Professional Documents
Culture Documents
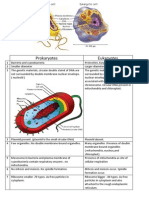
Difference Between Cell
Uploaded by
Jobelle Acena100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
714 views1 pageOriginal Title
Difference between Cell
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
714 views1 pageDifference Between Cell
Uploaded by
Jobelle AcenaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Difference between Cell-mediated Immunity and Humoral Immunity
BASIS FOR HUMORAL IMMUNITY CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY
COMPARISON
Meaning The humoral immunity is The cell-mediated immunity is
associated with the B-lymphocytes associated with the T-
and is responsible for destroying lymphocytes and is responsible
the pathogens by producing for destroying the pathogens or
antibodies against it. microorganism which have
invaded the cells.
Mediated by Humoral immunity is intimately These are associated with T-
associated with B-lymphocytes, T- lymphocytes, helper T cells,
lymphocytes and macrophages. natural killer cells and
macrophages.
Antibodies Present. Absent.
Function 1. It plays a major role in 1. Cell-mediated immunity is
recognizing antigen or any foreign related to T-lymphocytes, which
particle and in producing antibodies work by identifying viruses and
against it. microorganisms, thus destroying
them by the cell lysis or
2. Humoral immunity is known for phagocytosis or pinocytosis.
working against extracellular
pathogens. 2. It is known for working against
intracellular pathogens.
Secretes It secrets antibodies. It secretes cytokines.
Action against Humoral immunity is rapid or The Cell-mediated immunity
pathogen quick in their response. show delay though permanent
action against any pathogens.
Hypersensitivity It mediates hypersensitivity type I, Cell-mediated is the delayed in
II and III. response and mediates
hypersensitivity type IV.
Rejections Humoral immunity is involved in Cell-mediated immunity is
the early stage of graft rejections involved in the rejection of organ
due to the formation of antibodies. transplants.
You might also like
- Bioethics in Nursing Practice: Principles of Autonomy and Informed ConsentDocument5 pagesBioethics in Nursing Practice: Principles of Autonomy and Informed ConsentVhinny Macabontoc100% (1)
- ER Protocols in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesER Protocols in The PhilippinesJobelle Acena100% (1)
- Case Study (Lung Cancer)Document17 pagesCase Study (Lung Cancer)Jobelle Acena100% (1)
- Kuby Immunology Ch. 5Document14 pagesKuby Immunology Ch. 5eabazaNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Case StudyDocument15 pagesGeriatric Case StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Case Study (ACS)Document12 pagesCase Study (ACS)Kristel Joy Cabarrubias Acena100% (1)
- Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine, 8th Ed-Pages-233-267 PDFDocument35 pagesFitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine, 8th Ed-Pages-233-267 PDFHestin PrasantyNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelDocument11 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelSaeed AbdulhadiNo ratings yet
- Protein TransportDocument13 pagesProtein TransportvmshanesNo ratings yet
- Antigen Presenting CellsDocument27 pagesAntigen Presenting CellsSajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Micrology and Parasitology ReviewerDocument44 pagesMicrology and Parasitology Reviewermarjourie cadampog100% (1)
- Chapter 54 Practice Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesChapter 54 Practice Multiple ChoiceTim LiNo ratings yet
- Endosymbiotic TheoryDocument9 pagesEndosymbiotic TheoryFrancisco CañonNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Antibody Production and VaccinationDocument28 pages11.1 Antibody Production and VaccinationFRENCHONLYNo ratings yet
- Ib Animal Experimental PolicyDocument2 pagesIb Animal Experimental Policyapi-326269363No ratings yet
- Cell Mediated Immunity ExplainedDocument22 pagesCell Mediated Immunity ExplainedNova PamastaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 2 Cells ReviewDocument2 pagesAP Biology Unit 2 Cells ReviewPhilly CheungNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis WebquestDocument3 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Webquestapi-3156932390% (1)
- Antigen Processing and Presentation PDFDocument36 pagesAntigen Processing and Presentation PDFMarinero CzarNo ratings yet
- Three Mechanisms that Control Hormone ReleaseDocument19 pagesThree Mechanisms that Control Hormone ReleaseRishtaul AlamNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To MicrobiologyRealyn FababaerNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology - Mitosis and Meiosis Spies and TrainsDocument8 pagesGCSE Biology - Mitosis and Meiosis Spies and TrainsTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelDocument11 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelsalmaNo ratings yet
- Notes in GeneticsDocument2 pagesNotes in GeneticsRenz L. Salumbre100% (1)
- Answering Exam Questions On CellsDocument4 pagesAnswering Exam Questions On CellsTamicka Bonnick100% (1)
- Notes: Fungi Systematics: Yeasts Rusts Smuts Mildews Molds MushroomsDocument2 pagesNotes: Fungi Systematics: Yeasts Rusts Smuts Mildews Molds MushroomsPrabhavati GhotgalkarNo ratings yet
- Innate and Adaptive Immunity: Cells, Organs and FunctionsDocument17 pagesInnate and Adaptive Immunity: Cells, Organs and FunctionsBasma RagabNo ratings yet
- Lindsley-Drosophila Variation PDFDocument486 pagesLindsley-Drosophila Variation PDFKathia JazNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Discussion QuestionsDocument5 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Discussion QuestionsRichard Rna NaabNo ratings yet
- NPTEL Cellular and Molecular ImmunologyDocument32 pagesNPTEL Cellular and Molecular ImmunologyAygul RamankulovaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 SERIAL DILUTION OF MICROBIAL SAMPLEDocument6 pagesLab Report 1 SERIAL DILUTION OF MICROBIAL SAMPLERidma madusanka weerasinghaNo ratings yet
- Biology SL Paper 1novDocument10 pagesBiology SL Paper 1novidkNo ratings yet
- Genetics SyllabusDocument7 pagesGenetics SyllabusAnonymous q6VpovV6pTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture-Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism-MODIFIED2Document49 pagesChapter 8 Lecture-Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism-MODIFIED2E'Lasia LarkinNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument21 pagesBiotechnology NotesRommel BauzaNo ratings yet
- Genetics, Lecture 11 (Lecture Notes)Document16 pagesGenetics, Lecture 11 (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Gregor MendelDocument3 pagesGregor MendelhdNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis QuestionsDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis QuestionstrekNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - ProteobacteriaDocument63 pagesModule 3 - ProteobacteriaReginaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology PDFDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Immunology PDFanon_143800659100% (1)
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureL.y. Chong100% (1)
- Cell Structure Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument15 pagesCell Structure Multiple Choice QuestionsWesley Tan100% (2)
- Immune System Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument50 pagesImmune System Multiple Choice QuestionsErica MizzIndependent BubuchuNo ratings yet
- CSIR-NET Cell Biology NotesDocument32 pagesCSIR-NET Cell Biology NotesSrinivas Nakka100% (1)
- Specific Host Defenses: The Immune ResponseDocument54 pagesSpecific Host Defenses: The Immune Responseadyaly44No ratings yet
- CryptochromeDocument5 pagesCryptochromehannahlralstonNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Gene: Chapter ObjectivesDocument17 pagesMolecular Biology of The Gene: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- Introduction Immune System S2 DD 2020Document84 pagesIntroduction Immune System S2 DD 2020Belia Bima NafisaNo ratings yet
- Antigen Processing Process and MHC AssociationDocument3 pagesAntigen Processing Process and MHC AssociationMahathir Mohmed100% (2)
- A Cell Atlas of Human Thymic Development Defines T Cell Repertoire Formation PDFDocument12 pagesA Cell Atlas of Human Thymic Development Defines T Cell Repertoire Formation PDFCris BañadosNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Antigenic StructureDocument36 pagesBacterial Antigenic Structuredearsaran0% (1)
- Cell CycleDocument16 pagesCell CycleRose RomeroNo ratings yet
- Culturing Bacteria from the EnvironmentDocument7 pagesCulturing Bacteria from the EnvironmentSer Louis Fetilo FabunanNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Class 12 - Bio-Zoology-Zoology - English Medium - Possible 5 Mark Questions With Answer.Document34 pagesTamil Nadu Class 12 - Bio-Zoology-Zoology - English Medium - Possible 5 Mark Questions With Answer.revamanian57% (7)
- B Cell ActivationDocument62 pagesB Cell ActivationAYSHAMOHD88No ratings yet
- CH 22 Descent With ModificationDocument19 pagesCH 22 Descent With Modificationemmy hoNo ratings yet
- Format For Course Curriculum: Annexure CD - 01'Document2 pagesFormat For Course Curriculum: Annexure CD - 01'Rangoli KhareNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIFrom EverandSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Micro Assignment Unit 3 Group BDocument12 pagesMicro Assignment Unit 3 Group Bnabeelpatras19No ratings yet
- Immunity of Parasitic InfectionsDocument4 pagesImmunity of Parasitic InfectionsCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- MicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionDocument11 pagesMicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionRaven Joyce LabayenNo ratings yet
- Flash Cards 5Document7 pagesFlash Cards 5Brian Ernesto Leal NievesNo ratings yet
- Inmunidad y SepsisDocument6 pagesInmunidad y SepsisAmmarie SanchezNo ratings yet
- Immune Responses To Intracellular Bacteria: Stefan H.E. Kaufmann, Helen L. Collins, Ulrich E. SchaibleDocument21 pagesImmune Responses To Intracellular Bacteria: Stefan H.E. Kaufmann, Helen L. Collins, Ulrich E. SchaibleEmmanuela Stefany SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Case StudyDocument21 pagesPediatric Case StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 SY 2020-2021: Legal and Ethical Consideration of Euthanasia in India: A Choice Between Life and DeathDocument8 pagesNCM 107 SY 2020-2021: Legal and Ethical Consideration of Euthanasia in India: A Choice Between Life and DeathJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- GC ncp1 and 2Document4 pagesGC ncp1 and 2Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Date/Schedule Activities Expected Output Verified/Checked by Area in ChargeDocument2 pagesDate/Schedule Activities Expected Output Verified/Checked by Area in ChargeJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Union Christian College School of Health and Sciences City of San Fernando La UnionDocument11 pagesUnion Christian College School of Health and Sciences City of San Fernando La UnionJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Ventilation AssistanceDocument3 pagesSubjective: Ventilation AssistanceJobelle Acena100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY (Lung Cancer)Document10 pagesDRUG STUDY (Lung Cancer)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Leadership and Management RLEDocument4 pagesNCM 107 Leadership and Management RLEJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- GC ncp1Document2 pagesGC ncp1Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Online LectureDocument9 pagesOnline LectureJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Mechanism of Action of Cell Mediated Immune System and Humoral Mediated Immune SystemDocument4 pagesDifference Between Mechanism of Action of Cell Mediated Immune System and Humoral Mediated Immune SystemJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Normal Cell GrowthDocument5 pagesNormal Cell GrowthJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Fever, Wound Healing and Pressure UlcerDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plans for Fever, Wound Healing and Pressure UlcerJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Er Drugs StudyDocument80 pagesEr Drugs StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Michael Jimenez, PENTAGON Slovin'S Formula: N 1 + NeDocument10 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Michael Jimenez, PENTAGON Slovin'S Formula: N 1 + NeJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- PHARMAfdDocument7 pagesPHARMAfdJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests Guide for NursesDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Tests Guide for NursesBenedict AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Certify Baby'S Birth: Body TemperatureDocument9 pagesCertify Baby'S Birth: Body TemperatureJobelle Acena100% (1)
- SummaryDocument1 pageSummaryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing: Core Values of NursingDocument14 pagesNursing: Core Values of NursingJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Anti Psychotic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti Psychotic DrugscalfornianursingacadNo ratings yet
- Notes On Obstetrics: Normal Labor (Theories of Labor Onset)Document22 pagesNotes On Obstetrics: Normal Labor (Theories of Labor Onset)Jobelle Acena100% (1)
- CBC ReportDocument1 pageCBC ReportPranay BhosaleNo ratings yet
- The Complement System: An Introduction to Key Concepts and Biological FunctionsDocument38 pagesThe Complement System: An Introduction to Key Concepts and Biological Functionsprateek gangwaniNo ratings yet
- Nap - Food For PlaDocument64 pagesNap - Food For PlaDrake Wa YesuNo ratings yet
- Gell & Coombs Classification of Hypersensitivity ReactionDocument17 pagesGell & Coombs Classification of Hypersensitivity ReactionShia LevyNo ratings yet
- Infection and Host ResistanceDocument62 pagesInfection and Host ResistanceAndrea Marie T. Artajo-BoheromNo ratings yet
- Kuby Immunology 7th Edition by Judy Owen Ebook PDFDocument41 pagesKuby Immunology 7th Edition by Judy Owen Ebook PDFrandy.beard301100% (35)
- Interacciones NeuroinmunesDocument28 pagesInteracciones NeuroinmunesMiguel Andres RangelNo ratings yet
- I-SEMESTER SYLLABUS FOR AQUACULTURE COURSESDocument19 pagesI-SEMESTER SYLLABUS FOR AQUACULTURE COURSESLauda LessenNo ratings yet
- Toxicology Letters - 2002 Kollner Et Al.Document13 pagesToxicology Letters - 2002 Kollner Et Al.Dian Eka RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Case Report on Allergic RhinitisDocument11 pagesCase Report on Allergic RhinitisAnonymous XFDJfsGviNo ratings yet
- After Years of Telling People Chemotherapy Is The Only Way To Try (Try TheDocument2 pagesAfter Years of Telling People Chemotherapy Is The Only Way To Try (Try TheJacie MuiNo ratings yet
- Chronic DiseaseDocument75 pagesChronic DiseaseRaman KundraNo ratings yet
- Pak International Nursing College Hayatabad Peshawar Paper: Microbiology MCQS: 70Document8 pagesPak International Nursing College Hayatabad Peshawar Paper: Microbiology MCQS: 70anon_675257473No ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document4 pagesWa0005.science worldNo ratings yet
- ISBB DKDocument112 pagesISBB DKEl FiNo ratings yet
- Adoptive Immunotherapy Ludewig Hoffmann (Methods Molec Medicine 109 Humana 2005)Document517 pagesAdoptive Immunotherapy Ludewig Hoffmann (Methods Molec Medicine 109 Humana 2005)Cristian PopaNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Basic Immunodermatology 2017Document889 pagesClinical and Basic Immunodermatology 2017Angelo BaezaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Schematic DiagramDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Schematic DiagramTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- The Vitamin C Treatment of Whooping CoughDocument14 pagesThe Vitamin C Treatment of Whooping CoughoneclickgroupNo ratings yet
- Pharm.D 2nd Year SyllabusDocument21 pagesPharm.D 2nd Year Syllabus12 E 36 Yatri PatelNo ratings yet
- Active Hexose Correlated Compound - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesActive Hexose Correlated Compound - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopedianurpeekNo ratings yet
- Sesion 3 Articulo Seminario 2 PsoriasisDocument16 pagesSesion 3 Articulo Seminario 2 PsoriasisQuispe Canares MariangelesNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Body DefensesDocument125 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body DefensesRhea Joy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PG Brochure 2014Document59 pagesPG Brochure 2014ParinitaSahooNo ratings yet
- Class Code Name ListDocument494 pagesClass Code Name ListIndera KesumaNo ratings yet
- KVS PGT Syllabus PDFDocument36 pagesKVS PGT Syllabus PDFMondar Deb0% (1)
- Biology ProjectDocument18 pagesBiology ProjectSuyash BaghelNo ratings yet
- Aminoden Immunology Activity 1 2021Document3 pagesAminoden Immunology Activity 1 2021hanzala macabandoNo ratings yet
- Disease Questions 1 January 2021 No Mark SchemeDocument12 pagesDisease Questions 1 January 2021 No Mark SchemeGus PneumaticosNo ratings yet