Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise 7.3
Uploaded by
Luk HK0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pages1) The question asks to calculate the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation (ΔHθ) of 1,3-butadiene.
2) The reaction equation and standard enthalpy of formation values for the reactants and products are provided.
3) The answer uses an energy cycle approach with the standard enthalpy of combustion of butane and standard enthalpies of formation of the substances to calculate ΔHθ as -241.0 kJ mol-1.
Original Description:
Original Title
Exercise 7.3.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The question asks to calculate the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation (ΔHθ) of 1,3-butadiene.
2) The reaction equation and standard enthalpy of formation values for the reactants and products are provided.
3) The answer uses an energy cycle approach with the standard enthalpy of combustion of butane and standard enthalpies of formation of the substances to calculate ΔHθ as -241.0 kJ mol-1.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesExercise 7.3
Uploaded by
Luk HK1) The question asks to calculate the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation (ΔHθ) of 1,3-butadiene.
2) The reaction equation and standard enthalpy of formation values for the reactants and products are provided.
3) The answer uses an energy cycle approach with the standard enthalpy of combustion of butane and standard enthalpies of formation of the substances to calculate ΔHθ as -241.0 kJ mol-1.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Day 3
Question 1
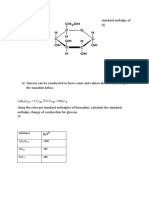
1,3-butadiene, C4H6, undergoes hydrogenation to produce butane, C4H10, according to
the equation
C4H6(g) + 2 H2(g) C4H10(g)
Calculate the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation, ΔHθ, of 1,3-butadiene.
Standard enthalpy of formation of 1,3-butadiene, C4H6 +112.0
Standard enthalpy of formation of water, H2O -286.0
Standard enthalpy of formation of carbon dioxide, CO2 -394.0
Standard enthalpy of combustion of butane, C4H10 -2877.0
(7M)
Question 1
1,3-butadiene, C4H6, undergoes hydrogenation to produce butane, C4H10, according to
the equation
C4H6(g) + 2 H2(g) C4H10(g)
Calculate the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation, ΔHθ, of 1,3-butadiene.
Standard enthalpy of formation of 1,3-butadiene, C4H6 +112.0
Standard enthalpy of formation of water, H2O -286.0
Standard enthalpy of formation of carbon dioxide, CO2 -394.0
Standard enthalpy of combustion of butane, C4H10 -2877.0
(7M)
Answer:
(1) Using energy cycle
(2) Using equations
4C(s) + 3 H2(g) C4H6 ΔH1 = +112.0 1M
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) H2O(l) ΔH2 = -286.0 2M
C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) ΔH3 = -394.0 3M
4CO2(g) + 5H2O(l) C4H10(g) + 13/2 O2(g) ΔH4 = +2877.0 4M
Reverse (1): C4H6(g) 4C(s) + 3H2(g) ΔH5 = -112.0
(2) X 5: 5H2(g) + 5/2 H2(g) 5H2O(l) ΔH6 = 5(-286.0)
(3) X 4: 4C(s) + 4O2(g) 4CO2(g) ΔH7 = 4(-394.0)
C4H6(g) + 2H2(g) C4H10 ΔH = ?
ΔH = ΔH4 + ΔH5 + ΔH6 + ΔH7 5M
ΔH =(+2877.0) + (-112.0) + 5(-286.0) + 4(-394) 6M
ΔH = -241.0 kJ mol-1 7M
You might also like
- Chemsheets A2 1014 Thermodynamics Booklet ANSDocument18 pagesChemsheets A2 1014 Thermodynamics Booklet ANSbigmanballs1230No ratings yet
- Hess's Law QuestionsDocument7 pagesHess's Law QuestionsFawwaaz KoodruthNo ratings yet
- Heat of Reaction Homework ChemistryDocument2 pagesHeat of Reaction Homework ChemistryJeison Stiven Martinez ViedaNo ratings yet
- Ley de Hess EjercDocument5 pagesLey de Hess EjercmrconnnstanzaNo ratings yet
- A-Levels Chem NotesDocument22 pagesA-Levels Chem Notesd-fbuser-69634921No ratings yet
- Hess's Law Exercise: H 97,2 KJ H 16,2 KJ H +8,10 KJ H +162 KJDocument1 pageHess's Law Exercise: H 97,2 KJ H 16,2 KJ H +8,10 KJ H +162 KJrosyad ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesHess's Law WorksheetsaadixNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law Examples With AnswersDocument1 pageHess's Law Examples With AnswersOri SeinNo ratings yet
- As Tute 1 September 2016Document2 pagesAs Tute 1 September 2016Piyumi ObeyesekeraNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 8 Chemical Reactions and Energy PDFDocument17 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 8 Chemical Reactions and Energy PDF6A(24) Marsh WongNo ratings yet
- Hess Law WsDocument7 pagesHess Law Wsedward hugoNo ratings yet
- Chem Last Min NotesDocument2 pagesChem Last Min NoteslegitmanofmenNo ratings yet
- Do Now:: Write Equations For The Following ExpressionsDocument14 pagesDo Now:: Write Equations For The Following ExpressionsJonh MhataNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' LawDocument2 pages2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' LawHorro8480100% (1)
- Intermediate Hess's Law 2018Document2 pagesIntermediate Hess's Law 2018MasonNo ratings yet
- Hesss LawDocument2 pagesHesss LawBiblee ChasNo ratings yet
- Hess' Law Problems PlusDocument5 pagesHess' Law Problems PlusPaulina IrigoyenNo ratings yet
- Homework Enthalpy CalculationsDocument2 pagesHomework Enthalpy CalculationsErnur Teginbaev100% (1)
- WK5 - Hesss Law Hard - Ib ServerDocument4 pagesWK5 - Hesss Law Hard - Ib Serverfuzzy pillowNo ratings yet
- CPC Assignment 6Document5 pagesCPC Assignment 6Para DiseNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - Entropy and Gibbs Free Energy - Answers PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial 5 - Entropy and Gibbs Free Energy - Answers PDFAlfaiz Radea ArbiandaNo ratings yet
- CPC Assignment 6Document5 pagesCPC Assignment 6Para DiseNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Review - Answers: CH OH (L) + / O (G) Î Co (G) + 2 H O (L) H - 727 KJDocument12 pagesThermochemistry Review - Answers: CH OH (L) + / O (G) Î Co (G) + 2 H O (L) H - 727 KJxyz7890No ratings yet
- Hess's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesHess's Law Worksheetronnie schwiersNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice Week 6Document2 pagesExtra Practice Week 6ShawnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 CHM 271Document11 pagesTutorial 1 CHM 271Fatin IzzatyNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law ProblemsDocument2 pagesHess's Law ProblemsTjrjfjdjNo ratings yet
- 6.9 Hess LawDocument13 pages6.9 Hess Law8grvqbm7ddNo ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument4 pagesHess LawDarlene Jane Taladro Caga-ananNo ratings yet
- Exercise 22-3-2022Document2 pagesExercise 22-3-2022TAN CHONG HYEN MoeNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentDocument4 pagesSorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentIzay Martinez CadagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Ideas Section 4 AnswersDocument2 pagesChemical Ideas Section 4 AnswersvkrmmahalNo ratings yet
- Sam Hess LawDocument24 pagesSam Hess LawPromise SangoNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentDocument4 pagesSorsogon State College: Engineering and Architecture DepartmentIzay Martinez CadagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document19 pagesChapter 19denisNo ratings yet
- Suggestion Anwer Scheme PSPM Sem 2 2014Document15 pagesSuggestion Anwer Scheme PSPM Sem 2 2014.....No ratings yet
- Test1B S23Document8 pagesTest1B S23Nivedha NatarajNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law HomeworkDocument3 pagesHess's Law Homeworkmaya 1DNo ratings yet
- Name - Honors Chemistry - / - / - Hess's LawDocument4 pagesName - Honors Chemistry - / - / - Hess's LawGunjee GunjeeNo ratings yet
- CHM1102 - Lecture 26Document6 pagesCHM1102 - Lecture 26EwartNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (Ch. 16) AP ProblemsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics (Ch. 16) AP ProblemsHasantha PereraNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2Document3 pagesThermo 2Prathamesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- 5 2+Hess's+Law+ExamplesDocument4 pages5 2+Hess's+Law+ExamplesBrad Randel SolisNo ratings yet
- Gcesoln 3Document4 pagesGcesoln 3api-3734333No ratings yet
- AP Hess Law WKSTDocument2 pagesAP Hess Law WKSTDrech LanadoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 QuestionsDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 Questionsiveco0% (1)
- Problem Set On Enthalpy: 3 (G) 2 4 (G) (G) (G) 2 (G) (G) (S) 2 (G) 2(s)Document1 pageProblem Set On Enthalpy: 3 (G) 2 4 (G) (G) (G) 2 (G) (G) (S) 2 (G) 2(s)Death BringerNo ratings yet
- 0877 App 1 PDFDocument1 page0877 App 1 PDFPhuppud Sii PutrysahidahNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy 2Document21 pagesEnthalpy 2Joseph Nathaniel V TalaveraNo ratings yet
- Hess Law QuestionsDocument2 pagesHess Law Questionsronnie schwiersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Second Law: Exercise 3.11 (A)Document7 pagesChapter 3: The Second Law: Exercise 3.11 (A)PrincessGabrielleLibetarioNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets AS 1205 QC Energetics C ANSDocument1 pageChemsheets AS 1205 QC Energetics C ANSchinkey lolNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Raja FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Hesss Law WorksheetDocument3 pagesHesss Law WorksheetAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsFrom EverandSynthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsTilman J. SchildhauerNo ratings yet
- Model Answers in Ordinary National Certificate Mathematics for EngineersFrom EverandModel Answers in Ordinary National Certificate Mathematics for EngineersNo ratings yet
- Gas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingFrom EverandGas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingDaniel BrosetaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.4Document4 pagesExercise 8.4Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Analysis of SPM Chemistry Paper 3Document3 pagesAnalysis of SPM Chemistry Paper 3Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.7Document3 pagesExercise 8.7Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Escribes The Manufacture of Chlorine by The of Sodium Chloride Solution Using ADocument2 pagesEscribes The Manufacture of Chlorine by The of Sodium Chloride Solution Using ALuk HKNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.3: Calculate The Cell Potential For The Voltaic Cell: PB - PB (0.500 M) - Fe (0.222 M), Fe (0.455 M) - PTDocument3 pagesExercise 8.3: Calculate The Cell Potential For The Voltaic Cell: PB - PB (0.500 M) - Fe (0.222 M), Fe (0.455 M) - PTLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.2 (Application of Standard Reduction Potential)Document3 pagesExercise 8.2 (Application of Standard Reduction Potential)Luk HKNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Selected Group 2 Elements and Their CompoundsDocument3 pages10.1 Selected Group 2 Elements and Their CompoundsLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7.4Document1 pageExercise 7.4Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.8Document2 pagesExercise 8.8Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Past Year Question: ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesPast Year Question: ElectrochemistryLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: GROUP 2Document4 pagesChapter 10: GROUP 2Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7.1Document3 pagesExercise 7.1Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Periodic TableDocument3 pagesChapter 9: Periodic TableLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Periodic TableDocument3 pagesChapter 9: Periodic TableLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Periodic TableDocument1 pageChapter 9: Periodic TableLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Describe The Reactions of Period 3 Elements With Oxygen and Water Interpret The Ability of Elements To Act As Oxidising and Reducing AgentsDocument3 pagesDescribe The Reactions of Period 3 Elements With Oxygen and Water Interpret The Ability of Elements To Act As Oxidising and Reducing AgentsLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7.4Document1 pageExercise 7.4Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9.1Document2 pagesExercise 9.1Luk HKNo ratings yet