Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Communicable Diseases of Childhoo1
Uploaded by
esmirik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Communicable Diseases of Childhoo1.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesCommunicable Diseases of Childhoo1
Uploaded by
esmirikCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
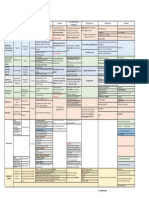
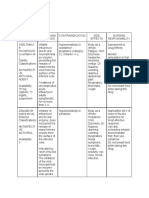
Communicable Diseases of Childhood
Disease Agent Source/ Incubatio Period of Clinical Complications Therapeutic Nursing
Transmission n Period Communicabilit Manifestations Management Management
y
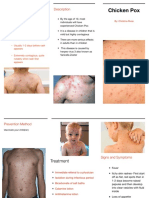
Chicken Varicella-Zoster Droplet, Direct 2-3 weeks 1 day before Slight fever, Encephalitis Supportive Airborne and
Pox virus contact eruption of malaise and Secondary anti-itch Contact
lesions until 6 anorexia for infection therapy precautions
days after crusts 1st 24 hrs. Herpes Zoster lies Distraction Avoid Aspirin
have started Highly pruritic dormant in nerves Antiviral (Reye’s
forming. rash and can become Immunization syndrome)
(centripedal) Shingles later in Skin
Lesions in life. Immunization assessment
three stages is available for
present Shingles,
recommended for
those 60 years and
older.
Diphtheria Corynebacteriu Secretions, 2-5 days 2-4 weeks Common cold Toxic Antibiotics Droplet
m diphtheriae direct contact symptoms cardiomyopathy Bed rest precautions
Sore throat Toxic neuropathy (myocarditis Observe for
Lymphadenitis Obstructed airway prevention) resp distress/
(bull’s neck) Immunization obstruction
Fever,
hoarseness,
cough
Fifth Human Secretions 4-14 days uncertain Slapped cheek Arthritis Antipyretics No isolation
Disease Parvovirus B19 appearance Analgesics Pregnant
(day 1-4) Anti- women should
Red lacy rash, inflammatory not be around
spreads child.
proximal to
distal (day 2-
greater than
week)
Rash comes
and goes
Roseola Human Saliva 5-15 days unknown Persistent high Febrile seizures (if Antipyretics Educate on
herpesvirus fever for 3-4 history) antipyretic use
type 6 days Seizure
Drop in fever, precautions
rash appears
for 1-2 days
(trunk, then
spreads to
neck, face &
extremities)
Disease Agent Source/ Incubatio Period of Clinical Complications Therapeutic Nursing
Transmission n Period Communicabilit Manifestations Management Management
y
Mumps Paramyxovirus Saliva 14-21 Immediately Fever, Encephalitis Analgesics Droplet and
days before swelling headache, Myocarditis Antipyretics contact
begins anorexia (day Sterility IV fluids precautions
1) Meningitis Immunization Rest
“ear ache” Fluids
(day 2) Neuro and
Parotid hydration
gland(s) assessment
enlarge (day 3)
for 1-3 days.
Measles Virus Secretions 10-20 4 days before to Fever, malaise Obstructive Vit A Airborne
days 5 days after rash (1st 24 hrs) laryngitis supplement precautions
appears Cough, Obstructive (reduces Rest, quiet
conjunctivitis, laryngo-tracheitis morbidity & Antipyretics
Koplik spots mortality) Skin care
(next 2 days) Supportive Airway and
Rash begins Immunization skin
on face and assessment
moves
downward
(days 3-4)
Abdominal
pain
Pertussis Bordetella Resp 6-20 days During resp Symptoms of Pneumonia (usual Antibiotics Droplet
(Whooping pertussis secretions/ symptoms resp tract cause of death) Supportive precautions
Cough) droplet & infection Atelectasis (O2 & Nasopharynge
direct contact Cough mostly Hemorrhage, humidity) al Cx for Dx.
at night, thick hernias (from Fluids Assess for
mucous plug forceful cough) Immunization obstructive
Dehydration airway
Polimyeliti Enteroviruses Feces, 7-14 days unknown General illness Permanent Bed rest Positioning
s (Polio) oropharyngeal in varying paralysis Sedatives (prevent
secretions. degrees Respiratory arrest (anxiety over contractures)
Direct contact, May have pain paralysis) Skin
fecal-oral, and stiffness Ventilation assessment
Pharyngeal- CNS paraylysis (resp Observe for
oropharyngeal paralysis) resp paralysis
. Phys Therapy
Immunization
Disease Agent Source/ Incubatio Period of Clinical Complications Therapeutic Nursing
Transmission n Period Communicabilit Manifestations Management Management
y
Rubella Rubella virus Secretions 14-21 7 days before Low-grade Teratogenic Antipyretics Droplet
(German days rash until 5 days fever, effects on fetus Analgesics precautions
Measles) after rash headache, Rarely- Immunization Avoid contact
appears. malaise (1-5 encephalitis with pregnant
days) women.
Rash (face
then rapidly
spreads
downward til
body is spread
in pinkish red
maculopapula
r exanthema,
within a day)
Scarlet Group A Beta- Naso- 2-5 days During High fever, Peritonsillar Full course of Droplet
Fever hemolytic strep pharyngeal incubation high HR abscess antibiotics precautions
secretions, period and Tonsils Acute Supportive Encourage
direct or clinical illness enlarged, glomerulonephriti (analgesics, fluids
droplet edematous s antipyretics) Soft diet
and beefy red Rheumatic fever Rest Education
White coated (inflammatory (prevent
tongue (1st 1-2 disease that can spread of
days), then involve heart, infection:
strawberry joints, skin and discard
tongue brain) toothbrush, no
Rash appears sharing
within 12 hrs eating/drinkin
(red, pinpoint) g utensils)
Skin sloughs
off end of 1st
week
You might also like
- ExanthemesDocument1 pageExanthemesomarragabselimNo ratings yet
- Table of Communicable Diseases PDFDocument12 pagesTable of Communicable Diseases PDFkayekristine2001No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Pruritis (Itch), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pruritis (Itch), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- DIPTHERIADocument1 pageDIPTHERIAGrace StephanieNo ratings yet
- Covid Update. Answers for curious minds: How's my health, doc?From EverandCovid Update. Answers for curious minds: How's my health, doc?No ratings yet
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderDocument12 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- Berongoy VirusDocument2 pagesBerongoy VirusGlaiza Mae BerongoyNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan RabiesDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan RabiesYanis Emmanuelle LimNo ratings yet
- Elise Tamayo - Infectious Disease PamphletDocument2 pagesElise Tamayo - Infectious Disease Pamphletapi-550823265No ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument2 pagesCommunicable DiseasesRCOANo ratings yet
- Definition of Chicken Pox:-: History Shows That Chicken Pox May Have Been Around SinceDocument4 pagesDefinition of Chicken Pox:-: History Shows That Chicken Pox May Have Been Around SincemomoNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox 2Document1 pageChicken Pox 2Kristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthem in PregnancyDocument3 pagesViral Exanthem in PregnancyCatherine Blanche LeeNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 LEC Alterations With Infectious Inflammatory and Immunologic Responses PDFDocument18 pagesNCM 109 LEC Alterations With Infectious Inflammatory and Immunologic Responses PDFcalliemozartNo ratings yet
- 191202-Fina Kartika Damayanti-2d Keperawatan-Leflet DifteriDocument2 pages191202-Fina Kartika Damayanti-2d Keperawatan-Leflet DifteriVinadmyNo ratings yet
- Name of Infection - Docx RabiesDocument2 pagesName of Infection - Docx RabiesGrace SabadoNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study PalivizumabDocument2 pagesDrug-Study PalivizumabIrize DenagaNo ratings yet
- Table of Communicable Diseases: Disease Signs & Symptoms Incubation Prevention Chicken PoxDocument10 pagesTable of Communicable Diseases: Disease Signs & Symptoms Incubation Prevention Chicken PoxJohn DamianNo ratings yet
- Equine Medicine DISEASESDocument14 pagesEquine Medicine DISEASESlowi shooNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - RabiesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Rabiesderic89% (9)
- DiseasesDocument7 pagesDiseasesPermalino Borja Rose AnneNo ratings yet
- Exanthems TableDocument3 pagesExanthems TableYana CovarNo ratings yet
- B. Natural History of Disease WorksheetDocument3 pagesB. Natural History of Disease WorksheetYahya MoralesNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenDocument20 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenMark oliver Gonzales100% (1)
- Case-Scenario-Oxygen Therapy-BuenconsejoDocument6 pagesCase-Scenario-Oxygen Therapy-BuenconsejoCarna BuenconsejoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudydubouzettheresaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases Infectious Diseases and Hematologic DrugDocument26 pagesCommunicable Diseases Infectious Diseases and Hematologic DrugAdrian LesiguesNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Cephalexin)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Cephalexin)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeAbijah Leris SarmientoNo ratings yet
- © 2015. Zoetis Inc - All Rights Reserved FINAL March 2015 TI-01254Document2 pages© 2015. Zoetis Inc - All Rights Reserved FINAL March 2015 TI-01254rahmaliaNo ratings yet
- ICC AUDIT TOOL AND TRIAGE ALGORHYTHM DGMC - WPS PDF Convert PDFDocument40 pagesICC AUDIT TOOL AND TRIAGE ALGORHYTHM DGMC - WPS PDF Convert PDFWendy Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- NameDocument2 pagesNamekorikonglibatNo ratings yet
- Jan 2006 Table Communicablediseases PDFDocument10 pagesJan 2006 Table Communicablediseases PDFBalwant kumarNo ratings yet
- Vaccine (Infant, Child)Document5 pagesVaccine (Infant, Child)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyDocument3 pagesAcyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyAnnahNo ratings yet
- The Epi Target DiseasesDocument7 pagesThe Epi Target DiseasesElizabeth Ivory ChuaNo ratings yet
- !DRUGSTUDY CasepresssDocument6 pages!DRUGSTUDY CasepresssAchi AxxxNo ratings yet
- Dengue Leaflet InfoDocument1 pageDengue Leaflet InfoMIJIN BAENo ratings yet
- Integumentary Disoder: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesIntegumentary Disoder: Nursing Care PlanFrancise Elyn OcubilloNo ratings yet
- Case Study BurnDocument3 pagesCase Study BurnInday BebeNo ratings yet
- Most Common Complication: Sabay SilaDocument6 pagesMost Common Complication: Sabay SilaSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Chicken+PoxDocument2 pagesCom +Nursing+Care+Plan+Chicken+PoxDahl Obañana Erojo100% (1)
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFAkeroNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken PoxDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Poxderic87% (62)
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseYana VillapacibeNo ratings yet
- PEDIA - Drug Study & NCPDocument24 pagesPEDIA - Drug Study & NCPCzarina Mae Lomboy100% (1)
- Brosure Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesBrosure Dengue FeverMadvi TadeoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverKenneth Lagman100% (1)
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureapi-340778375No ratings yet
- Case Study 4 CVD Infarct CAP MR HUD RDU DementiaDocument21 pagesCase Study 4 CVD Infarct CAP MR HUD RDU DementiaVictoria Mae Irong CabahugNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Purpose Form Dose Route of Administration Interval Bet. Doses Side EffectsDocument3 pagesVaccine Purpose Form Dose Route of Administration Interval Bet. Doses Side Effectsdeyna28No ratings yet
- Resource Unit 31finalDocument10 pagesResource Unit 31finalHector B. Jr PalacioNo ratings yet
- M-M-R Ii: Swollen GlandsDocument9 pagesM-M-R Ii: Swollen GlandsJoanne Alyssa Hernandez LascanoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease ChartDocument5 pagesCommunicable Disease ChartAuspice QatarNo ratings yet
- INFLUENZADocument4 pagesINFLUENZAJeanne CastroNo ratings yet
- List of Infectious DiseasesDocument17 pagesList of Infectious DiseasesRohit AhujaNo ratings yet
- Derma CD McqsDocument22 pagesDerma CD McqsheshamNo ratings yet
- TC in 200 Pages PDFDocument195 pagesTC in 200 Pages PDFWaleed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument2 pagesHerpes ZosterinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox - A New Epidemic of Disease and CorruptionDocument9 pagesChickenpox - A New Epidemic of Disease and CorruptionBryan GraczykNo ratings yet
- Handout CompilationDocument199 pagesHandout CompilationG Fab100% (2)
- Viral Anterior Uveitis.12Document10 pagesViral Anterior Uveitis.12morelaNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 6 Blok Saraf Dan KejiwaanDocument44 pagesPemicu 6 Blok Saraf Dan KejiwaanTommy WidjajaNo ratings yet
- The Infants, Toddler, and PreschoolerDocument128 pagesThe Infants, Toddler, and PreschoolerPiao Liang Jing100% (2)
- Case Presentation-ChickenpoxDocument41 pagesCase Presentation-ChickenpoxShaliniNo ratings yet
- Medicine II - Topical Past Papers (2007-2019)Document48 pagesMedicine II - Topical Past Papers (2007-2019)Humna YounisNo ratings yet
- RCOG Green Top Notes 1Document48 pagesRCOG Green Top Notes 1Anonymous LnLvsb100% (1)
- 9 Opportunistic InfectionsDocument14 pages9 Opportunistic InfectionsArini B. MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Colloidal Silver Testimonials PDFDocument17 pagesColloidal Silver Testimonials PDFADRNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Vesicular Bullous Lesions 1Document32 pagesUlcerative Vesicular Bullous Lesions 1Mustafa AliNo ratings yet
- ICD-10 CM All Diagnosis and Trigger Codes - Revised 9-17-2015Document6,507 pagesICD-10 CM All Diagnosis and Trigger Codes - Revised 9-17-2015Puskesmas MakaleNo ratings yet
- BHTbook StevenWmFowkes 141016Document67 pagesBHTbook StevenWmFowkes 141016Sparklight JackNo ratings yet
- Infectious QuestionDocument52 pagesInfectious Questionrayooona88No ratings yet
- January 31 2013 Mount Ayr Record-NewsDocument14 pagesJanuary 31 2013 Mount Ayr Record-NewsMountAyrRecordNewsNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Pain: Paul A. RosenbergDocument24 pagesEndodontic Pain: Paul A. RosenbergArturo Trejo VeraNo ratings yet
- TOPNOTCH Microbiology-Supertable-by-Dr - Cocoy-Calderon-Jaffar-Pineda-Troy-Soberano-UPDATED-NOVEMBER-2017 PDFDocument34 pagesTOPNOTCH Microbiology-Supertable-by-Dr - Cocoy-Calderon-Jaffar-Pineda-Troy-Soberano-UPDATED-NOVEMBER-2017 PDFWaiwit KritayakiranaNo ratings yet
- Traditional Chinese Dermatology: Zentral WellnessDocument14 pagesTraditional Chinese Dermatology: Zentral Wellnessan ssiNo ratings yet
- Research: Clinical and Epidemiological Profile of Herpes Zoster A Cross-Sectional Study From Tertiary HospitalDocument6 pagesResearch: Clinical and Epidemiological Profile of Herpes Zoster A Cross-Sectional Study From Tertiary HospitalIntan MirandaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination For The Prevention of Shingles (Herpes Zoster) - UpToDateDocument13 pagesVaccination For The Prevention of Shingles (Herpes Zoster) - UpToDateAlcemir JúniorNo ratings yet
- Ve Siculo Bull Ous DiseasesDocument73 pagesVe Siculo Bull Ous DiseasesAARYANo ratings yet
- Jurnal Herpes PDFDocument9 pagesJurnal Herpes PDFIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- Master Tung's Four Horses Combination - Master Tung's Magic PointsDocument12 pagesMaster Tung's Four Horses Combination - Master Tung's Magic PointsAWEDIOHEAD93% (14)
- This Is A Document About Chicken PoxDocument24 pagesThis Is A Document About Chicken Poxarul100% (1)
- Chickenpox - A Rare Case Involing Periodontal Tissues: ASE EportDocument4 pagesChickenpox - A Rare Case Involing Periodontal Tissues: ASE EportTunggul BagusNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument16 pagesHerpes ZosterColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- USMLE - VirusesDocument120 pagesUSMLE - Virusessapatel89No ratings yet
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.From EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineFrom EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicFrom EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicNo ratings yet
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusFrom EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanFrom EverandThe Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismFrom EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsFrom EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Narrative Gym for Medicine: Introducing the ABT Framework for Medical Communication with Peers, Professionals, and the PublicFrom EverandThe Narrative Gym for Medicine: Introducing the ABT Framework for Medical Communication with Peers, Professionals, and the PublicNo ratings yet
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyFrom EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Development of Questionnaires for Quantitative Medical ResearchFrom EverandDevelopment of Questionnaires for Quantitative Medical ResearchNo ratings yet
- The Price of Health: The Modern Pharmaceutical Industry and the Betrayal of a History of CareFrom EverandThe Price of Health: The Modern Pharmaceutical Industry and the Betrayal of a History of CareRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Heat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoFrom EverandHeat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (40)
- Coronary: A True Story of Medicine Gone AwryFrom EverandCoronary: A True Story of Medicine Gone AwryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeFrom EverandThe Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- The Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceFrom EverandThe Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceNo ratings yet
- Getting Pregnant Naturally: Healthy Choices To Boost Your Chances Of Conceiving Without Fertility DrugsFrom EverandGetting Pregnant Naturally: Healthy Choices To Boost Your Chances Of Conceiving Without Fertility DrugsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Inflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeFrom EverandInflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Environmental and Health and Safety Management: A Guide to ComplianceFrom EverandEnvironmental and Health and Safety Management: A Guide to ComplianceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mercury, Mining, and Empire: The Human and Ecological Cost of Colonial Silver Mining in the AndesFrom EverandMercury, Mining, and Empire: The Human and Ecological Cost of Colonial Silver Mining in the AndesNo ratings yet
- The Varicose Veins Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Varicose Veins ManagementFrom EverandThe Varicose Veins Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Varicose Veins ManagementNo ratings yet
- COVID-19: The Victims, The Heroes, The Comlicit, and Our New NormalFrom EverandCOVID-19: The Victims, The Heroes, The Comlicit, and Our New NormalNo ratings yet