Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2
Uploaded by
niru0980 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesOriginal Title
G4-BIOENERGETICS-and-EVIDENCE-OF-EVOLUTIION-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesG4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2
Uploaded by
niru098Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
The two types of membranous organelles
GROUP 4 that specialize in energy conversion are1:
Chloroplasts: use solar energy to make
MEMBERS:
carbohydrates by using photosynthesis.
Aera Faith Depetillo
Mitochondria: break down carbohydrates to
Rosever Rio Demaisip
produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP
Myra Amethyst Opina supplies the energy the cell needs to do
Gabrielle Nicole Benedicto work.
Daves Alido
Kurt Ydan Gerada PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Nahj Christian Dalde
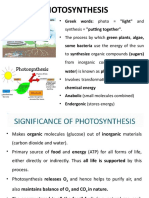
Vinz IIisan photo meaning ''light'' and synthesis
meaning "to make" Photosynthesis is the
BIOENERGETICS AND THE PROCESS OF
process by which plants use sunlight, water,
EVOLUTION and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and
energy in the form of sugar.
THE CELL AND ITS ENERGY
How do cells obtain energy? Energy and PHOTOSYNYHRSIS SONG
Metabolism: Bioenergetics is the study of https://youtu.be/m2XzeJQOY4g
energy flow in living systems, particularly in
cells. Cells perform chemical reactions, AUTOTROPH
some of which release energy while others An autotroph is an organism that can
require energy. Like how living organisms produce its own food using light, water,
need food to maintain their energy, cells carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. Because
must produce energy to support their various autotrophs produce their own food, they are
chemical reactions. The collective term for sometimes called producers.
all these cellular reactions, whether they
consume or produce energy, is referred to as Photosynthesis takes place in...
cell metabolism. CHLOROPLAST
A chloroplast is an organelle within the cells
PARTS OF THE CELL of plants and certain algae that is the site of
The cell membrane, which encloses the cell photosynthesis, which is the process by
and regulates the passage of substances in which energy from the Sun is converted into
and out of the cell. The nucleus, which chemical energy for growth also contain the
contains the genetic material (DNA) and pigment chlophyll that absorve light.
controls the cell's activities. The cytoplasm,
which is the fluid-filled space between the THYLAKOID
cell membrane and the nucleus, where Thylakoids are interconnected disc-like sacs
various organelles are located. The of the internal membrane system of the
organelles, which are specialized structures chloroplast. They are found suspended in the
that perform specific functions for the cell, stroma the thylakoids are arranged in tight
such as energy production, protein synthesis, stacks called grana (singular granum)
and waste disposal.
STROMA
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE OF The stroma is the part of the chloroplast
PLANT SELL AND ANIMAL CELLS where the ingredients for photosynthesis
Plant cells have a cell wall that provides (carbon dioxide, light, water) are mixed
structure and support, while animal cells do together. This mixture is turned into oxygen
not and sugar (food) for the plant.
Plant cells have a large central vacuole that GRANUM
stores nutrients and waste, while animal the thylakoids are arranged in tight stacks
cells have smaller or no vacuoles called grana (singular granum)
SPECIALIZED CELL ORGANELLES Photosynthesis involves carbon dioxide and
Organelle, any of the specialized structures water reacting with light energy to produce
within a cell that perform a specific function glucose and oxygen.
(e.g., mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic
reticulum). Organelles in unicellular
organisms are the equivalent of organs in
multicellular organisms.
PHOTOSYNTHESIS STAGES into the membrane and later pumped back
into the matrix.
LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTION
•requires photons from light What are the reactants of cellular
•takes place in between thylakoids respiration?
•uses light and water to produce oxygen and 2 The reactants of cellular respiration are
energy carrying molecules:
oxygen and sugar, which are the products of
a. ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) - energy
currency of the coll photosynthesis. Cellular respiration occurs
b. NADPH (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in plant and animal cells. Plants use sunlight
phosphate hydrogen) during photosynthesis to convert energy
from the sun in order to manufacture sugar
LIGHT-IDEPENDENT REACTIONS and the chemical energy ATP and to release
•also known as the calvin cycle oxygen.
•does not require light
•takes place in the stroma What are the products of cellular
•uses carbon dioxide and NADPH to produce respiration?
sugar Energy (or ATP)
Carbon dioxide
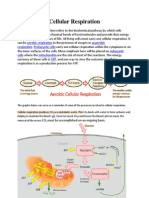
Cellular Respiration Water
What is cellular respiration? Cellular
respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses The products of respiration or breathing,
glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate come from the reactions of cellular
(ATP), an organic compound the body can respiration. In animals, carbon dioxide is
use for energy. transported back to the lungs through the
blood and exhaled through exhalation.
*One molecule of glucose can produce a net
of 30-32 ATP. What goes in the TCA or Krebs Cycle
The Krebs Cycle Memory Aid
What is the purpose of cellular
respiration? Anaerobic respiration
Cellular respiration is used to generate
usable ATP energy in order to support many With no oxygen oxidative
other reactions in the body. ATP is phosphorylation and Krebs cycle
particularly important for energetically cannot take place. (Cells without
unfavorable reactions that would otherwise mitochondria cannot respire
not occur without an energy input. aerobically - e.g. red blood cells)
What are the main steps of cellular In anaerobic respiration glycolysis
respiration? takes place as usual yielding
There are three main steps of cellular pyruvate and a small amount of
respiration: ATP.
Glycolysis;
The citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; If pyruvate levels were allowed to
And the electron transport chain, where build up it stop glycolysis and inhibit
oxidative phosphorylation occurs. ATP production, also the reduced
The TCA cycle and oxidative NAD produced must be oxidised
phosphorylation require oxygen, while back or else the cell would run out of
glycolysis can occur in anaerobic conditions. it again stopping - ATP production.
Where does cellular respiration take
place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the Anaerobic respiration
cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of
the body. Two solutions to this problem: Alcoholic
fermentation - used by fungi and plants
Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm,
while the TCA cycle occurs inside the Lactic fermentation - used by animals
matrix of the mitochondria.
Meanwhile, oxidative phosphorylation
occurs on the inner mitochondrial
membrane, with protons diffusing across
EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION an error during other forms of repair, or
cause an error during replication (translesion
FOSSIL RECORD`S synthesis). Mutations may also result from
insertion or deletion of segments of DNA
By studying the fossil record,experts found due to mobile genetic elements.
out the existence of animals that lived over
millons of years.fossil are the remains of
living things that were mineralized over a
long priod of time this remains could Adaptive Evolution
bones,imprints on rock,and a burrow or
tunnel of ancient worms.Most of the fossil What is Adaptive Evolution?
excavated are bones,seeds,imprints of plants
and shells,and pollen grains.scientists use Adaptive evolution is the process by which a
radioactive dating to measure the age of the population of organisms undergoes genetic
fossil or the age of the rock where the fossils changes over generations, leading to the
are found . development and proliferation of traits that
enhance the individuals' ability to survive
Geographic Distribution and reproduce in their specific environment.
These advantageous traits, which are often a
the Geographic distribution is the natural result of natural selection, become more
arrangement of various species or taxa of common in the population, while less
living organisms in thier appropriate habitats beneficial traits may decrease in frequency.
on the Earth . the mainly of three types of Adaptive evolution is a fundamental
geographic distribution are cosmopolitan mechanism of evolution that enables species
,endemic and disjunct distribution. to better adapt to their changing
surroundings and is essential for the
Comparative Anatomy diversity and adaptation of life on Earth.
the comparative study of the body structures Importance of adaptive evolution in
of different species of animals in order to biology
understand the adaptive changes they have
undergone in the course of evolution from Adaptive evolution is a cornerstone of
common ancestors.what seems to be entirely biology, as it represents the mechanism
different organisms like man,whale,bat,and through which species evolve and adapt to
dog, actually have similar anatomical their changing environments over time. It's a
features.the arm of man,the lateral fin of the fundamental process for the survival and
whale ,the wing of bat and the leeg of dog diversification of life on Earth. This
are similar in structure although their continual adaptation allows organisms to
functions. exploit new ecological niches, resist
diseases, and respond to environmental
The Common traits in embaryo challenges, ultimately driving the
remarkable diversity and complexity of life
the early developmental stage of an animal we observe today.
while it is in the egg or within the uterus of
the mother. In humans the term is applied to What is evolution?
the unborn child until the end of the seventh
week following conception; from the eighth Evolution is the process by which species of
week the unborn child is called a fetus. organisms change over time through the
gradual accumulation of genetic variations.
GENETIC CHANGES This change is driven by mechanisms like
natural selection, genetic mutation, and
mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid genetic drift. Charles Darwin was a British
sequence of the genome of an organism, naturalist who is famously known for his
virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral theory of evolution by natural selection. In
genomes contain either DNA or RNA. his seminal work, "On the Origin of
Mutations result from errors during DNA or Species" published in 1859, Darwin
viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other proposed that species evolve over
types of damage to DNA (such as generations due to the differential survival
pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to and reproduction of individuals with
ultraviolet radiation), which then may advantageous traits. This theory
undergo error-prone repair (especially revolutionized our understanding of the
microhomology- mediated end joining) cause
diversity of life on Earth and is a DIVERGENT EVOLUTION
fundamental concept in biology.
Divergent Evolution is when a species diverges
over time into two different species, resulting in
a species becoming less like the original one.
Here are some key facts about adaptive Live in different ways than the common
evolution: ancestor.
•Natural Selection: Adaptive evolution is
primarily driven by natural selection, a
process proposed by Charles Darwin. In Classification based on evolutionary
natural selection, organisms with traits that history
provide an advantage in a particular
environment are more likely to survive, What isclassification based on evolutionary
reproduce, and pass on their advantageous history?
traits to the next generation.
Classification based on evolutionary history,
•Genetic Variation: For adaptive evolution also known as phylogenetic classification, is
to occur, there must be genetic variation a method of organizing and categorizing
within a population. This variation arises organisms based on their evolutionary
from mutations, genetic recombination, and relationships. This approach utilizes the
other sources. principles of speciation and common
ancestry to determine the classification of
•Environmental Pressure: Environmental different species.
factors, such as changes in climate, habitat,
or the presence of predators, create selective 1. Phylogenetic Trees- classify organisms
pressures. Organisms with traits that enable based on their evolutionary history,
them to better adapt to these pressures have scientists construct phylogenetic trees,
a higher chance of survival and which are diagrams that show the
reproduction. relationships between different species.
These trees branching patterns represent the
•Differential Reproduction: Organismswith divergence of species from common
advantageous traits are more likely to ancestors.
reproduce and pass on those traits to their
offspring. This leads to an increase in the 2. Taxonomy- involves naming, defining,
frequency of those traits within the and classifying organisms whether it is alive
population. or extinct. Classification based on
evolutionary history is an integral part of
Evidence of Adaptive Evolution taxonomy, and it helps to establish a
hierarchical system for organizing
Fossil Records: Fossils show the gradual organisms into groups, or taxonomic ranks.
changes in species' physical characteristics
over millions of years, reflecting adaptations 3. Phylogenetic Inference- Scientists use
to changing conditions. Comparative various methods to infer evolutionary
Anatomy: Similarities and differences in the relationships between species. These
anatomy of different species reveal methods include analyzing morphological
adaptations to their respective environments traits, DNA sequences, and other genetic
and lifestyles. information. By comparing these
characteristics across species, scientists can
Molecular Biology: Genetic and molecular determine the degree of relatedness.
studies reveal changes in DNA sequences
over time, indicating how organisms have 4. Cladistics - is a method of classifying
adapted to different ecological niches. organisms based on shared characteristics,
known as "clades." A clade is a group of
Convergent Evolution organisms that includes an ancestor and all
of its descendants. This approach focuses on
Convergent evolution is the process by identifying and analyzing shared derived
which unrelated or distantly related characteristics, known as synapomorphies,
organisms evolve similar body forms, to establish evolutionary relationships.
coloration, organs, and adaptations.
5. Homology-Classification based on continuously being added to the population
evolutionary history relies heavily on the through the process of mutation. This
concept of homology. Homologous process increases the variety of organisms.
structures are similar in different species
because they are inherited from a common All individuals choose their own mates for a
ancestor, indicating a close evolutionary specific reason. The choosing of a mate
relationship. These homologous eliminates the less fit individuals. Animal
characteristics are used to establish breeders use nonrandom selection of mate
groupings and relationships between species for the animals they want to breed. Mostly,
they choose animals with advantageous
How did populations of organisms change traits and breed them to increase the
over time? frequency of animal offspring having their
chosen desirable traits. Nonrandom mating
Evolution in the population is brought about causes evolution because it disrupts the
by different agents. These are the genetic natural pool of gene variations.
drift, gene flow, mutations, nonrandom
mating, and natural selection. Genetic drift
is a change in the gene pool of a population
due to chance. There is an unpredictable References:
fluctuation in frequency of alleles from one https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/a
generation to another. Examples of genetic daptive-
drift are the bottleneck effect and the founder evolution#:~:text=Adaptive%20evolution%
effect. 20pertains%20to%20evolutionary,to%20fit
%20to%20an%20environment.
Bottleneck effect https://animaldiversity.org/animal_names/ph
ylogeny_ranks/
The bottleneck effect occurs when there is a http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/re
great reduction in size of populations due to ading-a-phylogenetic-tree-the- meaning-of-
environmental factors such as forest fires, 41956#:~:text=A%20phylogenetic%20tree
earthquakes, and floods. Reduction of %2C%20also%20known,genes%20from%2
genetic variation also occurs after events 0a%20common%20ancestor.
such as low genetic diversity of population https://www.cbd.int/gti/taxonomy.shtml
has passed on from generation to generation
with little or slow increase of variation due
to mutation. Low genetic variation reduces
the chance of a population to have a
representative that would adapt in a
changing environment. On the contrary,
depending on the kind of organisms in the
bottleneck, the survivor may have been the
most adaptive individual; thus, improving
the traits within the population gene pool.
Founder effect
The founder effect happens when a small
population of organisms breaks away from
the larger group to colonize a new area. As a
result, the population may not always
represent the diversity of their species. The
loss of genetic variations in the small
population happens.
Gene flow is defined as the movement of
alleles into or out of a population. It occurs
when there is migration of fertile individuals
between populations. This tends to increase
the gene diversity in the populations.
Mutation occurs when there is a change in
genetic makeup, during the DNA replication
caused by radiation or other environmental
stressors. New variants of genes are
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- ATP-ADP Cycle and Cellular Respiration ExplainedDocument4 pagesATP-ADP Cycle and Cellular Respiration ExplainedKurt IgotNo ratings yet
- Cell EnergyDocument29 pagesCell EnergyKimberly Anne T. RinNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist ButonDocument13 pagesLecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist Butonsifa al rishalNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration and Cellular Energy ProductionDocument14 pagesAnaerobic Respiration and Cellular Energy ProductionAbegail AcedoNo ratings yet
- Concept of Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesConcept of Cell Structures and FunctionsTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- ELS HardDocument3 pagesELS HardmppsregistrarNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesisJESSERYL MARGALLONo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesDocument11 pagesCH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesEvannaCoronaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFheby ValerieNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis converts sunlight into energyDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis converts sunlight into energyLJ RacadioNo ratings yet
- Q2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesQ2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationRaph tsuNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastAsma Adawiyah Idris100% (1)
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocument37 pagesPhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273No ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Power and Capture EnergyDocument4 pagesMitochondria and Chloroplasts Power and Capture EnergyCheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- GN 3.3 - Cell RespirationDocument7 pagesGN 3.3 - Cell RespirationJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- 04 Energy TransformationDocument53 pages04 Energy TransformationlyleandreihendersonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Photosynthesis and Plant ProcessesDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Photosynthesis and Plant ProcessesQuynh Dang PhuongNo ratings yet
- How Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Work TogetherDocument5 pagesHow Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Work TogetherKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIONDocument6 pagesMITOCHONDRIONCheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- Bio EnergeticsDocument36 pagesBio EnergeticsKimberly Jean EstoqueNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument32 pagesPhotosynthesis & RespirationCarson SchultzNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast: Nature's Food FactoryDocument8 pagesChloroplast: Nature's Food FactoryJerome GamitNo ratings yet
- Cemical Energy and ATP: ATP Is A Molecule With Three Phosphate Groups Attached To The EndDocument12 pagesCemical Energy and ATP: ATP Is A Molecule With Three Phosphate Groups Attached To The EndMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 4 EcosystemDocument21 pagesTOPIC 4 EcosystemLunaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument46 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationCarmsNo ratings yet
- 3 PhotosynthesisDocument21 pages3 Photosynthesisharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Pre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleDocument4 pagesPre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleGiao TranNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument14 pagesEnergy TransformationJoaquine ArateaNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 TOPIC 5: PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Unit 4 TOPIC 5: PhotosynthesisSamara HusainNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: How Plants Convert Light to FoodDocument38 pagesPhotosynthesis: How Plants Convert Light to FoodMae AlfaroNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledSameerNo ratings yet
- Module 12: How Animals Obtain and Use EnergyDocument13 pagesModule 12: How Animals Obtain and Use EnergyJohn Bernard VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Energy For LifeDocument41 pagesUtilizing Energy For LifeJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - ReviewerDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration - ReviewerJoyce Cañal100% (1)
- Energy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesEnergy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationlovepugsNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- GBIO1 Week15 Energy Transformation Part 2Document25 pagesGBIO1 Week15 Energy Transformation Part 2marcovy dela cruzNo ratings yet
- How To Be A PlantDocument12 pagesHow To Be A PlantsextansNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Crop ScienceDocument57 pagesLesson 3. Crop ScienceKa Hilie Escote MiguelNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit TwoDocument158 pagesBiology Notes Unit TwoBlohsh KeenenNo ratings yet
- Science Powerpoint OriginalDocument63 pagesScience Powerpoint OriginalAndrea EiramNo ratings yet
- Science Powerpoint OriginalDocument63 pagesScience Powerpoint OriginalAndrea EiramNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocument61 pagesBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNo ratings yet
- Energy MetabolismDocument4 pagesEnergy MetabolismKaren ParkNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguDocument20 pagesUnit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguUkwuma Michael ChijiokeNo ratings yet
- 12. RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-2Document1 page12. RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-2aytramakhiiral06No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Lesson Explains Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument22 pagesBioenergetics Lesson Explains Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationMicaela Castillo100% (4)
- Gen Bio Q2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGen Bio Q2 Reviewer2JoshDaveTernedaNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Cellular Enegy CH 4 and 5Document71 pagesCellular Enegy CH 4 and 5G TeenaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument13 pagesRespiration in Plantsc7zb7hhq64No ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Energy Synthesis of ATP Extracellular ATPDocument4 pagesMitochondria and Chloroplasts Energy Synthesis of ATP Extracellular ATPGiancarlo CasabarNo ratings yet
- Sciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioDocument56 pagesSciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioRETLAWNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Eals 11abma1 MangosingDocument34 pagesEals 11abma1 MangosingAndrea Mae V. MangosingNo ratings yet
- Photosenthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesPhotosenthesis and Cellular RespirationMonkey D. AilaNo ratings yet
- 2011 Fractal DNADocument7 pages2011 Fractal DNAAbby SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Undergraduate Course in Zoology (Bachelor of Science Examination)Document54 pagesSyllabus For Undergraduate Course in Zoology (Bachelor of Science Examination)Ajay BhakatNo ratings yet
- LifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionDocument173 pagesLifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionSamanta Arijit100% (1)
- UNIMAS Advanced Genetics Course DetailsDocument3 pagesUNIMAS Advanced Genetics Course DetailsAlex XanderNo ratings yet
- Animal Evolutionary, Comparative, and Ecological Perspectives (CUP 1998)Document289 pagesAnimal Evolutionary, Comparative, and Ecological Perspectives (CUP 1998)Programa Ondas Valle100% (1)
- Biology NIOSDocument927 pagesBiology NIOSApshar RizwanNo ratings yet
- StatDocument105 pagesStatRatish KakkadNo ratings yet
- Human Givens - A New Approach To Emotional Health and Clear Thinking PDFDocument67 pagesHuman Givens - A New Approach To Emotional Health and Clear Thinking PDFZen Halimana100% (1)
- Benson Saler-Understanding Religion - PDFDocument256 pagesBenson Saler-Understanding Religion - PDFJcdiaz Diaz100% (1)
- Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience: Tenth EditionDocument42 pagesFoundations of Behavioral Neuroscience: Tenth EditionKaalynn JacksonNo ratings yet
- The Seven Mysteries of Life - An Exploratio - Murchie, Guy, 1907 PDFDocument708 pagesThe Seven Mysteries of Life - An Exploratio - Murchie, Guy, 1907 PDFAnonymous gwFqQcnaX100% (2)
- The Embodied MindDocument29 pagesThe Embodied Mindrstarter_og7815100% (3)
- Animal Behavior ChaptestDocument4 pagesAnimal Behavior ChaptestRommel Bauza100% (4)
- Darwin Vs Lamarck Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesDarwin Vs Lamarck Worksheet PDFZhiyong Huang100% (2)
- Kantor, J. R. (1963) - The Scientific Evolution of Psychology IDocument438 pagesKantor, J. R. (1963) - The Scientific Evolution of Psychology Ivergi100% (1)
- Evolutionary Genetics SpeciationDocument18 pagesEvolutionary Genetics SpeciationDebosruti BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- How Recombinant DNA Technology Has Improved Our LivesDocument3 pagesHow Recombinant DNA Technology Has Improved Our LivesJovin Traigo JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Places - Media and The City - Vol.18 - No.2 - 2006Document88 pagesPlaces - Media and The City - Vol.18 - No.2 - 2006TheNextOne2No ratings yet
- Nils Barricelli-Artificial Life, Coevolution, Self-AdaptationDocument3 pagesNils Barricelli-Artificial Life, Coevolution, Self-AdaptationAlptekin TorunNo ratings yet
- Ecology and EvolutionDocument4 pagesEcology and EvolutionHanaNo ratings yet
- New - Mechanisms of SpeciationDocument33 pagesNew - Mechanisms of SpeciationAidyn TemirbekovaNo ratings yet
- The City of Tomorrow. Sensors, Networks, Hackers, and The Future of Urban LifeDocument95 pagesThe City of Tomorrow. Sensors, Networks, Hackers, and The Future of Urban Lifeamorfo618No ratings yet
- Evolution of Marketing Concept PDFDocument2 pagesEvolution of Marketing Concept PDFLizNo ratings yet
- Syllabus34 PDFDocument252 pagesSyllabus34 PDFAnnoymousNo ratings yet
- Pope, R. (2005) Creativity, History, Practice PDFDocument321 pagesPope, R. (2005) Creativity, History, Practice PDFsound hour100% (1)
- Ryan e V - 2000 - Asteroid Fragmentation and Evolution of AsteroidsDocument25 pagesRyan e V - 2000 - Asteroid Fragmentation and Evolution of AsteroidsAnderson De Oliveira RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary Algorithms PDFDocument2 pagesEvolutionary Algorithms PDFAdamNo ratings yet
- Advanced - Darwin's Theory of Evolution: Visit The - C 2009 Praxis Language LTDDocument4 pagesAdvanced - Darwin's Theory of Evolution: Visit The - C 2009 Praxis Language LTDmohNo ratings yet
- New Scientist Essential Guide - No14 - Human SocietyDocument100 pagesNew Scientist Essential Guide - No14 - Human SocietyHieu Trinh100% (1)
- The Evolution of Computerized AccountingDocument2 pagesThe Evolution of Computerized AccountingMohammad Essmaeel Ali JamiNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Younger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationFrom EverandYounger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Darwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeFrom EverandDarwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (523)
- Fearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageFrom EverandFearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)