Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nucleic Acids 4
Nucleic Acids 4
Uploaded by
Edgardo VILLASEÑOR0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesOriginal Title
nucleic acids 4.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesNucleic Acids 4
Nucleic Acids 4
Uploaded by
Edgardo VILLASEÑORCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
The building blocks of living organisms are the nucleic Minds on: Performance Task:
acids. They serve as the blueprint of life they are
responsible in encoding, transmitting, and expressing The Create a 100-word
genetic information. students essay titled,
will make “Nucleic Acid:
an online The Blueprint of
Nucleic acids are formed from polymerization of research Life”. The essay
nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three components: about the should give
structural emphasis on the
1. A phosphoric acid molecule phosphate (PO43-); formulas of structure,
2. A five carbon sugar molecule, pentose; and the composition, and
3. A molecule of a nitrogen-containing base. following importance of
(p. 359) nucleotides: Nucleic Acids to
thymine, the cell’s bodily
There are two types of nucleic acids. These are the adenine, function.
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). cytosine,
and Standards:
guanine.
The students will
DNA RNA
Hands on: be graded based on
the following
Deoxyribonucleic Ribonucleic acid The criteria:
acid students
will make a a. Organizatio
Definition A nucleic acid that The information model of n of ideas
contains the genetic found in DNA the b. Content
instructions used in determines which nucleotides c. Argument
the development and traits are to be they have d. Spelling
functioning of all created, activated, researched. and
modern living or deactivated, They will Grammar
organisms. DNA's while the various use
genes are expressed, forms of RNA do polystyrene (Refer to Rubrics 4
or manifested, the work. balls, in the appendices)
through the proteins plastic
that its nucleotides cups, or
produce with the discarded Traditional
help of RNA. materials of
their Identify the word
Function The blueprint of Helps carry out choice. in each number.
biological guidelines DNA's blueprint
that a living guidelines. ______1. A
organism must Transfers genetic Authentic: nucleic acid that
follow to exist and code needed for contains the
remain functional. the creation of The genetic instructions
Medium of long- proteins from the students used in the
term, stable storage nucleus to the will add development and
color to functioning of all
and transmission of ribosome. their modern living
genetic information. nucleotide organisms.
model for
Structure Double-stranded. It Single-stranded. presentatio _____2. They
has two nucleotide Like DNA, RNA n. serve as the
strands which is composed of its blueprint of life
consist of its phosphate group, they are
phosphate group, five-carbon sugar Hands on: responsible in
five-carbon sugar (the less stable encoding,
(the stable 2- ribose), and four The transmitting, and
deoxyribose), and nitrogen- students expressing genetic
four nitrogen- containing will be information.
containing nucleobases: grouped
nucleobases: adenine, uracil and they _____3. It is
adenine, thymine, (not thymine), will composed of its
cytosine, and guanine, and conduct an phosphate group,
guanine. cytosine. experiment five-carbon sugar
on (the less stable
Base Adenine links to Adenine links to extraction ribose), and four
Pairing thymine (A-T) and uracil (A-U) and of DNA nitrogen-
cytosine links to cytosine links to from containing
guanine (C-G). guanine (C-G). banana nucleobases
using
Location DNA is found in the Depending on the household
nucleus of a cell and type of RNA, this reagents. _____4.
in mitochondria. molecule is found Comprised of
in a cell's nucleus, Minds on: adenine (A) and
its cytoplasm, and guanine (G)
its ribosome. The
students ____5. Comprised
Stability Deoxyribose sugar Ribose sugar is will analyze of thymine (T),
in DNA is less more reactive the data cytosine (C), and
reactive because of because of C-OH obtained uracil (U).
C-H bonds. Stable in (hydroxyl) bonds. from the
alkaline conditions. Not stable in experiment.
DNA has smaller alkaline Key to correction:
grooves, which conditions. RNA
makes it harder for has larger grooves, Authentic: 1. DNA
enzymes to "attack." which makes it 2. Nucleic
easier to be The acids
"attacked" by students 3. RNA
enzymes. will design 4. Purine
their own bases
Propagatio DNA is self- RNA is experiment 5. Pyrimidine
n replicating. synthesized from on bases
extraction
DNA when of DNA
needed. using the
material of
Unique The helix geometry The helix their
Features of DNA is of B- geometry of RNA choice.
Form. DNA is is of A-Form.
protected in the RNA strands are
nucleus, as it is continually made,
tightly packed. DNA broken down and
can be damaged by reused. RNA is
exposure to ultra- more resistant to
violet rays. damage by Ultra-
violet rays.
(pp. 359-360)
Deoxyribonucleic acid is different from RNA due to the
sugar molecule that they contain. RNA contains the sugar
ribose while DNA contains a sugar known as deoxyribose.
The prefix deoxy- indicates a removal of oxygen atom.
(p. 360)
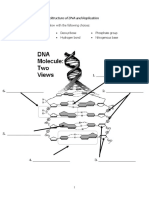
One prominent feature of DNA is its double-helix
structure. A double helix has two chains of DNA that are
coiled together in such a way that the bases are in the
interior of the coils.
There are two purine bases. These are the adenine (A) and
guanine (G). on the other hand, there are three pyrimidine
bases. These are the thymine (T), cytosine (C), and uracil
(U). the latter is not found in DNA but in RNA.
In a DNA structure, A and T complement each other like
the G and C does. When a cell divides, the DNA double
helix comes apart. Each chain contains the same genetic
information and becomes a template for the production of
a new complementary chain. This process is known as
genetic replication.
Ribonucleic acid, unlike DNA, is single stranded. There
are three types of RNA. These are the transfer RNA
(tRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), and ribosomal RNA
(rRNA). They are all essential in the process of building
proteins from DNA.
RNA employs the same base pairing as DNA except for
thymine , which is replaced by uracil.
The three bases of a code are known as codon, and their
complementary in tRNA are called anticodon.
(pp.361-363)
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Biochemistry Life at The Molecular Level 5th Edition Voet Test BankDocument28 pagesFundamentals of Biochemistry Life at The Molecular Level 5th Edition Voet Test BankGeorgeCobbjgbcs100% (15)
- Lesson Plan in GTK DNA and RNADocument7 pagesLesson Plan in GTK DNA and RNAJessah Largueza FetalverNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in GTK DNA and RNADocument7 pagesLesson Plan in GTK DNA and RNAJessah Largueza FetalverNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Nucleic Acid Lesson PlanDocument19 pagesBiochemistry - Nucleic Acid Lesson PlanMark Kevin Dumlao100% (1)
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry BrochureDocument2 pagesBiochemistry BrochureCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna-101Document30 pagesDna Rna-101Hazel SioseNo ratings yet
- 1367892649-5-Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pages1367892649-5-Nucleic AcidsKhan RiyazNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology Notes Ch06 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument14 pages12 Biology Notes Ch06 Molecular Basis of Inheritancehimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalDocument5 pagesComparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalNova Divine De la PeñaNo ratings yet
- Nucliec AcidDocument5 pagesNucliec AcidJoyce Fraulein T. LejosNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 8 Genes & Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesAssignment # 8 Genes & Nucleic Acidskyle james duclanNo ratings yet
- GenBIO REVIEWERDocument39 pagesGenBIO REVIEWERblismae genotivaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Fact SheetDocument1 pageNucleic Acids Fact Sheetasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Nuceic Acid ProjectDocument2 pagesNuceic Acid ProjectCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- Science Protein SynthesisDocument32 pagesScience Protein SynthesisKyla Rhain MedranoNo ratings yet
- Notes Chap 06Document21 pagesNotes Chap 06umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- DLP 3Document15 pagesDLP 3princessspbsedscicsuandrewsNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PresentationDocument14 pagesGroup 4 PresentationJanrei Devilla TeNo ratings yet
- Science 10-Dlp9-Dna-RnaDocument3 pagesScience 10-Dlp9-Dna-RnaSharlene Cecil PagoboNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument13 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceDikansha JasaiwalNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 4th QTDocument7 pagesGen Bio 4th QTZuri MaeNo ratings yet
- Bio 45. Chapter 2.3 - OBSDocument5 pagesBio 45. Chapter 2.3 - OBSVY VienNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 4.1: Protein SynthesisDocument32 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 4.1: Protein SynthesisMariiNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument2 pagesDNA Vs RNAMegat AmirulNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsDocument4 pagesDNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesNucleic AcidsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument10 pages04-Chemical Basis of HeredityBen Abella100% (1)
- The Central DogmaDocument37 pagesThe Central DogmaCharlotte Anne FelicianoNo ratings yet
- COT3Document27 pagesCOT3Vincent Franciz FernandezNo ratings yet
- SCIE1106 L3 Macromolecules 2 TM 2022Document26 pagesSCIE1106 L3 Macromolecules 2 TM 2022JamesNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Name: Miss Rabaya Akter ID: 1922247649Document8 pagesNucleic Acid: Name: Miss Rabaya Akter ID: 1922247649SymumNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument67 pagesProtein SynthesisLian Rose MendozaNo ratings yet
- Biol313 M5Document2 pagesBiol313 M5Fares SamirNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of DNA and RNADocument3 pagesStructure and Functions of DNA and RNAokonabasimfreke09No ratings yet
- The Structure of DNA and RNADocument2 pagesThe Structure of DNA and RNADanielNacordaNo ratings yet
- Biological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDocument2 pagesBiological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDr.Charles BhaskarNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument106 pagesDNA ReplicationJake GamingNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular Biology PDFDocument32 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biology PDFStephy LimboNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT HIGHLIGHT by SEEP PahujaDocument31 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT HIGHLIGHT by SEEP Pahujasafeerjavaid8No ratings yet
- Biology The Core 2Nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesBiology The Core 2Nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFCassieYangiosx100% (13)
- Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesBiology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manualaureliacharmaine7pxw9100% (22)
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritancesahanaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument23 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceParthNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Dna & Rna: Students NameDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dna & Rna: Students NameHisham MustafaNo ratings yet
- Biology IB SLDocument28 pagesBiology IB SLRaynaahNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication & TranscriptionDocument4 pagesDna Replication & TranscriptionGarren Jude AquinoNo ratings yet
- WK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2Document7 pagesWK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2opingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheetmichelle.baguioNo ratings yet
- The Role of RNA DNA and PROTEIN in The Transmission of TraitsDocument21 pagesThe Role of RNA DNA and PROTEIN in The Transmission of TraitsrebugiocosmeNo ratings yet
- All Chapters Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes 1 045329Document60 pagesAll Chapters Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes 1 045329ymadikane38No ratings yet
- Abo, Margaret Nicole Bsmls 2C Nucleic Acids FinalsDocument5 pagesAbo, Margaret Nicole Bsmls 2C Nucleic Acids FinalsMargaret Nicole AboNo ratings yet
- BioA4 27. Basic GeneticsDocument5 pagesBioA4 27. Basic Geneticsthanks btNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 7 Genes & Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesAssignment # 7 Genes & Nucleic AcidsCharlou SindacNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetDocument10 pagesLesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetEnriquez, Hannah Roniella R.No ratings yet
- Nu Cleo ShitDocument4 pagesNu Cleo ShitPretty Grace101No ratings yet
- AS - Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesAS - Nucleic AcidsAraijan AbaiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Material & PCR's PrincipleDocument14 pagesGenetic Material & PCR's PrincipleAndro Toga Gerson SNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Gas Laws: EO:ExplaiDocument9 pagesLesson 2: The Gas Laws: EO:ExplaiEdgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Motion Detectors: Lesson 1Document3 pagesMotion Detectors: Lesson 1Edgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- 19 Days Learning Content Learnin G Experien Ce Evaluation of Learning Outcomes Integrati OnDocument4 pages19 Days Learning Content Learnin G Experien Ce Evaluation of Learning Outcomes Integrati OnEdgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Rates of Chemical Reaction: EO: ExplainDocument5 pagesLesson 4: Rates of Chemical Reaction: EO: ExplainEdgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- TPO6Document2 pagesTPO6Edgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Occurrence of A Chemical Reaction: TPO: RelateDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Occurrence of A Chemical Reaction: TPO: RelateEdgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Chemical Reactions and Equation: EO: DefineDocument6 pagesLesson 3: Chemical Reactions and Equation: EO: DefineEdgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Unit X-XII Fourth Quarter: Matter 50 DaysDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Unit X-XII Fourth Quarter: Matter 50 DaysEdgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna Structure Worksheet - EddyDocument3 pagesDna and Rna Structure Worksheet - Eddyapi-429499161No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Nucleic Acids and Protein SynthesisDocument46 pagesChapter 17 Nucleic Acids and Protein SynthesisMohammad AlHamdanyNo ratings yet
- Purine NucleotideDocument61 pagesPurine NucleotideMayalu123100% (1)
- 6.5 DNA Strucuture and Replication OriginalDocument4 pages6.5 DNA Strucuture and Replication OriginalSteelcrow14No ratings yet
- Dna, Rna, Dan Protein 1Document26 pagesDna, Rna, Dan Protein 1R yNo ratings yet
- What Is RNA?Document19 pagesWhat Is RNA?ankitabeboNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA WorksheetsDocument6 pagesDNA and RNA WorksheetsA. Nurul Virninda YusufNo ratings yet
- US20210147837A1Document144 pagesUS20210147837A1avalosheNo ratings yet
- Dna WsDocument1 pageDna WsLovryan Tadena AmilingNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Practice PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Replication Practice PDFKim100% (1)
- IPPATH Remove and IPPOOL Add in NodeBDocument15 pagesIPPATH Remove and IPPOOL Add in NodeBasusf6veNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument17 pagesNucleotides and Nucleic AcidsFatma AdelNo ratings yet
- BC Lec M6 Lesson 2-1Document24 pagesBC Lec M6 Lesson 2-1Mershonthel MarquezNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Practice Problems Chromosomes and DNA ReplicationDocument7 pagesBio 102 Practice Problems Chromosomes and DNA ReplicationGhulam NabiNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.2 What's The MessageDocument1 pageActivity 3.2 What's The MessageorculloNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument9 pagesDNA StructureMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar Latihan Dalam Kepelatihan Olahraga: Fakultas Ilmu Keolahragaan, Universitas Negeri MedanDocument7 pagesDasar Dasar Latihan Dalam Kepelatihan Olahraga: Fakultas Ilmu Keolahragaan, Universitas Negeri MedanMuhammad Fauzi D4 ElektromedikNo ratings yet
- DNA RNA COT DLL New NormalDocument6 pagesDNA RNA COT DLL New NormalConnie Joy P. Calawag100% (2)
- Biochemistry COURSE CODE: Ichem.3052 Group AssignmentDocument6 pagesBiochemistry COURSE CODE: Ichem.3052 Group AssignmentBizuayehu Ze GeorgeNo ratings yet
- s15 Miller Chap 8a LectureDocument36 pagess15 Miller Chap 8a LectureShiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument38 pagesTranscription and RNA ProcessingRishi Kumar100% (1)
- 2.WS1.2Str - of.DNA 13.03.2020Document2 pages2.WS1.2Str - of.DNA 13.03.2020gajendra. khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Lesson 2 PrelimDocument74 pagesCytogenetics Lesson 2 PrelimSinining, Aera Kerl CharmNo ratings yet
- Difference Between DNA and RNA: February 2017Document10 pagesDifference Between DNA and RNA: February 2017JihanNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument9 pagesDNA and RNAAli DokmakNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure-Replication Quiz - Key 12-13Document4 pagesDNA Structure-Replication Quiz - Key 12-13Alvin Pabores100% (1)
- Handwritten Biochem U-2 NOTESDocument31 pagesHandwritten Biochem U-2 NOTESGayatri TiwaskarNo ratings yet