Professional Documents
Culture Documents
151 300 1 15 11 PDF
151 300 1 15 11 PDF
Uploaded by
miguelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
151 300 1 15 11 PDF
151 300 1 15 11 PDF
Uploaded by
miguelCopyright:
Available Formats
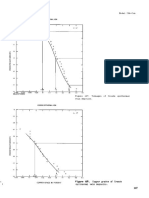
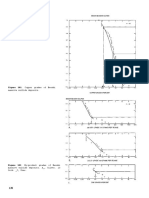
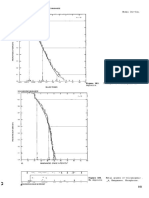
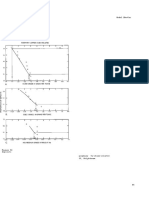
Model 25b
DESCRIPTIVE MODEL OF CREEDE EPITHERMAL VEINS
By Dan L. Mosier, Takeo Sato, Norman J Page, Donald A. Singer,
and Byron R. Berger
APPROXIMATE SYNONYM Epithermal gold (quartz-adularia) alkali-chloride-type, polymetallic veins (see
fig. 106).
DESCRIPTION Galena, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, sulfosalts, +_ tellurides +_ gold in quartz-carbonate
veins hosted by felsic to intermediate volcanics. Older miogeosynclinal evaporites or rocks with
trapped seawater are associated with these deposits.
GENERAL REFERENCES Buchanan (1980), Boyle (1979).
GEOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT
Rock Types Host rocks are andesite, dacite, quartz latite, rhyodacite, rhyolite, and associated
sedimentary rocks. Mineralization related to calc-alkaline or bimodal volcanism.
Textures Porphyritic.
Age Range Mainly Tertiary (most are 29-4 m.y.).
Depositional Environment Bimodal and calc-alkaline volcanism. Deposits related to sources of saline
fluids in prevolcanic basement such as evaporites or rocks with entrapped seawater.
Tectonic Setting(s) Through-going fractures systems; major normal faults, fractures related to doming,
ring fracture zones, joints associated with calderas. Underlying or nearby older rocks of continental
shelf with evaporite basins, or island arcs that are rapidly uplifted.
Associated Deposit Types Placer gold, epithermal quartz alunite Au, polymetallic replacement.
DEPOSIT DESCRIPTION
Mineralogy Galena + sphalerite + chalcopyrite + copper sulfosalts + silver sulfosalts ± gold ±
tellurides ± bornite ± arsenopyrite. Gangue minerals are quartz + chlorite ± calcite + pyrite +
rhodochrosite + barite ± fluorite ± siderite ± ankerite ± sericite ± adularia ± kaolinite. Specularite
and alunite may be present.
Texture/Structure Banded veins, open space filling, lamellar quartz, stockworks, colloform textures.
Alteration Top to bottom: quartz ± kaolinite + montmorillonite ± zeolites ± barite ± calcite;
quartz + illite; quartz + adularia ± illite; quartz + chlorite; presence of adularia is variable.
Ore Controls Through-going or anastomosing fracture systems. High-grade shoots where vein changes
strike or dip and at intersections of veins. Hanging-wall fractures are particularly favorable.
Weathering Bleached country rock, goethite, jarosite, alunite—supergene processes often important
factor in increasing grade of deposit.
Geochemical Signature Higher in system Au + As + Sb + Hg; Au + Ag + Pb + Zn + Cu; Ag + Pb + Zn, Cu + Pb
+ Zn. Base metals generally higher grade in deposits with silver. W + Bi may be present.
EXAMPLES
Creede, USCO (Steven and Eaton, 1975;
Barton and others, 1977)
Pachuca, MXCO (Geyne and others, 1963)
Toyoha, JAPN (Yajima and Ohta, 1979)
145
You might also like
- ChatGPT: Jack of All Trades, Master of NoneDocument40 pagesChatGPT: Jack of All Trades, Master of NonePeter SlavikNo ratings yet
- Gottman 4 Horsemen QuizDocument1 pageGottman 4 Horsemen QuizPeggy KeinNo ratings yet
- Vein Type Deposits QuatzDocument9 pagesVein Type Deposits QuatzSenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter K Geoenviromental Model For Low-Sulfide Gold-Quartz Vein DepositsDocument20 pagesChapter K Geoenviromental Model For Low-Sulfide Gold-Quartz Vein DepositsTony Yunus YudhantoNo ratings yet
- Speed and Acceleration v1.0Document46 pagesSpeed and Acceleration v1.0Ramesh Iyer100% (1)
- Rock Collecting for Kids: An Introduction to GeologyFrom EverandRock Collecting for Kids: An Introduction to GeologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Texas Rocks and Minerals: An Amateur's GuideFrom EverandTexas Rocks and Minerals: An Amateur's GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- EPITHERMAL Low-Sulphidation 210604Document9 pagesEPITHERMAL Low-Sulphidation 210604Adhy SahputraNo ratings yet
- Epithermal Au-Ag Low-Sulfidation - PanteleyevDocument4 pagesEpithermal Au-Ag Low-Sulfidation - Panteleyevnomyaz05No ratings yet
- Telluride Mineralogy of The Low-Sulfidation EpitheDocument23 pagesTelluride Mineralogy of The Low-Sulfidation Epitheazizfadly100% (1)
- Gold Deposit Classification - Robert Et AlDocument12 pagesGold Deposit Classification - Robert Et AlAngie Baliton SajonaNo ratings yet
- 250+ TOP MCQs On Petroleum - 2 and AnswersDocument8 pages250+ TOP MCQs On Petroleum - 2 and AnswersOxaLic AcidNo ratings yet
- 4-Mallet Exercises - 2017 PDFDocument26 pages4-Mallet Exercises - 2017 PDFjohap7No ratings yet
- Instant Download Facial Volumization An Anatomic Approach 1st Edition PDF FREEDocument32 pagesInstant Download Facial Volumization An Anatomic Approach 1st Edition PDF FREEchristina.walton573100% (48)
- Geology of Base-Metal DepositsDocument9 pagesGeology of Base-Metal DepositsAji SuhadiNo ratings yet
- Intro Quartz Veins 1Document106 pagesIntro Quartz Veins 1Aziz Fathiry Rahman0% (1)
- Azevedo 2022. Neoarchean Alkaline Magmatism PDFDocument21 pagesAzevedo 2022. Neoarchean Alkaline Magmatism PDFGabriel ArizaNo ratings yet
- Iron Oxide Copper Gold PDFDocument23 pagesIron Oxide Copper Gold PDFMurilo Santiago100% (2)
- 5 - Epithermal Gold Deposits - 2Document43 pages5 - Epithermal Gold Deposits - 2chengsrunNo ratings yet
- Richards PCD Shortcourse5 (Epithermal)Document7 pagesRichards PCD Shortcourse5 (Epithermal)Sergio ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gold Skarn DepositsDocument13 pagesGold Skarn DepositsEl Zurdo ObregonNo ratings yet
- Pacrim 1995 - EpithermalDocument9 pagesPacrim 1995 - EpithermalferrysubagjaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Epithermal Gold Deposits - 2Document43 pages5 - Epithermal Gold Deposits - 2chengsrunNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Geology of Salt and Related StructuresFrom EverandDynamical Geology of Salt and Related StructuresI. LercheNo ratings yet
- J 1751-3928 1998 tb00021 XDocument14 pagesJ 1751-3928 1998 tb00021 XJHOEL_GEONo ratings yet
- EPITHERMAL Low-Sulphidation 210604Document3 pagesEPITHERMAL Low-Sulphidation 210604AzkaaNo ratings yet
- Epithermal Au-AgDocument4 pagesEpithermal Au-Agdely susantoNo ratings yet
- 02 EmbsoDocument37 pages02 EmbsoHEBERT JHON RAFAEL AGUILARNo ratings yet
- Hydrothermal Geochemistry and Ore Genesis of Sea-Floor: Volcanogenic Copper-Bearing Oxide OresDocument24 pagesHydrothermal Geochemistry and Ore Genesis of Sea-Floor: Volcanogenic Copper-Bearing Oxide OresFrank Kleber García YaretaNo ratings yet
- Epithermal Au-Ag: Low SulphidationDocument4 pagesEpithermal Au-Ag: Low SulphidationdennysNo ratings yet
- GreissenDocument8 pagesGreissenCamilo GZNo ratings yet
- CloncurryDocument17 pagesCloncurryCarlos D. HernandezNo ratings yet
- Sillitoe. Intrusion-Related Vein Gold Deposits. TypeDocument14 pagesSillitoe. Intrusion-Related Vein Gold Deposits. Typehüseyin burak göktaşNo ratings yet
- Hitzman Et Al 2005, Sed CuDocument34 pagesHitzman Et Al 2005, Sed CuPauloNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Kipushi Cu-Pb-ZnDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Kipushi Cu-Pb-ZnRiston Belman SidabutarNo ratings yet
- 2023, Spry Et Al., Nodular Sillimanite Rocks As Field Indicators To Metamorphosed Massive Sulfide Deposits, Ore Geol RevDocument23 pages2023, Spry Et Al., Nodular Sillimanite Rocks As Field Indicators To Metamorphosed Massive Sulfide Deposits, Ore Geol RevSamuel PierreNo ratings yet
- 09 - Intrusion Related PDFDocument13 pages09 - Intrusion Related PDFArmando SanGuiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Associations Between Potassic Igneous Rocks, Shoshonites and Gold-Copper DepositsDocument24 pagesDirect and Indirect Associations Between Potassic Igneous Rocks, Shoshonites and Gold-Copper DepositsSergio SilvaNo ratings yet
- h04 High Sulphidation Epithermal Au Ag CuDocument6 pagesh04 High Sulphidation Epithermal Au Ag CuErenz Emerald AlexandriteNo ratings yet
- Metalurgia Del Oro - TraduccionDocument8 pagesMetalurgia Del Oro - TraduccionSintia Yuli Ponce AguirreNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Et Al, 1987Document26 pagesAhmad Et Al, 1987CesarVargasSalasNo ratings yet
- SelectionDocument33 pagesSelectionRandy SamosirNo ratings yet
- Fontbote BendezuSGA 2009 CordilleranDocument3 pagesFontbote BendezuSGA 2009 CordilleranapalpanNo ratings yet
- 5 Sedimentary, ExogenicDocument70 pages5 Sedimentary, ExogenicRaúl Tovar ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Alkalic Intrusion-Associated Au-AgDocument3 pagesAlkalic Intrusion-Associated Au-Agdely susantoNo ratings yet
- Metallic Mineral Deposits of NL, Part 2, Volcanic-HostedDocument42 pagesMetallic Mineral Deposits of NL, Part 2, Volcanic-HostedFrank Kleber García YaretaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Besshi Massive SulfideDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Besshi Massive SulfidemiguelNo ratings yet
- Wallrock Alteration Associated With Turbidite - Hosted Gold Deposits.Document36 pagesWallrock Alteration Associated With Turbidite - Hosted Gold Deposits.fotos gexegNo ratings yet
- Williams Et Al 2005 IOCG General SEGDocument36 pagesWilliams Et Al 2005 IOCG General SEGkissyxdNo ratings yet
- Geology 1990 Sillitoe 157 61Document6 pagesGeology 1990 Sillitoe 157 61JHOEL_GEONo ratings yet
- Ephitermal Au Ag GA3879 PDFDocument50 pagesEphitermal Au Ag GA3879 PDFAngelica RamirezNo ratings yet
- Ore Deposits and Ore Forming ProcessesDocument39 pagesOre Deposits and Ore Forming Processessanjay.nandaglNo ratings yet
- B - 280 - Front MatterDocument20 pagesB - 280 - Front MatterHAMZA LAMSALAHNo ratings yet
- Endapan SkarnDocument38 pagesEndapan SkarnCandraNo ratings yet
- What Is A Sediment Hosted Vein DepositDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Sediment Hosted Vein DepositLuis EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Model of ZN-PB SkarnDocument6 pagesModel of ZN-PB SkarnFlorencio Choque AyqueNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Exhalative ZNDocument3 pagesSedimentary Exhalative ZNRicardo UmasiNo ratings yet
- Moritz Gold BRGM 2000Document7 pagesMoritz Gold BRGM 2000Hamdi PutraNo ratings yet
- Ii,,il: Characteristics and Origin of Sediment-Hosted Disseminated Gold Deposits: A ReviewDocument21 pagesIi,,il: Characteristics and Origin of Sediment-Hosted Disseminated Gold Deposits: A Reviewjunior.geologiaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Diamond PlacersDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Diamond PlacersajnmboNo ratings yet
- VMS Deposits 171316509650746889661cd32820f29Document32 pagesVMS Deposits 171316509650746889661cd32820f29saurabhkumar7654491613No ratings yet
- Xiao 2007Document16 pagesXiao 2007Johan MondragonNo ratings yet
- Field Trips Stops For Days 1 & 2Document21 pagesField Trips Stops For Days 1 & 2Martin NguyenNo ratings yet
- 4 HydrothermalDocument47 pages4 HydrothermalRaúl Tovar ContrerasNo ratings yet
- HTTP ProxiesDocument47 pagesHTTP ProxiesmiguelNo ratings yet
- HTTP ProxiesDocument32 pagesHTTP ProxiesmiguelNo ratings yet
- 151 300 1 15 12Document1 page151 300 1 15 12miguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Simple SB DepositsDocument15 pagesDescriptive Model of Simple SB DepositsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Comstock Epithermal VeinsDocument15 pagesDescriptive Model of Comstock Epithermal VeinsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Volcanic-Hosted MagnetiteDocument15 pagesDescriptive Model of Volcanic-Hosted MagnetitemiguelNo ratings yet
- Epithermal Quartz-Alunite Vein: Model 25e-ConDocument15 pagesEpithermal Quartz-Alunite Vein: Model 25e-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- Creede Epithermal Vein: Model 25b-ConDocument1 pageCreede Epithermal Vein: Model 25b-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- 151 300 1 15 13 PDFDocument1 page151 300 1 15 13 PDFmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 25b-Con: Creede Epithermal VeinDocument1 pageModel 25b-Con: Creede Epithermal VeinmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Creede Epithermal VeinsDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Creede Epithermal VeinsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Blackbird Co-CuDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Blackbird Co-CumiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Hot-Spring Au-AgDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Hot-Spring Au-AgmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 25a-ConDocument1 pageModel 25a-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- 151 300 1 15 14 PDFDocument1 page151 300 1 15 14 PDFmiguelNo ratings yet
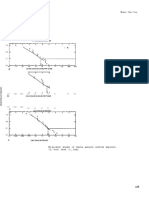
- Figure 109. Lead Grades of Creede: Model 25b-ConDocument1 pageFigure 109. Lead Grades of Creede: Model 25b-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Hot-Spring Au-AgDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Hot-Spring Au-AgmiguelNo ratings yet
- XXXXX ' ' ' ' X XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX ' XWVW VVVW VvvvyvvxxDocument19 pagesXXXXX ' ' ' ' X XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX ' XWVW VVVW VvvvyvvxxmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 24b - Con: Figure 101. Copper Grades of BesshiDocument1 pageModel 24b - Con: Figure 101. Copper Grades of BesshimiguelNo ratings yet
- Volcanogenic Manganese: I - 1 - I I - I ° ° IDocument1 pageVolcanogenic Manganese: I - 1 - I I - I ° ° ImiguelNo ratings yet
- Figure 100. Tonnages of Besshi Massive Sulfide DepositsDocument1 pageFigure 100. Tonnages of Besshi Massive Sulfide DepositsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Volcanogenic MNDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Volcanogenic MNmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 8a-Con: Oo Iiii '"I ' I '' I ' I I E. Platinum Grade in Parts Per BillionDocument15 pagesModel 8a-Con: Oo Iiii '"I ' I '' I ' I I E. Platinum Grade in Parts Per BillionmiguelNo ratings yet
- Porphyry Copper-Skarn-Related: Model 18a-ConDocument16 pagesPorphyry Copper-Skarn-Related: Model 18a-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 24a - Con: Cyprus Massive SulfideDocument1 pageModel 24a - Con: Cyprus Massive SulfidemiguelNo ratings yet
- Model 14a-Con. Quixaba BRZL Ray Gulch Cnyt Sang Dong Skor Stormy Group Cnyt Tem Piute District Usnv Tyrny-Auz Urrs Uludag Trky Victory CNBC Yellow Pine District Usid Ysxjoberg SWDNDocument15 pagesModel 14a-Con. Quixaba BRZL Ray Gulch Cnyt Sang Dong Skor Stormy Group Cnyt Tem Piute District Usnv Tyrny-Auz Urrs Uludag Trky Victory CNBC Yellow Pine District Usid Ysxjoberg SWDNmiguelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Model of Besshi Massive SulfideDocument1 pageDescriptive Model of Besshi Massive SulfidemiguelNo ratings yet
- U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1693Document15 pagesU.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1693miguelNo ratings yet
- Thelonious Monk - Life and Works 4Document4 pagesThelonious Monk - Life and Works 4giuseppe_capassoNo ratings yet
- Tupperware-Ultimo Lifestyle CatalougesDocument12 pagesTupperware-Ultimo Lifestyle CatalougesPradeep Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Papers For Class 7 Maths Fa4 PDFDocument5 pagesCbse Sample Papers For Class 7 Maths Fa4 PDFGirish LalaNo ratings yet
- NagarjunaDocument4 pagesNagarjunaCLG100% (1)
- Genetic DisordersDocument3 pagesGenetic DisordersN RATHORENo ratings yet
- QUIZ#2Document2 pagesQUIZ#2Elmera Lene CaballesNo ratings yet
- 8 Foundation: 8.1 Bearing CapacityDocument3 pages8 Foundation: 8.1 Bearing CapacityPiseth HengNo ratings yet
- 9701 TP3 Aldehydes v2.0Document30 pages9701 TP3 Aldehydes v2.0charlesma123No ratings yet
- New Plan Ai TS 2022-2023 - Revised As On 17.08.2022Document2 pagesNew Plan Ai TS 2022-2023 - Revised As On 17.08.2022VANo ratings yet
- IB BIO 10.1 - MeiosisDocument21 pagesIB BIO 10.1 - MeiosisPerson AnonymousNo ratings yet
- 7360022802PL AviatDocument75 pages7360022802PL Aviatclinton ruleNo ratings yet
- Mr. Rohit SinghaiDocument5 pagesMr. Rohit SinghaiDr. Sukhwant SinghNo ratings yet
- Sample Complaints LettersDocument4 pagesSample Complaints Lettersmuazzamali533No ratings yet
- HV-MX100: Simple ManualDocument28 pagesHV-MX100: Simple ManualSimon PapukyanNo ratings yet
- Hamlet AnnotationsDocument12 pagesHamlet Annotationsapi-612022780No ratings yet
- Elfmatic G3Document1 pageElfmatic G3Pancho CamposNo ratings yet
- Bill Gates Used To Be A HackerDocument2 pagesBill Gates Used To Be A HackerWajeeha ShahnawazNo ratings yet
- Quench Tower PerhitunganDocument7 pagesQuench Tower PerhitunganRizqia Putri ZakkaNo ratings yet
- 3-Tier Architecture in C#Document9 pages3-Tier Architecture in C#Matías PeronettoNo ratings yet
- Who Discovered America Anyway?: © Richard Lathe 2003Document3 pagesWho Discovered America Anyway?: © Richard Lathe 2003Servilab LudicasNo ratings yet
- Philippine Grid Code: What?Document12 pagesPhilippine Grid Code: What?Ian DimalantaNo ratings yet
- The Greatest of All Time Leonardo Da VinciDocument62 pagesThe Greatest of All Time Leonardo Da VinciJay RanganiNo ratings yet
- Edalina - Popular Protest Political Opportunities and Change in AfricaDocument252 pagesEdalina - Popular Protest Political Opportunities and Change in AfricaGuilherme Simões ReisNo ratings yet
- Davis and Lineweaver - Expanding Confusion Superluminal Expansion of The UniverseDocument13 pagesDavis and Lineweaver - Expanding Confusion Superluminal Expansion of The UniversedkahanNo ratings yet