Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(1st Edition) Lillian C. McDermott - Peter S. Shaffer - Tutorials in Introductory Physics - Homework-Pearson (2002) - 39-42
Uploaded by
Fryda AyudhaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(1st Edition) Lillian C. McDermott - Peter S. Shaffer - Tutorials in Introductory Physics - Homework-Pearson (2002) - 39-42
Uploaded by
Fryda AyudhaCopyright:
Available Formats
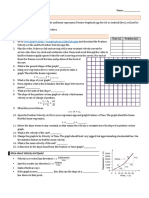
FORCFS
Name Mech
HW-35
6. A person pushes a book against a wall so that the book does not move.
r
a. Draw a free-body diagram for the book. Label the forces as you did in the
tutorial Forces.
b. For each force that appears on your free-body diagram, identify the corresponding force that
completes the Newton' s third law (or action-reaction) force pair.
©Prentice Hall, I nc.
First Edition. 2002
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
McDermott, Shaffer, & P.E.G., U . Wash.
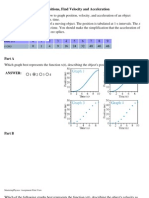
NEWTON•s SECOND AND THIRD LAWS Name ---- Mech
HW-37
l . A block initially at rest i s given a quick push by a hand. The block slides across the floor.
gradually slows down , and comes to rest.
a. In the spaces provided, draw and label separate free-body diagrams for the block at each of
the three i nstants shown.
I. $ (Initially at rest) 2. 3.
77777 7777;
A Quick
}
push by a hand ...
'77)777;
77 ;7�;
the slidinf.? block slows...
777777j7 777�
7 ,
and is finallv at rest.
b. Rank the magnitudes of all the horizontal forces in the diagram for instant 1 . Explain.
c. Are any of the forces that you drew for instant l missing from your diagram for instant 2?
If so, for each force that is missing, explain how you knew to include the force on the first
diagram but not on the second.
d. Are any of the forces that you drew for instant l missing from your diagram for instant 3?
If so, for each force that is missing, explain how you knew to include the force on the first
diagram but not on the third.
Tutorials in Introductory Physics �Prentice Hall, Inc.
McDermott, Shaffer, & P.E.G .• U. Wash. First Edition, 2002
Mech Newton's second and third laws
HW-38
2. Two crates, A and B , are in an elevator as shown. The mass of crate A is
greater than the mass of crate B.
a. The elevator moves downward at constant speed. Elevator
1. How does the acceleration o f crate A compare to that of crate B?
Explain.
A
B
ii. In the spaces provided below, draw and label separate free-body
diagrams for the crates.
Free-body diagram for Free-body diagram for
crate A crate B
iii. Rank the forces on the crates according to magnitude. from largest to smallest. Explain
your reasoning, including how you used Newton's second and third laws.
iv. In the spaces provided at right, draw arrows to
indicate the direction of the net force on each Direction of net force
crate. If the net force on either crate is zero, Crate A Crate B
state so explicitly. Explain.
Is the magnitude of the net force on crate A greater than, less than, or equal to tha t on
crate B? Explain.
Tu10ria/s in Introductory Physics ©Prentice Hall, Inc.
McDermott, Shaffer, & P.E.G . U. Wash.
. First Edition, 2002
NEWTON'S SECOND AND THIRD LAWS Name Mech
HW-39
b. As the elevator approaches its destination, its speed decreases. (It continues to move
downward.)
i. How does the acceleration of crate A compare to that of crate B ? Explain.
ii. In the spaces provided below, draw and label separate free-body diagrams for the crates
in this case.
Free-body diagram for Free-body diagram for
crate A crate B
iii. Rank the forces on the crates according to magnitude, from l argest to smallest. Explain
your reasoning, including how you used Newton's second and third laws.
iv. In the spaces provided at right, draw arrows to
Direction of net force
indicate the direction of the net force on each
crate. If the net force on either crate is zero, Crate A Crate B
state so explicitly. Explain.
Is the magnitude of the net force acti ng on crate A greater than, less than, or equal to th at
on crate B? Explain.
Tutorials i n lntroduc10ry Physics @Prentice Hall, I nc.
McDennon, Shaffer, & P.E.G., U. Wash. First Edition, 2002
You might also like
- Net - Force - and - Acceleration - Practice - Worksheet KEY 4Document1 pageNet - Force - and - Acceleration - Practice - Worksheet KEY 4brooo imlikeoverit0% (1)
- HW1 Mastering PhysicsDocument16 pagesHW1 Mastering PhysicsdominicNo ratings yet
- POGIL - KinematicsDocument4 pagesPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- 16 WEP-Work and PowerDocument6 pages16 WEP-Work and PowereltytanNo ratings yet
- Test - Unit 3 - Energy and MomentumDocument4 pagesTest - Unit 3 - Energy and Momentumascd_msvuNo ratings yet
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocument3 pagesPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Loeblein Physics clicker questionsDocument313 pagesLoeblein Physics clicker questionsDouglas Novaes100% (1)
- PC1431 Assignment 0 AnswersDocument32 pagesPC1431 Assignment 0 AnswersMikael Lee80% (5)
- H2 Physics DynamicDocument22 pagesH2 Physics DynamicTa Minh Trang100% (1)
- Homework 3 PDFDocument31 pagesHomework 3 PDFnaveena kumariNo ratings yet
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 7 - Forces Part OneDocument5 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 7 - Forces Part OneStrange Sht100% (1)
- Natsci5 Razon Newtons-Laws-Exercise 1Document5 pagesNatsci5 Razon Newtons-Laws-Exercise 1miles razorNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Using Part 2 - FrictionDocument3 pagesForces and Motion Using Part 2 - FrictionBluematwo TwoNo ratings yet
- Mastering Physics CH 05 HW College Physics I LCCCDocument20 pagesMastering Physics CH 05 HW College Physics I LCCCSamuel85% (13)
- AccelerationDocument2 pagesAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Phet Force and Newton's Laws ReviewDocument5 pagesPhet Force and Newton's Laws ReviewkhairatuddinariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Skill BuildingDocument21 pagesChapter 9 Skill BuildingLisa LimNo ratings yet
- Mastering Physics CH 11 HW College Physics I LCCCDocument50 pagesMastering Physics CH 11 HW College Physics I LCCCSamuel90% (10)
- Mastering Physics CH 04 HW College Physics I LCCCDocument43 pagesMastering Physics CH 04 HW College Physics I LCCCSamuel100% (16)
- Chapter 7 Written Problem SolutionsDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Written Problem SolutionsdavparanNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy & Power NumericalsDocument9 pagesWork, Energy & Power NumericalsSiddhartha Mukherjee100% (1)
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 5 - Forces Part OneDocument6 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 5 - Forces Part OneStrange Sht100% (1)
- Fluid Statics U-Tube Equilibrium and Pressure ProblemsDocument28 pagesFluid Statics U-Tube Equilibrium and Pressure ProblemsKyle Donaghey50% (2)
- Formal Homework Assignment 4Document69 pagesFormal Homework Assignment 4mhm00066690% (10)
- MasteringPhysics: HomeworkDocument5 pagesMasteringPhysics: HomeworkEric JonesNo ratings yet
- CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Document4 pagesCP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Anthony ButlerNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-03Document3 pagesPhysics 01-03KevleenNo ratings yet
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 10 - Motion in 2-DDocument4 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 10 - Motion in 2-DStrange Sht0% (2)
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 4 - Forces Part OneDocument7 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 4 - Forces Part OneStrange Sht100% (2)
- Newton's Laws ReviewDocument16 pagesNewton's Laws Reviewjaswid9607No ratings yet
- 1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetDocument8 pages1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetLudwig Van Beethoven100% (1)
- Newton's Third LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Third LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 8 - Forces Part OneDocument2 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 8 - Forces Part OneStrange Sht100% (1)
- GB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015Document2 pagesGB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015api-261277442No ratings yet
- Mastering Physics CH 07 HW College Physics I LCCCDocument39 pagesMastering Physics CH 07 HW College Physics I LCCCSamuel86% (7)
- HW10 Mastering Physics SolutionDocument6 pagesHW10 Mastering Physics SolutionCKNo ratings yet
- Intro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixADocument63 pagesIntro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixAGfour Maserati50% (2)
- Week 15 - Gravitational Force GizmoDocument6 pagesWeek 15 - Gravitational Force GizmoCamNo ratings yet
- POGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumDocument5 pagesPOGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumsydNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Laws of MotionDocument107 pagesSheet - 01 - Laws of MotionLakshya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7.1 - Enhanced - With Solution: Part ADocument29 pagesExercise 7.1 - Enhanced - With Solution: Part ASiva RamNo ratings yet
- Waves LabDocument6 pagesWaves Labsamarghai0% (1)
- Newton's Laws - Lesson 1 - Newton's First Law of MotionDocument5 pagesNewton's Laws - Lesson 1 - Newton's First Law of MotionRaj Komol100% (2)
- Kinematics - VELOCITY TIME GraphsDocument50 pagesKinematics - VELOCITY TIME Graphsshimoni rathoreNo ratings yet
- Momentum and ImpulseDocument10 pagesMomentum and ImpulseYuniar AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Forces in One Dimension-2Document3 pagesForces in One Dimension-2varaprasad100% (1)
- Unit TestDocument4 pagesUnit TestNicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument3 pagesEnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Wk2d2. Motion in One Dimension 1dDocument32 pagesWk2d2. Motion in One Dimension 1dAlex DeveldosNo ratings yet
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 6 - Motion in 1-DDocument3 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 6 - Motion in 1-DStrange Sht100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Skill BuildingDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Skill BuildingSmartGuiye67% (3)
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01Document56 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01topwarmachineNo ratings yet
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 10 - Motion in 1-DDocument5 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 10 - Motion in 1-DStrange ShtNo ratings yet
- 1D Kinematics ReviewDocument4 pages1D Kinematics ReviewAshir SaifNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument26 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionqpncsoriano100% (1)
- Chapter 4 (Friction) PDFDocument72 pagesChapter 4 (Friction) PDFRa Note A/l Som TebNo ratings yet
- 5 Displacement and Force in Two Dimensions: 2 FrictionDocument5 pages5 Displacement and Force in Two Dimensions: 2 Frictionalex murker100% (1)
- Two Dimensional Motion and VectorsDocument5 pagesTwo Dimensional Motion and VectorsSriram ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Webquest: Type in The Following Website and Answer The Problems BelowDocument5 pagesProjectile Motion Webquest: Type in The Following Website and Answer The Problems BelowEmmanuel GarciaNo ratings yet
- VelocityDocument4 pagesVelocityMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Reflection Refraction Diffraction of WavesDocument1 pageReflection Refraction Diffraction of WavesVictoria KairooNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Problems and SolutionsDocument38 pagesEngineering Mechanics Problems and SolutionsManish YadavNo ratings yet
- Mamelodi East Grade 11 Term 1 Control TestDocument10 pagesMamelodi East Grade 11 Term 1 Control TestPhilNo ratings yet
- 2010 2011 Midterm2Document4 pages2010 2011 Midterm2elif sNo ratings yet
- Crash Log 1Document1 pageCrash Log 1Fryda AyudhaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Nama Asisten Laboratorium Fisika Dasar IiDocument3 pagesDaftar Nama Asisten Laboratorium Fisika Dasar IiFryda AyudhaNo ratings yet
- Exploring Physics Concepts Among Novice Teachers Through CMAP ToolsDocument8 pagesExploring Physics Concepts Among Novice Teachers Through CMAP ToolsFryda AyudhaNo ratings yet
- Exploring Physics Concepts Among Novice Teachers Through CMAP ToolsDocument8 pagesExploring Physics Concepts Among Novice Teachers Through CMAP ToolsFryda AyudhaNo ratings yet
- Denah Eco Green ParkDocument1 pageDenah Eco Green ParkFryda AyudhaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Booster Test SeriesDocument22 pagesNcert Booster Test SeriesSwaraj MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- CoupleDocument4 pagesCoupleYugandhar Veeramachaneni100% (2)
- Newton's Second LawDocument5 pagesNewton's Second LawP.v.KumarNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion - Energy, Work and Power PDFDocument7 pagesForce and Motion - Energy, Work and Power PDFAnonymous ee5dOjNo ratings yet
- DLL 7es - Science 8 - q1w1Document4 pagesDLL 7es - Science 8 - q1w1asia bagayNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: Laws of Motion: Region I Division of Ilocos SurDocument15 pagesLesson Title: Laws of Motion: Region I Division of Ilocos SurJOHN MAYKALE FARRALESNo ratings yet
- Problem B: Standard:Hs-Ps2-1Document2 pagesProblem B: Standard:Hs-Ps2-1Mona Mohamed SafwatNo ratings yet
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 4 - Forces Part OneDocument7 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 4 - Forces Part OneStrange Sht100% (2)
- Static Equilibrium ConditionsDocument24 pagesStatic Equilibrium ConditionsAnita PatelNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS Revision-2023-04Document2 pagesELECTROSTATICS Revision-2023-04psikka23No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics NotesDocument46 pagesEngineering Mechanics NotesDevansh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics in Orthodontics - NandaDocument16 pagesBiomechanics in Orthodontics - NandaVerônica Polo Perez100% (2)
- Ball-Drop ExperimentDocument3 pagesBall-Drop Experimentapi-371293110No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rotational Motion: April 12, 2016Document16 pagesDynamics of Rotational Motion: April 12, 2016thebestNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsRowena Abdula BaronaNo ratings yet
- Learning Task No. 1: Fill in The Box The Correct Letter (S) Being Described in EachDocument3 pagesLearning Task No. 1: Fill in The Box The Correct Letter (S) Being Described in EachMa. Elpidia Caridad TuazonNo ratings yet
- 3 3 Newtons Second and Third LawsDocument5 pages3 3 Newtons Second and Third LawsHaneen Dweikat100% (1)
- L3 CH1 ElectrostaticsDocument92 pagesL3 CH1 ElectrostaticsRafig MammadzadehNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of MotionDocument5 pagesNewton Laws of MotionMannyCesNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: ProblemsDocument67 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: ProblemsangelicaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics - Part 3Document14 pagesBiomechanics - Part 3Kýñg ButlerNo ratings yet
- 3 Worksheet (AS) : Micro Mega A B C DDocument3 pages3 Worksheet (AS) : Micro Mega A B C DAlmas TalibNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument52 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Explainedraie saadNo ratings yet
- Science G8 Student Book ContentsDocument350 pagesScience G8 Student Book Contentslienuj100% (3)
- Daily Detailed Lesson Log (DLL) : ElicitDocument4 pagesDaily Detailed Lesson Log (DLL) : ElicitLovely Shiena C. AragoncilloNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.2 - Forces - StudentDocument48 pagesTopic 2.2 - Forces - Studentyilira4268No ratings yet