Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration Questions
Uploaded by
Tazeen Fatima0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesRespiration Questions
Uploaded by
Tazeen FatimaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
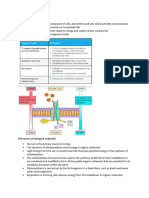
Q) Suggest the function of the DNA and ribosomes in the
mitochondrion.
Ans) Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes)
perform protein synthesis inside mitochondria, the organelles
responsible for energy conversion and adenosine triphosphate
production in eukaryotic cells. They are also used for the translation of
information. Mitochondrial DNA contains 37 genes, all of which are
essential for normal mitochondrial function. Thirteen of these genes
provide instructions for making enzymes involved in oxidative
phosphorylation. The remaining genes provide instructions for making
molecules called transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA),
which are chemical cousins of DNA. These types of RNA help assemble
protein building blocks (amino acids) into functioning proteins and the
synthesis of respiratory enzymes.
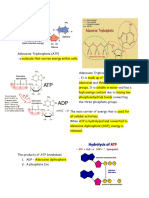
Q) Some parasitic worm, such as tape worms, live in a mammalian
gut where there is no oxygen. Suggest how at tape worm produces
ATP in such an environment.
Ans) Some organisms are able to continually convert
energy without the presence of oxygen. They undergo glycolysis,
followed by the anaerobic process of fermentation to make ATP.
During anaerobic respiration, only glycolysis occurs. The 2 molecules of
NADH that are generated during glycolysis are then converted back
into NAD+ during anaerobic respiration so that glycolysis can continue.
Since glycolysis only produces 2 ATP, anaerobic respiration is much less
efficient than aerobic respiration (2 ATP molecules compared to 36-ish
ATP molecules). However, 2 ATP molecules is much better for a cell
than 0 ATP molecules. In anaerobic situations, the cell needs to
continue performing glycolysis to generate 2 ATP per glucose because
if a cell is not generating any ATP, it will die.
You might also like
- 471 - BCH 201-Lecture Note On WebDocument10 pages471 - BCH 201-Lecture Note On WebShaikh SalmanNo ratings yet
- VCE Biology Summary Book 2013: Samantha TierneyDocument102 pagesVCE Biology Summary Book 2013: Samantha Tierneymickyhearts18No ratings yet
- c5 - Cellular Respiration - Fill in The BlankDocument1 pagec5 - Cellular Respiration - Fill in The Blankapi-316890085No ratings yet
- Biomolecules: The Raw Materials of Cell The Building Blocks of Life The Molecules of CellsDocument61 pagesBiomolecules: The Raw Materials of Cell The Building Blocks of Life The Molecules of CellsKenneth NicolasNo ratings yet
- Self Study Assignment On Marker Enzymes, Semiautonomous - PPTX 1740512Document20 pagesSelf Study Assignment On Marker Enzymes, Semiautonomous - PPTX 1740512aswinNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument56 pagesDna and Rna StructureZeah RealNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: MitochondriaDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration: MitochondriaMaryRoseTrajada100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids and NucleotidesDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids and NucleotidesWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Cellular Energy: Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument12 pagesCellular Energy: Photosynthesis & RespirationGobiNo ratings yet
- Recall: Central Dogma Is About Releasing Information Re The Information From Our GenomeDocument6 pagesRecall: Central Dogma Is About Releasing Information Re The Information From Our GenomePaigufanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument100 pagesRespirationColin RiddellNo ratings yet
- Energy and RespirationDocument11 pagesEnergy and Respirationririrachma fitriahNo ratings yet
- What Is A Gene? What Is DNA?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Gene? What Is DNA?aceofspades1004No ratings yet
- Topics For Bio Test-2Document15 pagesTopics For Bio Test-2nicolee martosNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument88 pagesNucleic AcidJoyce Jimenez100% (1)
- Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDDocument20 pagesGly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDfmd8421No ratings yet
- Body PhysiologyDocument88 pagesBody PhysiologyThe KittyNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument14 pagesBioenergeticsmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- How Protein Is Made Using Information From DNADocument30 pagesHow Protein Is Made Using Information From DNADainiel G. PerezNo ratings yet
- Bella Rhea Lavifa. S. Sakalus Wepe Nur Kholifatun Nisa Maya Umi Hajar Saltsa Ridlotul JDocument31 pagesBella Rhea Lavifa. S. Sakalus Wepe Nur Kholifatun Nisa Maya Umi Hajar Saltsa Ridlotul JSakalus Wepe100% (1)
- 05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeDocument48 pages05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeKinad DanikNo ratings yet
- 5 Biochemical PathwaysDocument33 pages5 Biochemical PathwaysYong AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Dna: Part Ii: Let"S Review Mitosis and Also Cover Protein SynthesisDocument67 pagesDna: Part Ii: Let"S Review Mitosis and Also Cover Protein SynthesisDev AshwaniNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To MetabolismDocument51 pagesAn Introduction To Metabolismhector axel macias lobatosNo ratings yet
- VCE Biology Unit 3.1 - Respiration - Main Stages in and Sites of Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesVCE Biology Unit 3.1 - Respiration - Main Stages in and Sites of Cellular Respirationehung01No ratings yet
- The Blueprint of Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Blueprint of Protein SynthesislamesaltheamoniqueNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 Energy and RespirationDocument34 pagesChap 12 Energy and RespirationGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Practical Work.Document25 pagesPractical Work.Adbhut YadavNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document6 pagesQ2 Module 5joseantoniolcastro408No ratings yet
- 2-Energy and RespirationDocument34 pages2-Energy and RespirationLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Notes On Nucleic AcidDocument6 pagesNotes On Nucleic AcidAbir Protik100% (1)
- Lecture 4 Human Physiology Enzymes StudentDocument6 pagesLecture 4 Human Physiology Enzymes StudentAlfonso RobertNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Mitochondria and ChloroplastsDocument24 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Mitochondria and ChloroplastsCeline BlancoNo ratings yet
- Imat Biologymock Test 5Document7 pagesImat Biologymock Test 5Phi BanNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules: Structure & Function of MacromoleculesDocument53 pagesBiological Macromolecules: Structure & Function of Macromoleculesmewmew2013No ratings yet
- Ribosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Document16 pagesRibosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Atikatul MutmainahNo ratings yet
- Lee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeDocument25 pagesLee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeShivaveerakumar S. Chandrikimath100% (1)
- A2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationDocument20 pagesA2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationArnel100% (1)
- Bio HLDocument34 pagesBio HLrishtit111No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesProtein Synthesisabisantiago6131100% (1)
- AP Biology Chapter 8 Reading GuideDocument7 pagesAP Biology Chapter 8 Reading GuideVal HathiramaniNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesA2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationKajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology (Zeb 361)Document7 pagesMolecular Biology (Zeb 361)Jacob WalterNo ratings yet
- DAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 3: Cellular EnergyDocument33 pagesDAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 3: Cellular EnergyEmilyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Food ATPDocument43 pagesCellular Respiration: Food ATPAmolkumar W DiwanNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Lecture 560B On LineDocument9 pagesWeek 15 Lecture 560B On LineTheNourishedSproutNo ratings yet
- Resume 293-305Document8 pagesResume 293-305Amirah NviNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument45 pagesCarbohydratescropion_78No ratings yet
- Genetics Auto Saved)Document7 pagesGenetics Auto Saved)natseeaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2Document7 pagesLesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Animal ReproductionDocument34 pagesAnimal ReproductionJenmae Dacullo MansiguinNo ratings yet
- Viernes BIOENERGETICS WorksheetDocument18 pagesViernes BIOENERGETICS WorksheetBelinda ViernesNo ratings yet
- Biochem NotesDocument8 pagesBiochem NotesKhay NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Concept ListDocument3 pagesBio 102 Concept ListLanae BraswellNo ratings yet
- NOTES 1 ATP and ADP CycleDocument4 pagesNOTES 1 ATP and ADP CycleJillian Reyes SantosNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Cellular Metabolism 2021Document23 pagesTopic 3 - Cellular Metabolism 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Biological Functions and Properties of Nucleosides, NucleotidesDocument30 pagesBiological Functions and Properties of Nucleosides, NucleotidesOlerhime BlessingNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument214 pagesBiology NotesbloomNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Metabolism: Santosh YadavDocument36 pagesBacterial Metabolism: Santosh YadavAurora ÇizmjaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level BiologyDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level BiologyTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- A2 Booklet 1 2019 PDFDocument466 pagesA2 Booklet 1 2019 PDFTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Parenting A Baby 018months Domestic AbuseDocument2 pagesLeaflet Parenting A Baby 018months Domestic AbuseTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Walking EssayDocument2 pagesWalking EssayTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- To What Extent Is The Government Responsible For The Increasing Divide Between The Rich and The Poor.Document11 pagesTo What Extent Is The Government Responsible For The Increasing Divide Between The Rich and The Poor.Tazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Similarity and Inequality GraphsDocument7 pagesSimilarity and Inequality GraphsTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Shapes of The GraphsDocument6 pagesShapes of The GraphsTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Dont Be A Kool FoolDocument1 pageDont Be A Kool FoolTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- You Are Contributing To Carbon FootprintDocument2 pagesYou Are Contributing To Carbon FootprintTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Responsible Consumption and Production NewDocument639 pagesResponsible Consumption and Production NewTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet