Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy and Respiration1 PDF
Uploaded by
Arafat HossainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy and Respiration1 PDF
Uploaded by
Arafat HossainCopyright:
Available Formats
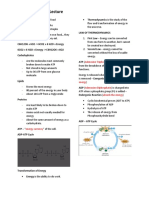
Respiration:
The physiological process by which plants and animals produce energy in cells by food
materials with or without oxygen is called respiration
Is defined as a biochemical process by which organisms produce kinetic energy by the oxidation
of food, with or without oxygen, producing water and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
Glycolysis:
It occurs in the cell cytoplasm (or cell cytosol)
The glucose is phosphorylated so it doesn't leave the less and so it is more soluble
1. Glucose + ATP →(hexokinase) Glucose 6-phosphate + ADP
2. Glucose 6-phosphate ⇄(phosphoglucoisomerase) Fructose 6-phosphate
3. Fructose 6-phosphate + ATP →(phosphoglucoisomerase) Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate+ADP
4. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate ⇄(aldolase) 3PGAL + DHP
5. 3PGAL ⇄(dehydroxyginase) 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid + ATP
6. 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid + ADP ⇄(kinase) 3phosphoglyceric acid + ATP
7. 3phosphoglyceric acid ⇄ 2phosphoglyceric acid
8. 2phosphoglyceric acid ⇄(enolase) 2phosphoenol pyruvic acid + H2O
9. 2phosphoenol pyruvic acid + ADP → pyruvic acid + ATP
DHP= dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Pyruvic acid= pyruvate
Link reaction:
Pyruvate +CoA =(NAD+= NADH +H+) Acetyl CoA + CO2
One glucose is two pyruvates, combines with CoA(nucleoside + vitamin) to produce Acetyl CoA,
releasing CO2 and hydrogen. Pyruvate is decarboxylated and dehydrogenated. Acetyl CoA is
needed for the next cycle, Kreb cycle.
Krebs cycle:
Occurs in the mitochondrion in the matrix, start with 4C molecule to 6C and goes through a
series of steps to slowly breakdown the molecule to 4C and 2 molecules of CO2 removed with 2
reduced NAD being formed too (NADH), its products are photons ( H+), CO2 and ATP.
Aerobic respiration is divided into 4 stages
1. Glycolysis
2. Link reaction (Formation of acetyl CoA)
3. Krebs cycle
4. Oxidative phosphorylation
Respiratory quotient = amount of CO2/ amount of O2
Factors affecting respiration:
External factors:
● Respiration is dependent on O2 density.
● Respiration is also dependent on CO2 density, high density of CO2 decreases in
respiration as less O2 can enter.
● Effectiveness of enzymes regulated by change in temperature.
● Respiration in plants affected by light intensity.
● Water is needed for metabolic reaction.
Internal Factors:
● food can affect rate of respiration, lipids are harder to breakdown, so after consumption
of lipids rate of respiration decreases for a while
● Age of cells, cells with more protoplasm live longer and has the ability to respire more.
● Inorganic salt presence of greater amount of inorganic salts can increase rate of
respiration
O2 debt: (O2 consumption during work) - ( O2 consumption at rest)
Difference between ATP and NAD:
ATP NAD
● Has 1 ribose ● Has 2 ribose
● Adenine base present ● Adenine is present
● No nicotinamide ● Nicotinamide is present
● Has 3 phosphate bonds ● Acts as hydrogen carrier
● Acts as coenzyme
● Has two phosphate bonds
Sirs email:abulhossainazad24@gmail.com
You might also like
- Unbelievers LarryDocument284 pagesUnbelievers LarryAvril CloudNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Section B: VocabularyDocument2 pagesMODULE 4 Section B: VocabularyvirinzoNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Discover DTSiDocument3 pagesBajaj Discover DTSinikunj_shahNo ratings yet
- Lec4 PhotosynthesisDocument50 pagesLec4 PhotosynthesisPLANARIANo ratings yet
- III UG Physiology Respiration AVJDocument27 pagesIII UG Physiology Respiration AVJHead 4KNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument55 pagesPhotosynthesischezkanoelleangeliebalolongNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: General Biology I Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDocument22 pagesCellular Respiration: General Biology I Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDyames TVNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument21 pagesAnaerobic RespirationRex IanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument33 pagesRespirationgosa seyoumNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument22 pagesRespiration Notesnitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- Respiration Revision NotesDocument2 pagesRespiration Revision NotesShivam PersadNo ratings yet
- Transportasi Gas RespirasiDocument48 pagesTransportasi Gas RespirasiAdriyan SikumalayNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis DR Maira Mahmood Associate Professor BiochemistryDocument145 pagesGlycolysis DR Maira Mahmood Associate Professor BiochemistryMaira MahmoodNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY 2nd Qtr. LectureDocument24 pagesBIOLOGY 2nd Qtr. LectureAnicah Kiersten SilvaNo ratings yet
- Botany - RespirationDocument17 pagesBotany - RespirationAira TanganNo ratings yet
- Botany - RespirationDocument17 pagesBotany - RespirationAira Germaine TanganNo ratings yet
- Respiration BiologyDocument25 pagesRespiration BiologyYoan YasrilNo ratings yet
- Note BiotechnologyDocument6 pagesNote BiotechnologyHala AlzuhairiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in PlantsDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration in PlantsMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document14 pagesChapter 14Yash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)Document47 pagesCalvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)L'ya Lieslotte100% (2)
- Tema 7quim Al17-18Document53 pagesTema 7quim Al17-18noelia100997No ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument23 pagesGlycolysiseilluj otilobNo ratings yet
- Gases and Vapours@rautbholaDocument12 pagesGases and Vapours@rautbholaBholakant RautNo ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 21 RespiDocument48 pagesBio Lesson 21 RespiChlzy ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Nursing L2-2Document39 pagesCarbohydrate Nursing L2-2Manoj SinghNo ratings yet
- Science Daily Lesson l44Document48 pagesScience Daily Lesson l44Audie Nocedo MontecastroNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument40 pagesCellular RespirationmsmimeeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Second PPP PDFDocument16 pagesLecture 10 Second PPP PDFMadani TawfeeqNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules BST NotesDocument11 pagesBiomolecules BST NotesAppuruNo ratings yet
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationDocument2 pagesC6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationHarleen BalNo ratings yet
- Biology 101 Lab Exam Ii Study GuideDocument9 pagesBiology 101 Lab Exam Ii Study GuideAllison100% (1)
- Energy TransformationDocument55 pagesEnergy Transformationelyza gwenNo ratings yet
- Respiration and PhotorespirationDocument29 pagesRespiration and PhotorespirationThảo UyênNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria Cellular RespirationDocument65 pagesMitochondria Cellular Respirationpotski413No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument36 pagesCellular RespirationWillow ItchiroNo ratings yet
- Biosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionDocument5 pagesBiosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionspenzercadienteeNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes (2022-2024 Syllabus) 2Document7 pagesSummary Notes (2022-2024 Syllabus) 2Maaz UsamaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument45 pagesPhotosynthesisUmarNo ratings yet
- MIT Environment 10-19-04Document3 pagesMIT Environment 10-19-04Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants LiveDocument73 pagesRespiration in Plants LiveGovind Mani BhattNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesMicrobiologymbkal3liNo ratings yet
- Types of RespirationDocument5 pagesTypes of RespirationJevelyn Mendoza FarroNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Notes: RespirationDocument46 pagesUnit 5 Notes: Respirationbody fayezNo ratings yet
- On Lesson 14 Nucleic Acids and LipidsDocument40 pagesOn Lesson 14 Nucleic Acids and LipidsKamto EzenwamaduNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Prof. S. Dutta GuptaDocument41 pagesPhotosynthesis: Prof. S. Dutta Guptahimanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Ch.14Document51 pagesGlycolysis Ch.14Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- 06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFDocument5 pages06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of FoodDocument13 pagesBiological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of Foodsagar sagu100% (1)
- Powering The Cell-Cellular RespirationDocument37 pagesPowering The Cell-Cellular RespirationMarjorie VistaNo ratings yet
- Apex Institute of Management Studies and ResarchDocument35 pagesApex Institute of Management Studies and ResarchSHEKHAR PRASADNo ratings yet
- Summary of Cellular RespirationDocument25 pagesSummary of Cellular RespirationHeric ValdemoroNo ratings yet
- B2 - Bacterial Metabolism - pptx-1Document151 pagesB2 - Bacterial Metabolism - pptx-1CIPSITNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceDocument35 pagesFundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceAlthea DoradoNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument10 pagesAnaerobic Respirationnadya munawwarohNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument31 pagesCellular Respirationyudi prakasaNo ratings yet
- 06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in PlantsDocument7 pages06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in PlantsAyush ShindeNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems EssayDocument2 pagesCarbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems EssayDavidIsmailBarkerNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture No.4 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Chapter:-Plant CellDocument14 pagesOnline Lecture No.4 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Chapter:-Plant CellwatashiwayakinikuNo ratings yet
- UNIT PhotosynthesisDocument51 pagesUNIT PhotosynthesisHamza MansoorNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in Animals Plants Notes-2022-2023Document17 pagesCellular Respiration in Animals Plants Notes-2022-2023MARIA ISABILLE DUALLO MUSONGNo ratings yet
- Go + Gerund List PDFDocument2 pagesGo + Gerund List PDFmangueiralternativo0% (1)
- Players Coalition Letter To Congress Re - Amash-Pressley Bill PDFDocument11 pagesPlayers Coalition Letter To Congress Re - Amash-Pressley Bill PDFNik DeCosta-KlipaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesMuscular SystemJane AngNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Plant Glycolysis and FermentationDocument8 pagesReactions of Plant Glycolysis and FermentationxbNo ratings yet
- Aramex PricelistDocument3 pagesAramex PricelistTonySaabNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 3 Prelim To MidtermDocument55 pagesPhysical Education 3 Prelim To MidtermJo CeNo ratings yet
- แบบฝึกหัด Present Continuous TenseDocument5 pagesแบบฝึกหัด Present Continuous Tenseพันธุ์เทพ คําพองNo ratings yet
- Training Load and Its ROle in Injury Prev Part 1Document8 pagesTraining Load and Its ROle in Injury Prev Part 1Barbara-Rose KolozsNo ratings yet
- Flange Moto EngDocument6 pagesFlange Moto EngalexandrubuduNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Object-Oriented ProgrammingDocument11 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Object-Oriented ProgrammingSebastianNo ratings yet
- Wimbeldon 2012 Prizemoney BreakdownDocument1 pageWimbeldon 2012 Prizemoney BreakdownVijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Workout PlanDocument3 pagesWorkout PlanRian DewantoNo ratings yet
- Cricket Rules 2021Document2 pagesCricket Rules 2021Niranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Start List: Ihsa Girls 3A Sectional 1Document8 pagesStart List: Ihsa Girls 3A Sectional 1Carson From MilesplitNo ratings yet
- Retailer Performance Report - Cargo Motors, AhmedabadDocument8 pagesRetailer Performance Report - Cargo Motors, AhmedabadJammieNo ratings yet
- Maradona WorksheetDocument2 pagesMaradona WorksheetCandela IllodoNo ratings yet
- BoxRec Mike TysonDocument4 pagesBoxRec Mike TysonSoniNo ratings yet
- OwnerManual Spigarelli DMSDocument8 pagesOwnerManual Spigarelli DMSPak Cik FauzyNo ratings yet
- 9 Al Bandar Swimming Pool Log FormDocument4 pages9 Al Bandar Swimming Pool Log Formabokoraa100% (1)
- Mental or Physical Action Verbs WorksheetDocument2 pagesMental or Physical Action Verbs Worksheetmyskss100% (1)
- Mundial Master BudapestDocument780 pagesMundial Master BudapestOscar SwimmerNo ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document39 pagesWa0005.kumarayush6047No ratings yet
- BadmintonDocument2 pagesBadmintonMarcus CaraigNo ratings yet
- What Will You Learn From This Module?: Module 8: Cheer Leading and Cheer DanceDocument9 pagesWhat Will You Learn From This Module?: Module 8: Cheer Leading and Cheer DanceRyuuki LaciaNo ratings yet
- Dual Sports Second QuarterDocument12 pagesDual Sports Second Quarterjanice may relampagos100% (1)
- Grade 9 P.E. Q4 Module 1 2 WK1 2raDocument16 pagesGrade 9 P.E. Q4 Module 1 2 WK1 2raRealyn Mabansag100% (2)
- 1v1 Attacking: What This Session Is About What To Think AboutDocument7 pages1v1 Attacking: What This Session Is About What To Think AboutNAYIM OZNAIMNo ratings yet