Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T T T T Y Y Δ Δ: 1 / Kgs 2 / Kgs 10 / Kj Kgk 5 / Kj Kgk
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T T T T Y Y Δ Δ: 1 / Kgs 2 / Kgs 10 / Kj Kgk 5 / Kj Kgk
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
www.gatehelp.
com
CHAP 7 HEAT TRANSFER PAGE 309
T − Tw = 3 y − 1 y 3 ,
T3 − Tw 2 b δt l 2 b δt l
where Tw and T3 are the temperature of plate and free stream respectively,
and y is the normal distance measured from the plate. The local Nusselt
number based on the thermal boundary layer thickness δt is given by
(A) 1.33 (B) 1.50
(C) 2.0 (D) 4.64
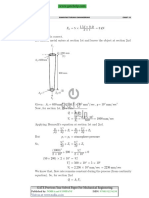
MCQ 7.21 In a counter flow heat exchanger, hot fluid enters at 60c C and cold fluid
leaves at 30c C . Mass flow rate of the fluid is 1 kg/s and that of the cold
fluid is 2 kg/s. Specific heat of the hot fluid is 10 kJ/kgK and that of the
cold fluid is 5 kJ/kgK. The Log Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) for
the heat exchanger in cC is
(A) 15 (B) 30
(C) 35 (D) 45
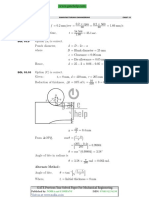
MCQ 7.22 The average heat transfer co-efficient on a thin hot vertical plate suspended
in still air can be determined from observations of the change in plate
temperature with time as it cools. Assume the plate temperature to be
uniform at any instant of time and radiation heat exchange with the
surroundings negligible. The ambient temperature is 25c C , the plat has a
total surface area of 0.1 m2 and a mass of 4 kg. The specific heat of the plate
material is 2.5 kJ/kgK. The convective heat transfer co-efficient in W/m2 K ,
at the instant when the plate temperature is 225c C and the change in plate
temperature with time dT/dt =− 0.02 K/s , is
(A) 200 (B) 20
(C) 15 (D) 10
• Common Data For Q.23 and Q.24
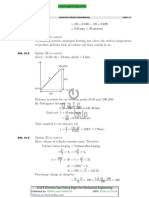
Consider steady one-dimensional heat flow in a plate of 20 mm thickness
with a uniform heat generation of 80 MW/m3 . The left and right faces are
kept at constant temperatures of 160c C and 120c C respectively. The plate
has a constant thermal conductivity of 200 W/mK.
MCQ 7.23 The location of maximum temperature within the plate from its left face is
(A) 15 mm (B) 10 mm
(C) 5 mm (D) 0 mm
MCQ 7.24 The maximum temperature within the plate in cC is
(A) 160 (B) 165
(C) 200 (D) 250
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 310 HEAT TRANSFER CHAP 7
YEAR 2006 ONE MARK
MCQ 7.25 In a composite slab, the temperature at the interface (Tinter ) between two
material is equal to the average of the temperature at the two ends. Assuming
steady one-dimensional heat conduction, which of the following statements
is true about the respective thermal conductivities ?
(A) 2k1 = k2 (B) k1 = k2
(C) 2k1 = 3k2 (D) k1 = 2k2
YEAR 2006 TWO MARKS
MCQ 7.26 A 100 W electric bulb was switched on in a 2.5 m # 3 m # 3 m size thermally
insulated room having a temperature of 20cC . The room temperature at the
end of 24 hours will be
(A) 321cC (B) 341cC
(C) 450cC (D) 470cC
MCQ 7.27 A thin layer of water in a field is formed after a farmer has watered it. The
ambient air conditions are : temperature 20cC and relative humidity 5%. An
extract of steam tables is given below.
Temp(c C) − 15 − 10 − 5 0.01 5 10 15 20
Saturation Pressure (kPa) 0.10 0.26 0.40 0.61 0.87 1.23 1.71 2.34
Neglecting the heat transfer between the water and the ground, the water
temperature in the field after phase equilibrium is reached equals
(A) 10.3cC (B) − 10.3c C
(C) − 14.5c C (D) 14.5c C
MCQ 7.28 With an increase in the thickness of insulation around a circular pipe, heat
loss to surrounding due to
(A) convection increase, while that the due to conduction decreases
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
You might also like
- Heat Transfer-3-4Document2 pagesHeat Transfer-3-4SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: YEAR 2012 One Mark MCQ 7.1Document44 pagesHeat Transfer: YEAR 2012 One Mark MCQ 7.1SreevathsaNo ratings yet
- 20 C C 20 C C 100 C C: YEAR 2008 Two Marks MCQ 7.16Document2 pages20 C C 20 C C 100 C C: YEAR 2008 Two Marks MCQ 7.16SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- YEAR 2005 One Mark MCQ 7.29: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument2 pagesYEAR 2005 One Mark MCQ 7.29: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Gate Solved Paper - Me: Heat TransferDocument38 pagesGate Solved Paper - Me: Heat Transferrudresh JmNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument38 pagesHeat TransferSumit BhanushaliNo ratings yet
- YEAR 2003 One Mark MCQ 7.41: Common Data For Q. - 44 and Q.45Document1 pageYEAR 2003 One Mark MCQ 7.41: Common Data For Q. - 44 and Q.45SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: YEAR 2012 One Mark MCQ 7.1Document44 pagesHeat Transfer: YEAR 2012 One Mark MCQ 7.1Mostafa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Conduction MCQsDocument4 pagesConduction MCQsyogesh shindeNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: YEAR 2012 One Mark MCQ 7.1Document2 pagesHeat Transfer: YEAR 2012 One Mark MCQ 7.1SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Gate QuestionDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Gate QuestionSANDEEP GautamNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer-11 PDFDocument1 pageHeat Transfer-11 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Technical QuestionsDocument19 pagesTechnical QuestionsKrishNo ratings yet
- QB Heat Transfer ME DBDocument16 pagesQB Heat Transfer ME DBmayilmazNo ratings yet
- Conduction (MDocument13 pagesConduction (Mthathalakshman121407No ratings yet
- Critical Thickness PDFDocument6 pagesCritical Thickness PDFSurya KiranNo ratings yet
- CHENG314 Ass1 S1 20 21Document1 pageCHENG314 Ass1 S1 20 21Imi_dash9No ratings yet
- 10c.heat TransferDocument4 pages10c.heat TransferJatin SonwalNo ratings yet
- Physics CPP - Cat-3Document14 pagesPhysics CPP - Cat-3faraazahmed70058No ratings yet
- HW 3Document14 pagesHW 3Mark LutherNo ratings yet
- HT Model Questions 2020-21Document5 pagesHT Model Questions 2020-21mohit pandeyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Question Bank - Part 2 1634501492967Document32 pagesHeat Transfer Question Bank - Part 2 1634501492967Inventory gammaNo ratings yet
- HeatTransferQuestionBank PydwdDocument39 pagesHeatTransferQuestionBank PydwdRB CreationNo ratings yet
- (Questions Only) ME 366 ONLINE REGULAR QUIZ 2 2022 - 2023Document10 pages(Questions Only) ME 366 ONLINE REGULAR QUIZ 2 2022 - 2023somenewguyonthewebNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer2 PDFDocument13 pagesHeat Transfer2 PDFChaitanya Kishore ChitikenaNo ratings yet
- HT DPP 04072022Document372 pagesHT DPP 04072022PRIYANSHU JAKHARNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass TransferDocument3 pagesHeat and Mass TransferSHISHIRNo ratings yet
- Quiz HMT Question PaperDocument2 pagesQuiz HMT Question Papersutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument15 pagesHeat Transferaddtadd6No ratings yet
- HMT 2Document2 pagesHMT 2Yathish YathiNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument20 pagesHeat TransferPeter Simon SantosNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: 3251.0 / KJ KG 15 Kpa 15 Kpa 225.94 / KJ KG 2598.3 / KJ KG 10 / KgsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics: 3251.0 / KJ KG 15 Kpa 15 Kpa 225.94 / KJ KG 2598.3 / KJ KG 10 / KgsSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer by S K Mondal-3-42Document40 pagesHeat Transfer by S K Mondal-3-42Arpit Thakur0% (2)
- HMT Obj Hand Book IDocument10 pagesHMT Obj Hand Book Ianikka reenaNo ratings yet
- JEE ADVANCED-Assignment-3: Presented by Kailash SharmaDocument7 pagesJEE ADVANCED-Assignment-3: Presented by Kailash SharmaGulafsha PerweenNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer-13 PDFDocument1 pageHeat Transfer-13 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- (Sem. Iv) Theory Examination 2013-14: PAPER ID: 151406Document2 pages(Sem. Iv) Theory Examination 2013-14: PAPER ID: 151406Sarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument68 pagesThermodynamicsAnuj SaliNo ratings yet
- Me6502 Nov Dec 2016 PDFDocument3 pagesMe6502 Nov Dec 2016 PDFKannan MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- 2 Kw 4.2 / Kj Kgk: Du Pd Ν S, U, Pressure P, Temperature T And Volume Ν, Which OfDocument2 pages2 Kw 4.2 / Kj Kgk: Du Pd Ν S, U, Pressure P, Temperature T And Volume Ν, Which OfSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document10 pagesTutorial Sheet 3kushalNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology RoorkeeDocument2 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Roorkeepushkal0% (2)
- Chn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Document2 pagesChn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Prashant RajNo ratings yet
- Heat (QB) FOR - FDocument8 pagesHeat (QB) FOR - FRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Problems Based On Conduction Basic Level: Transmission of HeatDocument11 pagesProblems Based On Conduction Basic Level: Transmission of HeatApoorvNo ratings yet
- Test - SET-B - Hear Transfer + Solid + CalorimetryDocument4 pagesTest - SET-B - Hear Transfer + Solid + CalorimetrySombir AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Common Data For Q. - 51 and Q.52: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument2 pagesCommon Data For Q. - 51 and Q.52: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- JEE Main DPYQ Full Syllabus PAPER-5Document5 pagesJEE Main DPYQ Full Syllabus PAPER-5mohammed irfanNo ratings yet
- February 21 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 375 Heat TransferDocument6 pagesFebruary 21 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 375 Heat TransferPandu WibowoNo ratings yet
- KJKG KJKG K MKG 350 C C: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.Co - inDocument2 pagesKJKG KJKG K MKG 350 C C: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.Co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- HMWRK 10Document10 pagesHMWRK 10shayanebraNo ratings yet
- Educspace - Heat Transfer - Problems SetDocument5 pagesEducspace - Heat Transfer - Problems SetCharlyn FloresNo ratings yet
- IES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2006Document10 pagesIES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2006aditya_kumar_meNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer Bergman 7th Edition Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer Bergman 7th Edition Solutions Manualcuongviolet1or0zm0% (1)
- A1 Batch NKC Sir Heat Thermodynamics KTG 1637843224143Document57 pagesA1 Batch NKC Sir Heat Thermodynamics KTG 1637843224143Harsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 170402: HEAT TRANSFER Unit IDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank 170402: HEAT TRANSFER Unit Iprakhar dubeyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Problems Solutions Rev 1Document22 pagesHeat Transfer Problems Solutions Rev 1Charlyn Flores100% (1)
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNo ratings yet
- F D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageF D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-54Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-54SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-55Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-55SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Processes Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4Document1 pageProcesses Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-53Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-53SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-53Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-53SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Column I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageColumn I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-51Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-51SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-52Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-52SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-48Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-48SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- For Metal: Atomic Weight Valency The Metal Removal Rate: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageFor Metal: Atomic Weight Valency The Metal Removal Rate: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-46Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-46SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-45Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-45SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-38Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-38SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-40Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-40SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inDocument1 pageADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- α 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1Document1 pageα 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- A N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageA N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Solution: Metal Forming Process Types of Stress 1. S. Compressive 2. P. Tensile 3. Q. Shear 4. R. Tensile and CompressiveDocument1 pageSolution: Metal Forming Process Types of Stress 1. S. Compressive 2. P. Tensile 3. Q. Shear 4. R. Tensile and CompressiveSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-38Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-38SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-32 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-32 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- 175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 page175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-34Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-34SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-32 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-32 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Montevecchi2018heat Accumulation Prevention in Wire-Arc-Additive-Manufacturing Using Air JetDocument9 pagesMontevecchi2018heat Accumulation Prevention in Wire-Arc-Additive-Manufacturing Using Air JetGustavo de CastroNo ratings yet
- Finned Tube R134a CondenserDocument12 pagesFinned Tube R134a CondensermattiturboNo ratings yet
- Mod ExercisesDocument6 pagesMod ExercisesAhmed GadNo ratings yet
- Aae009 - Fem - Question BankDocument16 pagesAae009 - Fem - Question BankChekka SudheerNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Heat Transfer in AirtoRefrigerant Airfoil Heat ExchangersDocument12 pagesConjugate Heat Transfer in AirtoRefrigerant Airfoil Heat ExchangersMohammed AshiqueNo ratings yet
- BDE 30603 - Ind - Ass - 1 PDFDocument1 pageBDE 30603 - Ind - Ass - 1 PDFIzwan SaifudinNo ratings yet
- The Basic of Electric Process HeatingDocument8 pagesThe Basic of Electric Process HeatingAmir AmkaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Study of Heat Transfer Analysis of Helical Coil Heat ExchangersDocument5 pagesA Review On Study of Heat Transfer Analysis of Helical Coil Heat ExchangersEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Experimental and CFD Analysis of Aluminium Heat Sinks For Avionics ApplicationsDocument7 pagesExperimental and CFD Analysis of Aluminium Heat Sinks For Avionics ApplicationsIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. Biotechnology Syllabus CDFSTDocument42 pagesB. Tech. Biotechnology Syllabus CDFSTlakshitaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Sizing of A S&T ExchangerDocument67 pagesThermal Sizing of A S&T Exchangerraja raniNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis AE2351Document5 pagesFinite Element Analysis AE2351Aghil BuddyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer PROBLEMSDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer PROBLEMSEcel Pablo PromentillaNo ratings yet
- Thermosyphons and Heat PipeDocument14 pagesThermosyphons and Heat PipespurwonofjpNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer (Mce-303) Bachelor of Technology5 Sem End Semester ExaminationDocument4 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer (Mce-303) Bachelor of Technology5 Sem End Semester Examinationsumeetsharma27No ratings yet
- Condensadro EspiralDocument13 pagesCondensadro EspiralAndresInforBJNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger HandoutDocument11 pagesHeat Exchanger Handoutchegg userNo ratings yet
- Fired HeaterDocument77 pagesFired HeaterEslamSheblNo ratings yet
- Ns QP PDFDocument68 pagesNs QP PDFRajesh SallaNo ratings yet
- MENG 412 Thermal Science Laboratory Expt. 6: Extended Surface Heat TransferDocument10 pagesMENG 412 Thermal Science Laboratory Expt. 6: Extended Surface Heat TransferFatima Khalid100% (1)
- Analysis of Effectiveness of Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube Type One Shell Two Tube Pass As Cooling OilDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Effectiveness of Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube Type One Shell Two Tube Pass As Cooling OilHendrik V SihombingNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Studies in A Spiral Plate Heat Exchanger For Water - Palm Oil Two Phase SystemDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Studies in A Spiral Plate Heat Exchanger For Water - Palm Oil Two Phase SystemhusseinNo ratings yet
- 2 1condenserDocument9 pages2 1condenserAhmed GadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Heat Exchanger PDFDocument22 pagesTutorial 3 Heat Exchanger PDFBipin GiriNo ratings yet
- Boiling Heat TransferDocument3 pagesBoiling Heat TransferAyush DubeyNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Lab ReportDocument3 pagesHeat Conduction Lab ReportJohnConor96% (23)
- Ex: No: Heat Transfer in Forced Convection Date: AimDocument8 pagesEx: No: Heat Transfer in Forced Convection Date: AimmuralidharanNo ratings yet
- HMT16 MarksDocument12 pagesHMT16 MarkstagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- IHMT sunmissionfINALDocument7 pagesIHMT sunmissionfINALANAND POZHATHNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Heat and Mass Transfer A Practical Approach 2nd Edition Cengel CHDocument62 pagesSolution Manual Heat and Mass Transfer A Practical Approach 2nd Edition Cengel CHJohn A. CenizaNo ratings yet