Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Annotated Physics Data Booklet 2016 PDF
Uploaded by
Clare ChenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Annotated Physics Data Booklet 2016 PDF
Uploaded by
Clare ChenCopyright:
Available Formats
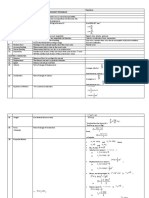
Equations—Core
Note: All equations relate to the magnitude of the quantities only. Vector notation has
not been used.
Sub-topic 1.2 – Uncertainties and errors Sub-topic 1.3 – Vectors and scalars
If: y = a ± b Adding/subtracting quantities:
uncertainty in result will be sum A
AV
then: ∆y = ∆a + ∆b of uncertainties of quantities.
y = Result. AH = Horizontal
component.
a, b, c = Quantities. Multiplying/dividing quantities: %
ab uncertainties of quantities are added AV = Vertical
If: y together to obtain % uncertainty in result.
Δ = Uncertainty. c component.
∆y ∆a ∆b ∆c
then: = + +
y a b c
AH
Powers of quantities: % uncertainty of
If: y an quantity is multiplied by power to obtain
AH = A cos θ Trigonometric rules of triangles are
applied when taking components of
% uncertainty in result.
∆y ∆a vector quantities.
then: = n A V = A sin θ
y a
F = Resultant force.
v = Final velocity. m = Mass.
Sub-topic 2.1 – Motion Sub-topic 2.2 – Forces
u = Initial velocity. Acceleration due to resultant force a = Acceleration.
v = u + at F ma
(Newton’s 2nd law of motion).
a = Acceleration (‘g’ 1 2 Ff ≤ µsR Frictional force on a static object. μs = Coefficient of
for gravitational). s = ut + at Equations applied to
static friction.
2 uniform motion (known as
‘suvat’ equations). Ff = µdR Frictional force on a dynamic object.
s = Displacement. v 2 = u 2 + 2as μd = “ dynamic “.
t = Time elapsed. (v + u ) t
s= Ff = Frictional force.
2
R = Normal reaction
Sub-topic 2.3 – Work, energy Sub-topic 2.4 – Momentum force.
W = Work done.
and power and impulse
F = Force. W = Fs cos θ Work done. p mv Momentum.
s = Displacement. 1 ∆p
p = Momentum.
EK mv 2 Kinetic energy.
2 F= Resultant force due to momentum.
EK = Kinetic energy. ∆t m = Mass.
1
Ep = k ∆ x 2 Elastic potential energy (in a spring).
p2 v = Velocity.
m = Mass. 2 EK Kinetic energy.
2m
v = Velocity. ∆Ep = mg ∆h Gravitational potential energy. F = Force.
EP = Potential energy. power Fv Power. impulse = F ∆t = ∆p t = Time.
k = Spring constant useful work out EK = Kinetic energy.
efficiency
total work in
x = Extension.
useful power out
g = Earth’s gravity.
total power in
h = Height.
4 Physics data booklet
You might also like
- Hans Wehr Searchable PDFDocument941 pagesHans Wehr Searchable PDFLars Bendixen100% (2)
- Chinese Dialect Versions BFBS CatalogueDocument65 pagesChinese Dialect Versions BFBS CatalogueLeo LawNo ratings yet
- Apology Strategies in Jordanian ArabicDocument17 pagesApology Strategies in Jordanian ArabicAla'a Bani KhalefNo ratings yet
- First Russian Reader For Business Bilingual For Speakers of English Beginner Elementary (A1 A2)Document19 pagesFirst Russian Reader For Business Bilingual For Speakers of English Beginner Elementary (A1 A2)vadimznNo ratings yet
- Arab For Non-Native SpeakersDocument49 pagesArab For Non-Native SpeakersIonut Bucur50% (2)
- Story of Ummara-Kamil KailaniDocument22 pagesStory of Ummara-Kamil KailaniskhananiNo ratings yet
- Declension of Russian AdjectivesDocument4 pagesDeclension of Russian Adjectivescndy31No ratings yet
- Linguistics and Religion David CrystalDocument14 pagesLinguistics and Religion David CrystalCatipasNo ratings yet
- Bahasa GermanDocument216 pagesBahasa GermanDion DionNo ratings yet
- Arabic Short Story Chapter 1Document54 pagesArabic Short Story Chapter 1Asmatullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Arabic Readers - Intellectual and Social Trends - Expository Writing - Volume 2Document144 pagesAdvanced Arabic Readers - Intellectual and Social Trends - Expository Writing - Volume 2Abdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9. Consonant Assimilation Pt.1Document10 pagesLesson 9. Consonant Assimilation Pt.1kizzie Andrea F BacosaNo ratings yet
- My Arabic Numbers Workbook 1 10Document18 pagesMy Arabic Numbers Workbook 1 10Surya Jatmika WaketurisNo ratings yet
- Phonetic Value Example: SymbolDocument5 pagesPhonetic Value Example: SymbolLookAtTheMan 2002No ratings yet
- مصطلحات القواعدDocument3 pagesمصطلحات القواعدNour AbuMeteirNo ratings yet
- Arabic LearningDocument81 pagesArabic Learningp_kumar777100% (1)
- Arabic AlphabetDocument4 pagesArabic AlphabetvineetaNo ratings yet
- Definitive Guide To Acing German PronunciationDocument5 pagesDefinitive Guide To Acing German PronunciationShekhar IyerNo ratings yet
- 140 Most Common Chinese CharactersDocument23 pages140 Most Common Chinese CharactersJewel PascuaNo ratings yet
- Sindhi LanguageDocument106 pagesSindhi LanguageJaved RajperNo ratings yet
- Discover The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia !Document23 pagesDiscover The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia !ti3mNo ratings yet
- German AlphabetDocument7 pagesGerman AlphabetadéjeunerNo ratings yet
- Learning IndonesianDocument125 pagesLearning IndonesianKoli Hau PoueuNo ratings yet
- 1 Pronunciationin GermanDocument4 pages1 Pronunciationin GermanJURANo ratings yet
- Comparative Morphology of Standard and EDocument260 pagesComparative Morphology of Standard and EknopeNo ratings yet
- A Dictionary of Idiomatic Expressions in Written Arabic - For The Reader of Classical and Modern TextsDocument290 pagesA Dictionary of Idiomatic Expressions in Written Arabic - For The Reader of Classical and Modern TextsAbdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Korean Complete LessonDocument82 pagesKorean Complete LessonMir Jabed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Review of A Grammar of Domari PDFDocument7 pagesReview of A Grammar of Domari PDFuliseNo ratings yet
- Story of Tanbori's Shoes-Kamil KailaniDocument60 pagesStory of Tanbori's Shoes-Kamil KailaniskhananiNo ratings yet
- Balg, Braune. A Gothic Grammar With Selections For Reading and A Glossary. 1895.Document252 pagesBalg, Braune. A Gothic Grammar With Selections For Reading and A Glossary. 1895.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et Orientalis100% (2)
- MR - Ibrahim.sultan - Prep 2.units 1-9.2017Document136 pagesMR - Ibrahim.sultan - Prep 2.units 1-9.2017yhgNo ratings yet
- A2 Yufa Chinese Grammar Level 2Document12 pagesA2 Yufa Chinese Grammar Level 2Yahia GamalNo ratings yet
- German ArticlesDocument6 pagesGerman ArticlesKostas G. PapNo ratings yet
- Four Character Idioms (05042014)Document61 pagesFour Character Idioms (05042014)Mika's TuitionNo ratings yet
- Assimil Arabic With Ease - TextDocument176 pagesAssimil Arabic With Ease - TextRajul Rahmad100% (1)
- TLoJaK 06 Korean Dialects - FinalDocument18 pagesTLoJaK 06 Korean Dialects - FinalElias CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- ArabicDocument12 pagesArabicmohammedabd123100% (1)
- Arabic On The MoveDocument32 pagesArabic On The MoveDJVLADIMIR7100% (1)
- Arabic Verbs - To PlayDocument52 pagesArabic Verbs - To PlayAl-Andalus AcademyNo ratings yet
- Arapski Jezik Za PočetnikeDocument38 pagesArapski Jezik Za Početnikeroze praseNo ratings yet
- 100 German Link Word ExamplesDocument28 pages100 German Link Word ExamplesOana IoanaNo ratings yet
- Arabic: Practice WorksheetDocument23 pagesArabic: Practice WorksheetVassiliki Amanatidou-KorakaNo ratings yet
- Arabic Language and The Study of Islam:who Studies Arabic and Why and How Can Theseskills Be Used at University and Beyond?Document52 pagesArabic Language and The Study of Islam:who Studies Arabic and Why and How Can Theseskills Be Used at University and Beyond?Mourad DiouriNo ratings yet
- Farsi Asan 1Document1 pageFarsi Asan 1Anonymous 6XVdBHNo ratings yet
- Spokenarabicofeg 00 WilluoftDocument488 pagesSpokenarabicofeg 00 WilluoftEdson LacirNo ratings yet
- Legal and Documentary Arabic ReaderDocument609 pagesLegal and Documentary Arabic Readernaziko14No ratings yet
- Swedish Level 1Document4 pagesSwedish Level 1nina gikaNo ratings yet
- Burmese Language IntroDocument106 pagesBurmese Language IntroelsasserNo ratings yet
- Ince PDFDocument1 pageInce PDFAnastasiya KryukovaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Formulas (Kinematic) Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesAP Physics Formulas (Kinematic) Cheat Sheet: by ViaRose AimanNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument3 pagesPhysics FormulasJames Patrick TorresNo ratings yet
- Physics Cheat SheetDocument21 pagesPhysics Cheat SheetDinu PereraNo ratings yet
- Tahsili Physics-Problems and QuestionsDocument75 pagesTahsili Physics-Problems and Questionsflynn riderNo ratings yet
- Equations+Sheet DynamicsDocument1 pageEquations+Sheet DynamicsMamon HoroubNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 EquationsDocument3 pagesPhysics 71 EquationsElah PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesCheat SheetKara CamitNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument35 pagesWork Energy and PowerManas ThakurNo ratings yet
- PHY DEF Half-UpdtedDocument13 pagesPHY DEF Half-Updted'Aqilah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- APSC 111 MT 2 WorkbookDocument17 pagesAPSC 111 MT 2 WorkbookMaya Kerzner100% (1)
- MECH2210 Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesMECH2210 Lecture NotesKeith WellsNo ratings yet
- Annotated Physics Data Booklet 2016 PDFDocument1 pageAnnotated Physics Data Booklet 2016 PDFClare Chen100% (1)
- D4 Antacids (PH Regulation of The Stomach)Document3 pagesD4 Antacids (PH Regulation of The Stomach)Clare ChenNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Chapter 1 - Linear EquationsDocument31 pagesLinear Algebra Chapter 1 - Linear Equationsdaniel_bashir808No ratings yet
- HIMCM National OutstandingDocument66 pagesHIMCM National OutstandingClare ChenNo ratings yet
- Ib English B Writing AssignmentDocument2 pagesIb English B Writing AssignmentClare ChenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8Clare ChenNo ratings yet
- Eco-Def - MidtermDocument2 pagesEco-Def - MidtermClare ChenNo ratings yet
- Physics IADocument11 pagesPhysics IAClare Chen100% (1)
- R - Linear Systems On Toric Varieties - LaterveerDocument8 pagesR - Linear Systems On Toric Varieties - LaterveerUnDueTreSberlaNo ratings yet
- Tap 04120288 PMLDocument7 pagesTap 04120288 PMLOzlem OzgunNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Rotation With Constant Angular Acceleration: OverviewDocument4 pagesLesson 8 Rotation With Constant Angular Acceleration: OverviewNadjer C. AdamNo ratings yet
- Math Gre Exercises: Christian ParkinsonDocument13 pagesMath Gre Exercises: Christian ParkinsonHan JuliaNo ratings yet
- I I R R 7 20 I: 1971 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1Document4 pagesI I R R 7 20 I: 1971 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1dawnNo ratings yet
- Ethington Et Al Placing The PastDocument66 pagesEthington Et Al Placing The PastbosnabosnaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 - Equations of CirclesDocument18 pages1.5 - Equations of CircleshaniebalmNo ratings yet
- MCQ On VELO and AcceDocument5 pagesMCQ On VELO and AcceLaxmikanth GurumurthyNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1 AIM: To Determine The Reduced Level of An Object When Base Is Instruments Used: Theodolite, Tape, Leveling Staff, Ranging RodDocument12 pagesExperiment - 1 AIM: To Determine The Reduced Level of An Object When Base Is Instruments Used: Theodolite, Tape, Leveling Staff, Ranging RodSakthi Murugan100% (1)
- Alvaro Siza VieiraDocument7 pagesAlvaro Siza VieiraAtshayaNo ratings yet
- Types and OpetopesDocument36 pagesTypes and OpetopesaaabbbzakNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ReflectionsDocument28 pagesMathematical ReflectionsinalalNo ratings yet
- Calculating Tank Wetted Area.Document17 pagesCalculating Tank Wetted Area.Shijumon KpNo ratings yet
- Robin Le Poidevin (Auth.) - Change, Cause and Contradiction - A Defence of The Tenseless Theory of TimeDocument170 pagesRobin Le Poidevin (Auth.) - Change, Cause and Contradiction - A Defence of The Tenseless Theory of TimeluizNo ratings yet
- Modul SBP SPM 2014 Perfect Score Add Math PDFDocument83 pagesModul SBP SPM 2014 Perfect Score Add Math PDFAiman JohariNo ratings yet
- Mazak Programming Manual For Mazatrol Matrix 3DDocument80 pagesMazak Programming Manual For Mazatrol Matrix 3DArturo LopezNo ratings yet
- Euler Spiral For Shape CompletionDocument24 pagesEuler Spiral For Shape CompletionplatlasNo ratings yet
- Amos 1Document134 pagesAmos 1Krishna Kumar AlagarNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering MechanicsDocument1 pageBasic Engineering MechanicsAditya BhattacharayaNo ratings yet
- Descartes Rule of SignsDocument1 pageDescartes Rule of SignsArindam GaraiNo ratings yet
- Anthony Dunne - Hertzian Tales - Electronic Products, Aesthetic Experience, and Critical Design-The MIT Press (2006) PDFDocument193 pagesAnthony Dunne - Hertzian Tales - Electronic Products, Aesthetic Experience, and Critical Design-The MIT Press (2006) PDFIhjaskjhdNo ratings yet
- Mathématiques Les Exercices Incontournables MPSIDocument4 pagesMathématiques Les Exercices Incontournables MPSIRobeny DjiakouNo ratings yet
- Brenner 1998Document23 pagesBrenner 1998Catalina AcostaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Theories of Design - George SalvanDocument514 pagesArchitectural Theories of Design - George SalvanOyo-gelo Cueco97% (63)
- r2 - Lecture - CO2 - Math 21-1Document38 pagesr2 - Lecture - CO2 - Math 21-1Benmar N. OcolNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Degree Examination, 2012: 140. Analytical Mechanics and Tensor AnalysisDocument2 pagesM.Sc. Degree Examination, 2012: 140. Analytical Mechanics and Tensor AnalysisKathiresan NagaiNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Maths Quiz 1 Q8-13Document2 pagesTerm 2 Maths Quiz 1 Q8-13Kok Siong OngNo ratings yet
- Kinematic EquationsDocument27 pagesKinematic EquationsImn MorrisNo ratings yet
- Add MathsDocument5 pagesAdd MathsDzul JefriNo ratings yet
- (Measure Theory) D. H Fremlin-Measure Theory-Torres Fremlin (2001)Document563 pages(Measure Theory) D. H Fremlin-Measure Theory-Torres Fremlin (2001)mnemoniaNo ratings yet