Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pump Components and Their Functions | Parts of a Pump Explained
Uploaded by
anmn123100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
44 views5 pagesParts of a pump include a casing that protects components, impellers that move fluid using blades, and bearings that reduce friction on moving shafts. Additional key components are mechanical seals that prevent leaks around rotating shafts, connecting rods that link crankshafts to pistons in reciprocating pumps, and valves that regulate fluid flow. Proper selection of high-quality components suited for the specific pumping application is important for reliability and efficiency.
Original Description:
pumps
Original Title
Parts of a Pump
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentParts of a pump include a casing that protects components, impellers that move fluid using blades, and bearings that reduce friction on moving shafts. Additional key components are mechanical seals that prevent leaks around rotating shafts, connecting rods that link crankshafts to pistons in reciprocating pumps, and valves that regulate fluid flow. Proper selection of high-quality components suited for the specific pumping application is important for reliability and efficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
44 views5 pagesPump Components and Their Functions | Parts of a Pump Explained
Uploaded by
anmn123Parts of a pump include a casing that protects components, impellers that move fluid using blades, and bearings that reduce friction on moving shafts. Additional key components are mechanical seals that prevent leaks around rotating shafts, connecting rods that link crankshafts to pistons in reciprocating pumps, and valves that regulate fluid flow. Proper selection of high-quality components suited for the specific pumping application is important for reliability and efficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Parts of a Pump | Components and
Workings of a Pump
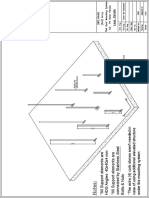
Pump and its parts
A wide range of processes and applications require the use of pumps for
their operations in various industries. They can also be used in
commercial and domestic applications. A great variety of high-pressure
pumps are available in different sizes, designs, and features. Pumps play
a significant role in the production process and are indispensable for
smooth operations. Therefore, buying a suitable high -efficiency pump
requires a thorough understanding of its parts as well, so that one can
buy the pump best suited to their needs.
Pump parts have been briefly described below:
Casing: A casing can be explained as a shell, cover or a housing which
protects and supports most of the components. In pumps, the casing is
basically used to seal it to prevent leakage and sometimes retain
pressure. It is also used to support some of the key parts such as shafts,
bearings, etc.
Impellers: An impeller is a rotating component in a centrifugal pump
which is equipped with vanes or blades that rotate and moves the fluid
in a pump. These vanes or blades are coupled to a shaft. When the
impeller rotates, it converts the energy derived from a source i.e. motor
to induce flow of the fluid. Impellers form an integral part of a pump
since it creates velocity to the fluid through its blades/vanes. Impeller
designs are considered as a major factor in deciding the efficiency of a
pump. There are two types of impeller: Axial flow impeller and Radial
flow impeller. In axial impeller, fluid moves axially to the shaft. In
radial flow impeller, fluid moves perpendicularly to the shaft. Axial
impellers are generally used for high flow and very low-pressure
applications, whereas radial impellers are often used in multi-stage
split case centrifugal pumps. Impellers are also categorized into open
and closed impellers. An open impeller has only one shroud and the
vanes are exposed on the other side. A closed impeller, often called a
double shrouded impeller, has a shroud on both sides of the vanes. Open
impellers are generally only used for single stage, end suction
centrifugal pumps, whereas double shrouded impellers are used on side
or top ported multistage centrifugal pumps. Impellers can also be
classified on the basis of their suction type: In a single-suction impeller,
liquid enters the centre of the blades from only one direction. Whereas,
in a double-suction impeller liquid enters the center of the impeller
blades from both sides simultaneously. Closed impellers are available in
single suction or double suction impeller designs. Impellers in in dustrial
grade centrifugal pumps are generally made of steel or stainless steel.
Some lower grade pumps will have brass/bronze material or some sort
of plastic. The material of the impeller should be considered carefully
when purchasing a pump since impellers are exposed to a variety of
corrosion, erosion, cavitation and general wear.
Mechanical Seals: Mechanical seals are used on the shafts of
centrifugal pumps and screw pumps, where the input shafts have to exit
the pressure chamber. It consists of two extremely smooth surfaces that
are generally held together with springs or the pump age pressure. They
can be relatively simple devices, but are generally highly engineered to
fit a specific application, and can get notably complex. Elaborate seal
support systems are often needed to cool, clean, and separate the fluid
in and around the seal. Mechanical seals and seal plans can be
categorized into 4 main categories: Single Seals, Double Seals, Quench
Seals and Gas Seals. Each category has distinct advantages and
disadvantages and their design and features must be considered carefully
in every pumping system. Mechanical seals are inherently troublesome
because of their function of sealing a pressurized fluid around a rotating
shaft. In ideal conditions, such as clean water or clean oil, mechanical
seals can be made very reliable. In harsh environments like unclean
fluid, extreme temperatures, high pressures, etc. elaborate seal systems
need to be put in place and long seal life cannot be expected.
Bearings: A bearing is a component that helps reduce friction on
moving parts in a pump. It supports the shaft to rotate smoot hly. They
are commonly used in pumps of all types, such as
centrifugal, reciprocating, or rotary pumps.
Roller bearings are bearings that use cylindrical shape rollers between
the moving parts. They reduce the friction and can support radial load
and axial load, depending on design. Roller bearings are of different
types such as cylindrical, tapered, and needle bearing. All these differ
in their shape, design, and sizes.
Ball bearings are a type of bearing that uses balls to support the
movement of the parts. They are simple in design and are suitable for
high speeds and easy to maintain. Ball bearings are good for radial lo ad
and axial load.
Babbit bearings are a type of sleeve bearings coated with Babbit metal,
i.e. tin or lead-based alloys, and commonly used in motors, pumps,
turbine generators and fans. They are available in different design and
features. The shaft speed, bearing load, shaft stability, bearing cooling
and overall machine load and speed are few factors that determine which
Babbit bearing should be chosen.
Sleeve Bearings are best suited for high speeds. They are ideal for radial
loads only, and are generally designed to “float”. They can be built of
metallic alloys, sintered metals, and plastics.
Pivot shoe Bearings sometimes known as Tilt Shoe Bearings or
Kingsbury Bearings, are ideal for an axial load. They are often installed
in high powered centrifugal pumps as the thrust bearing. Pivot Shoe
Beatings must always have pressurized lubrication in order to prevent
damage. Selecting a proper bearing is very crucial for the reliability of
the rotating equipment. One must consider all factors such as the
process, fluid/liquid used, speed, material of the bearing etc. to choose
the best one.
Connecting Rod: The Connecting rod is a part of a reciprocating pump
and is a rod which connects the crosshead to the crankshaft. It supports
the circular or rotational movement of the crankshaft. It is mounted to a
crank journal with a shell bearing on one end and the crosshead wrist
pin on the other end.
Connecting rod bearings: Connecting rod bearings, often called Shell
Bearings, helps to support or hold the crankshaft while forces and
motions of high velocity take place in the working/process through the
connecting rod.
Pistons: A piston is a component used in a reciprocating pump which is
tightly fitted in a cylinder and moves linearly back and forth to compress
and move the fluid/liquid. It is available with many manufacturers such
as Gaso, Gardner Denver, Wheatley, Oilwell, and National. A piston
liner is the cylinder in which the piston moves.
Plungers: A plunger in a reciprocating pump has the same function as
that of a piston and only differs in its shape and size. It also moves in a
closed fitted cylinder called a stuffing box. Plungers are used in positive
displacement pumps. Plungers are available in a variety of materials and
sizes. A few of them are Rokide plungers, which uses little lubrication
and is also known as Chrome Oxide. Rokide is used as a hardene d
coating to the base material. Ceramic plungers are also popular, made of
ceramic, they are resistant to abrasive substances if used in pumps.
Another type of plunger commonly used is Tungsten coated, in which a
tungsten coating is done to reduce the wear and tear of the plunger. They
are corrosion resistant. A few types of Hard-Co plungers are also
available where the coating is of nickel chrome alloy mainly used for
non-porous applications. Most common manufacturers of these kinds of
plungers are National, Gaso, Gardner Denver, Oilwell, and Union.
Wrist pins: A wrist pin is a part in a reciprocating pump that connects
the connecting rod and the crosshead. As the crosshead moves, the wrist
pin oscillates in a sleeve, called the wrist pin bushing, and acts as a
bearing. The lubricated joint helps the crosshead move smoothly.
Pump Valves: Valves in a pump perform a crucial function of
regulating, controlling and directing the flow of fluids in a reciprocating
pump. There are many types of valves available such as Disc Valve,
where the valve is opened and closed by a disc and provides excell ent
performance for lubricated, high-speed service. AR valves known as
Abrasion Resistant are suitable for applications that can cause heavy
wear and tear due to the nature of fluid or high pressure/temperature.
They come in stainless steel and other alloys. Other types of valves
include Wing Guided valves, Spherical valves and Cage valves. These
are used in Reciprocating or Diaphragm Pumps. Most common
manufacturers of these valves are National, Gardner Denver, Armstrong,
Standard and Aplex.
Relief Valves: Also known as PRV (Pressure relief valve) or PSV
(Pressure Safety Valves) is a type of valve used to regulate or control
the pressure in a system. These are designed to open when the pressure
exceeds its predetermined limits. It is commonly used in petroleum
refining, petrochemical and chemical manufacturing, natural gas
processing, oil and water pipelines, power generation industries and
more and form an integral part of the process because of its crucia l
functioning from safety and controls point of view. They are available
in different types such as Shear Pin Relief Valves, which uses one or
two shear pins to set relief the pressure, and Spring Relief Valves, where
a spring is used to push against the pressure. They come in different
sizes and pressure rating. PORV (Pilot Operated Relief valves) basically
uses system pressure to seal the valve. A good PORV can work with
pressures up to 420 bar (6000 psi) and very high flows in a reliable and
compact design. Spring relief valves are used in applications where very
high reliability and safety pressure is required such as in nuclear safety
related applications. These valves open to relieve excess pressure and
then re-close and prevent further flow. Ultimatel y, the main purpose of
all these valves is to mitigate accidents and accidental damages. Taylor,
Odrill, Leser, Crosby, Emerson are few of the key manufacturers of
relief valves.
Pressure Gauges: A pressure gauge is an instrument to measure and
display pressure level. It monitors a pump’s discharge or inlet pressure.
They should be used for all high pressure applications. Different models
are available in the market in brass or stainless steel material. In most
applications, pressure transmitters should be paired with a gauge and
wired to a central PLC to assist with safety and control of a system.
Couplers: A coupler is a device which connects or links two pieces of
rotating equipment, such as a pump or and a motor or gearbox. The
primary function of the coupler is to transmit power from the drive
equipment to the driven equipment. Most couplers, particularly on high
powered systems, are also made to allow for slight angular and parallel
misalignment and movement as the equipment operates. Flexible
couplings can come in many different styles and sizes. Some require
lubricant, such as grease, and others are designed to run dry. All feature
some sort of flexible metal disc, rubber insert, spring or a set of gears
that provide the movement required.
Oil Seals: An oil seal, usually made of oil and grease resistant rubber,
is a device used for preventing leakage or entry of oil from a chamber,
usually fit around a rotating or reciprocating shaft. This seal may also
be used to prevent outside materials such as dir t from moving in through
the clearance. They have great use in engines, pumps, blowers, motors
and gearboxes. Oil seals are available in many different types, materials
and sizes. Lip seals and Wiper seals are all types of oil seals that are
commonly used in the industry.
O ring seal: O'Rings close a gap between two surfaces so that liquids
or gases cannot pass through in any direction. An O ring seal, changes
its shapes when pressure is applied in the system, so it squeezes against
the surrounding surfaces, sealing them off. It is a very simple design
and, although it is has its limitations, is used in a wide variety of
applications. O-rings can be used in low pressure and high pressure
applications, on flat, stationary surfaces as well as round shafts.
There are various other parts of both Positive Displacement Pumps and
Centrifugal Pumps such as wrist pin bushings, Cross Heads, Stuffing
Boxes, Shim Packs, Screws, Screw Liners and Wear Rings etc. Each p art
or component in a pump plays a very crucial role in its efficient
functioning. Conversely, the cost and inconvenience of a poorly selected
part can be catastrophic.
You might also like
- Elements d'une pompe en anglaisDocument4 pagesElements d'une pompe en anglaismerouaneinconuNo ratings yet
- Components of Multistage Centrifugal PumpDocument4 pagesComponents of Multistage Centrifugal PumpAin SyazwinaNo ratings yet
- Positive Displacement PumpsDocument5 pagesPositive Displacement PumpsGabriel Andrés Barcha Angulo100% (1)
- Pumps, Pipes and FittingsDocument25 pagesPumps, Pipes and FittingsAjay PesadoNo ratings yet
- What's A Screw Pump? Understanding The Unique Characteristics and Operating Principles of 1, 2 and 3 Screw PumpsDocument4 pagesWhat's A Screw Pump? Understanding The Unique Characteristics and Operating Principles of 1, 2 and 3 Screw PumpsTapas ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Assignment Process Plant Utilities: Submitted ToDocument17 pagesAssignment Process Plant Utilities: Submitted ToMaham FatimaNo ratings yet
- Screw PumpsDocument4 pagesScrew PumpsElia MekdadNo ratings yet
- Gear Pump ArticleDocument5 pagesGear Pump ArticleGeoffrey AllenNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder AppDocument5 pagesHydraulic Cylinder AppwanradhiahNo ratings yet
- Heavy-Duty Hydraulic PumpDocument12 pagesHeavy-Duty Hydraulic PumpYabi ButaNo ratings yet
- Gear Pump OperationDocument7 pagesGear Pump Operationahmed el sayedNo ratings yet
- Pumps - Hassan ElBanhawiDocument20 pagesPumps - Hassan ElBanhawijesus_manrique2753No ratings yet
- 5 7-PumpsDocument46 pages5 7-PumpsMohamed Rafeek GhaniNo ratings yet
- Gear PumpDocument7 pagesGear PumpMuhammad QayyumNo ratings yet
- Types of Pump Casings (In Centrifugal Pumps & Others) + Pros & ConsDocument10 pagesTypes of Pump Casings (In Centrifugal Pumps & Others) + Pros & ConssarojNo ratings yet
- Compressor PartsDocument7 pagesCompressor PartsinamNo ratings yet
- CH3 Ibl ADocument70 pagesCH3 Ibl Anoorr66No ratings yet
- Water PumpsDocument3 pagesWater PumpsDubaiHMARNo ratings yet
- Articulo Bom 3 TornilloDocument4 pagesArticulo Bom 3 TornilloJosé Olivier RománNo ratings yet
- Types of PumpsDocument8 pagesTypes of Pumpskarthick_sailor100% (2)
- Hydraulic CylinderDocument6 pagesHydraulic Cylindermichol2014No ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Lab Group PresentationDocument131 pagesFluid Flow Lab Group PresentationMujadid KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction To Pump Pump DefinitionDocument44 pagesChapter One Introduction To Pump Pump DefinitionyoungNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction To Pump Pump DefinitionDocument44 pagesChapter One Introduction To Pump Pump DefinitionyoungNo ratings yet
- TC Manual Fluid PumpsDocument32 pagesTC Manual Fluid Pumpsvickers100% (1)
- Hydraulic Cylinder: The Hydraulic Cylinders On This Control The Machine'sDocument9 pagesHydraulic Cylinder: The Hydraulic Cylinders On This Control The Machine'smanojpro21_9131911970% (1)
- W Defa2715Document22 pagesW Defa2715Eduardo CastilloNo ratings yet
- CylindersDocument36 pagesCylindersNellai VprNo ratings yet
- Pump Installation & MaintenanceDocument116 pagesPump Installation & MaintenanceMohammed El-Shahat100% (8)
- Hydraulic Pump - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesHydraulic Pump - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAakash ChatakeNo ratings yet
- Project 2Document7 pagesProject 2Lalaine RamosNo ratings yet
- NEA PrepationDocument21 pagesNEA Prepationaziz100% (1)
- Volume-2. Design and Manufacturing of Hydraulic CylindersDocument53 pagesVolume-2. Design and Manufacturing of Hydraulic CylindersQ.S. Khan96% (48)
- Specifying The Right Hydraulic Cylinder For The Right JobDocument8 pagesSpecifying The Right Hydraulic Cylinder For The Right JobJosh WhiteNo ratings yet
- Bearing & Lub SystemDocument16 pagesBearing & Lub SystemmuazmaslanNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps CourseDocument108 pagesCentrifugal Pumps CoursefotopredicNo ratings yet
- Radial - Flow: (Centrifugal Pump)Document17 pagesRadial - Flow: (Centrifugal Pump)John A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder Demonstration at Cairo University Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument21 pagesHydraulic Cylinder Demonstration at Cairo University Mechanical Engineering DepartmentengmomoNo ratings yet
- How Tractor Brakes WorkDocument10 pagesHow Tractor Brakes WorkVengadasubramanianNo ratings yet
- AgitatorsDocument9 pagesAgitatorsB Santosh Kumar DoddalaNo ratings yet
- On Hydraulic Pumps: Design GuideDocument16 pagesOn Hydraulic Pumps: Design Guideali morisy100% (2)
- ME080 Section 8 - Other Hydraulic ComponentsDocument101 pagesME080 Section 8 - Other Hydraulic ComponentsAhmed FaragNo ratings yet
- Factors to Consider When Designing Agitators and MixersDocument9 pagesFactors to Consider When Designing Agitators and MixersRavindra V. LakhapatiNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument41 pagesCentrifugal PumpAbdallah MansourNo ratings yet
- Design Guide On Hydraulic CylindersDocument20 pagesDesign Guide On Hydraulic Cylindersvinod ybNo ratings yet
- Flygt Slurry HandbookDocument48 pagesFlygt Slurry Handbookrodolfocv92359100% (2)
- PumpsDocument38 pagesPumpsbernabasNo ratings yet
- Pump Working PrinciplesDocument7 pagesPump Working PrinciplesamirulbznNo ratings yet
- SJTVerticalTurbinePump en E10004 10 2011Document8 pagesSJTVerticalTurbinePump en E10004 10 2011amudhan_sivaNo ratings yet
- Vrtical ImpellerDocument63 pagesVrtical Impellerpramo_dassNo ratings yet
- WWJArticle20 VTP Part1May03Document5 pagesWWJArticle20 VTP Part1May03Tarık DikbasanNo ratings yet
- Types of PumpsDocument7 pagesTypes of PumpspakNo ratings yet
- Agitator Design FactorsDocument6 pagesAgitator Design Factorsserleb44No ratings yet
- Physical study of a centrifugal pumpDocument82 pagesPhysical study of a centrifugal pumpArthur Maderse Ramo Jr.100% (1)
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsFrom EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!From EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Turning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.From EverandTurning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.No ratings yet
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryFrom EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNo ratings yet
- TAUToRs13 54 36Document15 pagesTAUToRs13 54 36anmn123No ratings yet
- Address People RightlyDocument2 pagesAddress People Rightlyanmn123No ratings yet
- (2x3) Array Mounting SystemDocument9 pages(2x3) Array Mounting Systemanmn123No ratings yet
- Design of PV SystemDocument146 pagesDesign of PV Systemanmn123100% (1)
- Solar Energy For Rural Electricity in inDocument8 pagesSolar Energy For Rural Electricity in inanmn123No ratings yet
- 1mw Rooftop Solar PV Power Plant PermitDocument9 pages1mw Rooftop Solar PV Power Plant Permitamritmandal0191100% (1)
- Solar PV Guideline 7-16-18-ADocument8 pagesSolar PV Guideline 7-16-18-Aanmn123No ratings yet
- Solar PlanDocument37 pagesSolar PlanAbdulkhadir SuhairNo ratings yet
- 2018 Employee Benefits ReportDocument39 pages2018 Employee Benefits ReportMichael FekryNo ratings yet
- (Proceedings of The enviBUILD 2019) SOLAR IRRADIANCE AVAILABILITY BASED ON BRATISLAVA MEASUREMENTSDocument8 pages(Proceedings of The enviBUILD 2019) SOLAR IRRADIANCE AVAILABILITY BASED ON BRATISLAVA MEASUREMENTSanmn123No ratings yet
- Cetinkaya Pano A.S.: Catalogue Trade CatalogueDocument6 pagesCetinkaya Pano A.S.: Catalogue Trade Catalogueanmn123No ratings yet
- Advancing Multilevel Thinking in Human Resource Management Research Applications and Guidelines PDFDocument19 pagesAdvancing Multilevel Thinking in Human Resource Management Research Applications and Guidelines PDFanmn123No ratings yet
- 2nd Green Energy Summit 2014 IndiaDocument62 pages2nd Green Energy Summit 2014 Indiaanmn123No ratings yet
- Electronics Training Equipment 1-Electronics Trainer SS1101C Linear Circuit Lab Teaching EquipmentDocument103 pagesElectronics Training Equipment 1-Electronics Trainer SS1101C Linear Circuit Lab Teaching Equipmentanmn123No ratings yet
- Mark Z. Jacobson Stanford UniversityDocument48 pagesMark Z. Jacobson Stanford Universityanmn123No ratings yet
- Super High Power Mono Perc ModuleDocument2 pagesSuper High Power Mono Perc Moduleanmn123No ratings yet
- Hands-On Learning On Renewable Energy - A Proposed Approach For Technology DisseminationDocument7 pagesHands-On Learning On Renewable Energy - A Proposed Approach For Technology Disseminationanmn123No ratings yet
- XTM en 8Document1 pageXTM en 8anmn123No ratings yet
- The Environmental Impacts of Renewable EnergyDocument9 pagesThe Environmental Impacts of Renewable Energyanmn123No ratings yet
- Variotrack: Model Vt-80 Electrical Characteristics PV Array SideDocument1 pageVariotrack: Model Vt-80 Electrical Characteristics PV Array Sideanmn123No ratings yet
- Environmental Impacts of Renewable Energy ProjectsDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Impacts of Renewable Energy Projectsanmn123No ratings yet
- Mark Z. Jacobson Stanford UniversityDocument45 pagesMark Z. Jacobson Stanford Universityanmn123No ratings yet
- Lecture On SolarconcentratingcollectorsDocument14 pagesLecture On Solarconcentratingcollectorsanmn123100% (1)
- 1 2 Lectures Energy Conversion IntroductionDocument62 pages1 2 Lectures Energy Conversion IntroductionephremNo ratings yet
- Club's Occupational Health and Safety PolicyDocument29 pagesClub's Occupational Health and Safety Policyanmn123No ratings yet
- Kolektor ParabolaDocument14 pagesKolektor Parabolahamumar0% (1)
- ECE333 Spring2020 Lect9bDocument1 pageECE333 Spring2020 Lect9banmn123No ratings yet
- The 7 Reasons Why Nuclear Energy Is Not The Answer To Solve Climate ChangeDocument6 pagesThe 7 Reasons Why Nuclear Energy Is Not The Answer To Solve Climate Changeanmn123No ratings yet
- Photovoltaic System Design Diploma OverviewDocument2 pagesPhotovoltaic System Design Diploma Overviewanmn123No ratings yet
- Design Course For Solar Energy SystemsDocument2 pagesDesign Course For Solar Energy Systemsanmn12350% (2)
- Tables and Bar ChartsDocument7 pagesTables and Bar ChartsVictoria FedoseevaNo ratings yet
- Ras Abu Aboud Stadium Daily Report 040 (20190613)Document4 pagesRas Abu Aboud Stadium Daily Report 040 (20190613)tuan50% (2)
- Memories of HomeDocument14 pagesMemories of HomeMary Francis Edmer SayconNo ratings yet
- List of Students Allotted in Open Elective Subjects (B. Tech and M. Tech (Dual Degree) Integrated MSc. - 4th Semester - Regular - 2018 - 19) - 2 PDFDocument26 pagesList of Students Allotted in Open Elective Subjects (B. Tech and M. Tech (Dual Degree) Integrated MSc. - 4th Semester - Regular - 2018 - 19) - 2 PDFArpan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Well Rounded.: 360 CassetteDocument12 pagesWell Rounded.: 360 CassetteMonty Va Al MarNo ratings yet
- Seminar Application of Nitrous Oxide in AutomobilesDocument20 pagesSeminar Application of Nitrous Oxide in AutomobilesSaikat BadyakarNo ratings yet
- Hero LetterDocument3 pagesHero LetterArunachalam Muthiah0% (1)
- Queer Ecology Critique - Georgetown 2014Document104 pagesQueer Ecology Critique - Georgetown 2014Evan JackNo ratings yet
- Factory made uPVC windows installationDocument2 pagesFactory made uPVC windows installationAmit Singh100% (2)
- Hellstorm NotesDocument57 pagesHellstorm NotesDeni ZenNo ratings yet
- IAL Edexcel Pure Math 1 January 2020Document28 pagesIAL Edexcel Pure Math 1 January 2020Mohamed Said Daw100% (4)
- 3.1 Artifact OptimiserDocument120 pages3.1 Artifact Optimiseralex joNo ratings yet
- Osha Top 25 Physical HazardsDocument100 pagesOsha Top 25 Physical HazardsHasan Shakeel100% (2)
- Bio-Sil ULTRA 1050: Medically Pure Platinum-Cured Silicone Tubing With An Ultra-Smooth Inner SurfaceDocument2 pagesBio-Sil ULTRA 1050: Medically Pure Platinum-Cured Silicone Tubing With An Ultra-Smooth Inner SurfaceLari GrossiNo ratings yet
- Taylors 10 Minute Diagnosis Manual Symptoms and Signs in The Time Limited Encounter PDFDocument656 pagesTaylors 10 Minute Diagnosis Manual Symptoms and Signs in The Time Limited Encounter PDF19marvoloNo ratings yet
- 1992SGSDesignersGuidetoPowerProductsApplicationManual2Ed 1182713547Document1,298 pages1992SGSDesignersGuidetoPowerProductsApplicationManual2Ed 1182713547analog changeNo ratings yet
- Design of A Tuned Intake Manifold - H. W. Engelman (ASME Paper 73-WA/DGP-2)Document9 pagesDesign of A Tuned Intake Manifold - H. W. Engelman (ASME Paper 73-WA/DGP-2)david_luzNo ratings yet
- Proximity Sensing and Warning Technology For Heavy Construction Equipment OperationDocument10 pagesProximity Sensing and Warning Technology For Heavy Construction Equipment OperationAnand ReddyNo ratings yet
- Textiles and Clothing SustaninabilityDocument134 pagesTextiles and Clothing Sustaninabilitydike100% (1)
- Form WorkDocument25 pagesForm Workhina khanNo ratings yet
- Shock Classification and PathophysiologyDocument40 pagesShock Classification and PathophysiologyErick Anca100% (2)
- Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Excipient - LastpptDocument72 pagesPharmaceutical Ingredients and Excipient - LastpptFANTANo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas and Symbols: Physics I Symbol FormulaDocument5 pagesPhysics Formulas and Symbols: Physics I Symbol Formulakaparthy100% (9)
- Full Report-Disinfectant and SanitizerDocument19 pagesFull Report-Disinfectant and Sanitizermohd addinNo ratings yet
- Lista de Precios Tones y Staleks 01.04Document3 pagesLista de Precios Tones y Staleks 01.04Maria T. OliverosNo ratings yet
- Design & Operation of Clean Room-1Document39 pagesDesign & Operation of Clean Room-1Hafizur Rahman0% (1)
- IRRIGATION ENGINEERING MCQDocument40 pagesIRRIGATION ENGINEERING MCQpriya dharshini100% (1)
- AABB Accredited DNA Testing FacilitiesDocument2 pagesAABB Accredited DNA Testing Facilitiesjosueduran75No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4325 2H Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4325 2H Mark SchememuhajireenNo ratings yet
- General Description: Effective Distance Depends On Antenna, Tag and EnvironmentDocument2 pagesGeneral Description: Effective Distance Depends On Antenna, Tag and EnvironmentSHASHANK BHUSHANNo ratings yet