Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12
Uploaded by
JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12
Uploaded by
JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYCopyright:
Available Formats
Communicable Diseases
o No diet restriction
Dx Exam: Same as measles o Permanent immunity
Med Mgt: Same as measles o Communicable: Until all the rashes dry
Nrsg Care: Same as measles o Not Communicable: all rashes are dry; not
Prevention: Same as measles necessarily fall or peel off
o Communicable during the entire course of the Prevention:
disease – includes incubation period o Immunization:
o Permanent immunity Varivax
o Fatal – Pregnancy during the 1st to 2nd trimester o 12 to 18 months
(acquired or exposure) o 0.5 mL/ SC
Even exposure could cause defect o Deltoid
If exposed, needs gammaglobulin within 72 o 13 y/o – single dose
hours o 13 y/o – 2 doses with 1 month interval
Congenital defects o May have rash or fever
o Microcephaly o Same as measles
o Congenital Heart Defect o Proper disposal of nasopharyngeal secretions
o Congenital Cataract Blindness o Covering of mouth and nose when coughing and
o Deafness and Mutism sneezing
5. HERPES ZOSTER
Dormant type/ Inactive type
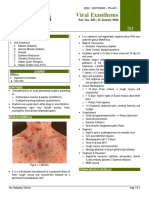
4. CHICKEN POX Cannot have herpes zoster without chicken pox first
AKA Varicella Adults
CA: Varicella-zoster virus AKA Shingles, Zona, Acute Posterior Ganglionitis –
o Nasopharyngeal secretions ganglion of the posterior nerve roots
o Secretions of rashes CA: Varicella-zoster virus
Can cause disease if the virus entered MOT: Direct (droplet)
the nasopharynx S/sx: Same as chicken pox
MOT: Airborne o Vesiculo-pustular rashes
S/sx: Painful – up to 2 months
o Pre-eruptive Stage – 24 to 48 hours Unilateral distribution – follows the nerve
Presence of absence of low grade fever pathway
Headache, body malaise, muscle pain o Vertical
Appears in cluster
o Eruptive Stage Dx Exam: Clinical observation
Vesiculo-papular/ pustular rashes Med Mgt: Symptomatic
o Macule Papule Vesicle Nrsg Care: Supportive
Vesiculopapular o NO permanent immunity
o Common: Vesiculo-pustular Prevention:
o Itchy – Pock Marks o Chicken pox and herpes zoster can appear
Take a bath everyday simultaneously
o Generalized distribution
o Covered part of the body first –
trunk and scalp RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
o Abundantly found on the Bacteria
covered parts o Diptheria
o Unifocular appearance – one at o Pertussis
a time and never fuses together o Pneumonia
o Different sizes o Tuberculosis
Virus
o Post-eruptive Stage o Colds
Rashes start to dry o Influenza
Crusts (dry), falls off (peels off)
o DO NOT peel it off by yourself 1. DIPTHERIA
o Let it fall of by itself Contagious disease
Leave pock marks All ages
On the road to recovery Generalized toxemia – causes systemic infection and
signs and symptoms
Dx Exam: Clinical Observation CA: Corynebacterium Diphteriae (Klebs-Loeffler
Bacillus)
Med Mgt: Symptomatic MOT: Direct (droplet)
o Acyclovir (Zovirax) S/sx:
o Antipruritic Agents o Irritating nasal discharge – sero-sanguinous; foul
Temporary relief of itchiness mousy odor
o Permanent relief: take a bath daily o Sore throat
Tepid water o Dysphagia
o Neck edema – bullneck appearance
Nrsg Care: Supportive o Hoarseness of voice, aphonia
o Increase body resistance Temporary, larynx is affected
University of Santo Tomas – College of Nursing / JSV
You might also like
- Childcare 2 - Communicable DiseasesDocument31 pagesChildcare 2 - Communicable DiseasesJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases 2.4-5.22Document9 pagesCommunicable Diseases 2.4-5.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthems ReviewerDocument4 pagesViral Exanthems ReviewerNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Exanthems GuideDocument4 pagesPediatric Exanthems GuideKaren Ivy BacsainNo ratings yet
- Notes - CDDocument4 pagesNotes - CDYuxin LiuNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- IM Assignment#4 Part5Section15Chapter202 MumpsDocument3 pagesIM Assignment#4 Part5Section15Chapter202 MumpsJason OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument8 pagesCommunicable DiseasesJamie John EsplanadaNo ratings yet
- IntffDocument2 pagesIntffLana AmerieNo ratings yet
- IM - Viral ExanthemsDocument5 pagesIM - Viral ExanthemsJoan Melissa SomeraNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionsDocument23 pagesViral InfectionsMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 4Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 4JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Pedia Ii 2.02 NewDocument7 pagesShanz - Pedia Ii 2.02 NewPetrina XuNo ratings yet
- R A B I E S: Dave Jay S. Manriquez RNDocument15 pagesR A B I E S: Dave Jay S. Manriquez RNOdylon CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Exanthematous DisordersDocument16 pagesExanthematous DisordersZweNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BDocument15 pagesFar Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lower Genital Infections GuideDocument2 pagesLower Genital Infections Guidecbac1990No ratings yet
- VaricellaDocument4 pagesVaricellasingcojericho11No ratings yet
- Vaccine (Infant, Child)Document5 pagesVaccine (Infant, Child)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology NotesDocument79 pagesOphthalmology NotesWise AmroNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 6Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 6JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Abscess Dr. Nasrin Sultana JuyenaDocument4 pagesAbscess Dr. Nasrin Sultana JuyenaShakil MahmodNo ratings yet
- Cluster of Lesions, PapularDocument3 pagesCluster of Lesions, PapularLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NotesDocument13 pagesPediatrics NotesYsa BonifacioNo ratings yet
- General Medicine 3Document60 pagesGeneral Medicine 3Zeyad AlhaimiNo ratings yet
- 17.1 SpirochetesDocument3 pages17.1 SpirochetesJoey Anne CastroNo ratings yet
- 8 Childhood Viral Skin Rashes: Chickenpox, Measles and MoreDocument9 pages8 Childhood Viral Skin Rashes: Chickenpox, Measles and MoreErik OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 4.3 InfectiousDocument29 pages4.3 InfectiousJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- Bullous MyringitisDocument5 pagesBullous MyringitisIca BatalipuNo ratings yet
- Cims Case 1 - SGD A4Document16 pagesCims Case 1 - SGD A4SGD A4No ratings yet
- Measles - German Measles - ChickenpoxDocument3 pagesMeasles - German Measles - Chickenpoxd3mooz13No ratings yet
- Phasmids 4: Angiostrongylus CantonensisDocument5 pagesPhasmids 4: Angiostrongylus CantonensisJack Ortega PuruggananNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Infections Dr. Mowafy 2nd EditionDocument26 pagesInfections Dr. Mowafy 2nd EditionMohammed RisqNo ratings yet
- 7.2 - Medical Virology Part 2Document39 pages7.2 - Medical Virology Part 2Kaela Beatrice Sy LatoNo ratings yet
- Del Rosario Ryan D. BSN 4C1-7 Mr. Daniel Mon Mamanao: Measles Pre-Eruptive StageDocument5 pagesDel Rosario Ryan D. BSN 4C1-7 Mr. Daniel Mon Mamanao: Measles Pre-Eruptive Stageryandelrosario9yahooNo ratings yet
- Community OmaraDocument33 pagesCommunity Omarasayf ahmedNo ratings yet
- Common Viral Infec - Part 2Document13 pagesCommon Viral Infec - Part 2d99452727No ratings yet
- Module 6.4 ParasitesDocument6 pagesModule 6.4 ParasitesPNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- ALMENIEDocument2 pagesALMENIEjenalyn01No ratings yet
- TRANS NOTES For CH15Document5 pagesTRANS NOTES For CH15Patricia CabisonNo ratings yet
- Cims Case 1Document14 pagesCims Case 1SGD A4No ratings yet
- Microbiology 19 PDFDocument6 pagesMicrobiology 19 PDFLyka Villagracia AsiloNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseVinceNo ratings yet
- A Brief Note On: Chicken PoxDocument29 pagesA Brief Note On: Chicken PoxRemesh ChandranNo ratings yet
- 2 Oral UlcersDocument27 pages2 Oral UlcersAhmed Abdelhady Mahmoud AbdelwahedNo ratings yet
- K22 Variola KBKDocument12 pagesK22 Variola KBKedelinNo ratings yet
- SGD 2Document1 pageSGD 2Thea PepitoNo ratings yet
- Surgery: The Appendix ExplainedDocument5 pagesSurgery: The Appendix ExplainedJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Virology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexDocument4 pagesVirology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexJaz CNo ratings yet
- Most Common Complication: Sabay SilaDocument6 pagesMost Common Complication: Sabay SilaSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted InfectionsMary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Infections DR MowafyDocument22 pagesInfections DR Mowafyeid.6116No ratings yet
- Final Topic For Finals - BacteDocument4 pagesFinal Topic For Finals - BacteAlthea Jam Grezshyl GaloNo ratings yet
- TB + MumpsDocument2 pagesTB + Mumpsd3mooz13No ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 7Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 7JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 19Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 19JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- What Is Chlamydia?: Contains Graphic ImageryDocument3 pagesWhat Is Chlamydia?: Contains Graphic Imageryflex gyNo ratings yet
- Methods of Specimen Collection For Diagnosis of Superficial and Subcutaneous Fungal InfectionsDocument5 pagesMethods of Specimen Collection For Diagnosis of Superficial and Subcutaneous Fungal InfectionssaadmcsNo ratings yet
- Drug Administration Route Needle Size EtcDocument1 pageDrug Administration Route Needle Size EtcRon AbuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8 - Agostina MininiDocument2 pagesAssignment 8 - Agostina MininiAgostina MiniNo ratings yet
- Aujeszky's Disease OverviewDocument23 pagesAujeszky's Disease OverviewSyikin Zolkefly100% (1)
- Parasitic Worms and Their CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesParasitic Worms and Their CharacteristicsMartin Clyde100% (5)
- The Diagnosis and Management of Tinea CapitisDocument4 pagesThe Diagnosis and Management of Tinea CapitisKeyla Kehara PutriNo ratings yet
- Reproductive HealthDocument21 pagesReproductive HealthRoanne Mae MañalacNo ratings yet
- Dole's Daily Health Checklist FormDocument2 pagesDole's Daily Health Checklist FormCasuncad GilbertNo ratings yet
- Sharma Et Al 2017Document8 pagesSharma Et Al 2017Kryzn NNo ratings yet
- Actinomycetes: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument37 pagesActinomycetes: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleHarsh Rajvanshi100% (1)
- Follow-Up of A Clinical Pathway For Varicella-Zoster Virus InfectionDocument6 pagesFollow-Up of A Clinical Pathway For Varicella-Zoster Virus InfectionRandi ResfanataNo ratings yet
- Submit Copy of Written Pledge for Japan Airport QuarantineDocument2 pagesSubmit Copy of Written Pledge for Japan Airport QuarantineRitesh KalleNo ratings yet
- Biosafety Levels: WWW - Techef.InDocument21 pagesBiosafety Levels: WWW - Techef.InSmk Mahmud KoliNo ratings yet
- Closing Date 2 NOVEMBER 2020: National E-Kokuria Carnival 2020 Online Organised by Sabah State EducationDocument4 pagesClosing Date 2 NOVEMBER 2020: National E-Kokuria Carnival 2020 Online Organised by Sabah State EducationJulie SuiminNo ratings yet
- Health Center - PaterosDocument5 pagesHealth Center - PaterosmawaaahNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step One Rna Helical Virus MnemonicDocument2 pagesUSMLE Step One Rna Helical Virus Mnemoniccschutt47No ratings yet
- Contingency PlanDocument3 pagesContingency PlanMichael LaguraNo ratings yet
- WWW Electroherbalism Com Bioelectronics FrequenciesandAnecdotes CAFL HTMDocument20 pagesWWW Electroherbalism Com Bioelectronics FrequenciesandAnecdotes CAFL HTMjackblack2002No ratings yet
- Ethics Case StudyDocument2 pagesEthics Case StudykruzipNo ratings yet
- How Safe Is Our FoodDocument3 pagesHow Safe Is Our FoodJhorman Andres FlórezNo ratings yet
- Biohazard Diseases Its Prevention in DentistryDocument8 pagesBiohazard Diseases Its Prevention in DentistryDavid SalasNo ratings yet
- Simple Guide Identification Bacteria: Dr. Khalil AlkuwaityDocument18 pagesSimple Guide Identification Bacteria: Dr. Khalil AlkuwaitySaid IsaqNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood GroupDocument12 pagesABO Blood GroupGhost AnkanNo ratings yet
- More Information: Help Stop The Spread of Covid-19Document2 pagesMore Information: Help Stop The Spread of Covid-19timgourNo ratings yet
- Acute Bacterial Meningitis During and After Pregnancy: CommentaryDocument3 pagesAcute Bacterial Meningitis During and After Pregnancy: CommentaryAyu Wedhani SpcNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease 2 AnswersDocument14 pagesCommunicable Disease 2 AnswersRika MaeNo ratings yet
- Blood Culture (Manual System)Document26 pagesBlood Culture (Manual System)SAMMYNo ratings yet
- MAPEH Test Results for Grade 8Document3 pagesMAPEH Test Results for Grade 8Antis VergelNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science Worksheetravilulla67% (3)