Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Notes
Uploaded by
EvannaCoronaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Notes
Uploaded by
EvannaCoronaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch.
9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation
Study Guide
A. Introduction
1. All living things need energy for metabolism.
a. Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis; break
down glucose during cellular respiration to release
energy (ATP).
b. Animals, Fungi, and non-photosynthetic Protists must
consume food & break the food molecules/organic
molecules (GLUCOSE) down to release energy (ATP).
They too carry out the process of cellular respiration.
NOTE: Photosynthetic protists such as Euglena also
metabolize glucose by the process of cellular
respiration.
2. When food molecules (a.k.a. organic molecules/carbs,
proteins, lipids) are broken down energy is released &
stored in ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
3. Production of ATP occurs in the MITOCHONDRIA of the
eukaryotic cells.
REMEMBER: MITOCHONDRIA ARE THE
POWERHOUSE OF THE CELLS.
4. Animal, fungi, protists, and plant cells are all eukaryotic
cells (have a nucleus) & all have mitochondria; therefore
they ALL produce ATP.
5. How do they produce ATP? By the process of cellular
respiration which occurs in all eukaryotic cells.
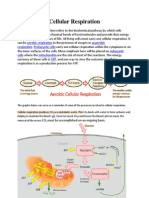
B. Anatomy of the Mitochondria
1. Outer & inner membranes are made of lipids & proteins;
has pores that allow substances to enter & leave the
mitochondria.
2. Inner membrane has folds called cristae which increase
surface area.
3. Fluid matrix refers to the fluid inside the mitochondria.
4. NOT SHOWN: Mitochondria also contain their own
ribosomes & DNA;
mitochondria are able to reproduce on their own.
REMEMBER:
mitochondria & chloroplasts are cousins to bacteria
because they all
have their own DNA, ribosomes & can reproduce on their
own (binary
fission).
C. Cellular Respiration occurs only if oxygen is present.
1. Have you ever stopped to think about how the foods you
consume on a daily basis are broken down to produce
energy? Not only do you eat food on a regular basis, but
you usually drink some type of water-based beverage
with your meal & you breathe in oxygen too.
2. All cells must do work to stay alive and maintain
homeostasis.
The energy needed for cell work comes from the bonds
of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Cells get their ATP by
breaking organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids,
& proteins), a process called cellular respiration.
Although many organic molecules can be broken down,
glucose, the main product of photosynthesis, is the
primary fuel molecule for the cells of living
organisms.
3. The energy stored in the foods organisms consume/eat is
released during the process of cellular respiration. Every
living organism, autotrophs and heterotroph,
must do cell respiration. In fact, the metabolic
pathways used in the process of cellular respiration are
the same in virtually all eukaryotic organisms, and many
prokaryotic organisms. Remember that organisms that
do photosynthesis or chemosynthesis (make their
own food molecules) are called autotrophs.
Heterotrophs obtain their food molecules by eating
other organisms. Animals, fungi, many protists and
many bacteria are heterotrophs. Plants, some
protists and some bacteria are autotrophs.
4. Eukaryotic organisms such as protists, fungi,
plants, and animals are
aerobic, meaning they need oxygen to survive. The
oxygen that you & I
breathe is needed during cellular respiration to break
down the organic
food molecules we eat and release energy that can be
stored in ATP.
5. Reactants of cellular respiration: glucose, oxygen,
water
Products of cellular respiration: carbon dioxide,
water, ATP (energy)
6. EQUATION FOR CELLULAR RESPIRATION
ENZYMES
glucose + 6 oxygen + 6 water 6 carbon dioxide + 12
water + 40 ATP/energy
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O ENZYMES
6 CO2 + 12 H2O
+ 40 ATP/energy
NOTE: What do you notice about this equation; why does it seem
familiar?
The equation for cellular respiration is the exact opposite of the equation for
photosynthesis. The products of photosynthesis become the reactants for cellular
respiration; the products of cellular respiration (carbon dioxide & water) become the
reactants for photosynthesis.
6 CO2 + 12 H2O sunlight/chlorophyll
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 +
6 H2O
sunlight/chlorophyll
6 carbon dioxide + 12 water glucose + 6 oxygen + 6
water
D. How Does Cellular Respiration Occur?
As with many metabolic processes, cell respiration has a
number of stages.
Glycolysis always occurs in the cytoplasm/cytosol of the
cell & produces
2 ATPs (Four molecules of ATP are produced during
glycolysis, but 2
molecules are consumed in activating the glucose.);
glycolysis is an
anaerobic process and does NOT need oxygen. All
living organisms go
through glycolysis; it is the most widespread
metabolic process on earth.
First prokaryotes on earth used glycolysis to produce
energy because early
atmosphere DID NOT contain oxygen.
The first stage of glucose metabolism, or cell respiration,
is a process
called glycolysis, which splits a glucose molecule
into two molecules of
pyruvate (a.k.a. pyruvic acid), a 3-carbon molecule
(these 6 carbons were
originally in glucose).
If oxygen is available and the organism has the enzymes to do
aerobic respiration, the 2 pyruvate molecules (a.k.a. pyruvic acid)
will be broken down in the next stages of aerobic respiration:
Krebs Citric Acid Cycle and Electron Transport Chain.
Krebs Citric Acid Cycle & Electron Transport Chain occurs
in the mitochondria of the cell & produces 36 ATPs. Both the
Krebs Citric Acid Cycle & Electron Transport Chain are aerobic
processes and need oxygen in order to occur.
The 2 pyruvate molecules leave the cytoplasm and enter the
mitochondria. When they enter the mitochondria they are broken
down into 6 carbon dioxide molecules during the Krebs Citric
Acid Cycle. The Electron Transport Chain takes the hydrogen from
glucose and use their energy to form ATPs. The hydrogens then
combine with the oxygen you breathe to form water.
NOTE: The 40 ATPs of energy released from a molecule of
glucose represents
40% of its stored energy; the other 60% of the energy
stored in glucose is
released as heat & helps you maintain a constant body
temperature.
E. Fermentation Cellular Respiration Without Oxygen
(Anaerobic Process)
1. Most living organisms must do aerobic cellular
respiration to stay alive and provide their cells with 40
ATPs of energy.
2. When no oxygen is available (or is in short supply) for
aerobic cellular respiration, or if the organism doesnt
have the enzymes needed for cellular respiration,
eukaryotic organisms, and some (bacteria), will break
down glucose by the process of fermentation and
produce 2 ATPs of energy.
3. Like cellular respiration, fermentation begins with
the process of
glycolysis occurring in the cytoplasm of the cell.
4. Two fermentation pathways in eukaryotes:
a. Alcoholic Fermentation occurs in yeast cells (fungi)
& some
bacteria. Used in making
bread, beer, & wine.
glucose (6C) 2 pyruvate molecules (3C) 2 ethyl alcohol (2C)
+ 2CO2 + 2ATPs
NOTE: The carbon dioxide gas makes bread dough rise & puts the
holes in bread.
Baking the dough causes the alcohol to evaporate.
b. Lactic Acid Fermentation occurs in human/animal
muscle cells.
glucose (6C) 2 pyruvate molecules (3C) 2 lactic acid
molecules(3C) + 2ATPs
NOTE: Once the bodys metabolism slows down, oxygen becomes
available and lactic acid changes back to pyruvate (pyruvic acid),
allowing continued aerobic metabolism (respiration) and energy
(ATP) for the body.
F. How Are Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Related?
PHOTOSYNTHESIS CELLULAR
RESPIRATION
OCCURS IN THESE PLANTS & SOME PROTISTS, FUNGI,
ORGANISMS: PROTISTS PLANTS, ANIMALS
(EUKARYOTES) (ALL EUKARYOTIC
SOME CYANOBACTERIA CELLS)
(PROKARYOTES)
ORGANELLES IN CHLOROPLASTS MITOCHONDRIA
WHICH THESE (PLANTS)
PROCESSES
OCCUR
REACTANTS CARBON DIOXIDE & GLUCOSE, OXYGEN,
NEEDED: WATER (INORGANIC WATER
MOLECULES)
PRODUCTS GLUCOSE, OXYGEN, CARBON DIOXIDE,
FORMED WATER WATER, ATP
(REMEMBER: ATP
STORES THE ENERGY
RELEASED FROM THE
BREAKDOWN OF FOOD
MOLECULES)
OTHER ENERGY FROM ENZYMES
REQUIREMENTS SUNLIGHT, GREEN
PIGMENT
CHLOROPHYLL
HOW PRODUCTS GLUCOSE-USED IN CARBON DIOXIDE-
ARE USED BY CELLULAR ANIMALS EXHALE IT
LIVING THINGS RESPIRATION BY ALL INTO THE AIR &
LIVING THINGS PLANTS USE IT IN
OXYGEN-RELEASED PHOTOSYNTHESIS TO
INTO AIR & USED TO MAKE GLUCOSE
BREAK DOWN GLUCOSE WATER-USED TO
IN CELLULAR REHYDRATE CELLS OR
RESPIRATION RELEASED INTO
WATER-RELEASED INTO AIR/ENVIRONMENT
AIR & BECOMES PART ATP-STORES ENERGY
OF WATER CYCLE RELEASED FROM
BREAKING DOWN
GLUCOSE & OTHER
ORGANIC MOLECULES
(LIPIDS, PROTEINS,
OTHER
CARBOHYDRATES)
Energy arrives from the sun and is captured by green photosynthetic plants, and stored
in the chemical bonds of glucose. But non-photosynthetic organisms must obtain their
energy by the breakdown of these energy rich storage molecules in order to release the
energy for their use.
Photosynthesis stores this energy in glucose, glycolysis and cellular respiration
release energy. Within plant cells themselves these same processes happen in
chloroplasts and mitochondria.
Provides energy to autotrophs/
plants for PHOTOSYNTHESIS
(in CHLOROPLASTS)
CARBON DIOXIDE &
OXYGEN & GLUCOSE
WATER
Taken in by heterotrophs
(animals, fungi, protists)& plants
(autotrophs)
for CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Glycolysis & Cellular
Respiration
(in CYTOPLASM) (in MITOCHONDRIA)
4040
HEAT
(60% of the energy
40 in glucose is
released
ATPs as heat energy)
of
ENE Used by cells for METABOLISM
RGY (The 40 ATPs represent 40% of
f ffo
the energy stored in glucose)
SUMMARY OF REACTIONS IN CELLULAR RESPIRATION &
THE NUMBER OF ATPs THEY PRODUCE
GLUCOSE
(in cytoplasm of cell)
GLYCOLYSIS
(anaerobic)
(in cytoplasm of cell) 4
ATPs produced (2 ATPs NET)
splits glucose into
2 PYRUVATE MOLECULES
(enter the fluid matrix of the mitochondria)
KREBS CITRIC ACID CYCLE
(aerobic)
(in fluid matrix of mitochondria) 2
ATPs & 6CO2 produced
Hydrogen from glucose are passed to the
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
(aerobic)
(inner membrane of mitochondria) 34
ATPs & 12 H2O produced
Hydrogen from glucose combine
with oxygen we breathe to form water
________________________
A total of 40 ATPs of
energy for
cells
to carry out metabolic activities.
You might also like
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument14 pagesAnaerobic RespirationAbegail AcedoNo ratings yet
- Today's Objective: SOL 3.dDocument11 pagesToday's Objective: SOL 3.dzameershahNo ratings yet
- Class 11 3 ChapDocument22 pagesClass 11 3 ChapMani TsheringNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguDocument20 pagesUnit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguUkwuma Michael ChijiokeNo ratings yet
- Corrina Pledger - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Guided NotesDocument4 pagesCorrina Pledger - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Guided NotesCorrina PledgerNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument32 pagesPhotosynthesis & RespirationCarson SchultzNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument39 pagesECOSYSTEMJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture No.4 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Chapter:-Plant CellDocument14 pagesOnline Lecture No.4 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Chapter:-Plant CellwatashiwayakinikuNo ratings yet
- G4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2Document6 pagesG4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2niru098No ratings yet
- Hsslive-xi-botany-RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-8Document7 pagesHsslive-xi-botany-RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-8diyakozhimalaNo ratings yet
- 04 Energy TransformationDocument53 pages04 Energy TransformationlyleandreihendersonNo ratings yet
- Respiration PowerpointDocument14 pagesRespiration Powerpointmmpanjwani4No ratings yet
- The Scientific Method Is A Way To SolveDocument72 pagesThe Scientific Method Is A Way To SolveLibia Cristina Camacho CorreaNo ratings yet
- Life Science Module 4 Lesson 5 and 6Document38 pagesLife Science Module 4 Lesson 5 and 6Mae AlfaroNo ratings yet
- GN 3.3 - Cell RespirationDocument7 pagesGN 3.3 - Cell RespirationJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocument61 pagesBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNo ratings yet
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument6 pagesRespirationfaithdanielleyNo ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument36 pagesENERGYdhonaNo ratings yet
- Eals 11abma1 MangosingDocument34 pagesEals 11abma1 MangosingAndrea Mae V. MangosingNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist ButonDocument13 pagesLecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist Butonsifa al rishalNo ratings yet
- Inbound 9168743087088869744Document9 pagesInbound 9168743087088869744MarkNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyDocument41 pagesMicrobial PhysiologyLiza Visbal- DionaldoNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 4 EcosystemDocument21 pagesTOPIC 4 EcosystemLunaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Biology Chapter I4Document13 pagesNcert Biology Chapter I4sai arunNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument13 pagesRespiration in Plantsc7zb7hhq64No ratings yet
- 3 7 Cell RespirationDocument3 pages3 7 Cell Respirationapi-296446683No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- 2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPDocument4 pages2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPTanvir KauraNo ratings yet
- Week 7 ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 7 ScienceKaru GreyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis & Cellular RespirationJhim IvyNo ratings yet
- ATP and NADPH,-Potosynthesis and RespirationDocument9 pagesATP and NADPH,-Potosynthesis and RespirationNicole Geba SamonteNo ratings yet
- Kebo112 PDFDocument13 pagesKebo112 PDFLukesh SadhNo ratings yet
- General Biology Q2W3Document2 pagesGeneral Biology Q2W3Geronimo, Jonamae S.No ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaeDocument29 pagesAerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaezulaikhaabdrahmanNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Group Challenge 3Document7 pagesGroup Challenge 3Acel PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Jinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDocument13 pagesJinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDEVIL GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration Digital Lab PosterDocument1 pageAerobic Cellular Respiration Digital Lab Posterapi-309712203No ratings yet
- Science Daily Lesson l44Document48 pagesScience Daily Lesson l44Audie Nocedo MontecastroNo ratings yet
- Bio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Document17 pagesBio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Gillion lordNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- RESPIRATION Notes 2ADocument9 pagesRESPIRATION Notes 2AGeorginah NjambiNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 14 (PDF)Document12 pagesRespiration in Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 14 (PDF)A. celestianNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - ReviewerDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration - ReviewerJoyce Cañal100% (1)
- Respiration in Plants: Negros Oriental State UniversityDocument18 pagesRespiration in Plants: Negros Oriental State UniversityGenelie Abuzo CadayonaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesWeek 7 PhotosynthesisCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Cellular RespirationDocument57 pagesLesson 12 Cellular RespirationNhelle IronVoltoxNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in PlantsDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration in PlantsMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Biology 1-3 Class 10Document3 pagesBiology 1-3 Class 10Binode SarkarNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate ATP ATP Currency Used Throughout The Cell. Energy Carrier For Cells Mechanical Work To Move Cilia and Vesicles Transport Substances Across The Membrane and Perform Variou 1Document4 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate ATP ATP Currency Used Throughout The Cell. Energy Carrier For Cells Mechanical Work To Move Cilia and Vesicles Transport Substances Across The Membrane and Perform Variou 1Kurt IgotNo ratings yet
- Respiration Part 1Document9 pagesRespiration Part 1FirozNo ratings yet
- How Animals Survive Lesson 5Document30 pagesHow Animals Survive Lesson 5Ellah LaguismaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Anatomy I Splanchnology 1Document17 pagesModule 5 Anatomy I Splanchnology 1neannaNo ratings yet
- Primo Vessels Dr. AshrafDocument7 pagesPrimo Vessels Dr. AshrafAshraful IslamNo ratings yet
- Lazcano y Pereto. 2021. BioSystemsDocument6 pagesLazcano y Pereto. 2021. BioSystemsRenato AmosNo ratings yet
- NANDA Nursing Diagnosis List 2018-2020: Domain 1: Health PromotionDocument6 pagesNANDA Nursing Diagnosis List 2018-2020: Domain 1: Health PromotionAngelaNo ratings yet
- Origin of Eukaryotic Cell PDFDocument8 pagesOrigin of Eukaryotic Cell PDFaco_golarNo ratings yet
- 1,4 ButanediolDocument6 pages1,4 ButanediolVictor VikeneNo ratings yet
- Sas 8Document12 pagesSas 8Reizel GaasNo ratings yet
- Sale Catalog - Diamond Genetics Online Elite Bull SaleDocument48 pagesSale Catalog - Diamond Genetics Online Elite Bull SaleHolstein PlazaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Nematoda 1 2019Document22 pagesTutorial Nematoda 1 2019Andre HimawanNo ratings yet
- Mushrooms-Rich Preparations On Wound Healing: From Nutritional To Medicinal AttributesDocument9 pagesMushrooms-Rich Preparations On Wound Healing: From Nutritional To Medicinal AttributesFilipe GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Instructions Template For Freshman ResumeDocument2 pagesInstructions Template For Freshman ResumeGuillaumeINo ratings yet
- International Union For The Protection of New Varieties of PlantsDocument31 pagesInternational Union For The Protection of New Varieties of PlantsBimo HariokusumoNo ratings yet
- Immunoproteasome: Dania Mohammad Abu NawasDocument27 pagesImmunoproteasome: Dania Mohammad Abu NawasDania MohNo ratings yet
- US Army Survival ManualDocument277 pagesUS Army Survival ManualRadoslavNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Living Soil - Manaloto - II-24Document1 pageReflection On Living Soil - Manaloto - II-24Ren Manaloto0% (1)
- Autonomic ReflexesDocument21 pagesAutonomic ReflexesJoe WeahNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Propagation Ludwigia - EgatiDocument12 pagesIn Vitro Propagation Ludwigia - EgatiendangNo ratings yet
- El KoalaDocument4 pagesEl KoalaGerzain OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Minorities and Mental HealthDocument33 pagesEthnic Minorities and Mental HealthAdrianoMascalzoneNo ratings yet
- Stingless Bee Tetragonula Laeviceps and T Aff BiroDocument9 pagesStingless Bee Tetragonula Laeviceps and T Aff Birojays itemNo ratings yet
- Een House Monitoring and Spray Water SystemDocument2 pagesEen House Monitoring and Spray Water SystemDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Nano Dox CarrierDocument7 pagesNano Dox CarrierMuanfan SuwanNo ratings yet
- Nail Structure and Growth: Chapter OutlineDocument8 pagesNail Structure and Growth: Chapter Outlinebritiena brownNo ratings yet
- The Involvement of Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in The Pathogenesis of ASDDocument13 pagesThe Involvement of Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in The Pathogenesis of ASDZeljko LekovicNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 4 GenBio2 EditedDocument12 pagesQ4 Week 3 4 GenBio2 EditedXyreen GalicinaoNo ratings yet
- R.S 10 MLDocument13 pagesR.S 10 MLShofwatul nadiaNo ratings yet
- Activity Book 2Document14 pagesActivity Book 2Josune Arévalo75% (4)
- Colloidal Silver and Viral InfectionsDocument13 pagesColloidal Silver and Viral Infectionsspencerjonesy100% (7)
- Disorders of PigmentationDocument45 pagesDisorders of PigmentationMoayad NawaflehNo ratings yet
- Eco Tourism DR Meeta Nihalani Kajol DhootDocument19 pagesEco Tourism DR Meeta Nihalani Kajol Dhootdr meetaNo ratings yet