summative Assessment Criteria C TessellationsDocument6 pagesMath MYP I Summative Assessment Criteria C TessellationsMich CastillejaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument10 pagesChapter IIMeka Ella Meka EllaNo ratings yet
- CH One Public AdminstrationDocument11 pagesCH One Public Adminstrationhesham hassanNo ratings yet
- HBO PPT Chap 6 8Document60 pagesHBO PPT Chap 6 8Beat Karb0% (1)
- Toward Safe Systems: Traffic Safety, Cognition, and The Built EnvironmentDocument13 pagesToward Safe Systems: Traffic Safety, Cognition, and The Built EnvironmentMarco DanielNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics I (U2) 72Document72 pagesEngineering Mathematics I (U2) 72SangeethaNo ratings yet
- The Starving Urban Poor During The Covid-19 Pandemic: Presented To The Faculty ofDocument2 pagesThe Starving Urban Poor During The Covid-19 Pandemic: Presented To The Faculty ofJohair Acob SultanNo ratings yet
- Tabla de RatioDocument33 pagesTabla de RatioLuis Antonio GuerraNo ratings yet
- MID 100 PART 1 LESSON 5 CommunicationDocument16 pagesMID 100 PART 1 LESSON 5 CommunicationHONEYLOUNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Laws of Sines and CosinesDocument25 pagesMathematics: Laws of Sines and CosinesHAZEL VIDARNo ratings yet
- Spelling Rubric - Within Writing: Advanced Proficient Proficient Approaching Proficiency NoviceDocument1 pageSpelling Rubric - Within Writing: Advanced Proficient Proficient Approaching Proficiency NoviceYani anggraeniNo ratings yet
- Body Language Week 7Document16 pagesBody Language Week 7carlosNo ratings yet
- CVS 215 - Course OutlineDocument2 pagesCVS 215 - Course OutlineBenard Omondi100% (1)
- CE272 Lecture CenterOfPressureDocument7 pagesCE272 Lecture CenterOfPressureCihan Barış ErdoğanNo ratings yet
- A Legacy of Caring - The History of Picker International: Some Recent Business HighlightsDocument17 pagesA Legacy of Caring - The History of Picker International: Some Recent Business Highlightsfran.pochettino95No ratings yet
- Ocr Gateway Core Science CourseworkDocument7 pagesOcr Gateway Core Science Courseworkshvfihdjd100% (2)
- 13.8kV MV Switchgear Operation and Maintenance Manual 3-10-2019 LowDocument144 pages13.8kV MV Switchgear Operation and Maintenance Manual 3-10-2019 LowOmar AlfNo ratings yet
- BME PHD Program (2017) - FinalDocument13 pagesBME PHD Program (2017) - FinalWubshet ShimelsNo ratings yet
- Physics CHP 4 Test#3Document2 pagesPhysics CHP 4 Test#3parsaNo ratings yet