Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metabolism: Lesson 4
Uploaded by
DASH0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views10 pagesOriginal Title
04_Metabolism
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views10 pagesMetabolism: Lesson 4
Uploaded by
DASHCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Metabolism
Lesson 4
This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY
• it is the total chemical reactions not occurs in
the body of the Organism .
Two types of metabolism
✓ Anabolic reactions: This type of reaction
builds molecules. Specifically, small molecules
are combined into large molecules for repair,
What is growth, or storage.
✓ Catabolic reactions: This type of reaction
metabolism breaks down molecules to release their stored
? energy.
Cells transfer energy between anabolic and
catabolic reactions by using an energy
middleman — adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Energy from catabolic reactions is transferred
to ATP, which then provides energy for
anabolic reactions
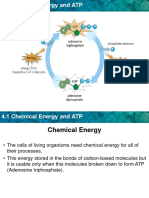
• ATP has three phosphates
attached to it. When ATP supplies
energy to a process, one of its
phosphates gets transferred to
another molecule, turning ATP
into adenosine diphosphate
(ADP). Cells re-create ATP by
using energy from catabolic
reactions to reattach a phosphate
group to ADP. Cells constantly
build and break down ATP,
creating the ATP/ADP cycle.
This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA
Consuming food for matter
and energy
• Food molecules — in the form of proteins,
carbohydrates, and fats — provide the matter
and energy that every living thing needs to fuel
anabolic and catabolic reactions and create
ATP.
✓ Organisms need matter to build their cells so
they can grow, repair themselves, and
reproduce.
✓ Organisms need energy so they can move,
build new materials, and transport materials
around their cells.
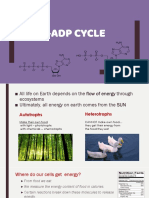
Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Autotrophs - can make their own food. Auto means “self,”
and troph means “feed,” so autotrophs are self-feeders.
Plants, algae, and green bacteria are all examples of
autotrophs.
Heterotrophs -have to eat other organisms to get their food.
Hetero means “other,” so heterotrophs are quite literally other-feeders.
Animals, fungi, and most bacteria are examples of heterotrophs. Food
is made through one process and broken down through another
Photosynthesis
and Cellular
respiration
Photosynthesis
• The process of making food using sunlight
• Occurs in plants , algae and some bacteria
• They produce glucose
• They use the energy from the sun ,Carbon dioxide from the air , in
water from the soil to produce sugar called glucose
• It is an example of a anabolic reaction
• Occurs in the chloroplasts of a plant cell
Cellular Respiration
• The process of breaking down glucose to produce
energy in the form of ATP .
• Occurs in all eukaryotic cells
• it uses oxygen To breakdown glucose molecule .
• It occurs in the mitochondria .
• it is an example of an catabolic reaction .
Photosynthesis:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Cellular respiration:
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Usable Energy
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Bio103 Fall 2022 T08Document28 pagesBio103 Fall 2022 T08Noshin TabassumNo ratings yet
- Flow of Energy Part 1Document18 pagesFlow of Energy Part 1nancie8No ratings yet
- Metabolism and AtpDocument20 pagesMetabolism and AtpAbdul Rafay ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Cell (Energy)Document15 pagesThe Cell (Energy)Luka IvanovicNo ratings yet
- The Energy of LifeDocument22 pagesThe Energy of LifeAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Nergy: Big PictureDocument2 pagesNergy: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- BionergeticsDocument4 pagesBionergeticsAriadna Adrienne CaparrosNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 Lec 5 NotesDocument15 pagesBio 101 Lec 5 NotesSumaita KhanNo ratings yet
- Metabolism:: Atp: ATP Is Produced by Almost All Living Things in Their Cell's OrganellesDocument3 pagesMetabolism:: Atp: ATP Is Produced by Almost All Living Things in Their Cell's OrganellesAngelo DecenaNo ratings yet
- ATP CYCLE: HOW CELLS HARNESS CHEMICAL ENERGYDocument28 pagesATP CYCLE: HOW CELLS HARNESS CHEMICAL ENERGYRahmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Second GradingDocument7 pagesGen Bio - Second GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- 04 Energy of Life Atp 2014Document10 pages04 Energy of Life Atp 2014api-240330821No ratings yet
- Coupled Reactions and Importance of Chloropyll and Other PigmentsDocument8 pagesCoupled Reactions and Importance of Chloropyll and Other PigmentsPerlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Part 1Document9 pagesRespiration Part 1FirozNo ratings yet
- Transes Biochem Cellular MetabolismDocument5 pagesTranses Biochem Cellular MetabolismPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- Cellular Energy Currency: ATP Powers MetabolismDocument29 pagesCellular Energy Currency: ATP Powers MetabolismClaire WeerepasNo ratings yet
- G10 Biology Chemical Energy and ATP Presentation 47795Document7 pagesG10 Biology Chemical Energy and ATP Presentation 47795haythamkhairallaNo ratings yet
- Energy and Life: Lesson SummaryDocument3 pagesEnergy and Life: Lesson Summaryandrea plalu100% (1)
- 8.1 How Do Organisms Obtain Energy?Document13 pages8.1 How Do Organisms Obtain Energy?Naledi Noxolo BhenguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Section 1 SciDocument3 pagesChapter 9 Section 1 SciThere is only 2 Genders100% (1)
- Module 8 PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesModule 8 PhotosynthesisSeann ReyesNo ratings yet
- BIO Mod1 Bioenergetics PDFDocument7 pagesBIO Mod1 Bioenergetics PDFyoufalltimeaftertimeNo ratings yet
- Biology RevisionDocument92 pagesBiology Revisionsohaila ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Energy and Metabolism Energy and MetabolismDocument17 pagesEnergy and Metabolism Energy and MetabolismSebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ExplainedDocument54 pagesCellular Respiration ExplainedAila Grace PeriodicoNo ratings yet
- Energy-ATP: How Cells Store and Use EnergyDocument18 pagesEnergy-ATP: How Cells Store and Use EnergyazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Stages of Metabolism IDocument29 pagesStages of Metabolism IKiran ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationsDocument21 pagesEnergy TransformationsLove CayaNo ratings yet
- 9.1. Energy and LifeDocument19 pages9.1. Energy and Lifehanatabbal19No ratings yet
- B 10 VRV 3081Document16 pagesB 10 VRV 3081api-283593849No ratings yet
- MYP Cell Respiration PDFDocument23 pagesMYP Cell Respiration PDFRishar bokNo ratings yet
- ATP-ADP Energy CycleDocument24 pagesATP-ADP Energy CycleIromeVan PaburianNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument19 pagesEnergy TransformationRicardo ErioNo ratings yet
- NHM - Ar Etapa 2 - LNDVDocument10 pagesNHM - Ar Etapa 2 - LNDVNatalia Hernandez MontelongoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document6 pagesAssignment 2Latifah EmamNo ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesCellular Respirationapi-329164492No ratings yet
- Metabolic ProcessesDocument6 pagesMetabolic ProcessesMark Andrian PontanalNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument5 pagesBio Notes20236637No ratings yet
- ATP's Role in Energy Coupling and TransferDocument10 pagesATP's Role in Energy Coupling and TransferKivo ZoshikoroNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document4 pagesUntitled 1Umang MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- All Cells Need Chemical Energy.: Key ConceptDocument15 pagesAll Cells Need Chemical Energy.: Key ConceptPrasanna Naresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Microbial Physiology and GeneticsDocument47 pagesChapter 7 Microbial Physiology and Geneticsmarilyngalutera8No ratings yet
- ReportDocument20 pagesReportJeth JuradoNo ratings yet
- Energy - MetabolismDocument45 pagesEnergy - MetabolismAngel GustasianaNo ratings yet
- 04 Energy TransformationDocument53 pages04 Energy TransformationlyleandreihendersonNo ratings yet
- Micropara Transes 1.2Document4 pagesMicropara Transes 1.2Kyla Marie BadanaNo ratings yet
- Module 12: How Animals Obtain and Use EnergyDocument13 pagesModule 12: How Animals Obtain and Use EnergyJohn Bernard VeloriaNo ratings yet
- How Animals Survive Lesson 5Document30 pagesHow Animals Survive Lesson 5Ellah LaguismaNo ratings yet
- SciFusTX Grade7 U03L05 PowerNoteDocument14 pagesSciFusTX Grade7 U03L05 PowerNoteEsther SaraviaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Anaerobic Cellular ResDocument21 pagesAerobic Anaerobic Cellular ResRex IanNo ratings yet
- II.C. The Energy Flow From Environment To CellsDocument14 pagesII.C. The Energy Flow From Environment To CellsDarwin NoolNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (Stem)Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Stem)Gladelyn Aquino MoralesNo ratings yet
- Energy Metabolism-General 3Document75 pagesEnergy Metabolism-General 3Amanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument5 pagesGenbioYkhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversions1Document3 pagesEnergy Conversions1api-327757745No ratings yet
- Key points on metabolism and its componentsDocument4 pagesKey points on metabolism and its componentsKathleen RamiloNo ratings yet
- G4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2Document6 pagesG4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2niru098No ratings yet
- Biology SimplifiedDocument59 pagesBiology Simplifiedoussama6928No ratings yet
- 06 PhotosynthesisDocument63 pages06 PhotosynthesisDASHNo ratings yet
- 07 - Cell CycleDocument65 pages07 - Cell CycleDASHNo ratings yet
- 05 - Cellular RespirationDocument31 pages05 - Cellular RespirationDASHNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument39 pagesSkeletal SystemDASHNo ratings yet
- 03 - Cell Transport PDFDocument30 pages03 - Cell Transport PDFDASHNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument45 pagesIntegumentary SystemDASHNo ratings yet
- 02 - The CellDocument91 pages02 - The CellDASHNo ratings yet
- The Four Primary Tissue TypesDocument33 pagesThe Four Primary Tissue TypesDASH100% (2)
- Observation - Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument4 pagesObservation - Sub Atomic ParticlesDASHNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Part IIDocument42 pagesSkeletal System Part IIDASHNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Human AnatomyDASHNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Force: Definition of Force and The Type of ForcesDocument15 pagesMeaning of Force: Definition of Force and The Type of ForcesDASH100% (1)
- Gen. Tiburcio de Leon National High School Table of Specification in 1 Quarter Science Unit TestsDocument2 pagesGen. Tiburcio de Leon National High School Table of Specification in 1 Quarter Science Unit TestsDASHNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument7 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceHanny AusteroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Energy Transformation 1 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan - Energy Transformation 1 1api-313793053No ratings yet
- Enviromental Awareness in StudentsDocument9 pagesEnviromental Awareness in StudentsAvinash GodaraNo ratings yet
- Q1 Science 9 Module 5Document28 pagesQ1 Science 9 Module 5Shiena Lou Tucasan CudadaNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument80 pagesEcologyaryan aggarwal100% (1)
- SHS Earth and Life Science Quarter 2 Module 2 Colored.Document17 pagesSHS Earth and Life Science Quarter 2 Module 2 Colored.Naima KahlenNo ratings yet
- Life Processes & Nutrition ModesDocument2 pagesLife Processes & Nutrition ModesTechnical Ayush100% (1)
- Ge Elect 103 Environmental Science: Amabel Marina C. Marcaida, Mase Assistant Professor 3Document22 pagesGe Elect 103 Environmental Science: Amabel Marina C. Marcaida, Mase Assistant Professor 3Paula Bianca DomingoNo ratings yet
- Man's Impact on EnvironmentDocument14 pagesMan's Impact on EnvironmentdimpledblissNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument46 pagesBiological ClassificationParulNo ratings yet
- 13 PDFDocument40 pages13 PDFThiên Trang TrầnNo ratings yet
- Module 5 EALSDocument9 pagesModule 5 EALSKleffer YnanNo ratings yet
- 2 Flow of Energy in An EcosystemDocument3 pages2 Flow of Energy in An EcosystemNikolai MooreNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessDocument8 pagesLife ProcessKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Ecosystem and Its ComponentDocument12 pagesModule 2 The Ecosystem and Its ComponentJonaria CopisNo ratings yet
- Microbial Growth Requirements and Nutrient Transport ProcessesDocument71 pagesMicrobial Growth Requirements and Nutrient Transport ProcessesSumit RaiNo ratings yet
- Notes - Life Processes - Nutrition - C-X - PART-IDocument5 pagesNotes - Life Processes - Nutrition - C-X - PART-Ipratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- FoodforthoughtDocument5 pagesFoodforthoughtapi-235959158No ratings yet
- IBecologyDocument85 pagesIBecologyOscar CosmeNo ratings yet
- LESSONS ON MICROSCOPES AND LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATIONDocument28 pagesLESSONS ON MICROSCOPES AND LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATIONkentxy ddfsNo ratings yet
- GED110 Quiz 1 6Document52 pagesGED110 Quiz 1 6Christian PatrickNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Ariana Boisvert - GLWeek25Document9 pagesKami Export - Ariana Boisvert - GLWeek25Ariana BoisvertNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem EssayDocument3 pagesEcosystem Essaymichelle_14100% (1)
- LESSON 1 NotesDocument6 pagesLESSON 1 NotesManish YarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Components and InteractionsDocument31 pagesEcosystem Components and InteractionsBirraa TajuNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 10 Notes - Nutrition, Photosynthesis, ExperimentsDocument232 pagesBiology Class 10 Notes - Nutrition, Photosynthesis, ExperimentsAnonymous njBpxOMBvWNo ratings yet
- G7 Lesson5 PhotosynthesisDocument19 pagesG7 Lesson5 PhotosynthesisAbdulrahman KhabbazNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENTDocument112 pagesPRINCIPLES OF INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENTShimul DasNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: Ecosystems and BiodiversityDocument55 pagesEnvironmental Science: Ecosystems and BiodiversityRohith VKNo ratings yet
- Biology Summary NotesDocument2 pagesBiology Summary NotesD'zite JereNo ratings yet