Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Descriptive Model of Volcanogenic MN
Uploaded by
miguelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Descriptive Model of Volcanogenic MN
Uploaded by
miguelCopyright:
Available Formats
Model 24c
DESCRIPTIVE MODEL OF VOLCANOGENIC Mn
By Randolph A. Koski
APPROXIMATE SYNONYM Volcanogenic-sedimentary (Roy, 1981)
DESCRIPTION Lenses and stratiform bodies of manganese oxide, carbonate, and silicate in volcanic-
sedimentary sequences. Genesis related to volcanic (volcanogenic) processes.
GENERAL REFERENCE Roy (1981).
GEOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT
Rock Types Chert, shale, graywacke, tuff, basalt; chert, jasper, basalt (ophiolite); basalt, andesite,
rhyolite (island-arc); basalt, limestone; conglomerate, sandstone, tuff, gypsum.
Age Range Cambrian to Pliocene.
Depositional Environment Sea-floor hot spring, generally deep water; some shallow water marine; some
may be enclosed basin.
Tectonic Setting(s) Oceanic ridge, marginal basin, island arc, young rifted basin; all can be
considered eugeosynclinal.
Associated Deposit Types Kuroko massive sulfide deposits.
DEPOSIT DESCRIPTION
Mineralogy Rhodochrosite, Mn-calcite, braunite, hausmannite, bementite, neotocite, alleghenyite,
spessartine, rhodonite, Mn-opal, manganite, pyrolusite, coronadite, cryptomelane, hollandite,
todorokite, amorphous MnOj.
Texture/Structure Fine-grained massive crystalline aggregates, botryoidal, colloform in bedded and
lensoid masses.
Alteration Spilitic or greenschist-facies alteration of associated mafic lavas, silicification,
hematitization.
Ore Controls Sufficient structure and porosity to permit subsea-floor hydrothermal circulation and sea-
floor venting; redox boundary at seafloor-seawater interface around hot spring; supergene enrichment to
upgrade Mn content.
Weathering Strong development of secondary Mn oxides (todorokite, birnessite, pyrolusite, amorphous
Mn02) at the surface and along fractures.
Geochemical Signature Although Mn is only moderately mobile and relatively abundant in most rocks, Mn
minerals may incorporate many other trace elements such as Zn, Pb, Cu, and Ba.
Examples
Olympic Peninsula, USWA (Park, 1942, 1946; Sorem and Gunn,
1967)
Franciscan type, USCA, USOR (Taliaferro and Hudson, 1943; Crerar
and others, 1982; Snyder 1978; Kuypers
and Denyer, 1979)
GRADE AND TONNAGE MODEL OF VOLCANOGENIC Mn
By Dan L. Mosier
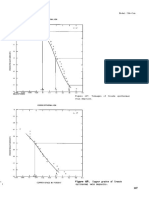
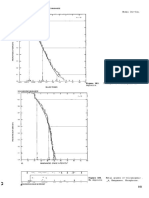
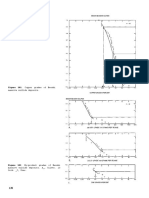
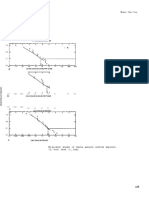
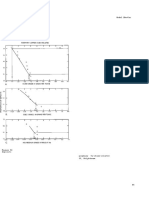
COMMENTS Tonnage is correlated with manganese grade (r = -0.32) and with phosphorus grade (r = -0.94, n
= 8). See figs. 103-104.
139
You might also like
- Greensmith 1988 Petrology of The Sedimentary RocksDocument271 pagesGreensmith 1988 Petrology of The Sedimentary RocksGuido Soto Mamani100% (1)
- Extraction of Caffeine From Tea LeavesDocument4 pagesExtraction of Caffeine From Tea LeavesHeather Gutierrez100% (4)
- Anthony, Julia, and Cindy - Lab 13Document12 pagesAnthony, Julia, and Cindy - Lab 13Anthony HowerNo ratings yet
- Quantitative X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of Clay-Bearing Rocks From Random Preparations-Srodon 2001-OKKK Importante PDFDocument15 pagesQuantitative X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of Clay-Bearing Rocks From Random Preparations-Srodon 2001-OKKK Importante PDFGina AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Argillaceous Rock AtlasDocument146 pagesArgillaceous Rock Atlasyaku1618No ratings yet
- Ore Mineral Textures PDFDocument20 pagesOre Mineral Textures PDFAnonymous Lrw61wNo ratings yet
- Use of The Other Ingredients in Cleaning Agents: By: Group 9Document56 pagesUse of The Other Ingredients in Cleaning Agents: By: Group 9Camille PasionNo ratings yet
- Bow Tie DiagramDocument2 pagesBow Tie DiagramKoay Kang HaoNo ratings yet
- Module in Properties, Changes, and Classification of MatterDocument5 pagesModule in Properties, Changes, and Classification of MatterRaymart MesugaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Optical Mineralogy And Petrography - The Practical Methods Of Identifying Minerals In Thin Section With The Microscope And The Principles Involved In The Classification Of RocksFrom EverandIntroduction To Optical Mineralogy And Petrography - The Practical Methods Of Identifying Minerals In Thin Section With The Microscope And The Principles Involved In The Classification Of RocksRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sediment-Hosted Cu DepositsDocument11 pagesSediment-Hosted Cu DepositsAndrés RuizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 14 AnswersBenecia odogu100% (1)
- ProteinDocument23 pagesProteinsamantha garciaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Alaskan PGEDocument2 pagesDescriptive Model of Alaskan PGERiston Belman SidabutarNo ratings yet
- Model of ZN-PB SkarnDocument6 pagesModel of ZN-PB SkarnFlorencio Choque AyqueNo ratings yet
- Sumaco ReventadorDocument4 pagesSumaco ReventadorRoberto PulupaNo ratings yet
- The Mukundpura MeteoriteDocument6 pagesThe Mukundpura MeteoriteValen RamiirezNo ratings yet
- Mineral Resources of The Ocean: G. N. BaturinDocument2 pagesMineral Resources of The Ocean: G. N. BaturinRahul Kumar MíšhřâNo ratings yet
- Journal of African Earth Sciences: Yawooz A. Kettanah, Sabah A. IsmailDocument20 pagesJournal of African Earth Sciences: Yawooz A. Kettanah, Sabah A. IsmailJega AlinNo ratings yet
- Bookstrom 1995Document5 pagesBookstrom 1995Kend BasalNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Diamond PlacersDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Diamond PlacersajnmboNo ratings yet
- 2011CarrasqueroetalNeuejahrbuch PDFDocument13 pages2011CarrasqueroetalNeuejahrbuch PDFVíctor Adolfo ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- TMP CC05Document15 pagesTMP CC05FrontiersNo ratings yet
- 2023, Spry Et Al., Nodular Sillimanite Rocks As Field Indicators To Metamorphosed Massive Sulfide Deposits, Ore Geol RevDocument23 pages2023, Spry Et Al., Nodular Sillimanite Rocks As Field Indicators To Metamorphosed Massive Sulfide Deposits, Ore Geol RevSamuel PierreNo ratings yet
- TMP DB95Document10 pagesTMP DB95FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Metasomatic Zoning Mineralizations and G PDFDocument12 pagesMetasomatic Zoning Mineralizations and G PDFPaul Ibarra SalasNo ratings yet
- Snowball Earth 2002Document27 pagesSnowball Earth 2002sheldon souzaNo ratings yet
- Krishnamurthy 1977Document23 pagesKrishnamurthy 1977shakilamkarunaNo ratings yet
- Organic Matter Diagenesis As The Key To A Unifying Theory For The Genesis of Tabular Uranium-Vanadium DepositsDocument14 pagesOrganic Matter Diagenesis As The Key To A Unifying Theory For The Genesis of Tabular Uranium-Vanadium Depositsjunior.geologiaNo ratings yet
- SilicificationinthephosphatedepositsofMaastrichtian LutetianoftheOuledAbdounBasinMoroccoSedimentologymineralogyandgeochemistry245 536 1 SMDocument9 pagesSilicificationinthephosphatedepositsofMaastrichtian LutetianoftheOuledAbdounBasinMoroccoSedimentologymineralogyandgeochemistry245 536 1 SMFadiliAhmedNo ratings yet
- Frimmel INTRODocument11 pagesFrimmel INTROBrett Gonzalez CardenasNo ratings yet
- 卫星断裂和斑岩铜矿Document5 pages卫星断裂和斑岩铜矿daxianqwerNo ratings yet
- Deepwater Environment: Start From HereDocument8 pagesDeepwater Environment: Start From HereCharisah AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Besshi Massive SulfideDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Besshi Massive SulfidemiguelNo ratings yet
- Mudstones ClasificacionDocument17 pagesMudstones ClasificacionPatricia TorresNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 625 3048 PDFDocument20 pages10 1 1 625 3048 PDFShankar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Bendezu Morococha PGC 08Document6 pagesBendezu Morococha PGC 08ajreateguicNo ratings yet
- Geology and Geochemistry of High-Grade Mercury MineralizationDocument12 pagesGeology and Geochemistry of High-Grade Mercury MineralizationHeri GeologistNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary MN Deposits (MODEL 34b Cannon and Force, 1986)Document4 pagesSedimentary MN Deposits (MODEL 34b Cannon and Force, 1986)Muhammad ZakyNo ratings yet
- Claymin 1994 029 4 20Document15 pagesClaymin 1994 029 4 20Shaukat H.KhanNo ratings yet
- Kloprogge p623-629 02Document7 pagesKloprogge p623-629 02mauricio rojas alvarezNo ratings yet
- TMP C02Document17 pagesTMP C02FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Raman Spectroscopy Study of Manganese Oxides: Tunnel StructuresDocument16 pagesRaman Spectroscopy Study of Manganese Oxides: Tunnel StructuresMarcelo CalegaroNo ratings yet
- Article in PressDocument12 pagesArticle in PressyustisianatikahNo ratings yet
- MORB PetrogenesisDocument68 pagesMORB Petrogenesisharidas palNo ratings yet
- Podiform Chromite PDFDocument3 pagesPodiform Chromite PDFBonjovi VerdejoNo ratings yet
- Podiform Chromite - Mineral Deposit Profiles, B.C. Geological SurveyDocument4 pagesPodiform Chromite - Mineral Deposit Profiles, B.C. Geological SurveyRatna QiaNo ratings yet
- 16 Pyrrhotite-Rich, Polymetallic Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide Marcoux-OreGeologyReviews-2007Document36 pages16 Pyrrhotite-Rich, Polymetallic Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide Marcoux-OreGeologyReviews-2007Salvadora1No ratings yet
- 1286pg227 254Document28 pages1286pg227 254Marcio AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- Ore Geology Reviews: SciencedirectDocument23 pagesOre Geology Reviews: SciencedirectjfsilvaNo ratings yet
- N-Cartigny-Marty 2013Document8 pagesN-Cartigny-Marty 2013ivan rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Associations Between Potassic Igneous Rocks, Shoshonites and Gold-Copper DepositsDocument24 pagesDirect and Indirect Associations Between Potassic Igneous Rocks, Shoshonites and Gold-Copper DepositsSergio SilvaNo ratings yet
- Alberdi Genolet1999Document20 pagesAlberdi Genolet1999JavierNo ratings yet
- Noyan2006, Jurnal Permukaan Keasaman BentonitDocument7 pagesNoyan2006, Jurnal Permukaan Keasaman Bentonitbwj8sk6nncNo ratings yet
- Tectonophysics 2010 BomDocument16 pagesTectonophysics 2010 BomRodrigo TavaresNo ratings yet
- Njonfang Et Al., 2013Document30 pagesNjonfang Et Al., 2013JiozangNo ratings yet
- HeinDocument67 pagesHeingigio marinoNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument71 pagesRocksBikash ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Viva - Voce PresentationDocument28 pagesViva - Voce Presentationapi-439638408No ratings yet
- Sir20105070q 3Document30 pagesSir20105070q 3Ahmet ÇelikNo ratings yet
- Diorite and Gabbro of The Dromedary Mafic Complex South Victoria Land AntarcticaDocument13 pagesDiorite and Gabbro of The Dromedary Mafic Complex South Victoria Land Antarcticafrederick.121370105No ratings yet
- Nakhla: - 10 Kilograms ClinopyroxeniteDocument15 pagesNakhla: - 10 Kilograms ClinopyroxeniteAlberto RSNo ratings yet
- GEOLOGÍA DEL YACIMIENTO DE MN DE CRIVILLEN (TERUEL)Document25 pagesGEOLOGÍA DEL YACIMIENTO DE MN DE CRIVILLEN (TERUEL)Cesar Veliz LopezNo ratings yet
- Cochrane Et Al., 2014aDocument71 pagesCochrane Et Al., 2014aAlexander DavydNo ratings yet
- Review On SkarnsDocument43 pagesReview On Skarnspliiilq1No ratings yet
- Paper PlacerDocument27 pagesPaper PlacerjohnNo ratings yet
- Geochemistry, Classification and Geotectonic Studies of Pan-African Rocks Around Akure, Southwestern NigeriaDocument17 pagesGeochemistry, Classification and Geotectonic Studies of Pan-African Rocks Around Akure, Southwestern NigeriaHenry MYNo ratings yet
- HTTP ProxiesDocument32 pagesHTTP ProxiesmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Comstock Epithermal VeinsDocument15 pagesDescriptive Model of Comstock Epithermal VeinsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Epithermal Quartz-Alunite Vein: Model 25e-ConDocument15 pagesEpithermal Quartz-Alunite Vein: Model 25e-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- HTTP ProxiesDocument47 pagesHTTP ProxiesmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Simple SB DepositsDocument15 pagesDescriptive Model of Simple SB DepositsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Volcanic-Hosted MagnetiteDocument15 pagesDescriptive Model of Volcanic-Hosted MagnetitemiguelNo ratings yet
- 151 300 1 15 14 PDFDocument1 page151 300 1 15 14 PDFmiguelNo ratings yet
- Figure 109. Lead Grades of Creede: Model 25b-ConDocument1 pageFigure 109. Lead Grades of Creede: Model 25b-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 25b-Con: Creede Epithermal VeinDocument1 pageModel 25b-Con: Creede Epithermal VeinmiguelNo ratings yet
- 151 300 1 15 12Document1 page151 300 1 15 12miguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Creede Epithermal VeinsDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Creede Epithermal VeinsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Creede Epithermal Vein: Model 25b-ConDocument1 pageCreede Epithermal Vein: Model 25b-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- 151 300 1 15 13 PDFDocument1 page151 300 1 15 13 PDFmiguelNo ratings yet
- Volcanogenic Manganese: I - 1 - I I - I ° ° IDocument1 pageVolcanogenic Manganese: I - 1 - I I - I ° ° ImiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Creede Epithermal VeinsDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Creede Epithermal VeinsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Hot-Spring Au-AgDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Hot-Spring Au-AgmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 25a-ConDocument1 pageModel 25a-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 24b - Con: Figure 101. Copper Grades of BesshiDocument1 pageModel 24b - Con: Figure 101. Copper Grades of BesshimiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Blackbird Co-CuDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Blackbird Co-CumiguelNo ratings yet
- Figure 100. Tonnages of Besshi Massive Sulfide DepositsDocument1 pageFigure 100. Tonnages of Besshi Massive Sulfide DepositsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Hot-Spring Au-AgDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Hot-Spring Au-AgmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Besshi Massive SulfideDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Besshi Massive SulfidemiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 14a-Con. Quixaba BRZL Ray Gulch Cnyt Sang Dong Skor Stormy Group Cnyt Tem Piute District Usnv Tyrny-Auz Urrs Uludag Trky Victory CNBC Yellow Pine District Usid Ysxjoberg SWDNDocument15 pagesModel 14a-Con. Quixaba BRZL Ray Gulch Cnyt Sang Dong Skor Stormy Group Cnyt Tem Piute District Usnv Tyrny-Auz Urrs Uludag Trky Victory CNBC Yellow Pine District Usid Ysxjoberg SWDNmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 24a - Con: Cyprus Massive SulfideDocument1 pageModel 24a - Con: Cyprus Massive SulfidemiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 8a-Con: Oo Iiii '"I ' I '' I ' I I E. Platinum Grade in Parts Per BillionDocument15 pagesModel 8a-Con: Oo Iiii '"I ' I '' I ' I I E. Platinum Grade in Parts Per BillionmiguelNo ratings yet
- XXXXX ' ' ' ' X XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX ' XWVW VVVW VvvvyvvxxDocument19 pagesXXXXX ' ' ' ' X XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX ' XWVW VVVW VvvvyvvxxmiguelNo ratings yet
- Porphyry Copper-Skarn-Related: Model 18a-ConDocument16 pagesPorphyry Copper-Skarn-Related: Model 18a-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1693Document15 pagesU.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1693miguelNo ratings yet
- Redox & Soln Reactions PDFDocument18 pagesRedox & Soln Reactions PDFKim Na NaNo ratings yet
- Blood Gases, PH, and Buffer SystemDocument22 pagesBlood Gases, PH, and Buffer SystemAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Soft DrinksDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Soft DrinksUsamakhan009No ratings yet
- Whole 4th Year SyllabusDocument161 pagesWhole 4th Year SyllabusPravesh NiraulaNo ratings yet
- Wasserlab Brochure Autwomatic Plus 1+2Document10 pagesWasserlab Brochure Autwomatic Plus 1+2Lloid LauretaNo ratings yet
- Inductive EffectDocument38 pagesInductive EffectJoe JNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Water Desalination and Wastewater TR - 2017 - DesalinatDocument16 pagesMechanical Properties of Water Desalination and Wastewater TR - 2017 - DesalinatTalha ShaukatNo ratings yet
- High-Performance Fumasep Ion Exchange Membranes For Electro Membrane ProcessesDocument6 pagesHigh-Performance Fumasep Ion Exchange Membranes For Electro Membrane ProcessesshadyghanemNo ratings yet
- Module IIDocument160 pagesModule IIALL TIME STUDYNo ratings yet
- 4914 11168 2 PBDocument5 pages4914 11168 2 PBthiagoNo ratings yet
- Ujian 3 Form 4 KimiaDocument6 pagesUjian 3 Form 4 KimiaNazreen NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Matching To CrucibleDocument6 pagesMatching To CrucibleLorena SuarezNo ratings yet
- Fats & Oils - PociiDocument91 pagesFats & Oils - PociiSiddhant BanwatNo ratings yet
- Thesis Sewage Water TreatmentDocument31 pagesThesis Sewage Water Treatmentbalaji xeroxNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Cycles: Igcse BiologyDocument19 pagesNutrient Cycles: Igcse BiologyTanyaradzwa MugutaNo ratings yet
- VESTA Exercise SheetsDocument5 pagesVESTA Exercise SheetsMarcos BHNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy: Pre-Medical: Chemistry AllenDocument15 pagesMetallurgy: Pre-Medical: Chemistry AllenscarceboyzNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0016236121017002 MainDocument22 pages1 s2.0 S0016236121017002 MainbcherejiNo ratings yet
- Mepron - Metionina Recubierta Pasa RumenDocument13 pagesMepron - Metionina Recubierta Pasa RumenMiguel HoyosNo ratings yet
- S Block ChemhaackDocument13 pagesS Block ChemhaackDrushya SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Hexamethylenetetramine: ManufacturerDocument4 pagesHexamethylenetetramine: ManufacturerpmNo ratings yet
- Sikagard - 700 S: Siloxane Based Water Repellent ImpregnationDocument3 pagesSikagard - 700 S: Siloxane Based Water Repellent Impregnationthe pilotNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Sellos Economos - SKFDocument6 pagesCatalogo Sellos Economos - SKFdani sanNo ratings yet