Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exanthemes
Uploaded by
omarragabselimOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exanthemes
Uploaded by
omarragabselimCopyright:
Available Formats
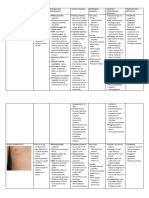
Causative Incubation Rash Morphology &
Disease Transmission History Infectivity Unique features Complications Treatment
organism period Distribution
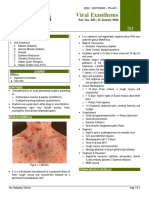
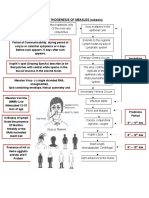
First day: Fever & Malaise with 3Cs 5 days prior to onset of Maculopapular erythematous Koplik's spots on On 2nd day of Otitis media (m.c) Supportive (Antipyretic & hydration)
(cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis) symptoms until 5 to 6 days rash appear on forehead illness Opposite molars
Measles Contact with
Para-myxovirus 10-14 days Then Koplik's spot after the onset of rash downward, after three days, Encephalitis Vit A if admitted
(Rubeola) droplets Confers lifelong immunity Disappear coincident with the Pneumonia (m.c of death)
start to fade in reverse order
(discrete macular lesions) appearance of the rash Antbiotics if Complications occur
Then On 3-5 day: Rash appears Vaccine available Death (1:5000)
Prodrome 1-6 days Before rash: < 16 wk: Cataract, deafness, IUGR, Cardiac,
Few days before and 5 to 7
headache, malaise, sore throat, Post-auricular Lymphadenopathy Encephalitis
Rubella (aka; days after the onset of the Transient pink or red first on
Contact with coryza, and fever. Disappear 24 hours
German Measles Rubella 14-21 days rash face and Neck, then trunk and Supportive
droplets after rash 16-20 wks: min risk of deafness
or third disease) limbs
Tender Post-auricular Forscheimer spots
Vaccine available >20 wks> no documented risk
Lymphadenopathy
Roseola infantum 6 mo - 3 years Pink or rose colored macules
During whole period of Encephalitis (very rare) Not necessary
(aka; exanthem Herpesvirus 6 or Abrupt high fever upto 41 C First on Trunk, then arms &
Saliva 10-15 days Last for 3-4 days disease & may be even neck
subitum or 6th 7
disease) before pyrexia Febrile seizure Prognosis is Excellent
Rash when fever subside Last for 1-2 days
Erythema Contact with Mild prodrome Biphasic: Rash is intensely red Fetal lose in 10%
infectiosum aerosolized Arthritis common in adults but rare in Not infectious once rash on the face (4-5 days), then
parvovirus B19 4-14 days Slapped-cheek appearance May recur with Temp changes Supportive
(aka; fifth respiratory children appears A reticular (netlike)
disease) droplets Mainly 4-10 years of age maculopapular eruption Aplastic crisis in SCA
Fever, chills, malaise, and sore throat, Begins on the chest and Early: Ear, tonsil, throat and meningeal
Oral penicillin VK for 10 days
Group A strep followed within 12 to 48 Can be infectious for 2 to 3 spreads rapidly, usually within infection
Scarlet fever Respiratory
infection (strept 1-7 days hours by a distinctive rash weeks after the symptoms Sandpaper-like Late: ARF or GN
(aka; scarlatina) droplets Facial flushing, perioral pallor
pyogenes) appear if not treated Single I.M benzathine pencillin 1.2
2-8 years of age >> Strawberry tongue
Erythema marginatum may be seen in 10%.
Highly contagious in Appearance of lesions in ALL Encephalitis / meningitis Supportive
Low-grade fever, malaise, and three stages in one region
Direct contact prodromal and vesicular Pneumonia (adult) Avoid Salicylates
Varicella (aka;
Varicella Zoster 14-21 days headache stage till they dry (Crops, clusters), appear 3-4 Thrombocytopenia
chickenpox) Air: sneezing, Acyclovir (if e/in 24 hr of rash)
Vaccine available (live days after symptoms Cellulitis
coughing < 10 years of age
attenuated) Start on the trunk and Face Reactivation > Shingles VariZIG Ig
Coxsackievirus < 5 years of age (m.c < 3) Erythematous macule Supportive
Viral meningitis
Direct contact Oral: Painful Vesicles & ulcer Symptomatic
HFM disease A16 or
Low grade fever, anorexia, malaise, H & F: non-tender vesicles
enterovirus 71 Meningoencephalitis Diligent hand washing
URTI (2-3 days) THEN Rash Lesions resolve over 4 to 7 days
Sneezing First 5 days after
3-6 days Myocarditis
symptoms start Small whitish ulcers, typically
Coxsackievirus located on the soft palate and Viscous lidocaine should not be used
Herpangina Fever, mouth pain, and oral ulcers
group A subtype posterior pharynx, without in children
Coughing Sepsis
accompanying skin lesions
HSV-1 1) Gingivostomatitis: Persists for life in a latent Umbilicated vesicles that are
Oral acyclovir 200 mg 5x1x7
Orofacial (m.c) Fever, malaise, and vesicles form extremely painful
Liver, lung, CNS Herpes labialis if reactivate
Viral shedding may occur Recurrent: 400 mg 5x1x5
& genitalia Oral secretions less severe if reactivate
from an asymptomatic source
In childhood 2) Genital Herpes:
Oral acyclovir 200 mg 5x1x7-10
Lays latent in Painful vesicles and ulcers
sensory ganglia Fever, malaise & dysurea Recur: 200x5x5
3) HSV-1 Encephalitis:
Temporal lobe
Acute onset
HSV infection 2-14 days Focal deficit Diagnosis:
70% mortality if not treated C/S, PCR or DFA = difinitive IV Acyclovir 10 mg/kg x3x 14-21 days
4) HSV-2 Meningitis: PCR is more sensitive than C/S
Benign Serology: acute or reactivation
more in women PCR for CSF
5)HSV-2 neonatal encephalitis High WBC (Lymphocytes)
HSV-2 6) Herpetic whitlow: Normal CSF in rare cases
During childbirth Oral acyclovir 200 mg 5x1x7
Genitalia (m.c) Painful vesicles (immunocompromised)
Other systems 7) Ocular herpes: Resending CSF PCR in 72 hours
Usually in adults keratitis, conjunctivitis, and acute CT/MRI of brain is suggestive & Oral acyclovir 400 mg 5x1x7
Sexual contact
Neonate retinal necrosis may be NAD early in course
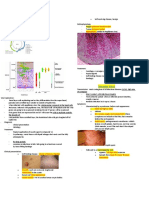
Fever >/= 5 days + 4 of the following (CRASH) High WBC, high platelets Admission
Vasculitis of Peaks at age 18 to 24 months, 1) Conjunctivitis: Bilateral & nonexudative CRP > 3, ESR > 40
Palmar lesions: Diffuse IVIG; 2 g/kg over 10 to 12 hrs
small &medium with most cases occurring by 2) Rash: Polymorphous, generalized Albumin < 3
erythema, may later
KAWASAKI’S vessels - age 10 years and the majority 3) Adenopathy: cervical node more than one > 1.5 cm High ALT
desquamate (see measles) Coronary artery aneurysm 1:5 patient
DISEASE unknown of patients being seen by age 4) Straberry tonge: erythema, or cracked and red lips Pyuria Aspirin (initially 80 to 100 mg/ kg
5 years 5) Hands and feet: erythema and swelling Anemia for age daily divided QID till afebrile
Echocardiography
Dr. Sadiq Ameen
You might also like
- Communicable Diseases of Childhoo1Document3 pagesCommunicable Diseases of Childhoo1esmirikNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Pocket GuideDocument19 pagesAntibiotic Pocket GuideNaomi Liang100% (1)
- Poliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaDocument4 pagesPoliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaJeanna Chong100% (1)
- EncoperesisDocument6 pagesEncoperesisRishi SelvamNo ratings yet
- Form No. 10iDocument2 pagesForm No. 10iTempuserNo ratings yet
- Why Cell Phone Towers Are So Bad For Your Health?Document6 pagesWhy Cell Phone Towers Are So Bad For Your Health?Dr. Sirish100% (1)
- Common Diseases Review - Community MedicineDocument15 pagesCommon Diseases Review - Community Medicinelas85% (13)
- Mnlkaxi QH: Manisha M.Sc. NursingDocument57 pagesMnlkaxi QH: Manisha M.Sc. NursingManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction With CABG Concept MapDocument1 pageMyocardial Infarction With CABG Concept MapMaria Therese100% (1)
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseVinceNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Practice TestDocument4 pagesPsychiatric Practice TestARIS100% (1)
- Table of Communicable Diseases PDFDocument12 pagesTable of Communicable Diseases PDFkayekristine2001No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverKenneth Lagman100% (1)
- Internation Classification ICSD III BetaDocument8 pagesInternation Classification ICSD III BetaRikizu HobbiesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderDocument12 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- Beckman Coulter CasesDocument34 pagesBeckman Coulter Caseszachabe100% (3)
- Measles (Case Presentation)Document19 pagesMeasles (Case Presentation)Zam Pamate100% (3)
- 2 Pemeriksaan Laboratorium Klinik GinjalDocument80 pages2 Pemeriksaan Laboratorium Klinik Ginjallintang aNo ratings yet
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy, HBOT: Mohammad Guritno SURYOKUSUMODocument63 pagesHyperbaric Oxygen Therapy, HBOT: Mohammad Guritno SURYOKUSUMOAkbar AmirullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenDocument20 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenMark oliver Gonzales100% (1)
- Exanthems TableDocument3 pagesExanthems TableYana CovarNo ratings yet
- Fever With RashDocument78 pagesFever With RashRiyan AgusNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- K21-Fever With RashDocument76 pagesK21-Fever With RashMarisa Perucana SinambelaNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthems ReviewerDocument4 pagesViral Exanthems ReviewerNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- IM - Viral ExanthemsDocument5 pagesIM - Viral ExanthemsJoan Melissa SomeraNo ratings yet
- NRSG 206 Communicable Disease: What Will You See?Document3 pagesNRSG 206 Communicable Disease: What Will You See?GirlwithnonameNo ratings yet
- IntffDocument2 pagesIntffLana AmerieNo ratings yet
- Exanthematous DisordersDocument16 pagesExanthematous DisordersZweNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthem in PregnancyDocument3 pagesViral Exanthem in PregnancyCatherine Blanche LeeNo ratings yet
- Filariasis: Wuchereria BancroftiDocument6 pagesFilariasis: Wuchereria BancroftibeautyNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BDocument15 pagesFar Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Chicken Pox:-: History Shows That Chicken Pox May Have Been Around SinceDocument4 pagesDefinition of Chicken Pox:-: History Shows That Chicken Pox May Have Been Around SincemomoNo ratings yet
- Pediatria 2021Document34 pagesPediatria 2021Bryan MelendezNo ratings yet
- Spots Are A Fleeting Enanthem Seen As Small, Red Spots (Petechiae) On The Soft PalateDocument6 pagesSpots Are A Fleeting Enanthem Seen As Small, Red Spots (Petechiae) On The Soft PalateFret Ramirez Coronia RNNo ratings yet
- MEASLESDocument68 pagesMEASLESMonysyha AtriNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Pedia Ii 2.02 NewDocument7 pagesShanz - Pedia Ii 2.02 NewPetrina XuNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Syndrome Can Cause Many of The Same Findings As Measles But Lacks Discrete Intraoral Lesions and A Severe Prodromal CoughDocument5 pagesKawasaki Syndrome Can Cause Many of The Same Findings As Measles But Lacks Discrete Intraoral Lesions and A Severe Prodromal Coughนีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanth EMS: Rabano Somera Tiburcio ZabalaDocument24 pagesViral Exanth EMS: Rabano Somera Tiburcio ZabalaJoan Melissa SomeraNo ratings yet
- Del Rosario Ryan D. BSN 4C1-7 Mr. Daniel Mon Mamanao: Measles Pre-Eruptive StageDocument5 pagesDel Rosario Ryan D. BSN 4C1-7 Mr. Daniel Mon Mamanao: Measles Pre-Eruptive Stageryandelrosario9yahooNo ratings yet
- General Medicine 3Document60 pagesGeneral Medicine 3Zeyad AlhaimiNo ratings yet
- TB + MumpsDocument2 pagesTB + Mumpsd3mooz13No ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Viral ExanthemsDocument30 pagesViral ExanthemsMiaMDNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Word Sasbel 3Document6 pagesWord Sasbel 3Muhammad Naufal WidyatmakaNo ratings yet
- H - Communicable Disease MatrixDocument3 pagesH - Communicable Disease MatrixAnjelica BanaderaNo ratings yet
- Huiduitslag KinderenDocument3 pagesHuiduitslag KinderenKelsey van SonNo ratings yet
- Table of Communicable Diseases: Disease Signs & Symptoms Incubation Prevention Chicken PoxDocument10 pagesTable of Communicable Diseases: Disease Signs & Symptoms Incubation Prevention Chicken PoxJohn DamianNo ratings yet
- Measles PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMeasles PathophysiologyAl TheóNo ratings yet
- K22 Variola KBKDocument12 pagesK22 Variola KBKedelinNo ratings yet
- Common Exanthems PDFDocument4 pagesCommon Exanthems PDFKaren Ivy BacsainNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases Chart With PicsDocument3 pagesCommunicable Diseases Chart With PicsesmirikNo ratings yet
- Treatment:: Most LikelyDocument4 pagesTreatment:: Most LikelyRichlie Magtulis IINo ratings yet
- Measles: Introduction: - Highly Contagious VirusDocument14 pagesMeasles: Introduction: - Highly Contagious VirusPrabhat RanjanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis: o Also Called PPD - ID (Purified Protein Derivative)Document9 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis: o Also Called PPD - ID (Purified Protein Derivative)LoramaematuteNo ratings yet
- Paralisis FacialDocument25 pagesParalisis FacialItzel Estephany ANo ratings yet
- Virology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexDocument4 pagesVirology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexJaz CNo ratings yet
- Activities in Airborne DiseasesDocument5 pagesActivities in Airborne DiseasesAizel ManiagoNo ratings yet
- VARICELLADocument1 pageVARICELLAWendy Laura Sanchez FloresNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox: VaricellaDocument3 pagesChickenpox: VaricellaPauline Mae RobertoNo ratings yet
- Comm DiseasesDocument5 pagesComm DiseasesZaireXandraReyesNo ratings yet
- Vaccine (Infant, Child)Document5 pagesVaccine (Infant, Child)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Most Common Complication: Sabay SilaDocument6 pagesMost Common Complication: Sabay SilaSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- RubellaDocument29 pagesRubellaRose PeranteNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) Hepatitis B Vaccine DTP Poliovirus (OPV/IPV) Haemophilus Influenza B (Hib) Rotavirus Type Dose Route ScheduleDocument3 pagesBacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) Hepatitis B Vaccine DTP Poliovirus (OPV/IPV) Haemophilus Influenza B (Hib) Rotavirus Type Dose Route ScheduleLISETTE TRICIA MALIPERONo ratings yet
- Vaccine Preventable Diseases (Chicken Pox)Document7 pagesVaccine Preventable Diseases (Chicken Pox)Sadia Akter EmaNo ratings yet
- 7.2 - Medical Virology Part 2Document39 pages7.2 - Medical Virology Part 2Kaela Beatrice Sy LatoNo ratings yet
- Measles and Scarlet Fever Kawasaki Disease: Fatin & EileenDocument30 pagesMeasles and Scarlet Fever Kawasaki Disease: Fatin & EileenbyteNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Medication: Aspirin (Ascriptin, Bayer Aspirin, Aspirtab, Ecotrin, Durlaza)Document11 pagesMyocardial Infarction Medication: Aspirin (Ascriptin, Bayer Aspirin, Aspirtab, Ecotrin, Durlaza)Ashutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Williams Obstertics, Twenty-Second Edition - Page 619 630Document57 pagesWilliams Obstertics, Twenty-Second Edition - Page 619 630Bharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Side Effects.: Aripiprazole (Abilify)Document3 pagesSide Effects.: Aripiprazole (Abilify)Vera El Sammah SiagianNo ratings yet
- CPD Januari 2013Document36 pagesCPD Januari 2013ledyNo ratings yet
- Image Production and Evaluation: Radiographic ContrastDocument30 pagesImage Production and Evaluation: Radiographic ContrastLyht TVNo ratings yet
- Interleukin 31 A New Cytokine Involved in Inflammation of The SkinDocument220 pagesInterleukin 31 A New Cytokine Involved in Inflammation of The SkinRemaja IslamNo ratings yet
- Dengue (Lancet)Document16 pagesDengue (Lancet)Roberth Mero100% (1)
- LaborDocument2 pagesLaborAngelyn FlorenososNo ratings yet
- Tumor Marker Uebersicht Englisch-InternetDocument2 pagesTumor Marker Uebersicht Englisch-InternetAbdullah Ali100% (1)
- Intestinal Ischemia in Neonates and Children: ReviewDocument5 pagesIntestinal Ischemia in Neonates and Children: Reviewriri siahaanNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis Powerpoint (Week 2) REVISEDDocument33 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Powerpoint (Week 2) REVISEDJustin CacheroNo ratings yet
- Herbal NclexDocument2 pagesHerbal Nclexdarryl delgado100% (1)
- Critical Thinking Exercises Pediatric NursingDocument8 pagesCritical Thinking Exercises Pediatric NursingCharmaine Rose Inandan TriviñoNo ratings yet
- Final Year MBBS Continental Medical College Obsetrics Test Topic: Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy, Diabetes in Pregnancy, Anemia in PregnancyDocument6 pagesFinal Year MBBS Continental Medical College Obsetrics Test Topic: Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy, Diabetes in Pregnancy, Anemia in PregnancyAli SohailNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration UnderlineDocument16 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration Underlinelove.mansijhaNo ratings yet
- Map 3 - ChoroplethDocument1 pageMap 3 - Choroplethapi-352028176No ratings yet
- Abastract Book 2018 PDFDocument327 pagesAbastract Book 2018 PDFTatiana SchiopuNo ratings yet
- LercanidipineDocument8 pagesLercanidipineddandan_2No ratings yet
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No093 PDFDocument11 pagesACOG Practice Bulletin No093 PDFMarco DiestraNo ratings yet